What is hacking, who are hackers, and how can you protect yourself?
Hackers are constantly finding new ways to gain unauthorized access to devices and systems. In this guide, we’ll break down the different types of hackers, the techniques they use, and how strong digital security can help you protect against hackers, scams, and other online threats.

The first recorded use of the hacking definition as we use it now dates back to 1963. Fast forward to today and hacking has become a much more complex, widespread, and dangerous threat. And it continues to grow — from 2018 to 2023, there was a 239% increase in hacks resulting in large breaches in the healthcare sector.
Curious about how hacking works and, more important, how you can protect against hackers? Keep reading to learn more.
What is a hacker?
A hacker is an individual who leverages their technical skills to identify and exploit vulnerabilities in systems, networks, or software to achieve specific goals that may be ethical or malicious.
- Demographics: Early depictions of hackers — in film, TV, or online — often portrayed them as precocious teens breaching major organizations' systems for notoriety. Today, hackers span a wide range of demographic profiles.
- Skills: While many hackers possess advanced technical skills and knowledge of computer systems, the rise of copy-paste attacks, AI-assisted hacking, and other advancements have enabled even low-skilled hackers to exploit vulnerabilities and carry out dangerous attacks.
- Motives: Whether the hacker is trying to make some extra cash, exploit injustices, or simply catch a thrill, hackers often have a specific motivation for their hacking efforts.

How does hacking work?
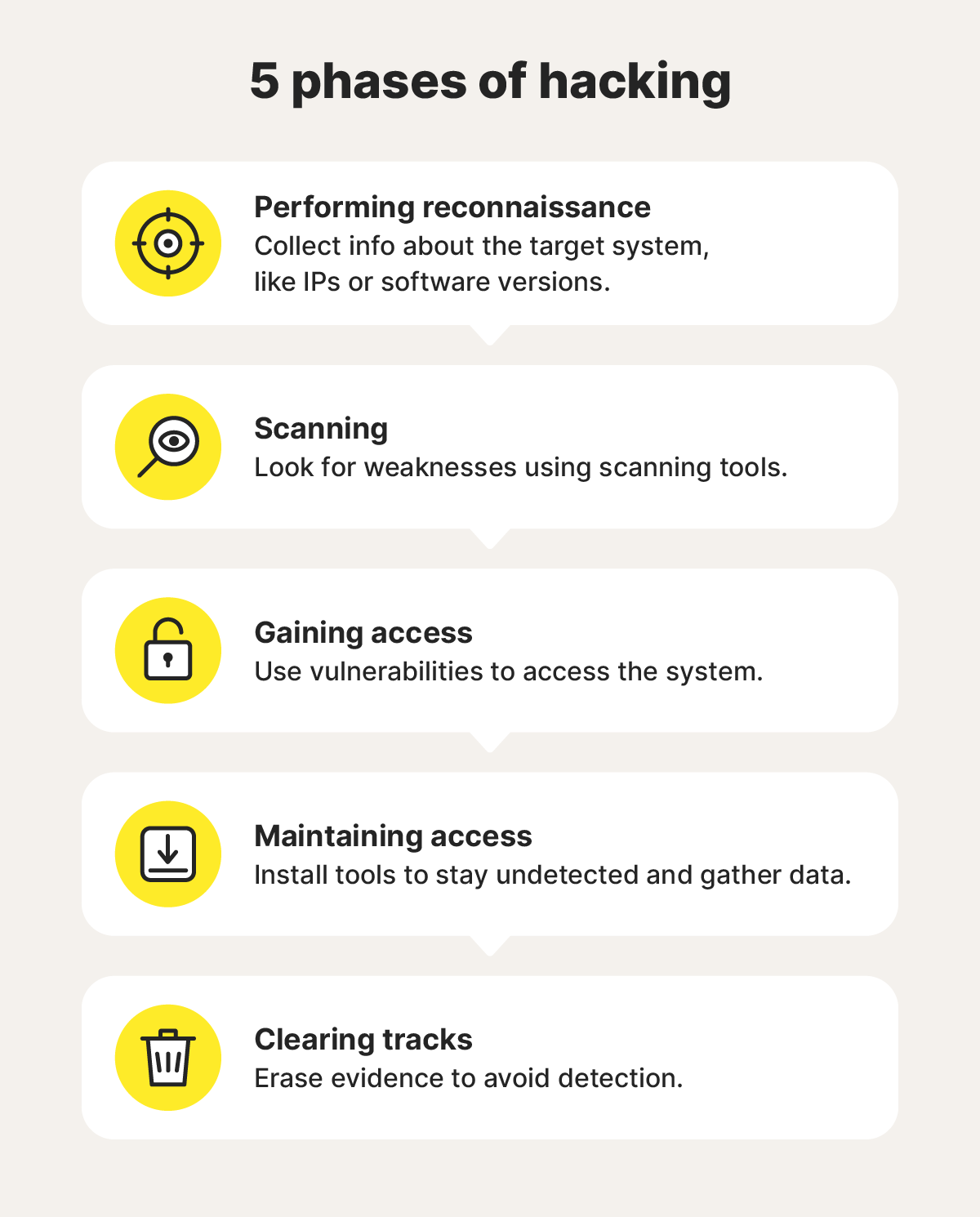
Hacking works by exploiting vulnerabilities in cybersecurity defenses to achieve specific goals, such as gaining unauthorized access to networks, devices, or sensitive data. Hackers may target anything from computers and phones to IoT devices and specific software to carry out their attacks.
First, the hacker gathers information about their target to understand how the system works. Then, they look for any vulnerabilities they can exploit to gain access. Once they find a way into a system, they can spy on activity, collect sensitive data, inject malware, or carry out other aims. After, they’ll try to hide their tracks by removing evidence of the hack.
Exploiting social weaknesses
Hackers can use social engineering techniques to exploit social weaknesses. For example, a hacker might impersonate a high-level executive to trick another senior manager into giving out confidential information — a tactic known as a whaling attack. Or, they might target an organization with a phishing attack to try to trick a lower-level employee into exposing system-access credentials.
Exploiting technical vulnerabilities
A hacker may exploit a technical vulnerability by using their technical skills to inject a device with malware or find security flaws in software that allow them to gain unauthorized access to private data.

Types of hackers
Some types of hackers use their skills for good, while others can take a more malicious approach. And some of them use advanced technical skills to carry out their attacks, while others might be mere novices employing relatively simple methods.
Some of the most common types of hackers include:
- Threat actors: Also known as black hat hackers, threat actors use their skills to break into systems, networks, and devices with malicious intent. Whether they're making money off ransomware or stealing someone’s identity, threat actors use their skills for personal gain without regard for the law or others.
- Ethical hackers: Also known as white hat hackers, ethical hackers use their hacking skills for good. They spot security flaws to help cybersecurity experts update systems to prevent criminal hackers from exploiting those weaknesses in the future.
- Red hat hackers: Also known as vigilante hackers, red hat hackers also use their skills for good, doing whatever’s necessary to take down a threat actor, even if it means breaking a few rules.
- Gray hat hackers: While they usually aren’t malicious, gray hat hackers may hack into systems for fun without proper authorization. Once the hacker gains access to their desired target, they may alert system owners of the security flaws or even offer to fix them.
- Green hat hackers: Green hat hackers are the new kids on the block, with little hacking experience. Because green hat hackers often don’t know what they’re doing, they may accidentally do some damage, whether they mean to or not.
- Blue hat hackers: Blue hat hackers are kind of like ethical hackers, except they are given access to software to test it for security flaws before a business commits to using it. This helps businesses avoid settling on a new piece of technology that could be susceptible to threat actors.
- Script kiddies: Amateur hackers known as script kiddies use pre-written scripts and computer hacking software to carry out their hacking endeavors. Unlike a green hat hacker who attempts to do the hacking on their own, script kiddies take a lazier approach and ride the coattails of other hackers.
- Hacktivists: These types of hackers perform hacktivism, which is when they use their hacking expertise to try to influence political change. They may do this by exposing information such as private communications and photos or by drawing attention to a cause they believe in.


Common hacking techniques
Be it a carefully crafted piece of ransomware or an elaborate smishing text, hackers can have a vast set of hacking methods up their sleeves. Some of the most common hacking techniques to watch out for include:
Phishing
Hackers often use phishing attacks to trick you into clicking a malicious link or giving up personal information they can use to their advantage. Examples include emails pretending to be from a customer service representative or a coworker.
Smishing
Smishing, a phishing and SMS hybrid, is a phishing attack that targets individuals via mobile text messages. Like their email-based counterparts, smishing texts often include requests for personal information and suspicious links that lead to malicious websites.
Malware
Short for “malicious software,” hackers use malware to steal information or damage and disrupt devices and systems. There are many different types of malware, from spyware to botnets.
Ransomware
As the name suggests, this form of malware infects devices, encrypts system or user data, and demands a ransom to unlock it. A notorious example is CryptoLocker, which caught global attention after encrypting innocent users’ files to scare them into paying a ransom.
Trojans
Trojans are a type of malware that masquerades as legitimate applications or files to trick users into downloading them willingly. Once installed, Trojan applications can wreak havoc on your device and privacy.
Brute force attacks
A brute force attack occurs when a hacker uses trial and error to attempt to gain unauthorized access to computer systems or online accounts. For instance, a hacker could automate the testing of millions of login credentials in the hope of gaining access to someone’s private account.
Distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks
A DDoS attack is when a hacker tries to crash a website by flooding it with enormous volumes of traffic. They can do this by using an army of remotely controlled computers known as botnets.
Domain Name System (DNS) spoofing
DNS spoofing is an attack in which hackers redirect internet traffic away from its legitimate destination to a malicious website. Once the users are redirected to the unsafe site, the hacker can try to install worms or other types of malware on unsuspecting visitors.
Website spoofing
Sometimes referred to as domain spoofing, website spoofing is a technique hackers use to create fraudulent websites that imitate those of legitimate companies. Once you visit a spoofed site, it may infect your device with malware or steal your credit card information or login credentials.
Structured Query Language (SQL) injection
SQL injection is a hacking method in which attackers manipulate database queries by injecting malicious code into input fields. This allows them to gain back-end access to private information databases, such as user data and login credentials.
Keyloggers
A keylogger is a hardware or software component that captures and records a user's keystrokes, allowing hackers to spy on people's activity. By tracking everything you type from passwords to account numbers, they may be able to capture enough information to steal your identity.
Which devices are most vulnerable to hacking?
Hackers can use their skills to target a wide range of devices. However, some forms of hardware, such as smartphones and IoT devices, are more vulnerable than others due to their system architecture and typical use cases. Here’s a rundown of the top device types that hackers target:
Smartphones
Hackers often target smartphones as they hold valuable personal information, such as credit card numbers, login credentials, and two-factor authentication (2FA) codes. Additionally, smartphones are frequently used on unsecured networks like public Wi-Fi, increasing their susceptibility.
When comparing Android and iPhone security, iPhones are generally considered more secure due to Apple’s oversight of third-party apps in the App Store and the closed nature of the iOS system. However, iOS users are not immune — iPhones can still be hacked. Regardless of the type of phone you use, it’s essential to take security measures to protect against hackers.
Laptop and desktop computers
Laptops and desktop computers can store very large volumes of sensitive personal and company information and are typically used for accessing sensitive systems — making them prime targets for hackers.
Although Macs are vulnerable to malware and other hacking techniques, Windows computers are targeted more often due to their widespread use — holding 72% of the market share for desktop operating systems as of 2024. This popularity makes them a bigger target for hackers, who create more computer viruses aimed at Windows users.
Internet of Things (IoT) devices
IoT devices, such as sensors, appliances, cars, and medical equipment, are prime targets for hackers due to their often weak security and potential to serve as entry points to larger networks. Many IoT devices also collect and store sensitive data, including location, contact information, and financial details.
In one instance, a hacker hacked a family’s Ring camera, spied on them, and demanded money. A more recent example involved a teenage hacker who used a vulnerability in a third-party app to hack Tesla vehicles, enabling him to unlock the doors, flash the headlights, and play loud music.
Routers
Hackers target Wi-Fi routers and modems because they serve as gateways to access any device connected to them, but lack the security protections typically found on computers or phones. In fact, infected routers are responsible for 75% of IoT attacks, according to cybersecurity statistics.
What damage can hackers cause?
Hackers can cause severe damage and disruption, from draining your bank account and harming your credit to stealing personal information and invading your privacy. While it’s easy to assume hackers have bigger targets, that’s not always true.
Hackers could impact you personally by:
- Bricking your device: Hackers may permanently disable your device to disrupt operations or as part of a ransom or revenge tactic.
- Draining your finances: Hackers can steal money from your bank accounts and make fraudulent charges to your credit cards.
- Stealing your identity: By accessing your personal information, such as your name, address, and Social Security number, hackers may be able to commit identity theft.
- Selling your information: Instead of keeping your personal information for their own nefarious use, some hackers will sell it to other bad actors on the dark web.
- Tanking your credit score: Hackers can open up credit accounts in your name, racking up debt and causing significant damage to your credit that can take years to sort out.
- Invading your privacy: Hackers can access your browsing history, monitor your webcam, and steal your financial records.
How to protect yourself from hackers
Protecting yourself from hackers requires a combination of awareness, proactive measures, and best practices. By using strong, unique passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, keeping software updated, and using robust security software, you can significantly reduce your risk of falling victim to cyberattacks.
To help protect yourself, follow these tips:
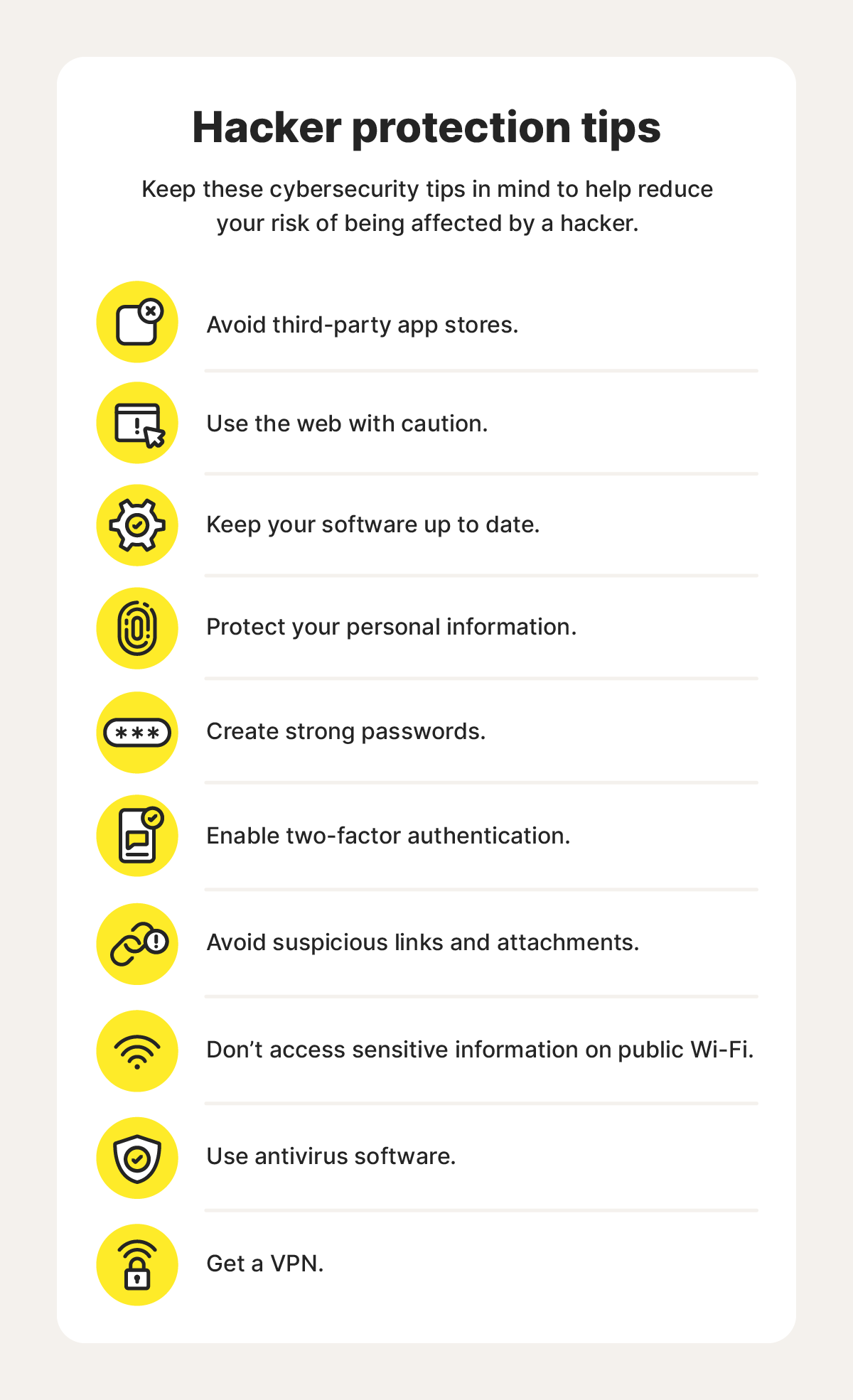
Avoid third-party app stores
Whenever you download new applications for your device, stick to trusted app stores and websites, as third-party app stores can be riddled with malware in disguise.
Use the web with caution
From casual browsing to online shopping, always use common sense and caution when using the internet. By staying vigilant and thinking before you click, you can reduce the risk of falling for hacking methods like phishing emails or spoofed websites.
Keep your software up to date
Threat actors often exploit security vulnerabilities in outdated software, so it's crucial to keep your operating system updated, as well as your apps and other software. This ensures you receive the latest updates designed to help protect against hackers.
Protect your personal information
Whenever you’re online, think twice before sharing any sensitive details, and try to minimize your digital footprint. Prioritize safeguarding your personal information to reduce the risk of your private info getting into the hands of a hacker.
Create strong passwords
Be sure to create a secure password for each of your devices and accounts. Layered protection is the key to robust protection, and a strong password could be the hacking prevention measure that keeps a hacker from accessing your most sensitive data.
Enable two-factor authentication (2FA)
Enabling two-factor authentication (2FA), such as biometrics or SMS codes, adds an extra layer of protection against hackers. Even if a hacker obtains your login credentials, they won’t be able to access your account without the second authentication factor.
Avoid suspicious links and attachments
Cybercriminals often use malicious links to distribute malware or initiate phishing scams. Always take the time to check the URL and verify the source before clicking links or downloading files, especially from unknown senders.
Don’t access sensitive information on public Wi-Fi
While convenient, using public Wi-Fi is also risky. These networks are often unsecured, allowing hackers on the same network to monitor or intercept your online activities. To help stay safe, avoid accessing sensitive information or logging into important accounts when connected to public Wi-Fi.
Use antivirus software
The best way to detect and block malware, hacking attempts, and other malicious threats is to use antivirus software that actively protects your device by scanning files, emails, and websites for potential risks, and alerting you before your security is compromised.
Get a VPN
A VPN uses powerful encryption to scramble your internet data, making it unreadable to hackers who may attempt to intercept it and launch a man-in-the-middle attack. It also hides your IP address, which can help prevent hackers from identifying you as a potential victim to target.

Stay one step ahead of hackers
Hackers are always on the lookout for vulnerabilities, but with the right protection, you can stay a step ahead.
With Norton 360 Deluxe, you gain powerful defenses that can help stop hackers in their tracks, prevent account takeovers, and block malware in real time. Plus, it includes a built-in VPN to keep your IP address private and your internet data secure. Don’t wait until it’s too late — secure your digital life today.
FAQs
What is ethical hacking?
Ethical hacking is when a hacker is authorized to attempt to gain access to a device, network, or application. This practice helps companies identify and address security flaws that could be exploited by malicious hackers.
Is hacking illegal in the US?
According to the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act, hacking to defraud or cause harm may be a federal crime. Depending on the severity of the offense, hacking could result in a felony or misdemeanor charge and may result in a fine or custodial sentence.
What can a hacker do with an IP address?
Hackers can use your IP address as a starting point to gather more information about you or your device. With it, they can launch DDoS attacks, target you with phishing links, or try to exploit vulnerabilities in your network or device.
Does a VPN prevent hacking?
VPNs encrypt your internet connection and mask your IP address, making it harder for hackers to intercept your data, or locate you online. But unlike antivirus software, VPNs don’t offer device-level protection against hacking, which is why combining them with other security tools is essential for comprehensive protection.
Why do hackers hack?
Hackers hack for various reasons, including financial gain, political motives, personal vendettas, or even just some twisted idea of fun. Some aim to disrupt services, steal sensitive data, or cause chaos, while others may seek to challenge their skills or expose weaknesses in systems to promote change or awareness.
Editorial note: Our articles are designed to provide educational information for you. They may not cover or protect against every type of crime, fraud, or threat we write about. Our goal is to increase awareness about Cyber Safety. Please review the complete Terms during enrollment or setup. Remember that no one can prevent all identity theft or cybercrime, and that LifeLock does not monitor all transactions at all businesses. The Norton and LifeLock brands are part of Gen Digital Inc. For more details about how we create, review, and update content, please see our Editorial Policy.









Want more?
Follow us for all the latest news, tips, and updates.