Tor vs. VPN: What's the difference and which is more private?
When it comes to online privacy, the Tor vs. VPN debate never seems to end — and for good reason. Both tools protect your anonymity in different ways. In this guide, we’ll break down when Tor makes sense, when a VPN is the smarter choice, and how Norton VPN keeps your daily activity private.

The main differences between Tor and a VPN lie in how they route traffic and what they’re best suited for. Tor sends your data through a decentralized network of volunteer-run servers, offering strong anonymity — ideal for users in high-risk environments or those seeking maximum anonymity — and access to the dark web.
A VPN, on the other hand, routes your traffic through an encrypted tunnel to a secure server managed by a trusted provider. This setup allows you to customize your virtual location for flexible internet access, and can help deliver more reliable performance, faster speeds, and easier everyday use while still protecting your online privacy.
Both tools enhance online anonymity by hiding your IP address and helping to shield your activity from surveillance or tracking by internet service providers (ISPs), governments, and advertisers.
Here’s an at-a-glance comparison:
Tor |
VPN |
|
|---|---|---|
Best for |
Maximum anonymity and bypassing strict censorship |
General online privacy and secure browsing |
Often used by |
Whistleblowers, activists, journalists, criminals, and law enforcement |
Remote workers, travelers, gamers, and streaming fans |
How it works |
Routes traffic through a decentralized network of volunteer-run nodes, with multiple layers of data encryption |
Creates an encrypted "tunnel" between your device and a VPN server, masking your IP address and scrambling internet data |
Privacy level |
Very high browsing anonymity, but your ISP and other third parties may be able to see that you’re connected to Tor |
Strong privacy and encryption, but the VPN provider can see your connection logs unless it enforces a no-logs policy |
Provider trust |
Distributed trust — no single relay knows both your origin and destination |
Centralized trust — you rely on your VPN provider to protect your data |
Speed |
Typically slower, since traffic travels through multiple relays and encryption layers |
Generally faster, though speed varies by server load, distance, and protocol |
Cost |
Free and open source |
Usually subscription-based ($2 to $30 per month) though limited free options exist |
What is Tor?
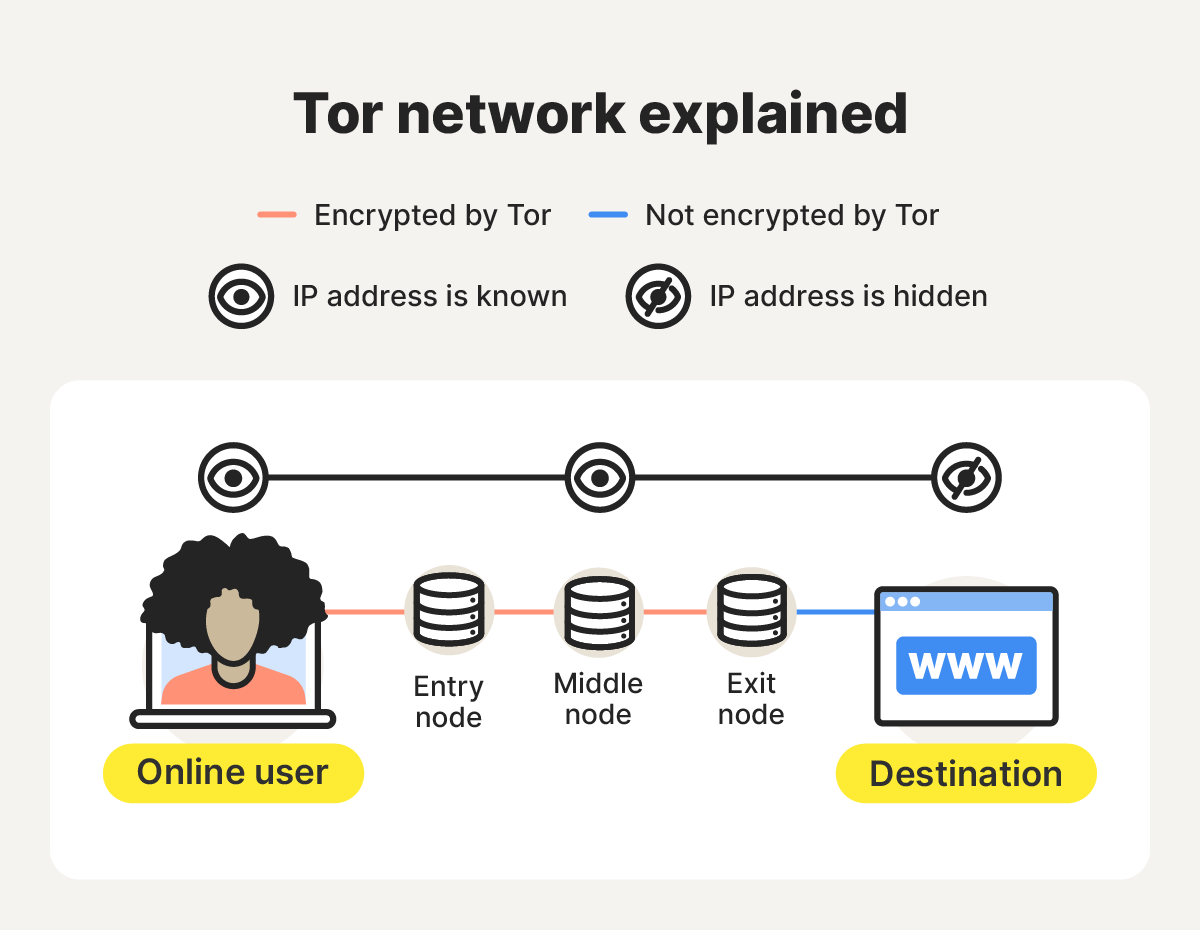
Tor, short for “The Onion Router,” is a free browser designed to keep your online activity and location private. It does this by routing your traffic through a decentralized network of volunteer-operated servers, or nodes, located around the world.
When you use the Tor Browser, your data is encrypted in multiple layers and passed through a random sequence of nodes before reaching its destination, making it extremely difficult for anyone to trace your activity or identify you online.
Theoretically, someone could deanonymize you on Tor through traffic-correlation attacks, especially if they can observe traffic near both your device and the sites you visit, or control key relay nodes. Such attacks are difficult but not impossible, which is why Tor stresses it cannot guarantee perfect anonymity.
Here’s how Tor helps protect your privacy step by step:
- Triple encryption and path selection: Tor Browser wraps your request in three layers of encryption and selects a circuit consisting of an entry (guard) node, middle node, and exit node for your data to pass through.
- Entry (guard) node: The first node receives the encrypted request, removes the outer layer of encryption, and forwards it to the next node. It can see your IP address, but not the content or destination of your request.
- Middle node: The middle relay removes the second layer of encryption and passes your request to the exit node. It knows only the adjacent relays, not your IP address or the final destination of your traffic.
- Exit node: The last node removes the final layer of encryption and forwards traffic to the destination site, which sees the exit node’s IP, not yours.

Tor pros
Tor offers exceptional privacy, and can help users access the dark web, avoid third-party tracking, and even bypass censorship (although in some countries it’s blocked or penalized, and using it may not be worth the risk).
Here are some of the top benefits of using Tor:
- Free and easy to download: Thanks to numerous anonymous volunteers, users can easily download the Tor browser for free.
- Difficult to shut down: The Tor network is run by thousands of volunteers worldwide, making it extremely difficult for a single entity to shut it down.
- Bypass censorship: If you’re in a country with strict censorship, the Tor browser can allow you to bypass it and visit blocked websites.
- Access to the dark web: The Tor browser allows you to access onion websites on the dark web, which are only accessible through the Tor browser.
- Browse the surface web: Tor allows users to reach both onion and non-onion sites without switching browsers.
- Reduce tracking and fingerprinting: Tor makes it much harder for websites and advertisers to track your online behavior unless you log in to personal accounts or change default settings.
- Enhanced privacy: Because Tor conceals users’ identities and locations, it’s often used by individuals who need a higher level of anonymity — such as whistleblowers — to communicate safely and protect their privacy online.
In short, Tor is a great option if you require a high level of anonymity for activities like bypassing censorship, accessing the dark web, or protecting extremely sensitive communications. But it’s not without its limitations.
Tor cons
Tor has some downsides as well. Most drawbacks relate to speed, accessibility, and legal restrictions, depending on where you are and how you use it.
Here are some of Tor’s main limitations:
- Slow browsing speeds: Because Tor routes your data through multiple nodes for maximum anonymity, browsing can feel noticeably slower than with a traditional private browser or VPN.
- Impractical for downloading files: The slower data transfer speeds make Tor unsuitable for downloading large files or streaming high-quality media.
- Restricted accessibility: Some websites block Tor traffic altogether. If you’re denied access, you can contact the site’s administrator to request permission — Tor Support provides sample messages you can adapt for this.
- Blocked in some countries: Tor use is illegal, blocked, or restricted in countries like China, Russia, and Iran. In response, Tor emphasizes that it’s intended to promote free expression, privacy, and human rights — not for illegal activity.
- Node vulnerability: Tor hides your identity, but traffic leaving an exit node isn’t inherently encrypted. If a website doesn’t use HTTPS, a malicious observer or node operator could view or modify your data.
- Difficulty finding safe, active .onion sites: Finding legitimate Tor sites is difficult because they aren’t indexed by regular search engines. Users depend on dark web search engines or directories, but onion sites often go offline or change domains due to law enforcement or owner actions.
If you decide to use Tor to access dark web sites, exercise extreme caution. Many .onion pages host or facilitate illegal activities such as drug trafficking, hacking services, or cryptocurrency scams.
Visiting or interacting with such platforms can expose you to serious legal risks — if law enforcement traces your activity to these sites, you could face legal consequences.
What is a VPN?
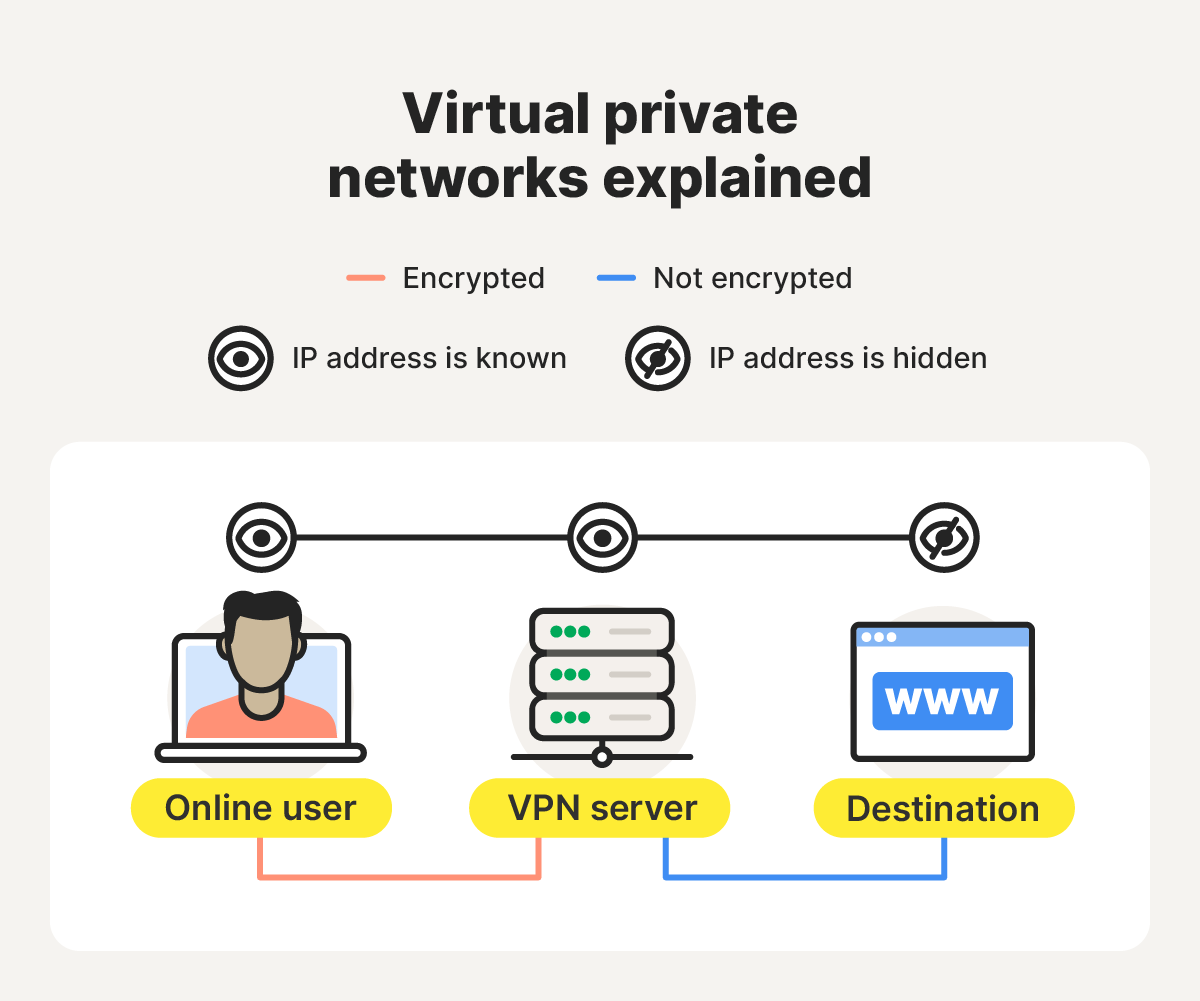
A VPN, short for “virtual private network,” is a service that sends your internet traffic to the internet through a secure, encrypted tunnel between your device and a VPN server. This process masks your IP address and helps keep the data that you send and receive online more private.

Here’s a closer look at how VPNs work to protect your privacy:
- Encryption and tunneling: When you connect to a VPN, your internet traffic is encrypted using a VPN protocol (such as OpenVPN, IKEv2, or WireGuard). The data is sealed within an encrypted “tunnel,” which hides its contents from your ISP, hackers, or anyone monitoring your connection.
- Secure transmission: Your encrypted traffic is sent via the tunnel to a remote VPN server, which decrypts the data and forwards it to the destination website or online service. Because the request appears to come from the VPN server, your real IP address remains hidden.
- Return path: When the website sends data back, the VPN server encrypts the response before transmitting it to your device. Your VPN client then decrypts the data locally, completing the protected round trip.
Unlike Tor, which runs on a decentralized network, most VPNs are centralized and managed by commercial providers. VPNs are ideal for securing your connection on public Wi-Fi, bypassing geographic restrictions, and keeping your browsing private from ISPs, snoops, and cybercriminals.
While not quite as anonymous as Tor, a reputable VPN such as Norton VPN delivers strong privacy, fast speeds, and practical features for everyday use. It uses bank-grade encryption to help keep hackers' hands off your data and prevent third parties from tracking your online activity.
VPN pros
VPNs offer a bunch of benefits, especially for everyday users. They’re fast, versatile, and provide strong privacy for routine online activity. Here’s what you can expect from a VPN:
- Enhanced privacy and security: VPNs encrypt your online traffic and hide your IP address, making it much harder for ISPs, advertisers, and cybercriminals to monitor your activity.
- Greater flexibility: Unlike the Tor browser, a VPN encrypts data across all apps and browsers on your device, not just within a single browser window.
- Bypass geographic restrictions: Many premium VPNs allow you to select the location of the VPN server you’d like to use, bypassing geo-blocks and accessing local content. But before doing so, ensure that VPNs are legal in your area.
- Thwart throttling: Some ISPs slow down specific sites or services. A VPN conceals your activity from your ISP, helping prevent targeted bandwidth throttling.
In general, a VPN is the way to go if you want fast, reliable privacy for everyday browsing and streaming, need to connect to public Wi-Fi, or want to change your virtual IP address to access the internet like a local.
VPN cons
But VPNs are not the perfect tool for every job. As well as encountering VPN blocks and experiencing slightly slower internet speeds, you typically have to pay for a quality service. And it’s important to choose your provider carefully to avoid privacy risks.
Here’s a closer look:
- Premium features for a fee: Free VPNs exist, but they often have limited features, slower speeds, or weaker privacy protections. A reliable, full-featured VPN usually requires a paid subscription.
- Traffic vulnerability: Some VPNs — especially free ones — log and even sell user data to third parties. To stay protected, choose a no-log VPN that guarantees it doesn’t collect or share your browsing activity.
- Reduced internet speeds: Because your traffic is encrypted and routed through remote servers, you may notice slightly slower browsing speeds. However, premium VPNs typically remain much faster than Tor.
- Site blocking: Certain websites and streaming platforms use VPN detection technology to block access from VPN users, particularly to enforce regional content restrictions.
Can you use Tor and a VPN at the same time?
Yes, you can use the Tor browser and a VPN together — a setup known as Tor-over-VPN — though it offers limited benefits for most users. When configured correctly, it can provide a small privacy boost.
The main advantage is that your ISP can’t detect Tor usage when you’re connected through a VPN, since your traffic is encrypted on your device before being forwarded to the Tor network. It can also help you access sites that block Tor, as the VPN tunnel hides Tor traffic from network filters.
However, there are notable downsides. This setup can significantly slow browsing speeds, and your ISP can still tell that you’re connected to a VPN, even if your Tor usage is hidden. It also doesn’t protect against malicious Tor exit nodes, since the VPN only encrypts your data before it enters the Tor network — not after it leaves.
For most users, using either Tor or a trustworthy VPN individually provides strong, practical privacy without the performance hit.
Keep your daily browsing activity private
For everyday privacy made simple, choose Norton VPN. It keeps your connection private on public Wi-Fi, stops your ISP from tracking you, and delivers fast, secure browsing backed by ultra-secure AES-256 encryption — no complicated setup required. Stay protected and enjoy the internet with confidence.
FAQs
Is Tor better than a VPN?
Tor provides stronger anonymity by routing your traffic through multiple encrypted nodes, making it ideal for activists, journalists, or anyone needing maximum privacy. However, a VPN is faster, easier to use, and better suited for everyday browsing, streaming, and secure connections on public Wi-Fi.
Does Tor have a VPN?
No, Tor and VPNs are distinct privacy tools. Tor focuses on anonymity by hiding your identity through a distributed network, while a VPN encrypts your internet traffic and routes it through a secure server. You can use both together for even stronger protection, though this may reduce connection speed.
Is Tor legal in the U.S.?
Yes, using Tor is legal in the United States. However, what you do while using it must still comply with U.S. law. Accessing illegal content or engaging in criminal activity through Tor remains prohibited, as on any network.
Can Tor-over-VPN be traced?
Tracing traffic protected by Tor-over-VPN is extremely difficult. However, no setup is completely foolproof. Tracing can still occur if the VPN or Tor is misconfigured, compromised, or used in combination with personally identifying online behaviors.
What is the difference between Tor, VPN, and proxy?
Tor routes your traffic through multiple encrypted relays for strong anonymity. Proxies can hide your IP from the sites you visit, but usually lack encryption and can inspect (and potentially log and share) your browsing activity. A VPN encrypts your data and sends it through a secure server, balancing privacy with flexibility and speed.
Editorial note: Our articles provide educational information for you. Our offerings may not cover or protect against every type of crime, fraud, or threat we write about. Our goal is to increase awareness about Cyber Safety. Please review complete Terms during enrollment or setup. Remember that no one can prevent all identity theft or cybercrime, and that LifeLock does not monitor all transactions at all businesses. The Norton and LifeLock brands are part of Gen Digital Inc.








Want more?
Follow us for all the latest news, tips, and updates.