How to hide your IP address in 4 ways
Internet-connected devices have addresses, just like your home does. They’re called IP addresses, and they link your personal data and location with your device. Learn how to hide your IP address to help keep your online activity more private and secure. Then, get a powerful VPN to safeguard your data as you browse the web.

An internet protocol address (or IP address for short) is a unique number assigned to every device that connects to the internet. Your IP address links your web activity with your device, which can help regulators, authorities, and marketers track what you’re doing. But being tracked isn’t always a good thing. In fact, failing to protect your IP address may put you at risk.
Luckily, it’s possible to hide your IP address to make it more difficult for businesses, cybercriminals, and other snoops to track you. Here are four ways to hide your IP address so you can enjoy more privacy online.
1. Get a VPN
Using a virtual private network, or VPN, is one of the easiest and most effective ways to hide your IP address. Nearly 1 in 4 global internet users use a VPN, with certain countries having VPN usage as high as 42%.
VPNs work by acting as an intermediary between your device and the internet, routing all of your internet traffic through a dedicated VPN server. In other words, instead of connecting directly to the internet, you connect to a remote server which is itself connected to the internet. That means your connection will use the VPN server’s IP address, masking your own.
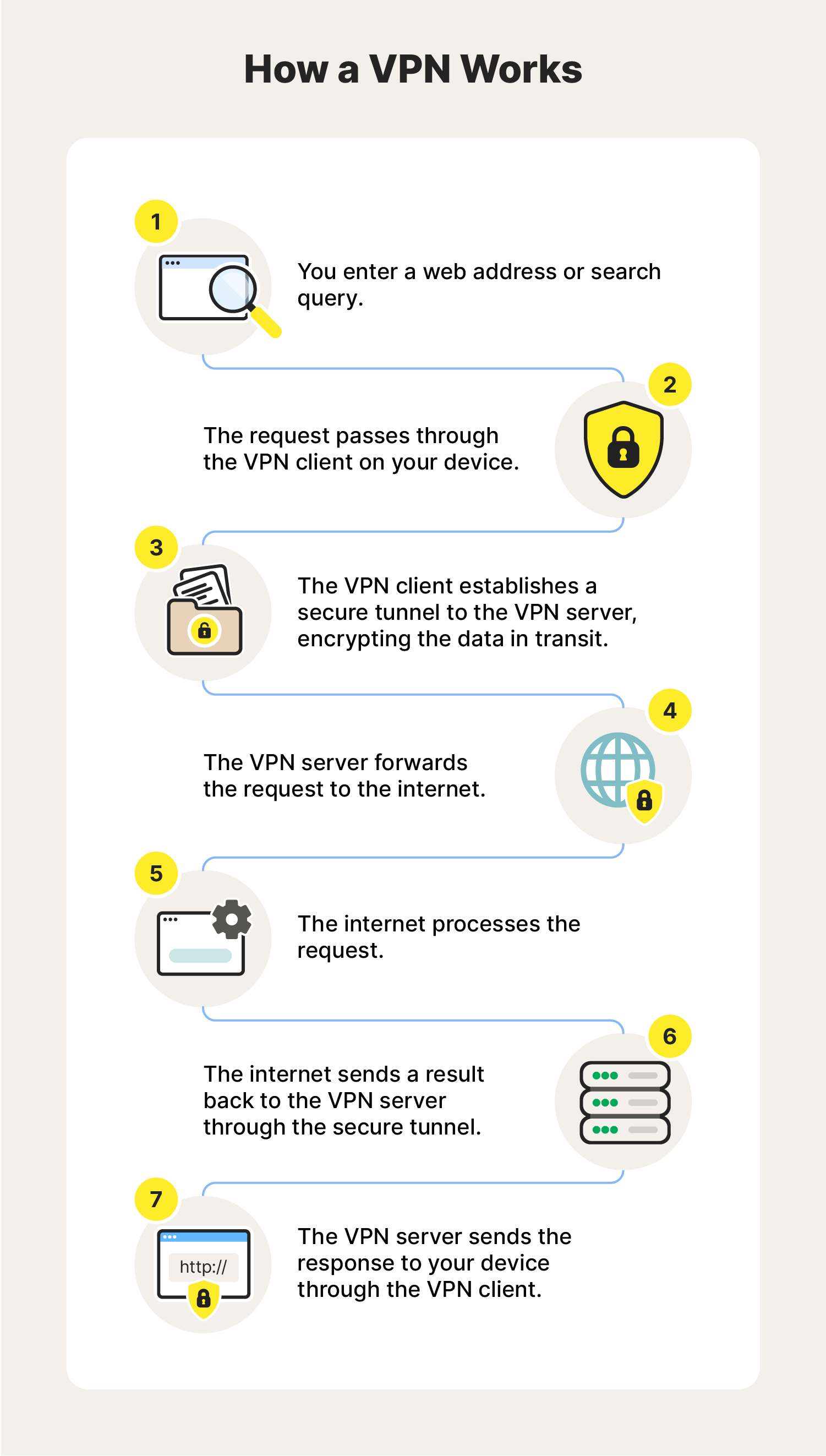

Your connection to the VPN is encrypted and anonymous, so no one can link your “fake” IP address to your real one. If anybody tries to track your activity, they’ll see the IP address of your VPN server and not the address assigned to your computer.
There are lots of VPN providers to choose from, including some free options. However, a study by Comparitech found that no free VPNs tested offered adequate data protection, and most displayed ads or sold user data. Another report found that nearly 1 in 5 free VPNs were flagged as malware by antivirus scanners.
Whether it’s poor performance or shady data privacy policies that allow them to sell your info to data brokers, if you’re serious about using a VPN, it’s best to choose a trustworthy and provably reliable provider.
The best VPN services, which may only cost a few dollars a month, allow you to browse at high speeds while maintaining a secure connection. They also tend to have advanced features such as a “kill switch” which protects against data vulnerability if your VPN coverage drops, “split tunneling” which allows you to choose what traffic is routed through the VPN, and antivirus protection.
Pros of using a VPN:
- Online privacy: A VPN improves your privacy online, helping you change your IP address to hide from marketers, hackers, and government surveillance.
- Data encryption: VPNs encrypt your connection, helping protect important info like your passwords from being intercepted.
- Access more content: VPNs allow you to browse the internet more freely and access a greater range of regional content.
Cons of using a VPN:
- Reduced internet speeds: Using a low-quality VPN may result in lower internet speeds, but this can largely be avoided by choosing a highly-rated option.
- Security risks: Free VPNs may make money by selling your data and could lack the necessary security features to provide truly private browsing.
If you’re looking for a VPN that offers speed, stability, and security, choose Norton VPN. It ranks #1 overall for network performance†, with download speeds nearly 1.26 times as fast as the closest competition†, and also offers a range of security features that can help keep you safer on the web.
2. Use a proxy server
A proxy server is an intermediary server you use to connect to the internet instead of connecting directly from your device. Your web activity appears under the proxy’s IP address instead of your own. Proxy servers are similar to VPNs, but there’s a key difference. VPNs encrypt the data you send and receive, while proxy servers don’t.
The encryption offered by a VPN means it’s much more difficult for hackers to intercept and view the data passing between your VPN provider and your computer (aka your web activity). This isn’t true when you’re using a proxy server, and your browsing data may still be visible to your ISP, lurking hackers, or other unauthorized third parties.
Pros of using a proxy server:
- Online privacy: Proxy servers mask your IP address, preventing anyone from accessing data associated with your device’s IP.
- Access more content: Like a VPN, a proxy server can help you access regional content while traveling.
- Faster surfing: Unlike VPNs, proxy servers cache your browsing data. This helps web pages you frequently visit load faster.
Cons of using a proxy server:
- No encryption: Proxy servers don’t encrypt your online activity. So, while you may be surfing anonymously, you are not doing so invisibly.
- Security concerns: Like free VPNs, free proxy servers may be run by bad actors who sell your data or target you with malware.
3. Use the Tor web browser
The Onion Router (more commonly known as Tor) is a web browser like Google Chrome, Internet Explorer, or Safari, but it’s designed specifically for anonymous and secure browsing. When you use the Tor browser, your data is encrypted and sent through a network of servers (or nodes) before you reach the site you want to visit, helping to protect your location and identity.
You can use Tor to access the regular internet or the dark web, a hidden layer of the internet that’s inaccessible through conventional browsers. Although it sounds complicated, it’s relatively simple to use. You download it onto your computer and open it whenever you want to search the web — just like any other web browser.
However, it's important to remember that Tor is different from a VPN. It’s decentralized, relying on multiple user-run relay nodes instead of dedicated servers. While it may offer greater anonymity, it’s also likely to slow your connection down more than a VPN would.
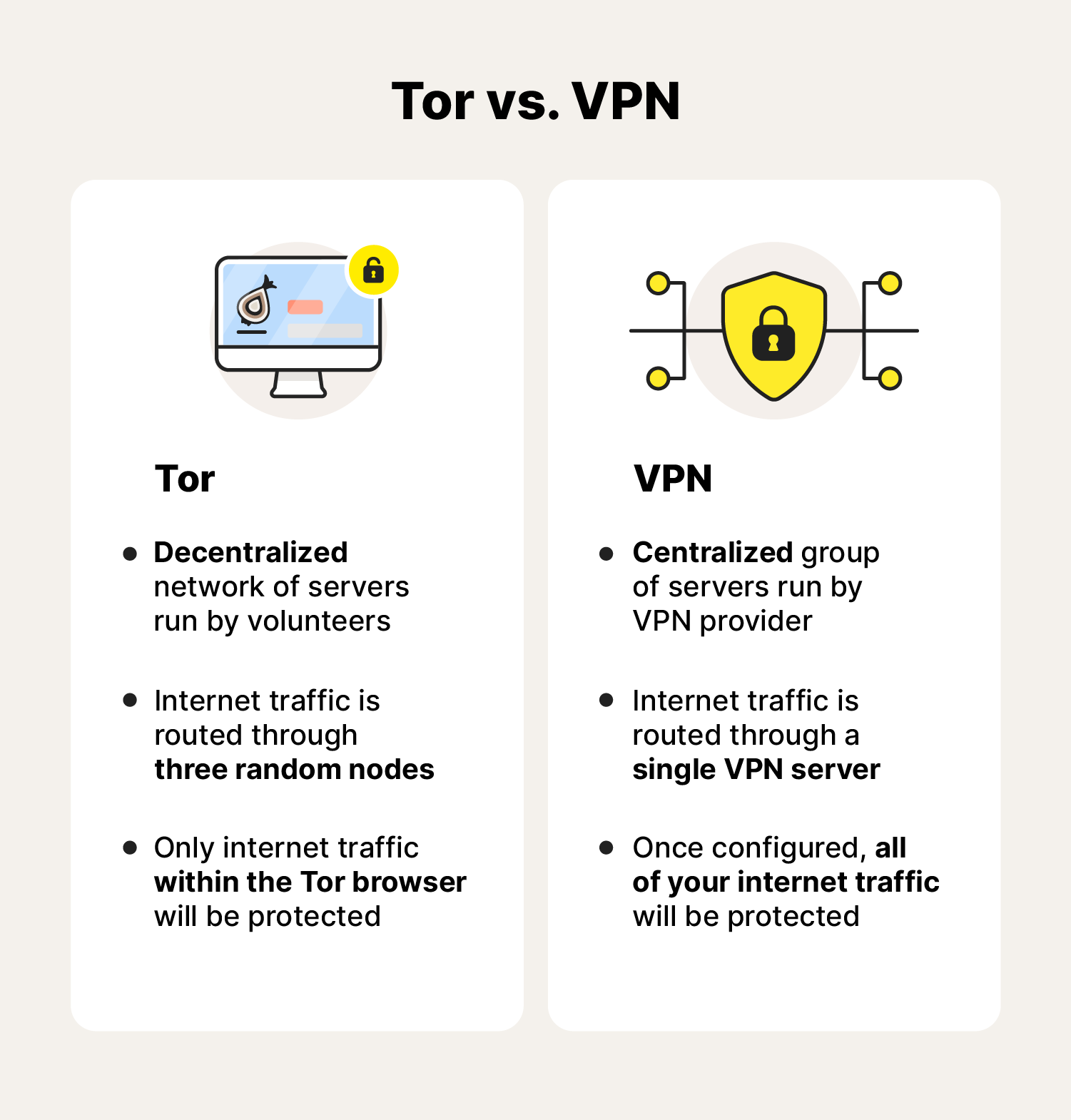

Advantages of using Tor:
- Anonymous browsing: Tor takes anonymity seriously, with the intricate process of routing your traffic through nodes helping to protect your IP address from snoops.
- Strong encryption: Tor has strong encryption protocols to keep your web activity invisible to others. It also lacks centralized control, so there’s no “man behind the curtain” who can view your activity.
- Access to the dark web: Unlike standard web browsers, Tor is a dark web search engine. It allows access to .onion websites which make up the dark web.
Disadvantages of using Tor:
- Slow speeds: Due to its many security protocols, Tor is likely to be significantly slower than using a VPN with a normal browser.
- Limited web access: Some websites, including many banks, social media platforms, and online marketplaces, block all traffic from Tor users.
4. Connect to a public Wi-Fi network
By connecting to a public Wi-Fi network, you connect to websites using the public IP address assigned to you instead of connecting with your device’s IP address. This hides your real IP address while online. However, it isn’t a good option for safety or anonymity because it can be hard to verify if public Wi-Fi networks are secure.
These networks generally aren’t encrypted, so they’re top targets for hackers seeking to intercept personal info such as passwords and account details. Your activity can also still potentially be tracked by ISPs and other users on the same network.
While connecting to public Wi-Fi technically hides your IP address, it’s not a great choice for the best web security or anonymity. In fact, it’s typically advised that you use a VPN when connecting to public Wi-Fi networks to help protect your activity and personal info from being exposed.
Pros of using public Wi-Fi:
- Masks your IP address: Connecting to public Wi-Fi will hide your device’s IP address, masking it with the public address of the Wi-Fi network.
- Easy and free: Public Wi-Fi is accessible almost everywhere for free. It’s a good option if you need to access another IP address for any non-sensitive browsing.
Cons of using public Wi-Fi:
- Not a secure option: Public Wi-Fi isn’t encrypted and is among the least secure ways to connect to the internet. Accessing or transmitting personal or sensitive data via public Wi-Fi can leave you vulnerable.
- Not truly anonymous: Due to a lack of encryption, your online activity may be visible to ISPs, network providers, and other network users.
- High cybercrime risk: Public Wi-Fi’s lack of security and easy access make it an easy hunting ground for cybercriminals. Packet sniffing and man-in-the-middle attacks are common on these networks.
Why hide your IP address?
Hiding your IP address can help protect your online privacy by reducing the risk of third parties tracking your activity, figuring out your location, or intercepting your personal data.
Here are some of the main reasons to hide your IP address:
- Hide your physical location: Your IP address can be used to track your physical location. Advertisers use this info to serve personalized region-specific ads, but bad actors could theoretically also use it to figure out where you are.
- Access more content: Many websites restrict users from accessing certain content based on where they’re browsing from. Hiding or masking your IP address gives you more freedom to reach the content you’re looking for.
- Stop online tracking: Advertisers may track your online activity to follow you around the web serving personalized ads. If you don’t want companies tracking your browsing habits, hiding your IP address can help. For more robust protection against advertisers and corporate snoops, get Norton AntiTrack.
- Avoid government surveillance: Government agencies can track your browsing activity to support their work policing the web. While they may have legitimate reasons to do so, hiding your IP address can offer personal protection for those who need it, like journalists.
- Protect against cyberattacks: Hackers and cybercriminals can potentially use your IP address to access your online accounts, steal your identity, and launch cyberattacks. Hiding your IP address makes it harder for these bad actors to track and target you.
- Avoid throttling: Your internet provider can use your IP address to “throttle” your connection, slowing down your internet based on your web activity (such as streaming). Hiding your IP address makes it harder for them to monitor your usage and throttle you.
Hide your IP address with Norton VPN
Hiding your IP address is a great way to boost your online privacy, and it’s easy to do with Norton VPN. Our VPN helps you maximize your privacy and security while browsing on up to 10 devices, with bank-grade encryption, a variety of VPN servers to choose from, and fast speeds that allow for seamless streaming.
FAQs
Can your IP address be truly hidden?
No, your IP address can’t be hidden completely. Using a reliable VPN hides your IP address very effectively, but total anonymity is never guaranteed. Service interruptions or data leaks can expose your IP address.
Governments and law enforcement can also force ISPs and VPN service providers to identify your real IP address or use advanced surveillance techniques to crack VPN protocols. However, these methods require a warrant and are generally reserved for investigating serious criminal activity.
How do I find my IP address?
The easiest way to find your IP address is to search “What is my IP address?” on your web browser. Just remember if you’re using a VPN or another IP masking method the IP address shown will be the one assigned by the VPN, not your actual one.
How do I install a VPN?
Installing a VPN is similar to installing any other application. Choose a VPN provider, purchase a subscription, download and install the app or program, and then open it to connect to a VPN server. Many VPN providers offer apps for multiple device types, including Windows PCs, Apple Macs, and smartphones.
What can hackers do with my IP address?
Hackers with access to your IP address can target you in a variety of ways. They may:
- Use it to harvest your personal information, which they might use for phishing attacks.
- Spoof your IP address to make it look like their criminal activity is coming from your device.
- Target you with a distributed denial of service (DDoS) attack, causing your device to crash.
- Potentially access your network and infiltrate other connected devices (like your phone or tablet).
- Track your physical location.
† Based on a test of eight other leading VPN products selected by Gen in the VPN Products Performance Benchmarks report conducted by PassMark Software commissioned by Gen, November 2023.
Editorial note: Our articles are designed to provide educational information for you. They may not cover or protect against every type of crime, fraud, or threat we write about. Our goal is to increase awareness about Cyber Safety. Please review the complete Terms during enrollment or setup. Remember that no one can prevent all identity theft or cybercrime, and that LifeLock does not monitor all transactions at all businesses. The Norton and LifeLock brands are part of Gen Digital Inc. For more details about how we create, review, and update content, please see our Editorial Policy.








Want more?
Follow us for all the latest news, tips, and updates.