What is the dark web and how do you access it?
The dark web is home to the internet’s hidden sites, services, and products — some innocent, others downright dangerous. Read on to learn the pros and cons of the dark web, how to access it, and get tips for staying safe. Then, install Norton 360 Deluxe to get AI-powered scam detection to help secure your browsing against online threats.

What is the dark web?
The dark web is a non-indexed part of the internet hosting hidden sites that can only be accessed using a specialized overlay network and anonymizing dark web browsers like Tor (The Onion Router) that encrypt and hide your web traffic by routing it through a series of decentralized nodes.
Key dark web terms
- Anonymizing browser: A web browser designed to hide your online activity and identity by routing your internet traffic through multiple servers and encrypting your data.
- Darknet: An overlay network you need specific software or configurations to access; dark web content is hosted on the darknet.
- Nodes: The individual computers or devices that make up a decentralized network, relaying encrypted traffic and contributing to the anonymity of users.
- Overlay network: A network built on top of another existing network, like the internet, that adds new functionalities, often for anonymity.
Though often associated with illegal activities like drug sales, illicit content, and data breaches, the dark web also enables access to restricted information, academic resources, and secure communication for activists. Estimates suggest around 43% of dark web content and activity is legal, but finding it requires a specialized dark web search engine.
Surface web vs. deep web vs. dark web
Unlike the publicly accessible surface web, the deep web includes sites requiring login credentials but is still accessible via traditional browsers. The dark web is a small, hidden subset of the deep web that requires special tools to access.
It’s estimated that the surface web makes up about 5%–10% of the internet, while the deep web comprises as much as 90%–95%. The dark web only makes up about 0.01% of the deep web.
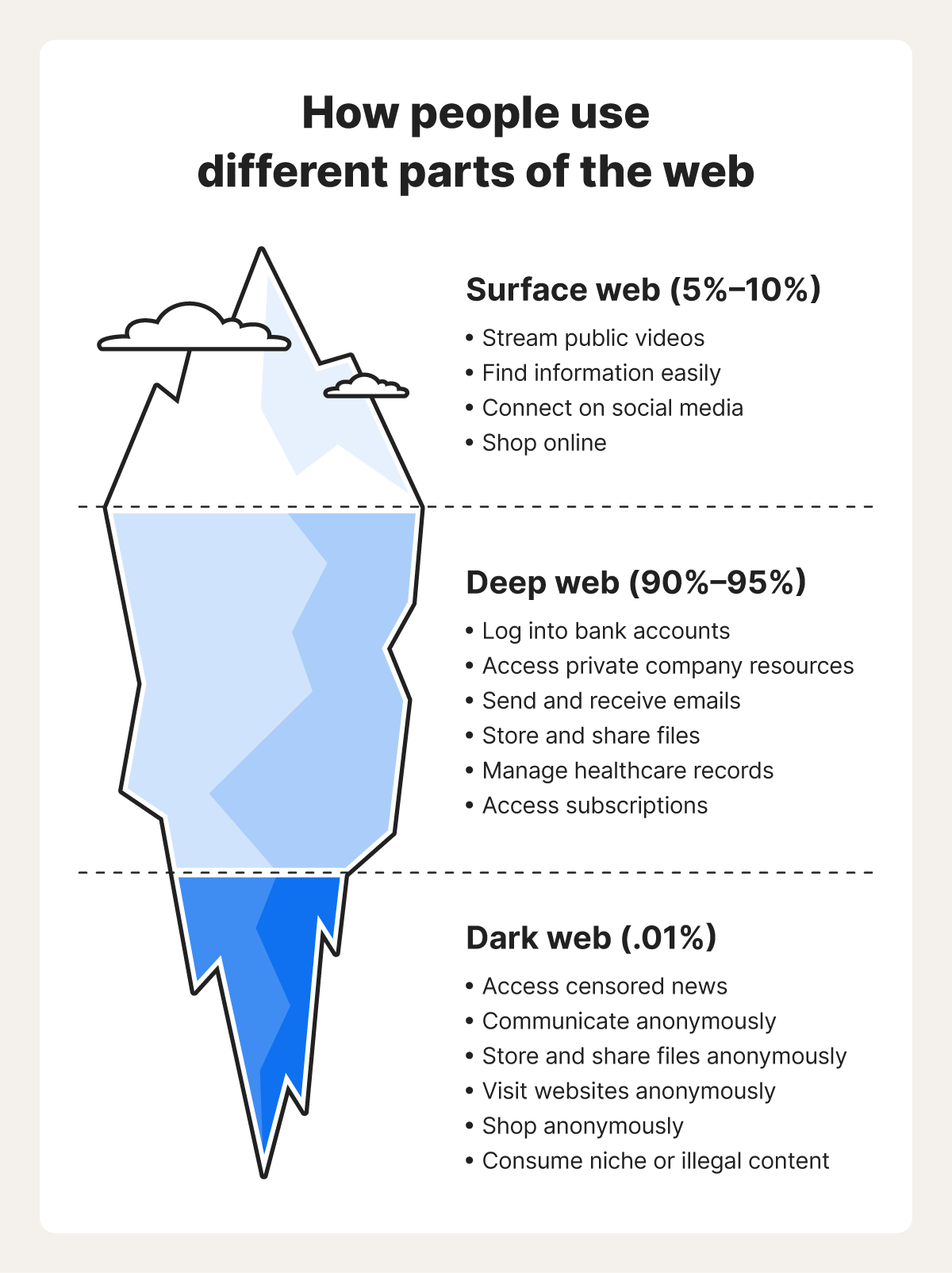

Here’s a closer look at the characteristics and use cases for each part of the internet:
- Surface web (or clear web): You can use the visible part of the web to easily find information via search engines, connect on social media, shop online, read free news articles, watch public videos, and access government resources through a normal web browser.
- Deep web: You likely access the non-indexed deep web daily for online banking, email, storing files, streaming subscription content, managing healthcare records, accessing educational materials, and using company intranets.
- Dark web: The dark web can be used to communicate anonymously, bypass censorship, access restricted information, share files securely, and protect privacy. However, cybercriminals also exploit it for illegal activities.
What does the dark web look like?
In most ways, the dark web resembles the clear web, but dark web sites often have a text-heavy, minimalistic design focused on anonymity and functionality. Another difference you’ll notice is that instead of seeing web addresses with a “.com,” “.org,” “.edu,” or “.gov” suffix, they’ll end in “.onion.”

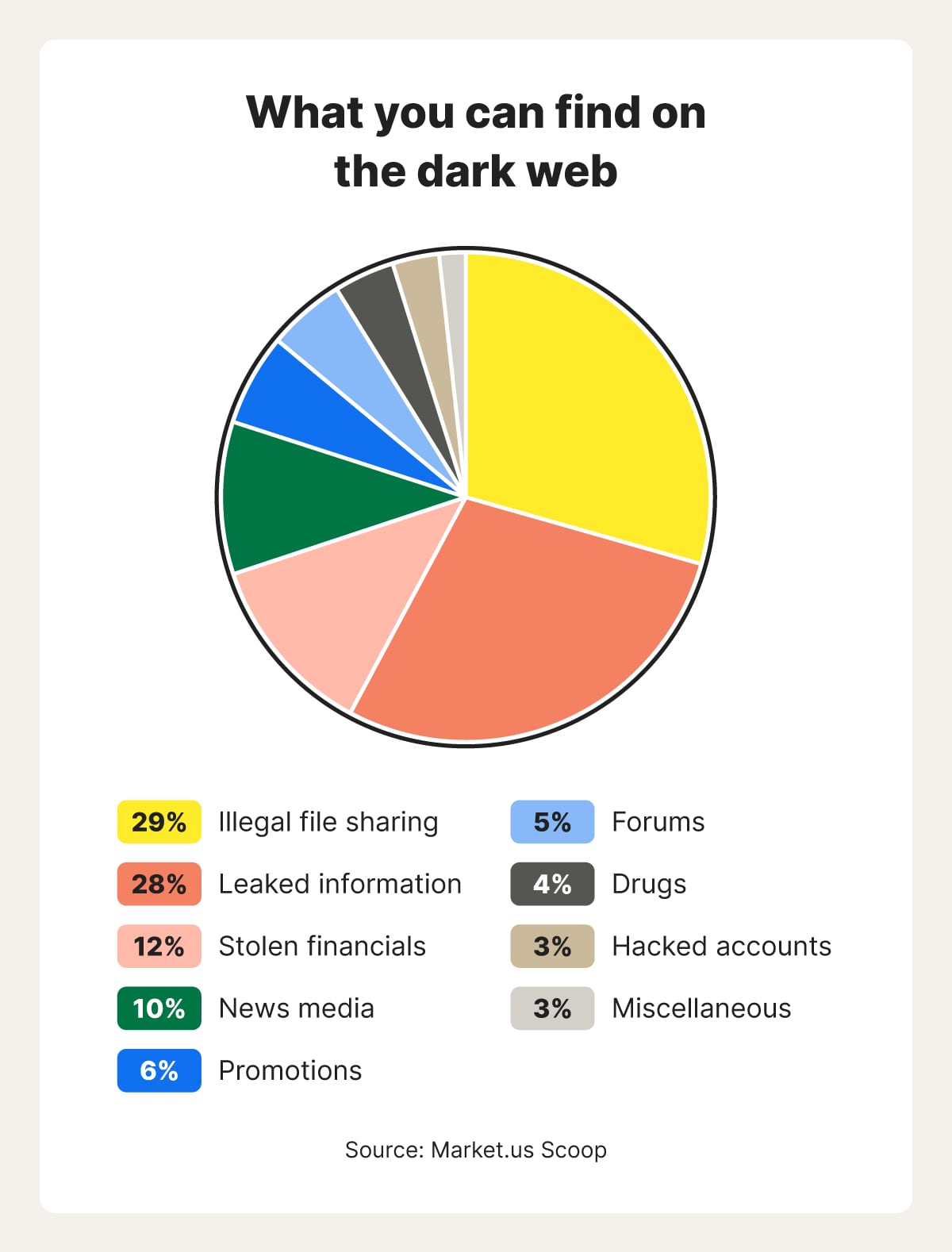
What is on the dark web?
The dark web hosts a variety of content, including anonymous forums, marketplaces selling illegal goods (like drugs and weapons), hacking services, and information stolen in data breaches. While some content is legal, much of it is associated with illicit activities.
Legitimate content on the dark web includes freely accessible news from independent or international sources, and forums and communities centered around niche interests. Less commonly, activists and dissidents may use these channels to exchange information, recruit, and plan activities.

How to access the dark web safely
To access the dark web safely, it’s necessary to use a dark web browser like Tor in combination with trusted dark web directories and search engines to help you find reliable sites. You should also make sure your device is protected by strong antivirus software, and consider using a VPN to mask your activity on the dark web.
Follow along for step-by-step instructions on how to access the dark web, but keep in mind that no matter how careful you are, the dark web can expose you to risks like malware, scams, and illegal content, so proceed with caution.
1. Download a dark web-friendly web browser
When accessing the dark web, the first step is to install a dark web-friendly browser on your computer. Unlike traditional browsers, this will route your internet traffic through an anonymizing network and mask your IP address.
Many dark internet users favor Tor which uses a network architecture originally developed by the U.S. Naval Research Lab as a system of decentralized, anonymous nodes to enable anonymous online communication.
2. Choose a dark web search engine
Next, select a dark web search engine like DuckDuckGo that can help you find dark web websites that cannot be indexed by traditional surface web search engines, such as Google or Bing.
Some popular dark web search engines include:
- DuckDuckGo: This is the Tor browser's default search engine. DuckDuckGo's main selling point is its privacy features. Because it doesn’t track users, people can use it to browse the dark web anonymously.
- Torch: With a main screen similar to Google’s, users who search the dark internet with Torch will feel more at home. However, remain vigilant about clicking links you’re unfamiliar with.
- Ahmia.fi: This search engine lets you see links to dark web websites using a traditional browser like Chrome, Firefox, or Microsoft Edge. To access those sites, you'll still need to navigate via Ahmia.fi through the Tor browser, though.
3. Visit the dark web websites of your choice
Finally, you need to enter website addresses to access content on the dark web since you can’t browse by entering a search query as you can on the clear web.
To help find functioning .onion URLs, look to dark web directories and forums — Reddit users recommend tor.taxi, tor.watch, daunt.link, or one of the Hidden Wikis. You can access all of these directories via the surface web.
Here are some other surface web URL examples and their dark web links:
Surface web websites |
Dark web URLs |
Used for |
|---|---|---|
Archive.today |
archiveiya74codqgiixo33q62qlrqtkgmcitq |
Seeing snapshots of past websites |
International BBC |
https://www.bbcweb3hytmzhn5d532owb |
Accessing international news |
DuckDuckGo |
https://duckduckgogg42xjoc72x3sjasowo |
Browsing anonymously |
facebookwkhpilnemxj7asaniu7vnjjbiltxjqhy |
Social networking |
|
Pro Publica |
http://p53lf57qovyuvwsc6xnrppyply3vtq |
Accessing investigative journalism |
Proton Mail |
https://protonmailrmez3lotccipshtkleeget |
Communicating securely and anonymously |
Sci-Hub |
http://scihub22266oqcxt.onion/ |
Accessing scholarly articles and research papers |
The New York Times |
nytimesn7cgmftshazwhfgzm37qxb44r64 |
Accessing international news |
Another challenge of finding dark web sites is that they don’t often last long. Many sites become defunct quickly, either because they are shut down due to illegal activity, their founders lose interest, or they change addresses and names to avoid detection.
Dark web threats
The dark web presents various threats, including malicious software and computer viruses, posing risks to users' systems and data security. Users also face the potential danger of government monitoring and surveillance — or scams and fraud, and other activities that can lead to financial loss and identity theft.
Here are some threats you could encounter on the dark web:
- Malicious software: It’s all too easy to pick up malware by visiting compromised websites or downloading files from untrustworthy sources on the dark web. Protect yourself by using a strong antivirus program, keeping your software updated, and being extremely cautious about what you download or click.
- Government monitoring: Governments can monitor dark web activity by analyzing traffic patterns, infiltrating networks, and using sophisticated surveillance tools. You’re unlikely to be monitored unless you're engaging in criminal activity, but even just accessing the dark web may draw unwanted attention.
- Non-governmental surveillance: Corporations, hackers, and other third parties may surveil you on the dark web by exploiting software vulnerabilities, infiltrating networks, using tracking tools, monitoring online activity, or employing social engineering tactics. To protect yourself, be cautious about what you share, use a VPN, and avoid interacting with unverified links.
- Phishing attacks: Fake login pages for popular sites or messages that appear to be from legitimate services are popular dark web phishing tactics designed to steal your credentials or personal information. Check all URLs carefully, be cautious of unexpected messages, and never enter sensitive information on sites you don’t fully trust.
- Emotional distress: The dark web can expose you to disturbing or illegal content, including graphic violence if you visit the wrong site. Protect your mental health by verifying the purpose of a site before visiting and seek help if you encounter upsetting materials.
Browse the web more safely
If you decide to venture into the dark depths of the deep web, make sure you’ve bolstered your device’s security with powerful privacy and security tools that can defend against dark web threats.
Norton 360 Deluxe provides a comprehensive suite of protection that can help block malware and dangerous links in real time, and even detect scams using cutting-edge AI detection. Plus, it features a built-in VPN to encrypt your connection, hiding your IP address and online activity, for more anonymous and private browsing.
FAQs
Is the dark web illegal?
It’s not illegal to visit the dark web in the United States. But you can face criminal charges if you use the dark web to engage in illegal activity, such as the sale or purchase of illegal firearms, drugs, pornography, stolen passwords, hacked credit card account numbers, or other illicit items.
Legitimate ways to use the dark web include purchasing legal goods, joining hobbyist communities and political forums, and visiting websites anonymously.
What does CP stand for on the dark web?
On the dark web, "CP" most commonly stands for "Child Pornography." Engaging with or distributing such content is a serious criminal offense. If you encounter this content label online, report it to the authorities immediately.
Who created the dark web?
The “onion routing” technology underpinning the dark web was developed by researchers at the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory in the mid-1990s. Initially designed for secure military communications, it evolved into a broader tool for online anonymity, later expanding to public use with the Tor network.
What should I do if my Social Security number is on the dark web?
If your Social Security number is found on the dark web, take immediate action to protect yourself. Place a credit freeze or lock on your credit reports, monitor your credit reports and financial accounts closely for any unauthorized activity, and consider enrolling in a credit monitoring service. Additionally, contact the Social Security Administration to report the breach and discuss further protective measures.
My email is on the dark web; what should I do?
If your email address is on the dark web, immediately change your email password and any other linked accounts’ passwords, enable two-factor authentication if possible, and be on the lookout for suspicious account activity.
Editorial note: Our articles are designed to provide educational information for you. They may not cover or protect against every type of crime, fraud, or threat we write about. Our goal is to increase awareness about Cyber Safety. Please review the complete Terms during enrollment or setup. Remember that no one can prevent all identity theft or cybercrime, and that LifeLock does not monitor all transactions at all businesses. The Norton and LifeLock brands are part of Gen Digital Inc. For more details about how we create, review, and update content, please see our Editorial Policy.







Want more?
Follow us for all the latest news, tips, and updates.