What is TCP/IP and how does it work?
TCP/IP is the internet’s playbook for packing, addressing, and routing data. Find out more about this key data-sharing protocol and how it enables seamless communication between devices and systems. Then, get a VPN to fortify your internet connection and protect your internet traffic with powerful encryption.

What is TCP/IP?
Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) is a set of rules and procedures that enable reliable and efficient information sharing between devices across networks. TCP/IP facilitates connections across the internet, as well as intranets and extranets.
Whenever you transfer files via cloud-based services, print documents, log in remotely, or send emails and messages—or transmit data of any sort via a networked connection—TCP/IP works in the background to make it happen.
How does TCP/IP work?
TCP/IP works by breaking data into packets, assigning the data packets source and destination IP addresses, and routing them through various networks to their final destination. Once at the destination, TCP reassembles data packets into their original format, ensuring correct delivery to the receiver.
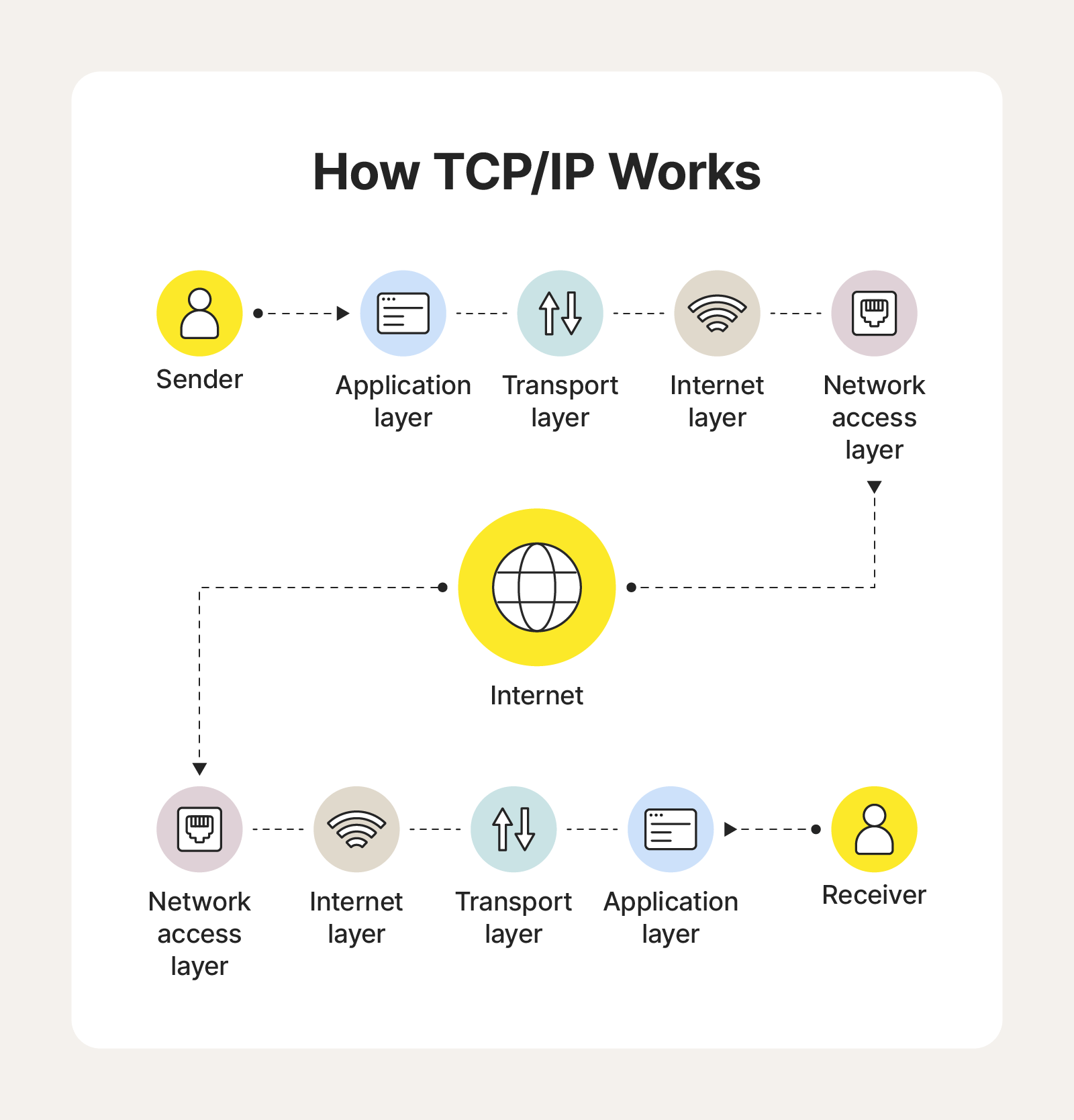

Here’s a more detailed look at how this set of protocols works.
- Three-way handshake: A three-step process establishes a reliable connection between devices.
- Data deconstruction: Large data is divided into smaller packets for efficient transmission.
- IP addressing: Each packet is assigned source and destination IP addresses for routing.
- Packet routing: Packets travel through networks, often taking different paths.
- TCP reassembly: At the destination, TCP reassembles packets into the original data format.
- Error checking: TCP verifies data integrity and requests retransmission of corrupted packets.
How are TCP and IP different?
The TCP and IP components have different roles within the TCP/IP procedures. TCP is responsible for reliable data delivery, ensuring data packets arrive in the correct order and without errors. IP is responsible for addressing and routing data packets across networks, determining the best path for data to travel.
| TCP | IP | |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Reliable data delivery | Addressing and routing data packets |
| Function | Establishes a connection between sender and receiver; guarantees data integrity and order | Determines the best path for data to travel |
| Reliability | High | Low |
The 4 layers of the TCP/IP model
The TCP/IP model consists of four layers: Application, Transport, Internet, and Network Access.
The Application layer handles user interactions and data formatting. The Transport layer ensures data delivery, prioritizing either reliability (TCP) or efficiency (UDP). The Internet layer addresses and routes data packets and determines the best transmission route. The Network Access layer handles physical data transmission, connecting devices to the network.
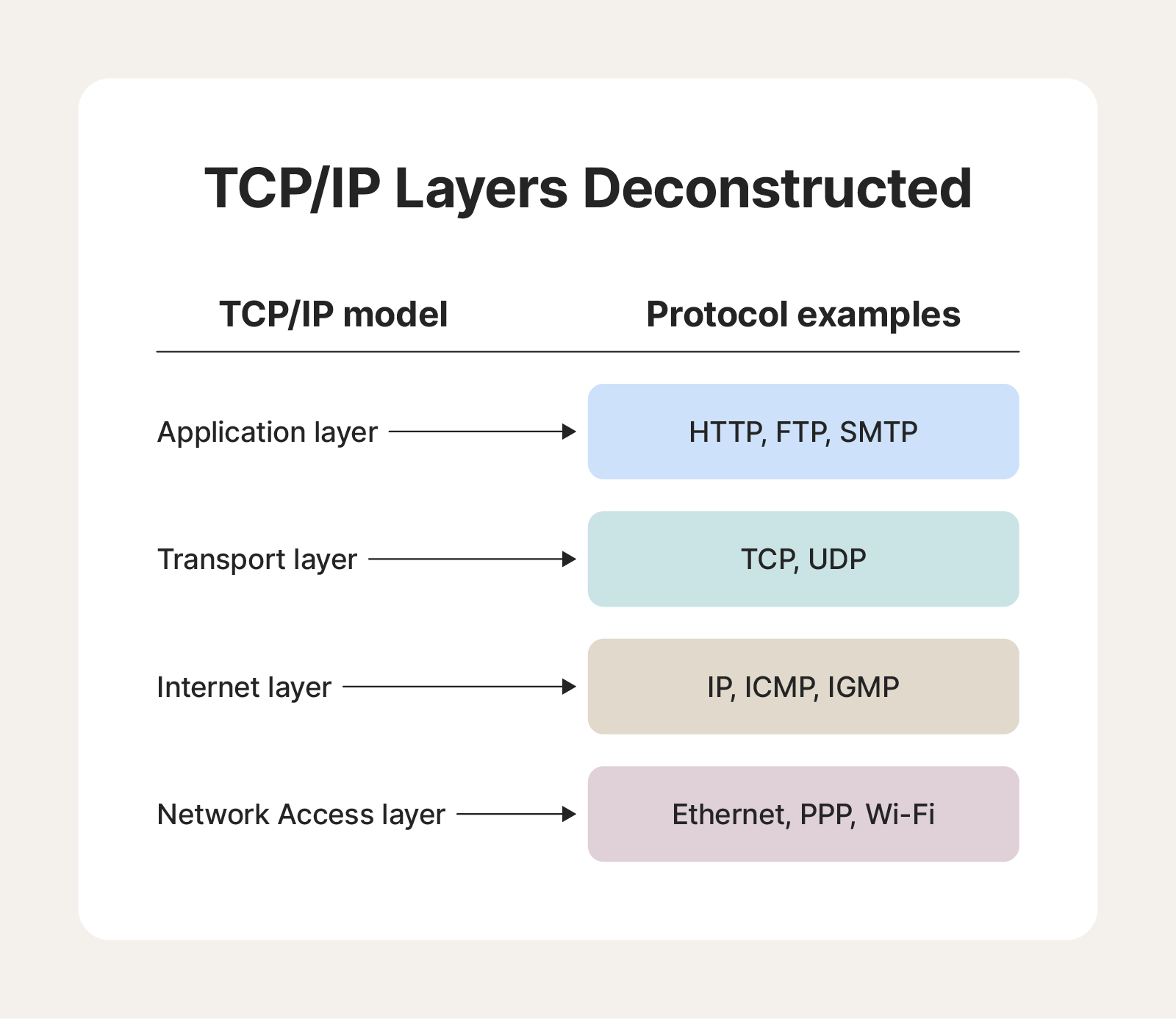

These layers work together to enable seamless communication between devices. Here’s a more detailed breakdown of how the TCP/IP layers work:
- Application layer: The Application layer is the top layer of the TCP/IP model, providing network services to users. It includes protocols like HTTP for web browsing, FTP for file transfer, and SMTP for email.
- Transport layer: The transport layer ensures reliable end-to-end communication between applications, handling error control, information flow control, and network congestion management. Protocols like TCP provide the reliable, ordered, and error-checked delivery of data between applications, whereas UDP offers a connectionless delivery service for applications that can tolerate data loss.
- Internet layer: The Internet layer, also known as the Network layer, is responsible for routing data packets across networks. It uses IP addresses to determine the best path for data transmission. It includes protocols like ICMP for error reporting, IGMP for managing multicast group memberships, and ARP for mapping IP addresses to physical MAC addresses.
- Network Access layer: The Network Access Layer is the lowest layer of the TCP/IP model, responsible for physical data transmission. It handles the interface between the network and the physical link, using protocols like Ethernet for wired LANs, Wi-Fi for wireless networks, and PPP for dial-up connections.
OSI vs. TCP/IP
Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) differs from TCP/IP because the OSI model is a seven-layered conceptual framework for network communications functionality, while TCP/IP is a practical implementation of the networking protocol suite. OSI provides a theoretical understanding of network communication, while TCP/IP is the actual set of protocols used in real-world networks.
Here’s a comparison of TCP/IP and OSI’s layers:
| OSI Model Layers |
TCP/IP Model Layers |
Application layer Presentation layer Session layer Transport layer Internet layer Data Link layer Physical layer |
Application layer Transport layer Internet layer Network Access layer
|
Protect your data on unsecured networks
TCP/IP ensures the smooth and effective transmission of data across networks, but the information you send is vulnerable to interception and manipulation if the network itself is unsecured.
Enhance your security with Norton VPN, which encrypts your connection to establish a secure tunnel between your device and the internet. That helps keep your data safe from prying eyes and hackers, and it helps keep your online activity hidden. Turn your network into a digital fortress with Norton VPN today.
FAQs about TCP/IP
Still have questions about TCP/IP? Here’s what you need to know.
Are TCP/IP data packets encrypted?
No, TCP/IP data packets are not inherently encrypted. You’d need an additional protocol like SSL/TLS or a VPN to fully secure your communications.
What is TCP and IP mainly used for?
TCP is primarily used to ensure data packets arrive in the correct order and without errors. IP is responsible for addressing and routing data packets across networks, determining the best path for data transmission.
What is the difference between TCP/IP and HTTP?
TCP/IP is the underlying framework that enables communication between devices on a network. HTTP is a higher-level protocol built on top of TCP/IP that specifically handles the communication between web browsers and servers, allowing for the exchange of web resources like HTML, images, and videos.
Why is TCP/IP so important?
TCP/IP is the backbone of the internet, providing a standardized framework for reliable communication between devices worldwide. It enables the seamless exchange of data, powering everything from email and web browsing to online streaming and business applications.
Editorial note: Our articles provide educational information for you. Our offerings may not cover or protect against every type of crime, fraud, or threat we write about. Our goal is to increase awareness about Cyber Safety. Please review complete Terms during enrollment or setup. Remember that no one can prevent all identity theft or cybercrime, and that LifeLock does not monitor all transactions at all businesses. The Norton and LifeLock brands are part of Gen Digital Inc.





Want more?
Follow us for all the latest news, tips, and updates.