23 cloud security risks, threats, and best practices to follow
Cloud security risks include data breaches, insufficient access management, malware infections, and more. Learn how to better protect your data in the cloud.

When it comes to storing your most sensitive data, the days of clunky file cabinets and flash drives are over. The cloud has proven itself as a Cyber Safe location for housing private information such as employment files, health documentation, and family photos and videos. However, for those who rely heavily on cloud storage, there are cloud security risks businesses and individuals should be aware of.
From user error to cyberattacks, there’s a lot to keep in mind when managing your cloud network security. That’s why we’ve put together a comprehensive guide to the different cloud computing risks you should know in 2023, as well as best practices to protect yourself.
Need a quick and easy cloud security solution? With features like advanced malware and antivirus protection, a password manager, and Dark Web Monitoring, Norton 360 Deluxe has your cloud covered.
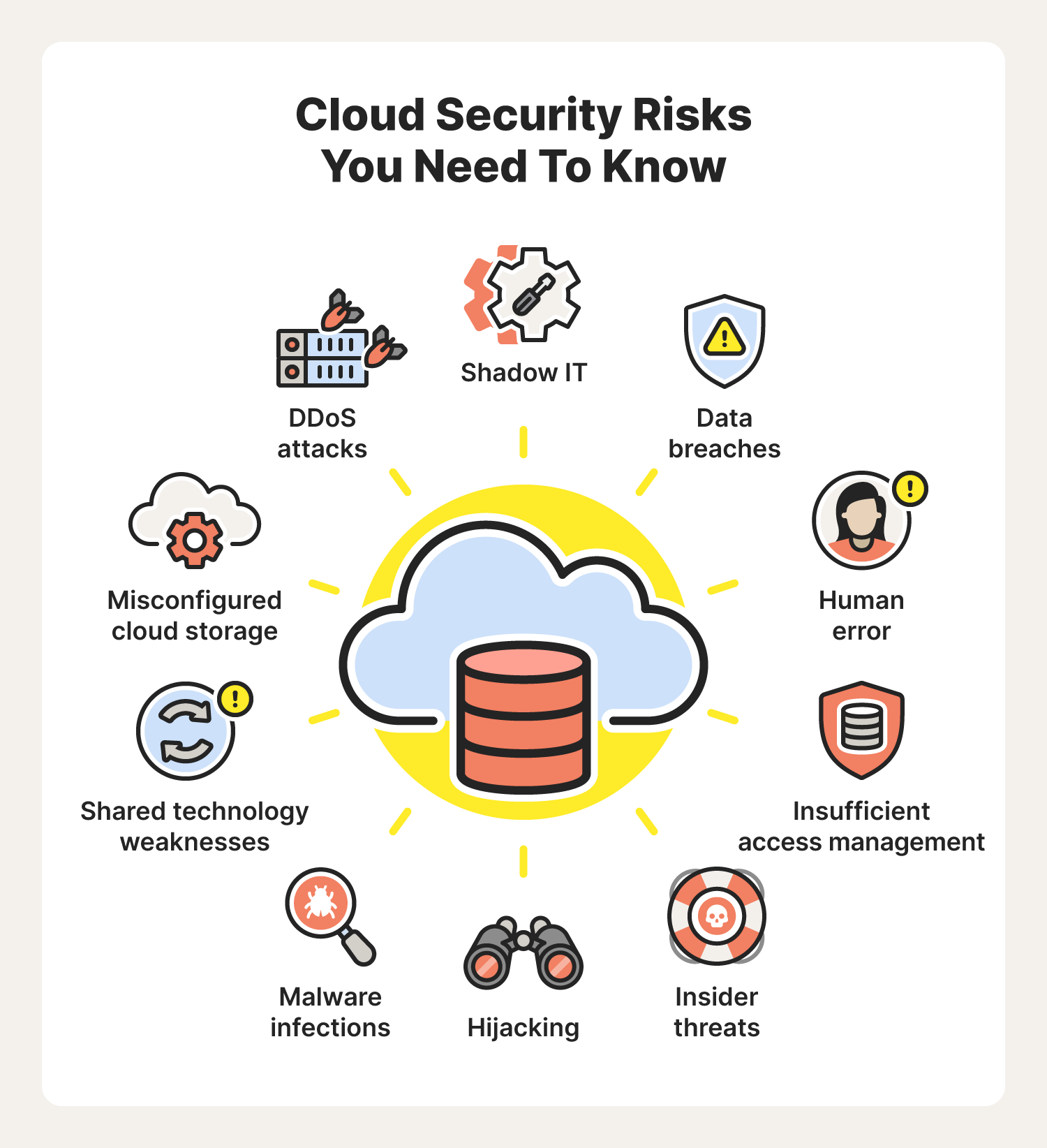
Cloud security risks, threats, and challenges
Giving a cloud service provider (CSP) like Google Cloud or Oracle Cloud the responsibility of storing and protecting your confidential data can make some people uneasy. After all, you might have no idea how well CSPs are protecting the servers used to house your private photos, videos, and files.
However, the truth is that giving up that bit of control can better protect your personal or professional information. CSPs have access to robust cloud cybersecurity technologies that may be inaccessible to regular people and businesses. This technology can better safeguard your information from malware and cyberattacks.
But despite being considered a more secure method of storing sensitive information, cloud-based systems come with their own risks, threats, and challenges. Here are some of the most common cloud security issues.
1. Data breaches
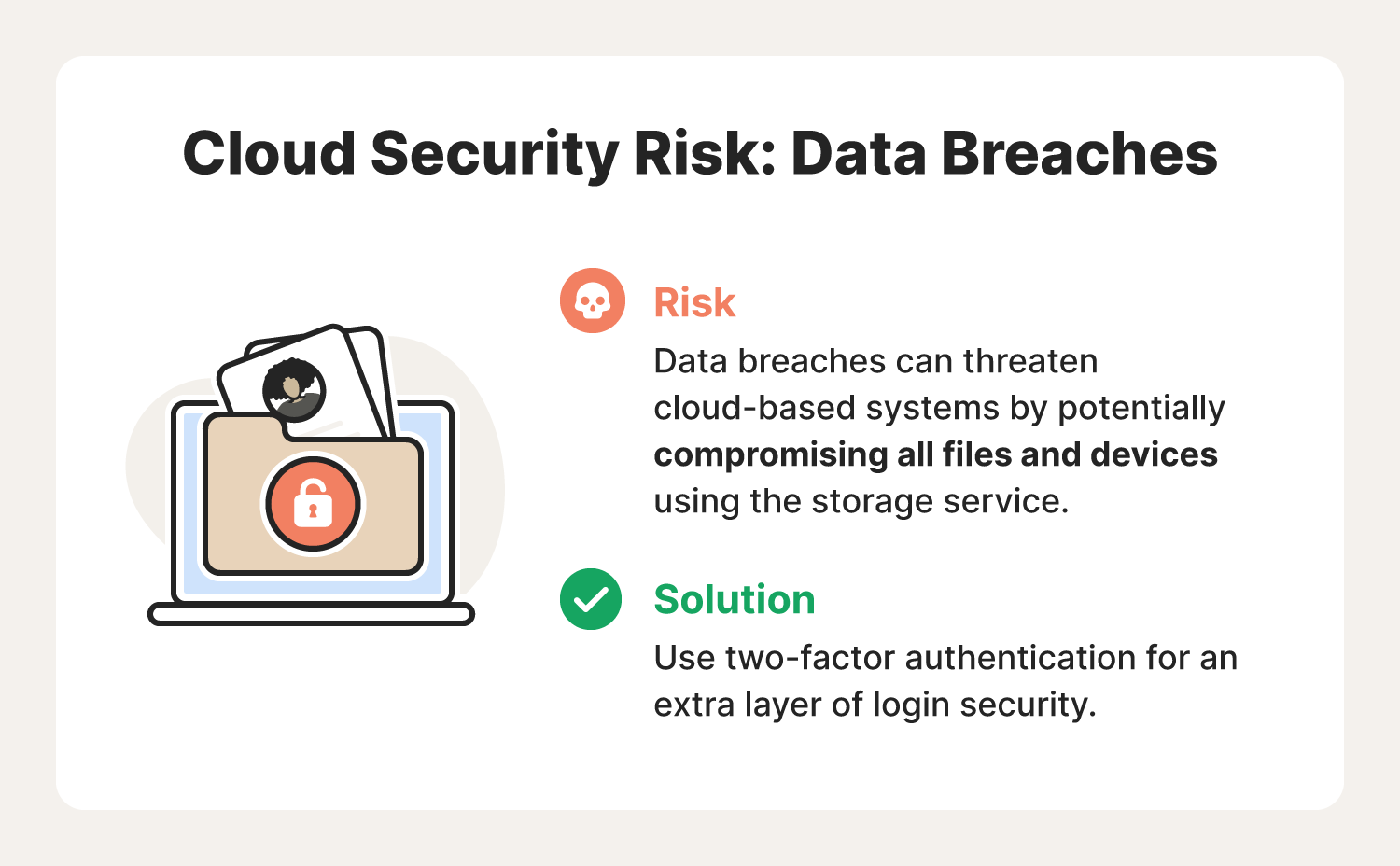
Hackers are often after one thing: data. So why wouldn’t they target the one place they could potentially steal tons of it?
A data breach occurs when information is accessed without authorization. As individuals and organizations migrate to the cloud, data breaches are becoming more prevalent.
The overwhelming amount of data CSPs store for people and businesses makes them a prime target for a data breach. Often performed by experienced cybercriminals in search of private information, this cloud security risk could put medical documents, financial records, and customer information in jeopardy.
2. Unmanaged attack surface
The term “attack surface” is a new concept born from cloud computing. Prior to the cloud, data was all stored in one location so it was much easier to secure the perimeter around the data center.
But cloud computing blurred the boundaries—the cloud is ever-changing, and it’s not always clear where data is housed or who is responsible for it. Traditional asset discovery, risk assessment, and vulnerability management processes were developed when networks were more stable and centralized. They simply can’t keep up with the speed at which new vulnerabilities and attack vectors arise in cloud computing. The sum of these vulnerabilities makes up the attack surface.
Organizations have seen their attack surfaces expand by 67% in 2022, and 69% have been compromised by an unknown or poorly managed internet-facing asset. To limit your attack surface:
- Classify your data both by sensitivity and security posture.
- Use two-factor authentication and encrypt sensitive data.
- Keep track of who has access to your documents.
- Delete any unused or exposed data stores.
The idea is to only keep the data you need so it’s easier to manage and identify the proper security measures for each file.
3. Data loss
Cloud-based systems can also fall victim to data loss—just like home and office networks. Data loss can happen as a result of a data breach, natural disaster, or a system-wide malfunction. Truly protecting your documents means:
- Reviewing your CSP’s backup strategy to ensure there are steps in place to guarantee the Cyber Safety of your digital assets
- Taking the initiative to back up your data yourself, making the complete destruction of your data near impossible
4. Insufficient access management
Access and identity management is used to authorize access to information stored in the cloud. It limits:
- Who has access to certain documents
- Where users are allowed to access documents
- Which devices are permitted access
From ensuring only safe devices are able to connect to your network to creating employee guidelines prohibiting the use of public Wi-Fi, limiting who has access and where is important for cloud cybersecurity. Insufficient access management of data stored in the cloud could result in valuable information ending up in the wrong hands.
5. Shadow IT
You can’t protect what you can’t see, and that rings true for cloud security. Shadow IT is any information technology an employee uses without IT knowledge approval. This includes:
- Peer-to-peer collaboration tools
- Bluetooth-based sharing tools
- Messaging apps
- Personal laptops, phones, or tablets
The rapid migration to cloud services has made shadow IT a prevalent issue, exposing organizations to security hazards the company’s IT department likely isn’t aware of.
6. Hijacking
Ineffective security resources and protocols could potentially lead to the hijacking of a cloud network.
Cloud account hijacking occurs when a cyberattacker manages to gain control of a cloud-based account. Cybercriminals use phishing scams and botnets to infiltrate and infect cloud-based systems, taking complete control once successful. Hackers can then steal your credentials and information, or in the case of a business, highly sensitive customer or corporate files.
7. Malware infections

Today’s hackers have many means to infiltrate cloud-based systems. One of them is malware, a type of software that’s installed on a computer without the user’s consent in order to disrupt, damage, or take control of the system.
Cybercriminals who wish to gain access to your cloud may use malware to trick the cloud service into thinking the malicious actor is a part of the system. Once the malware works in tandem with the cloud service, it is able to siphon, destroy, and withhold information as it pleases.
8. Insider threats
Unlike insufficient access management, insider threats refer to those who already have access to your cloud network. These users ignore the cloud cybersecurity rules you’ve put in place to protect your privacy and data. They could be websites you don’t want your guests visiting or files employees shouldn't share outside of the company network.
Protecting your cloud network starts with managing how people within your immediate circle utilize it.
9. Zero-day exploits
Information stored in the cloud—or any computer network or software application—is essentially managed in another organization’s data center. For example, photos and videos you store in your iCloud are actually being stored on servers owned by Apple. This introduces the threat of zero-day exploits, which target vulnerabilities in popular software and cloud computing systems the vendor hasn’t patched up.
These attacks earned their name because developers essentially have zero days to mitigate them once they’ve been detected. Zero-day exploits are especially difficult to protect against since even the most up-to-date cloud configuration can’t stop them.
10. Shared technology weakness
The Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) and Platform as a Service (PaaS) technology computers use to connect to the cloud allows them to share cloud security vulnerabilities hackers can take advantage of.
Once a cybercriminal successfully gains access to one computer on your network, it is likely they will be able to hack other users in the system.
11. Misconfigured cloud storage
The cloud-computing landscape is constantly changing to account for emerging opportunities and threats. Many businesses have adopted multi-cloud environments to reap the benefits of different CSPs, but they may have also increased their vulnerability to misconfigurations in doing so.
Misconfigurations are any glitches, gaps, or errors that could be viewed as cybersecurity risks during cloud adoption. The more cloud networks you have operating simultaneously, the more difficult it is to detect and remediate misconfigurations. Lack of adequate controls and oversight lead to almost 31% of misconfiguration cases reported in 2021.
12. Compliance
Professional organizations need to comply with regulation standards when it comes to the safe storage and protection of customer data.
Whether it’s the Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA), Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), or another type of regulatory body, a state of noncompliance could put a company in very hot legal water with their government.
13. Data and privacy contract breaches
In addition to complying with government regulations, businesses also have to abide by the data and privacy contracts they make with their customers.
These contracts outline how the company protects, stores, and shares information with third parties. If customer information is compromised while managed in the cloud, it could be considered a contract breach. Any violations of these contracts could result in legal action, affecting customer loyalty and the brand’s reputation.
14. Human error

Cybercriminals often prey on internal vulnerabilities to launch their attacks. But in some cases, users may not even know where their personal security efforts fall short. In fact, human error and misuse were both primary causes of 82% of data breaches in 2022. Human errors are unintentional actions or lack of action that can result in a data breach, like:
- Downloading malware from an infected software
- Using weak passwords
- Compromising an IP address
- Sending information to the wrong recipient
- Not updating web-based software
Hosting information on a public cloud amplifies security risks because if one system is breached, every user on the network is prone to attack.
15. Insecure APIs
Application programming interfaces (APIs) allow two software components to communicate with each other without having to know how they’re integrated. Every time you order a rideshare, check your weather app, or send a mobile payment, you’re using an API.
As organizations secure their web applications, some APIs may be overlooked and left unprotected. This opens the door to API breaches, which are predicted to be the next big threat to cybersecurity.
16. Denial of service attacks
Denial of service (DoS) attacks tie up a website’s resources so that users who want/need access cannot do so. They work by disrupting the services of a cloud environment by overwhelming the computer processing unit (CPU) with thousands upon thousands of attack packets until the network is rendered inoperable.
This can bring computer operations to a halt, effectively holding your documents and files hostage until the traffic is cleared.
17. Advanced persistent threats
An advanced persistent threat (APT) occurs when an intruder establishes an unauthorized long-term connection to the network in order to mine sensitive data. While large organizations are typically the targets of APTs, more and more small and midsize businesses are becoming targets.
Defending against APTs in a cloud environment is especially difficult because it can be nearly impossible to identify an attacker once they’ve gotten a foothold in the system.
6 cloud computing security best practices to follow
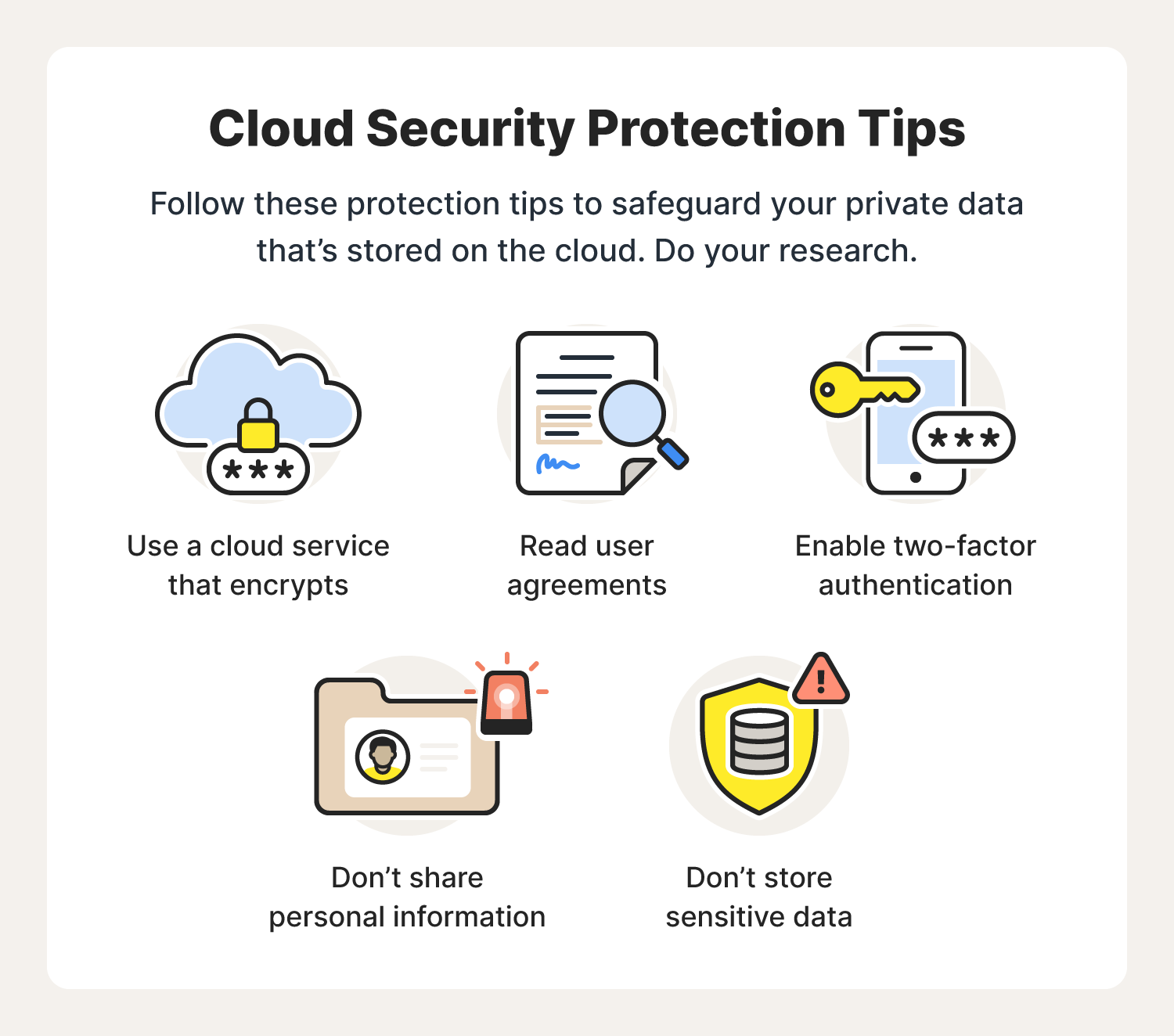
1. Use a cloud service that encrypts
One of the best weapons in your cyberthief defense arsenal is a cloud service that encrypts your files both in the cloud and on your computer. Encryption ensures service providers and their service administrators, as well as third parties, do not have access to your private information.
2. Read user agreements
Never sign up for cloud service without reading the user agreement completely. It includes vital information that details how the service protects your data and whether you give permission for them to use or sell your information in any way by signing up.
Avoid signing anything without a complete understanding of what every clause in the agreement means. Anytime your service provider updates its privacy policies, it will notify you via email, text, or an alert when you log in. Always read these notifications to ensure changes do not negatively affect your data.
3. Enable two-factor authentication
When provided with the option, always use two-factor authentication to avoid cloud security issues. This means anyone who signs into your account will need information in addition to your password. Common methods of authentication include:
- Biometric logins
- Security questions
- Personal PINs
- Temporary codes
- Authenticator apps
Not all accounts will automatically ask you to set up a secondary identifier, so be sure to check your settings to see if the option is available.
4. Don’t share personal information
Some of your personal information may seem unimportant, but if it falls into the wrong hands, it could compromise your identity. Always avoid publicly providing information that may be used to answer a security questions, like:
- Your birthdate
- Your mother's maiden name
- The name of the street you grew up on
- The name of your first pet
- The city where you met your significant other
Some providers allow you to choose your own questions to answer for verification. If you have the option, use questions and answers that you can remember but that most people wouldn't easily be able to learn about you, such as an embarrassing childhood nickname or where you went on your first date.
5. Don’t store sensitive data
Avoid storing sensitive information on the cloud to prevent blackmail or embarrassment if it falls into the wrong hands. In addition to the obvious, such as your Social Security number, copies of your IDs, or important financial statements—even old ones—consider what other information someone could get their hands on.
Never keep racy pictures or intimate interactions with partners in the cloud, and if you are sensitive about items such as diet progress pictures, avoid storing those as well.
6. Do your research
Before deciding to move your personal or professional data to the cloud, it’s important to do your research. You need to understand the ins and outs of the CSP you've chosen to help mitigate the chances of you becoming a victim of today’s cloud security risks. You should know who has access to your information, who’s in charge of data security, and the current cloud network security protocols in place.
Use the cloud safely
Despite cloud computing allowing you the convenience of accessing your data at your fingertips from almost anywhere in the world, there are still cloud security risks to keep in mind that could threaten your Cyber Safety. Take note of these cloud security issues and best practices for peace of mind when managing your most precious documents, photos, and files.
Get a jump start on protecting your information in the cloud with Norton 360 Deluxe security software. With powerful protection against hackers, malware, and data breaches, you can rest assured that your most valuable information remains in good hands.
Editorial note: Our articles provide educational information for you. Our offerings may not cover or protect against every type of crime, fraud, or threat we write about. Our goal is to increase awareness about Cyber Safety. Please review complete Terms during enrollment or setup. Remember that no one can prevent all identity theft or cybercrime, and that LifeLock does not monitor all transactions at all businesses. The Norton and LifeLock brands are part of Gen Digital Inc.





Want more?
Follow us for all the latest news, tips, and updates.