Special Issue Norton Cyber Safety Pulse Report – The Cyber Risks of ChatGPT
In this special issue of the Norton Pulse Report, Norton Labs explores how cyber criminals could leverage Chat GPT to enhance their scams.

Advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) are bringing many exciting innovations, and one technology that is generating buzz is large language models. You may be more familiar with OpenAI’s ChatGPT. It was trained on a huge amount of text data so that it can understand the relationship between words and predict which word is most likely to come next given the prior context.
What makes ChatGPT stand out is that it is the first widely available system that can generate highly convincing and natural-sounding text in pretty much any context. From helping you write a thank you note to generating code, OpenAI is currently allowing users to explore ChatGPT and its vast uses to simplify everyday tasks.
But Norton Labs is anticipating scammers are also eyeing the capabilities of large language models and testing ways to enhance their cybercrimes to make them more realistic and believable.
In this special issue of the Norton Cyber Safety Pulse Report, we’re spotlighting three ways scammers can leverage large language models like ChatGPT to create more realistic threats, and we’re sharing tips for what you can do to help protect yourself.
- Spotlight #1 – Deepfake content generation
- Spotlight #2 – Phishing campaigns
- Spotlight #3 – Malware creation
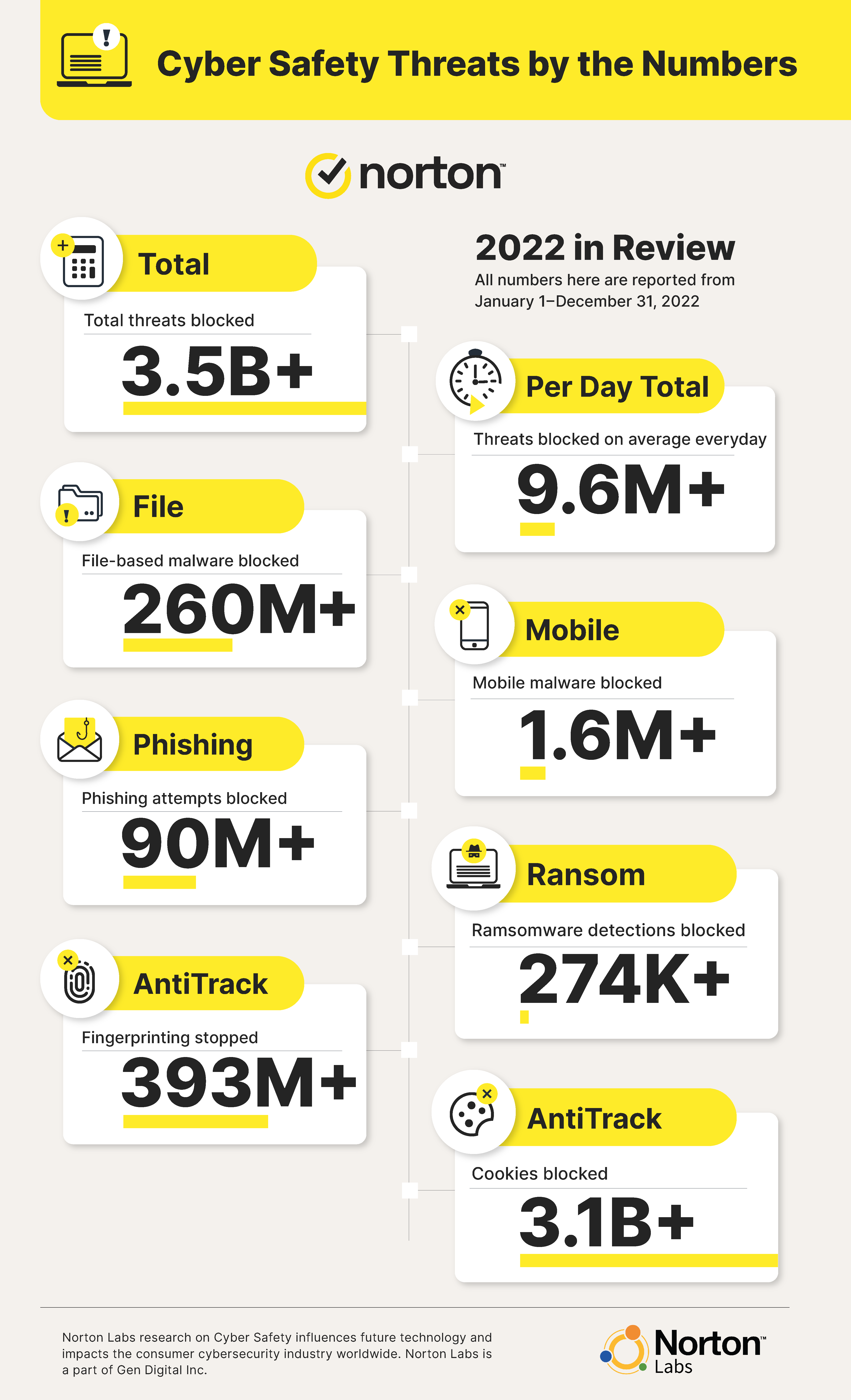
Before we dive in, let's review the latest cyber threat statistics from the past few months and a full recap of 2022.

Spotlight #1: The Threat of Deepfake Content Generation

Background: ChatGPT can generate highly convincing and natural-sounding text. People have already started using it to automate some of the more mundane tasks that they perform at work.
While creating realistic text at scale will have many upsides, there are also many potential drawbacks. Not only is the content generated by ChatGPT sometimes unintentionally incorrect, but a bad actor can also use these tools to intentionally create content used to harm people in some way. Just to name a few:
- The ability to generate high quality misinformation or disinformation at scale could change the way that bot farms work to sow mistrust and shape narratives in different languages.
- It could also become a big problem for online product reviews, making it much more challenging to spot fake reviews and shoddy products in many online shops.
- Using these tools in harassment campaigns on social media to silence or bully people is also a possible outcome that would have a chilling effect on speech.
While none of these scenarios are new, the ability to automate them in a high-quality and low-cost way can make these problems worse before we can adapt and make them better.
Advice for Consumers: In the coming months and years, we will start to see more automatically generated content, so it will be important to be skeptical and think critically of anything you read or see online. Fact checking services and identity solutions may become crucial to how we interact with other people and information online.
Spotlight 2: The Use of ChatGPT in Phishing Campaigns

Background: ChatGPT’s impressive ability to generate human-like text and adapt to different languages and audiences is so good that it is almost impossible to distinguish it from a real person. Even OpenAI has a hard time deciphering whether text is AI-generated. OpenAI recently released a tool to discover if a text had been written by an AI, and it failed, stating that they recognize it “is impossible to reliably detect all AI-written text.”
Malicious actors can use ChatGPT to craft phishing emails or social media posts that appear to be from legitimate sources, making it more difficult to detect and defend against these types of threats.
As ChatGPT becomes more widely used, it is likely that we will see an increase in the number of phishing campaigns and other kinds of AI cyber attacks. Malicious actors can feed ChatGPT with real life examples of non-malicious messages from the companies they want to impersonate and order the AI to create new ones based on the same style with malicious intent. These campaigns can be highly effective in tricking individuals into providing personal information or money to criminal sources.
Advice for Consumers: Always be cautious when clicking on links or providing personal information in response to unsolicited phone calls, emails, or messages. When in doubt, reach out to the company directly through their official channels.
Spotlight 3: The Influence of ChatGPT on Malware Creation

Background: ChatGPT can generate code and adapt to different programming languages. With the right prompt, novice malware authors can describe what they want to do and get working code snippets. One example is to generate code to detect when a bitcoin wallet address is copied to the clipboard so that it can be replaced with a malicious address controlled by the malware author. They could then convert that code to different languages for use in different places.
As a result, we could see an increase in the number and sophistication of malware. There are programming languages that are rarely used to create malware, and using ChatGPT to “translate” source code from a language to another less common one is simple. Cybersecurity products have a certain bias toward known attacks, and using these techniques (compiling known malware in new programming languages) could lead to bypassing certain protection layers present in cybersecurity solutions.
Advice for Consumers: Always keep your devices’ software up to date. And if you’re concerned about malware, it’s a good idea to consider trusted cybersecurity software like Norton 360 Deluxe to help protect your devices.
Looking ahead
Norton Labs continues to track scams and threats targeting the digital lives of consumers. Stay tuned for more cybersecurity intel when we publish our next Norton Cyber Safety Pulse Report.

Cyber threats have evolved, and so have we.
Norton 360™ with LifeLock™, all-in-one, comprehensive protection against viruses, malware, identity theft, online tracking and much, much more.
Try Norton 360 with Lifelock.
Editorial note: Our articles are designed to provide educational information for you. They may not cover or protect against every type of crime, fraud, or threat we write about. Our goal is to increase awareness about Cyber Safety. Please review the complete Terms during enrollment or setup. Remember that no one can prevent all identity theft or cybercrime, and that LifeLock does not monitor all transactions at all businesses. The Norton and LifeLock brands are part of Gen Digital Inc. For more details about how we create, review, and update content, please see our Editorial Policy.





Want more?
Follow us for all the latest news, tips, and updates.