What is multi-factor authentication?
Hackers do not like multi-factor authentication, which is exactly why you should use it. Learn how MFA works, and why pairing this security feature with Cyber Safety software that includes a password manager is like creating a digital fortress.

Without multi-factor authentication (MFA), a stolen password could give hackers access to your digital life. In a single three-month period in 2024, more than 400 million data records, including login credentials, were exposed in data breaches, putting everything from emails to bank accounts at risk. MFA provides an added layer of security in these situations, helping keep your personal information safe even if your password is leaked.
Keep reading to learn how MFA works and how it helps prevent your accounts from being hacked.
Multi-factor authentication definition
Multi-factor authentication adds extra security to accounts by requiring two or more forms of verification, like a password and a one-time code, before granting account access. This helps protect your sensitive information from hackers and your accounts being used in scams.
Without MFA, criminals can use a stolen password to access your email, bank account, or other personal data. Adding another layer of verification makes it significantly more difficult for attackers to break in, even if they know your password.
How does multi-factor authentication work?
MFA uses two or more identity checks, like a password, a code sent to your phone, and a fingerprint. Each factor is verified separately, so hackers can’t log into accounts without the others, even if one is compromised. This layered approach offers much stronger protection than even a secure password can on its own.
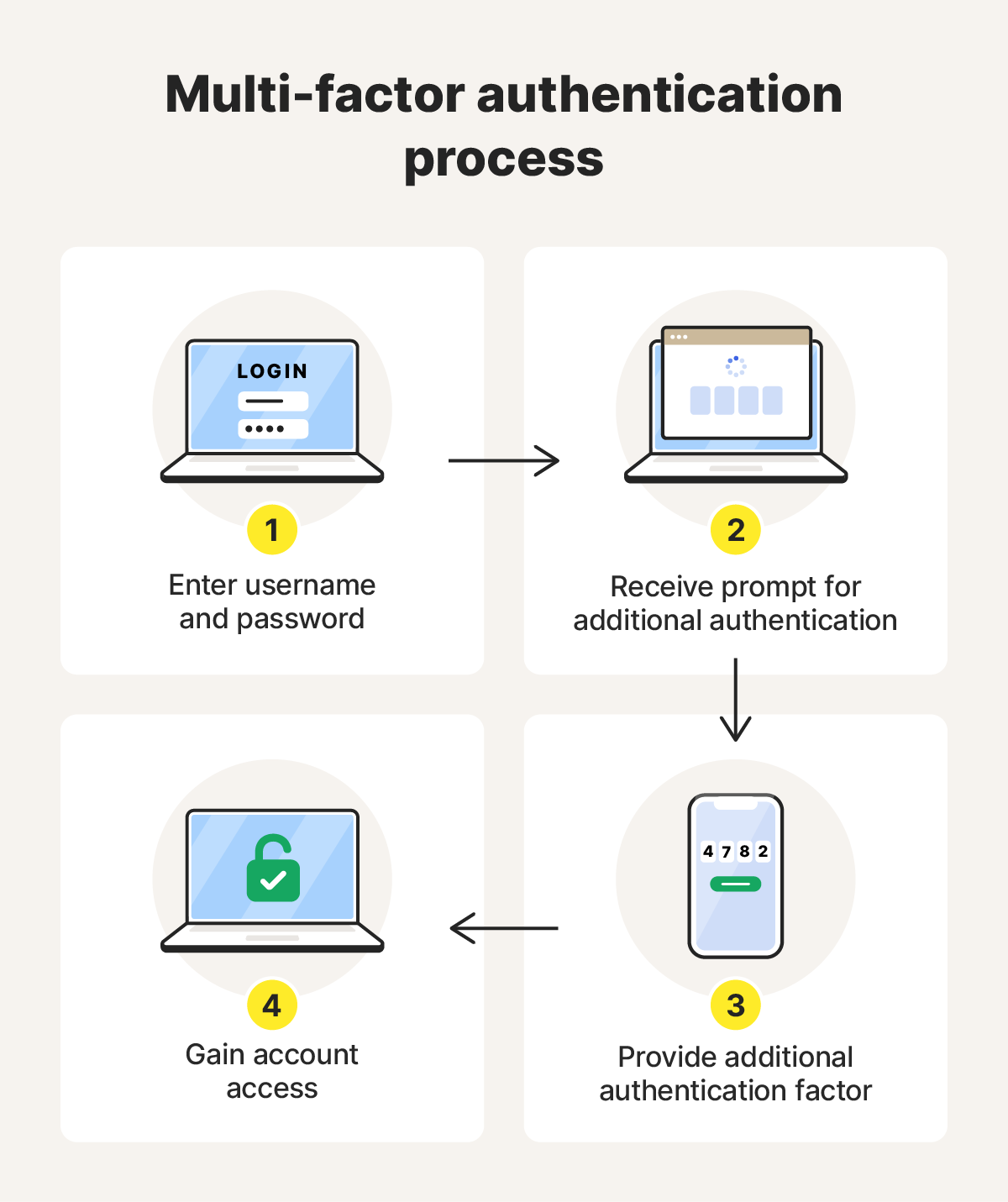
Here’s a closer look at how MFA security works:
- You enter your username and password on a login page, and the system verifies these credentials.
- The system prompts you for a second verification method (e.g., a code from an app or biometric scan). This second factor uses a different device or method than your password, helping block hackers even if they’ve stolen your login credentials.
- You provide the second factor.
- If three or more factors are enabled, you’ll be prompted to complete each one.
- Once all required factors are verified, you’re granted access.
You’ve likely encountered MFA when logging into everyday accounts like banking, email, or social media. Here are a few common account types that use MFA:
- Google: Google prompts you to enter a code sent to your phone or generated by an authenticator app after entering your password on a new device.
- Amazon: Amazon enhances account security by sending a one-time code to your phone or authenticator app if you log in from a new device.
- Facebook: Facebook’s security involves receiving a code on your registered mobile number, using an authenticator app, or tapping a security key on a compatible device.

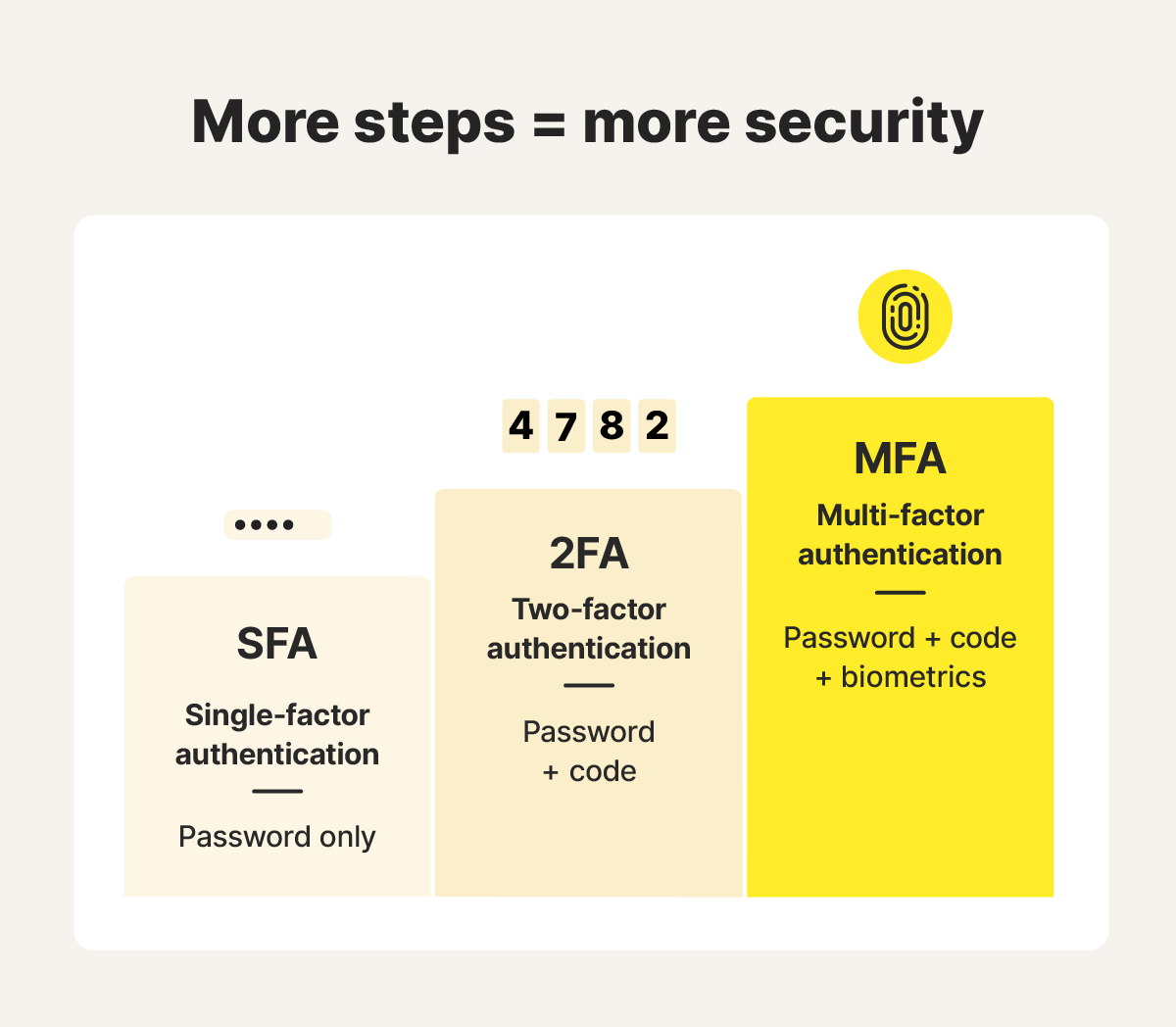
Difference between multi-factor authentication and two-factor authentication
Two-factor authentication (2FA) uses two types of verification, such as a password and a code. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) includes 2FA but can involve more than two factors. Adding extra layers of security makes unauthorized access even harder. In short, all 2FA is MFA, but MFA isn’t limited to two factors.

Types of multi-factor authentication
Multi-factor authentication relies on different types of verification to confirm your identity. These include what you know, what you have, who you are, and where you are. Here’s a closer look at the types of MFA in each category.
What you know
This knowledge-based factor relies on information only the user knows. It often forms the first layer of MFA by asking users to enter familiar details during login.
Examples include:
- Password.
- PIN.
- Answer to a security question.
What you have
This possession-based factor verifies identity through a physical object the user carries.
Examples include:
- SMS codes.
- Smart card.
- Hardware token or security key.
Who you are
This identity-based factor uses biometrics to verify identity through unique physical traits.
Examples include:
- Fingerprint.
- Facial recognition.
- Voice recognition.
Where you are
This location-based factor verifies identity by checking where the login attempt originates. It uses geographic data to confirm the user is in an expected or trusted location, helping detect suspicious access attempts.
Examples include:
- GPS data from your phone.
- Restrictions on logging in from new regions or IP addresses.
- Recognition of familiar Wi-Fi networks.
Benefits of multi-factor authentication
Multi-factor authentication is one of the strongest security measures you can implement to protect your accounts and sensitive data.
Here’s a closer look at some security benefits MFA provides:
- Reduces risk of identity theft: By requiring multiple forms of verification, MFA makes it much harder for attackers to impersonate you with stolen credentials and commit identity theft.
- Notifies you of suspicious activity: MFA systems often alert you to login attempts, helping you spot unauthorized access attempts in real time.
- Protects against compromised passwords: Even if your password gets leaked or stolen, or a hacker guesses it through a brute force attack, it will be nearly impossible for them to access your account.
The cost of skipping MFA
A breach at Change Healthcare highlights how important MFA is for protecting data. Attackers used stolen credentials to access the company’s systems through a Citrix portal with no MFA. Without that extra layer of security, they moved through the network unchecked, stole data, and deployed ransomware. Had Change Healthcare used MFA, hackers may not have gained access.
Additional ways to secure your data
To better protect your personal information and accounts, use a password manager, update your software, connect only to secure Wi-Fi, and limit how much data you share. While multi-factor authentication offers strong security, combining it with these practices lowers the risk of criminals gaining unauthorized access.
Use the following strategies, along with MFA, to protect your data:
- Use a password manager: A password manager helps you create and store strong, unique passwords for every account, so you don’t have to remember them all. This reduces the chance of using weak or repeated passwords that hackers can easily guess.
- Keep software updated: Regularly update your software and operating system to patch known security vulnerabilities that cybercriminals could exploit to access your data.
- Limit data sharing: Limit the personal information you share online or with apps to reduce the likelihood of your data getting exposed following a breach.
- Always use a VPN: Public Wi-Fi networks are often unsecured, making it easy for attackers to spy on your activity, including passwords you enter. Using Norton VPN encrypts your connection, protecting your data even on public networks.
- Use a robust antivirus: Always have a strong malware scanner and remover on all your devices. That way, you can help keep spyware and other data-stealing malware at bay.
Safeguard your information and identity
A password alone won’t cut it these days. MFA adds extra layers of protection to keep your account safe from prying eyes. Combine it with powerful Cyber Safety software like Norton 360 Deluxe and you’ve got a security combo that can stop cyber threats in their tracks.
FAQs
Are MFA and 2FA the same thing?
No, MFA and 2FA aren’t quite the same. 2FA is a type of MFA that requires exactly two verification methods. MFA can involve two or more steps, offering extra security. These steps may include a security key, biometric scans, or a one-time code sent to your device.
Can MFA be hacked?
Yes, MFA can be hacked, but it’s much more complicated than breaking a password alone. Attackers may use techniques like phishing, SIM swapping, or exploiting software vulnerabilities. However, MFA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access by requiring multiple forms of verification, making hacking attempts far less successful.
What’s the best MFA method to use?
The best MFA method combines strong security with user convenience. Biometric factors (like fingerprint or facial recognition) paired with authenticator apps (which generate time-based codes) offer high security and ease of use. While SMS codes still provide valuable added security above and beyond just a password, they’re more vulnerable to interception and SIM-swapping attacks.
What’s the difference between MFA and single sign-on?
Multi-factor authentication adds extra steps to verify your identity, while single sign-on (SSO) lets you access multiple apps with one set of login credentials. MFA focuses on stronger security during login, whereas SSO improves convenience by reducing how often you need to sign in.
Editorial note: Our articles provide educational information for you. Our offerings may not cover or protect against every type of crime, fraud, or threat we write about. Our goal is to increase awareness about Cyber Safety. Please review complete Terms during enrollment or setup. Remember that no one can prevent all identity theft or cybercrime, and that LifeLock does not monitor all transactions at all businesses. The Norton and LifeLock brands are part of Gen Digital Inc.









Want more?
Follow us for all the latest news, tips, and updates.