2FA: A simplified guide to two-factor authentication
Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) for an added level of security against hackers and identity thieves. Learn what 2FA is and how it helps secure your data. Then get Norton™ 360 with LifeLock™ Select to help secure your personal information and protect against identity theft.

It’s no secret that cybercriminals are hungry for passwords and other user data.
An unprotected password can help cybercriminals access your bank account, credit cards, or personal websites. From there, they can:
- Sell your personal information.
- Access your money.
- Compromise your overall digital security.
But the battle isn’t lost. One way to quickly boost the safety of your online accounts is to enable two-factor authentication. From safeguarding mobile banking details to shielding your medical history, 2FA verification should be a pillar of your internet safety practices.
What is 2FA?
2FA, or two factor authentication, is when a site or app requires you to enter an extra form of identification to verify your identity and log into your account. 2FA requires people to verify their identity based on two of the three factors that can confirm identity:
- Something you know (e.g., a password)
- Something you have (e.g., a phone)
- Something you are (e.g., a fingerprint or facial scan)
That extra ID can be a code generated and sent directly through a text message or authenticator app. It can also be in the form of a piece of hardware like a USB drive or a biometric ID like a fingerprint.
Let’s break this down even further, including how two-factor authentication works, types of two-factor authentication, and why two-factor authentication is so important.
2FA vs. multi-factor authentication (MFA)
MFA refers to any type of authentication that requires two or more factors. That means that while 2FA is a form of MFA, not all forms of MFA have only two factors. Increasing the level of security by adding an extra factor makes it much more difficult for hackers to gain entry into a system.
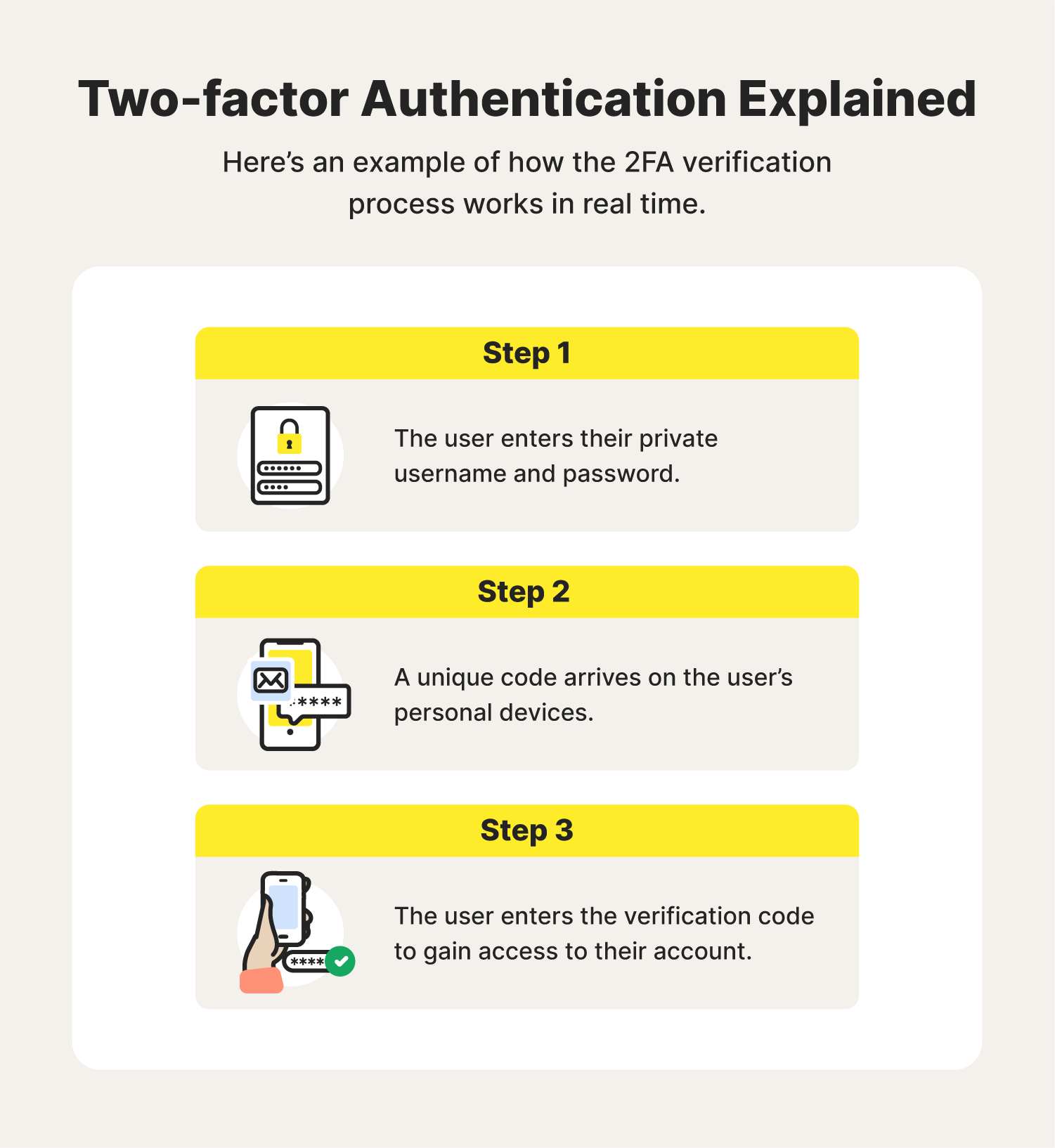
How does 2FA work?
As the name suggests, two-factor authentication requires one extra step—a second factor—to log into an account. The process works as follows:
- The user enters their username and password.
- The account, platform, or site prompts users to input another verification form, such as a one-time password or code sent to their mobile phone.
- The user enters the verification code to access their account.
An ATM card is a good example of two-factor authentication in the real world. In addition to physically presenting the card (something you have), you must also type in your PIN (something you know) to verify your identity and access your account.
Why is two-factor authentication important?
Two-factor authentication is important because adding an extra layer of verification before you can access your account means thieves will struggle to get your personal information. As cybercriminals continue to use brute force or password spraying attacks, even if you’re following good password security practices you need 2FA as well. It might seem like a hassle to add an extra step to your web surfing. But without it, you could be leaving yourself vulnerable to:
- Cybercriminals who want to steal your personal information
- Hackers trying to access your bank accounts
- Thieves breaking into your online credit card portals
If you add a knowledge factor to your bank account, a cybercriminal who knows your password due to a data breach or phishing operation won’t be able to access the account. This is because your phone will receive the verification code.
That way, those still relying on simple passwords have a better shot at keeping their bank accounts secure.

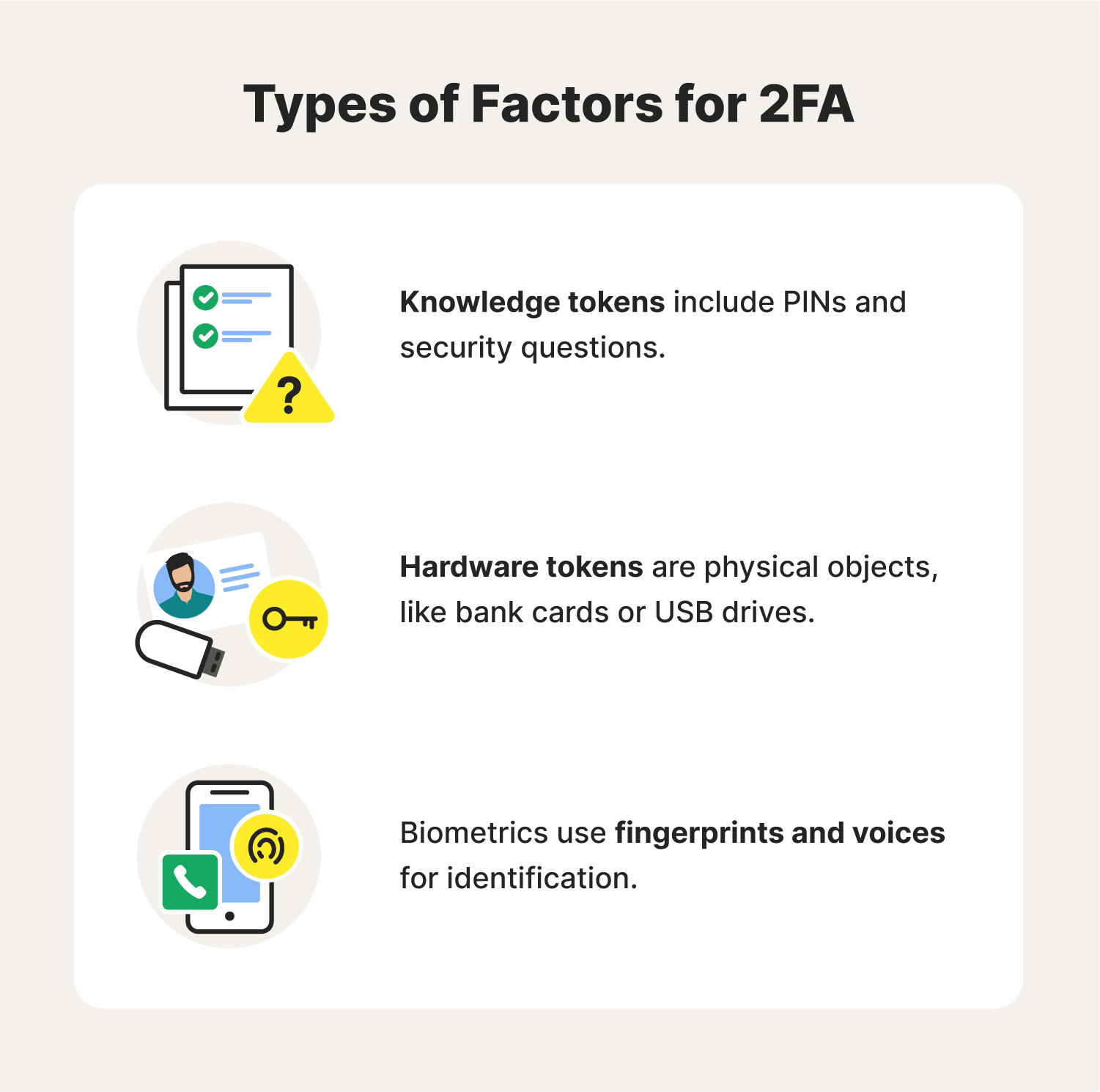
Types of 2FA security
There are several types of two-factor authentication security, including:
- Something you know: These kinds of 2FA use a code, question, or password that are unique to you. Using your PIN at an ATM is a form of 2FA that requires something you know.
- Something you have: This type of 2FA requires users to possess a type of physical token or device, such as a phone or USB token, that they need to use to log in. When you need to enter a code you receive via email or text before you can log in, or when you use an Authenticator app, you’re using this method of 2FA.
- Something you are: This type of 2FA requires biometrics like fingerprint or facial recognition or a physical location (confirmed by GPS) to confirm your identity.
Now that you know the different types of 2FA verification, let’s learn how to enable it on your devices.
How to get 2FA on your accounts
Though not all sites use 2FA, some give you the option to activate it for your account. For sites that allow you to enable 2FA, you can turn it on in your account security or privacy settings.
Some popular websites that do enable 2FA include:
- Amazon
- Facebook and Instagram
- Dropbox
- LastPass
- Intuit
- TurboTax
- Mint
- PayPal
- Yahoo
If a site or platform you use doesn’t offer 2FA yet, consider using a secure password manager to help you store and create stronger passwords.
Adding two-factor authentication to your high-priority accounts can help keep you, your money, and your personal information more secure.
Tip: If you’re using your phone as your 2FA method, make sure it’s also password-protected. Otherwise, if your phone is lost or stolen, scammers could access your accounts.
3 benefits of 2FA
The added security and protection that two-factor authentication gives you is a net positive. But there are a few extra benefits that you might not know about, including:
- Account monitoring: You’ll know if someone is trying to access your accounts because you’ll receive a message or prompt on your device. That allows you to report it and further strengthen your security by changing your password to something stronger.
- Dynamic process: 2FA authenticator apps, push notifications, and texts are generated and sent when you log in, meaning you don’t have to worry about securely storing another factor.
- Account recovery assistance: 2FA means that you don’t have to put in a help desk ticket or try to get on the phone with a support team member to reset your logins or secure your account.
Safeguard your information and identity
Now that you know how 2FA can improve the Cyber Safety of your online accounts and your personal data, enable it wherever you can. Then, install a comprehensive security software and identity theft protection tool like Norton 360 with LifeLock Select, which helps protect against malware, encrypt your connection with a VPN, and safeguard your identity against scammers. Plus, our restoration specialists will help you restore your identity should the unthinkable happen.
FAQs about 2FA
Check out some frequently asked questions concerning the 2FA login process.
Is 2FA safe?
For the most part, 2FA is safe. Still, like most online activities, there are ways that criminals can bypass 2FA security and access your account. For example, lost password recovery usually resets your password via email, and it can bypass 2FA.
Even though it's not 100% secure, 2FA can bolster your online security and is recommended.
Can two-step verification be hacked?
Yes, hackers can use certain phishing messages and SIM swapping to work around 2FA login processes. That being said, having a second authentication factor makes it more difficult for hackers because more information is required to gain access.
What is the strongest 2FA method?
Hardware-based 2FA is the strongest form of 2FA verification. Because a physical item is needed, whether it’s a phone, a thumb drive, an ID card, or another object, it’s much more difficult for a hacker or criminal to access all parts of 2FA logins.
Is MFA better than 2FA?
Multi-factor authentication that uses three or more authentication factors is more secure than 2FA. For most sites, apps, and platforms, 2FA should be secure enough. Groups that have higher security needs (governments, healthcare providers, and financial institutions, for example) may require additional verification factors.
How do I know if I have two-factor authentication?
You can check if your account or device has 2FA by entering your account security or privacy settings. You should see options for the different types of 2FA security offered.
Editorial note: Our articles are designed to provide educational information for you. They may not cover or protect against every type of crime, fraud, or threat we write about. Our goal is to increase awareness about Cyber Safety. Please review the complete Terms during enrollment or setup. Remember that no one can prevent all identity theft or cybercrime, and that LifeLock does not monitor all transactions at all businesses. The Norton and LifeLock brands are part of Gen Digital Inc. For more details about how we create, review, and update content, please see our Editorial Policy.







Want more?
Follow us for all the latest news, tips, and updates.