What is cybersecurity and why is it important?
Cybersecurity is the set of systems, tools, and practices that protect devices and networks from cyberattacks that could put your devices and data at risk. Learn why cybersecurity is important for individuals, and how powerful Cyber Safety software like Norton 360 can safeguard your data and help protect you from digital threats.

Cybersecurity refers to the practice of using technologies, processes, and controls to protect networks, devices, programs, and data from cyberattacks, damage, or unauthorized access.
Today, common cyberthreats facing consumers include various types of phishing, malware attacks, and online scams. Threat researchers at Gen Digital, Norton’s parent company, warn that the emergence of generative AI is making these attacks easier to launch and more convincing than ever before.
While some people may associate cybersecurity with corporations or governments, following cybersecurity best practices is essential for individuals, too. Protecting yourself means combining smart habits with robust Cyber Safety software that goes beyond basic antivirus.
This article explores what cybersecurity is in today’s context, how it works, and what practical steps you can take to protect yourself in an increasingly insecure digital world.
Why is cybersecurity important?
Cybersecurity is important because it helps you protect your money, identity, personal information, and privacy. Consider how much of your life now happens online: without a solid cybersecurity strategy, you’re exposed to threats like social media account takeovers, online scams, identity theft, and ransomware. These incidents can take significant time and effort to resolve, and often come with serious financial costs.
Here are some findings from a recent Gen Threat Report that underscore the evolving nature of today’s cybersecurity landscape:
- Threat researchers noted a 77% increase in mobile adware attacks quarter-over-quarter in Q3 2025, driven by fake apps that can conceal themselves after installation.
- In the third quarter of 2025, more than 83% of data breaches included passwords, indicating that cybercriminals are getting better at stealing “quality” data, according to Gen Digital.
- There were $470 million in losses from smishing (text message scams) reported to the FTC in 2024: five times higher than in 2020.
With so much of our lives happening online, cybersecurity is no longer optional. Protecting your data and staying alert to new digital risks are now part of modern life, just like setting up a home alarm system.


How cybersecurity works
Cybersecurity works by creating multiple layers of defense to help protect against potential threats. It combines tools like firewalls, antivirus software, encryption, and strong passwords to keep information private and secure.
While some of these defensive layers consist of tools or software, others are rooted in user behavior. Being wary of suspicious links, scammy messages, and too-good-to-be-true social media ads counts as cybersecurity, too.
Companies have used cybersecurity measures to ensure safe internet access and protect the sensitive information they’re entrusted with since the dawn of the digital age. But cybersecurity isn’t just a business’s responsibility. With most people using multiple devices that store sensitive data, individuals need to take cybersecurity just as seriously.
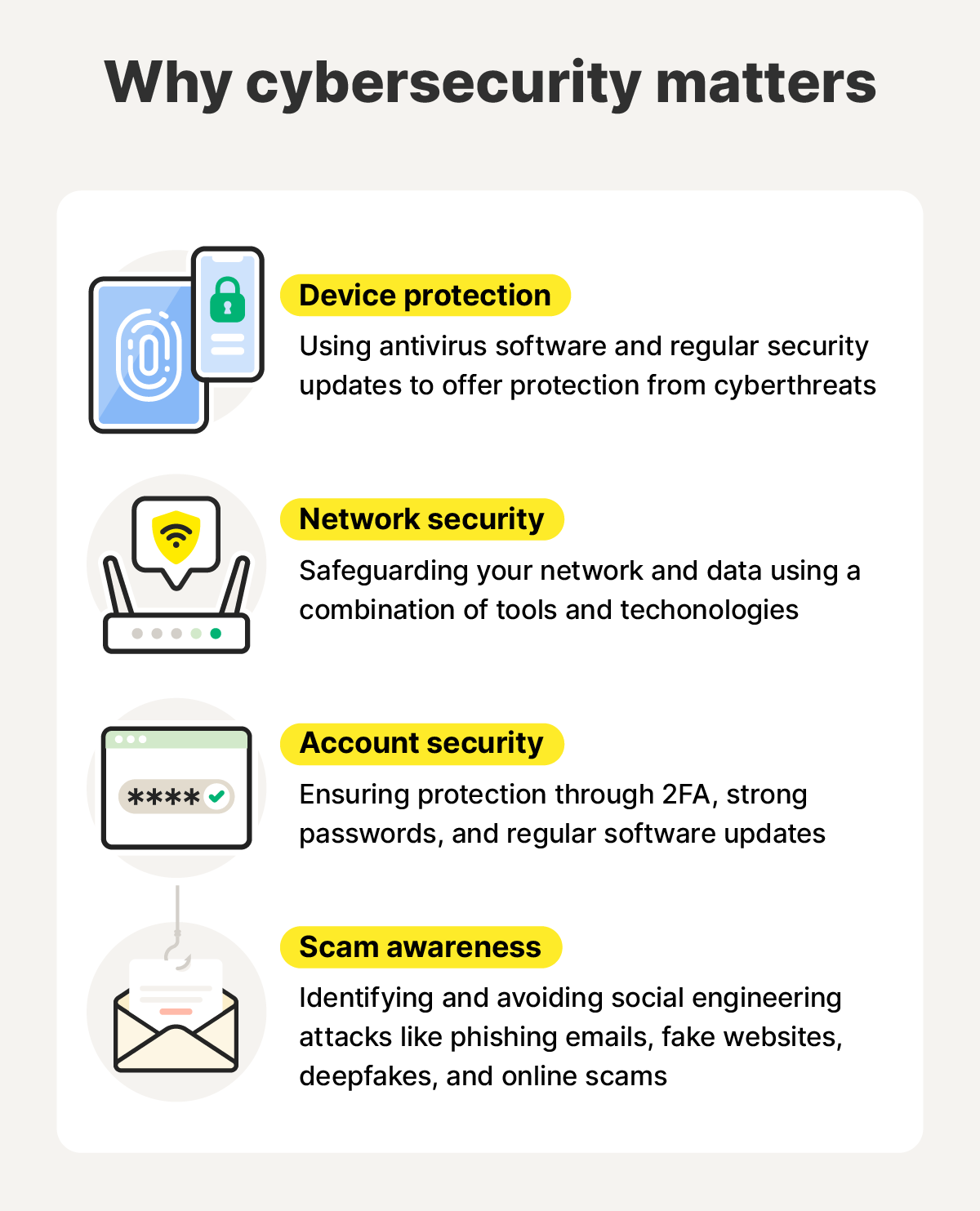
Here’s how cybersecurity works for individuals:
- Device protection: Using antivirus software, keeping systems updated, and enabling automatic security patches.
- Network security: Securing your Wi-Fi with a VPN and firewall and steering clear of dangerous websites.
- Account security: Using unique, complex passwords and enabling two-factor authentication (2FA).
- Scam and phishing awareness: Identifying and avoiding social engineering attacks like phishing emails, fake websites, deepfakes, and online scams.
Together, these layers of protection help keep your information safer and your devices more secure.

The most common cybersecurity threats
FBI data indicates that the most common cybersecurity threats for individual consumers are phishing and online scams. However, the cybersecurity landscape is diverse. Most cyberthreats fall into three main categories, comprising confidentiality, integrity, and availability attacks.
- Confidentiality attacks target personal information such as passwords, banking details, or Social Security numbers. The ultimate goal of confidentiality attacks is often to sell data on the dark web or commit identity theft or financial fraud.
- Integrity attacks aim to alter, corrupt, or manipulate data or systems without authorization. The attacker’s goal isn’t necessarily to steal information or shut systems down. Data tampering, man-in-the-middle attacks, and code injection attacks are examples of integrity attacks.
- Availability attacks focus on blocking access to files, devices, or online services. For consumers, this often shows up as ransomware, which locks you out of your own data until a payment is demanded.
In practice, these categories can overlap, and they encompass a wide range of threats you may have heard of, including phishing scams, malware, and ransomware. Let’s take a closer look at some common cyberthreats.
Social engineering, phishing, and scams
Social engineering is a manipulation tactic where cybercriminals trick people into sharing sensitive information or taking unsafe actions by exploiting human emotions such as trust, fear, or urgency.
In the digital world, social engineering often takes the form of phishing and online scams, where attackers impersonate trusted organizations or individuals through fake emails, texts, social media messages, or websites to trick people into clicking malicious links, revealing sensitive information, sending money, or granting access to accounts or devices.
While many phishing attacks get relegated to your spam folder (hopefully like these 10 real-life examples of phishing emails), cyberscammers are using AI to upgrade their tactics. They’re building fake websites that feel real (dubbed vibe scams by threat researchers) and launching scam ad campaigns on social media. According to the Pew Research Center, digital scams remain a massive problem, with 73% of adults in the U.S. having experienced some kind of scam online.
Malware
Malware is malicious software designed by threat actors to infect devices, steal sensitive information, or take control of systems.
Some well-known types of malware include spyware (such as infostealers and keyloggers, which can record what you type and transmit that information to hackers), viruses, and worms. Using malware, hackers might be able to steal your online banking login credentials, commandeer your computer, or detonate decompression bombs that crash your system.
The malware landscape is constantly evolving, requiring cybersecurity researchers to track new variants and come up with solutions to protect users. In 2025, for example, threat researchers at Gen Digital, Norton’s parent company, noted the rise of AuraStealer, a new type of malware capable of stealing data from browsers and applications, as well as ghost pairing attacks, which allow hackers to take over WhatsApp accounts.
Many types of malware can be effectively neutralized by robust Cyber Safety software, such as Norton 360 Deluxe, which offers strong safeguards against spyware, ransomware, and viruses.
Ransomware
Ransomware is a particularly insidious form of malware. As an availability attack, it infiltrates your system and encrypts or locks your files, with attackers demanding a ransom in exchange for restoring access, often within a strict deadline. Some types of ransomware include crypto-ransomware, locker ransomware, and some forms of scareware.
In one recent series of incidents, a ransomware variant called FunkSec targeted more than 100 organizations worldwide, encrypting files and demanding modest Bitcoin payments in exchange for decryption. The cybersecurity team behind Norton and other Gen products worked closely with law enforcement to dismantle the operation.
What made FunkSec stand out wasn’t the ransom itself. It was the fact that the group openly admitted to using AI tools to help write code, design phishing templates, and automate parts of their attacks.
DoS and DDoS attacks
A denial-of-service (DoS) attack is an attempt to overwhelm a website, app, or online service with excessive traffic so it becomes slow or unavailable. A distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack works the same way but is carried out from many devices at once, often using large networks of compromised computers, making the attack harder to stop.
While these cyberattacks usually target businesses or online platforms, consumers can still feel the effects, as they can knock popular websites offline. In some cases, home networks can also be abused as part of a DDoS attack if a device has been infected with malware and ensnared in a botnet.
Cybersecurity tools like firewalls and security software can block suspicious traffic and detect malware, helping prevent your devices from being misused in DoS attacks.
Man-in-the-middle attacks
In a man-in-the-middle attack (MITM), cybercriminals secretly intercept the connection between you and a website or app. By positioning themselves in the middle, attackers can spy on your activity or actively change the information being sent, redirecting you to malicious websites or fake login pages that look legitimate.
This risk is particularly relevant on unsecured public Wi-Fi networks, such as in cafés or airports. In these situations, a bad actor could intercept data traveling between your device and the server, allowing them to capture passwords, payment card information, or other sensitive details without you realizing it.
A cybersecurity tool you can use to reduce the risk of MITM attacks is a VPN, which encrypts your traffic, making it much harder for attackers to read or manipulate the data being transmitted.
Advanced persistent threats
Advanced persistent threats (APTs) are a type of attack in which an unauthorized actor infiltrates a network undetected and stays there for a long time, spying on users and exfiltrating data. APTs often happen in sectors with high-value information, such as national security, manufacturing, and the finance industry.
Recent examples include campaigns like Lumma Stealer and AMOS (Atomic Stealer). These infostealers maintained long-term access to compromised devices, continuously harvesting credentials, crypto wallets, and 2FA tokens over time, allowing attackers to silently collect valuable data without immediate detection.
AI-powered attacks
AI-powered attacks use generative AI tools to create realistic, personalized, and large-scale scams faster than ever. Instead of crafting each message or fake website manually, scammers use AI to generate convincing emails, deepfake videos, and phishing websites in seconds.
One emerging threat is AI-generated fake online shops. These scams spike in the fall as the holiday season approaches, with scammers using legitimate e-commerce platforms and AI store builders to create product pages that look authentic. They often test multiple versions to see which performs best, making these sites difficult to distinguish from real online businesses.
Individuals can use cybersecurity software with built-in scam detection, like Norton 360, to help see through cleverly camouflaged AI scams.
Risks of poor cybersecurity
Having weak cybersecurity in place doesn’t just mean dealing with annoying pop-ups or spam risk calls. It can lead to identity theft, drained bank accounts, and ongoing exposure to scams or fraud. Here are some of the main risks of weak cybersecurity:
- Identity theft: When hackers gain access to your personal details, they can impersonate you to open credit cards, apply for loans, or make unauthorized purchases.
- Personal data exposure: A weak password or unprotected device can allow attackers to access sensitive files, emails, or photos. Once your data is leaked, it can end up for sale on the dark web, where bad actors can buy and misuse it.
- Account takeovers: Once cybercriminals gain access to your online accounts, they can lock you out, take control, make purchases, and scam your contacts.
- Financial loss: Cybercriminals often target online banking, shopping, and investment accounts. Just one successful phishing email or fake app download can give them access to your payment information, leading to unauthorized transactions.
- Increased scam risk: When your personal data is exposed on the dark web, fraudsters can craft more compelling, personalized scam stories. They might use your personal details to make their phishing emails or calls sound more convincing. For example, it only takes three seconds of recorded audio for AI to clone someone’s voice for use in a “hey mom scam.”
- Corrupted devices: Malware can slow down your device, cause crashes, display unwanted ads, allow attackers to monitor your activity, or make your device complicit in illicit activity.
- Lost files: Cyberattacks like ransomware can delete, encrypt, or permanently lock you out of important files, including photos and documents.
- Reputation damage: Compromised accounts can be used to send scams, post harmful content, or impersonate you online, which can damage personal relationships or your professional reputation.
- Lost time and stress: Recovering from cybercrime often takes significant time and emotional effort, from securing accounts to disputing fraudulent charges and restoring lost data.
Cybersecurity myths
There are many misconceptions associated with cybersecurity. For example, many people believe that hackers only target large corporations, or that their devices’ built-in antivirus software is enough to keep them safe.
Here are five common cybersecurity myths and the truth behind them:
- I’m not important enough to be hacked: Most cyberattacks aren’t personal, they’re automated. Attackers use bots and scripts to scan the internet for weak passwords, outdated software, or exposed data. If your defenses are down, you’re a potential target, no matter who you are.
- Apple devices don’t get viruses: macOS and iOS are generally more secure by design, but they’re not immune. In fact, the Gen Q1/2025 Threat Report reported a rise in macOS-targeted attacks, including FakeCaptcha campaigns that tricked users into installing malware.
- My default protection is good enough: Built-in security features provide a helpful baseline, but they’re not designed to stop every threat. Modern AI-powered scams, phishing attacks, and malware often slip past default protections, which is why layering security tools is essential.
- Cybersecurity is only a concern for businesses: Individuals are now at the front line of cybersecurity. From identity theft to phishing scams and malware, cybercriminals are doubling down on harvesting personal data.
- Long passwords are enough to prevent a hack: Even the most complex password can be stolen in a data breach, phished, or captured by malware. That’s why you need additional protection like multi-factor authentication and online security tools.
Cybersecurity is as much about awareness as it is tips and tools. The better you understand how attackers operate, the easier it is to spot red flags and stop threats before they spread.
Cybersecurity best practices
Whether you’re protecting your personal accounts or a small business network, simple, proactive measures can ensure your digital life stays private and protected.
Here are some essential cybersecurity measures to help you stay safe online:
- Use strong, unique passwords: Create secure passwords that are long, complex, and different for every account. You can also use a password manager to securely store them so you don’t have to remember them all.
- Activate multi-factor authentication (MFA): Even the best password can be stolen. MFA adds an extra layer of protection by requiring a second step — like a one-time code or biometric verification — to confirm your identity.
- Update software regularly: Outdated software often contains security flaws that hackers exploit to gain access. Enable automatic updates on your devices to ensure you’re always protected against the latest vulnerabilities.
- Back up important data: Always maintain secure backups of your critical files, either in the cloud or on an external hard drive. This helps you recover data if your system is hit by ransomware, hardware failure, or accidental deletion.
- Secure your Wi-Fi and networks: Change default router passwords and use strong encryption (WPA3, if available). Make sure your network firewall is enabled, or upgrade it with Norton Smart Firewall.
- Use a VPN: Avoid public Wi-Fi for sensitive tasks like banking or shopping, or use a VPN to encrypt your connection.
- Be scam and phishing aware: Treat unexpected messages with caution, avoid clicking unknown links, and never share personal or financial information without verifying the source. Be aware that ads on social media can lead to scam websites.
- Use reputable Cyber Safety software: Consumer cybersecurity tools help detect and block malware, scams, and other cyberthreats before they can cause harm. Choose a trusted provider that offers real-time protection, phishing detection, and automatic scans.
Norton 360 is your cybersecurity sidekick
Staying safe online doesn’t have to be complicated. Norton 360 Deluxe provides a layered protection system that helps safeguard every aspect of your digital life, from your devices and accounts to your privacy and identity.
The bristling cybersecurity features included with Norton 360 Deluxe include real-time threat protection, AI-powered scam detection, a secure VPN, a stalwart password manager, dark web monitoring, and a 100% Virus Protection Promise.
Meaningful cybersecurity requires strong defenses on multiple fronts. Norton 360 provides the tools you need, all in one place, so you can breathe easy on the internet.
FAQs
What is big tech’s role in cybersecurity?
Big Tech companies play a major role in global cybersecurity by building advanced security tools, protecting massive amounts of user data, and collaborating with governments on cyber defense.
They’re the ones who invest in AI-driven threat detection, encryption, and rapid response teams to protect both their systems and users from evolving online threats.
What is cybersecurity software?
Cybersecurity software protects your devices, networks, and data from unauthorized access, theft, or damage. Common examples include antivirus programs, firewalls, encryption tools, and intrusion detection systems.
What is cybersecurity compliance?
Cybersecurity compliance means following laws, regulations, and industry standards to protect digital data and systems from cyber threats. This includes using security measures like encryption, firewalls, and access controls to safeguard sensitive information and avoid legal or financial penalties.
What is cybersecurity risk management?
Cybersecurity risk management is the ongoing process of identifying, assessing, and addressing digital security risks to minimize the impact of cyber threats. This means implementing measures like continuous monitoring, strong security controls, and incident response planning to prevent cybersecurity incidents — or at least reduce their impact.
Editorial note: Our articles are designed to provide educational information for you. They may not cover or protect against every type of crime, fraud, or threat we write about. Our goal is to increase awareness about Cyber Safety. Please review the complete Terms during enrollment or setup. Remember that no one can prevent all identity theft or cybercrime, and that LifeLock does not monitor all transactions at all businesses. The Norton and LifeLock brands are part of Gen Digital Inc. For more details about how we create, review, and update content, please see our Editorial Policy.









Want more?
Follow us for all the latest news, tips, and updates.