Proxy vs. VPN: What’s the difference and which one should you use?
In a VPN vs. proxy match-up, which is best for protecting your privacy and security? Spoiler: A proxy might mask your IP, but it won’t safeguard your data. This article explains the differences between proxies and VPNs, how they work, and why you should use a VPN to shield your online activity from trackers and prying eyes.

Worried about who might be watching you online? If so, you’re not alone. A recent survey found that 89% of respondents were concerned that their data was accessed and misused. If that includes you, and you’re weighing up VPNs and proxies as an internet privacy and security solution, there’s a clear winner: Pick a VPN from a trusted brand.
While proxies mask your IP address, they lack encryption and robust security protocols. VPNs provide both, making them the better option for safeguarding your data and online activity.
Here’s a closer look at how each works and the differences between proxies and VPNs. Or, skip ahead to learn which option is right for you.
What is a proxy?
A proxy is a server that sits between you and the wider internet, forwarding your requests and returning data on your behalf. Proxies hide your real IP address behind their own, helping to hide your identity, mask your location, and bypass geo-restricted or blocked content.
Common uses for proxies include:
- Spoofing your IP address to maintain basic privacy online.
- Accessing geo-blocked or restricted content.
- Improving internet speeds by efficiently managing network traffic.
- Filtering content and enforcing security policies in organizations.
- Enabling remote access to internal resources.
Proxies handle internet traffic in different ways. Some are built for everyday web browsing, while others handle high-volume data or sit in front of web servers to manage incoming requests and load distribution. Understanding the main types of proxies — and what each does best — can help you choose the right one for your needs.
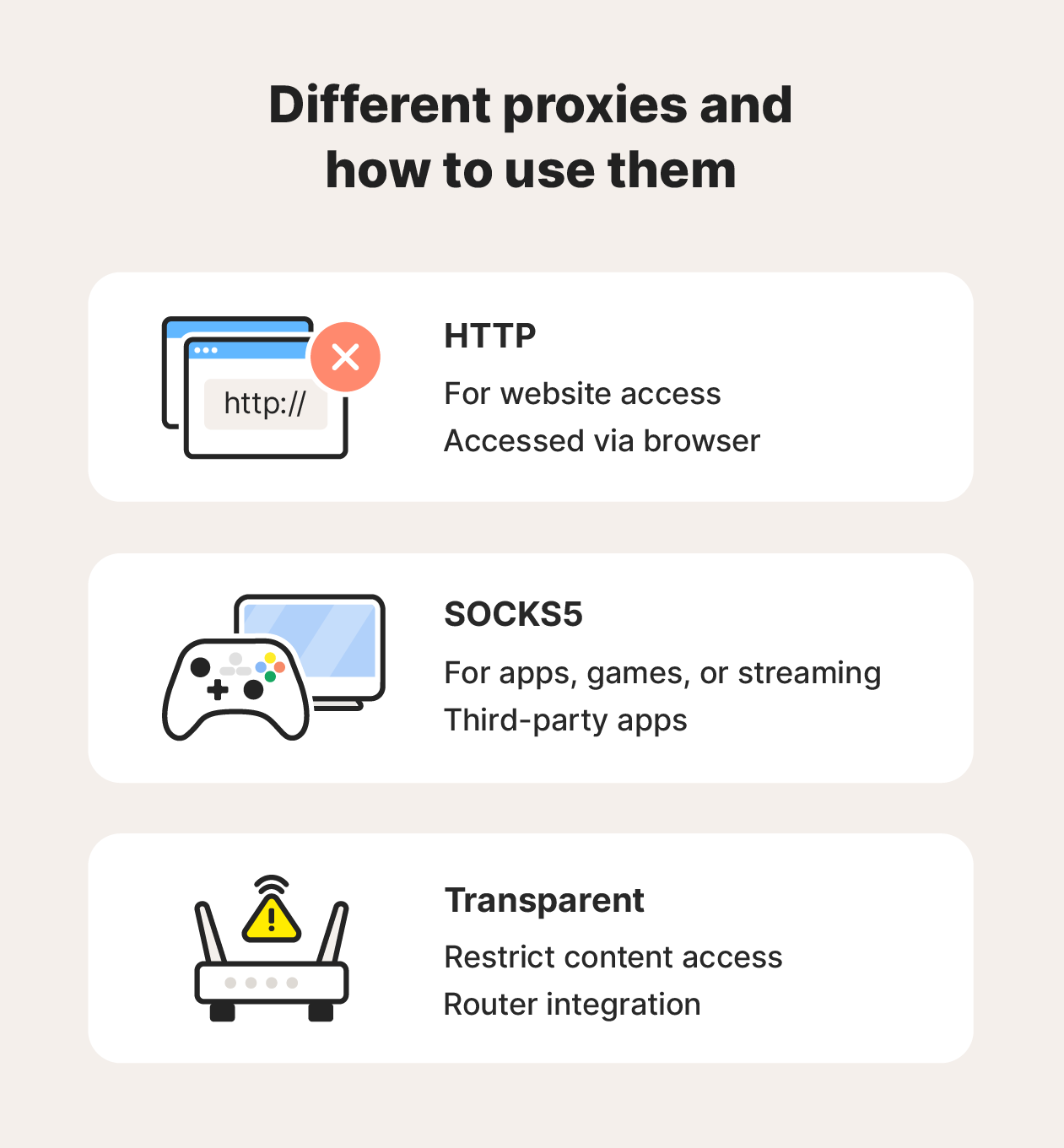
Here are some of the main types of proxies.
- HTTP proxies route HTTP (web) traffic through an intermediary server, helping to filter content, or bypass regional website restrictions.
- SOCKS5 proxies work with any type of traffic (HTTP, FTP, P2P), making them suitable for torrenting, online gaming, or applications that require versatile protocols.
- Transparent proxies redirect traffic without modifying data, so institutions often use them at the router level to filter content without hiding the user’s IP, and restrict access to certain content.
- Reverse proxies sit in front of web servers to handle incoming requests, improve load balancing, add caching, and hide the origin server’s IP address.

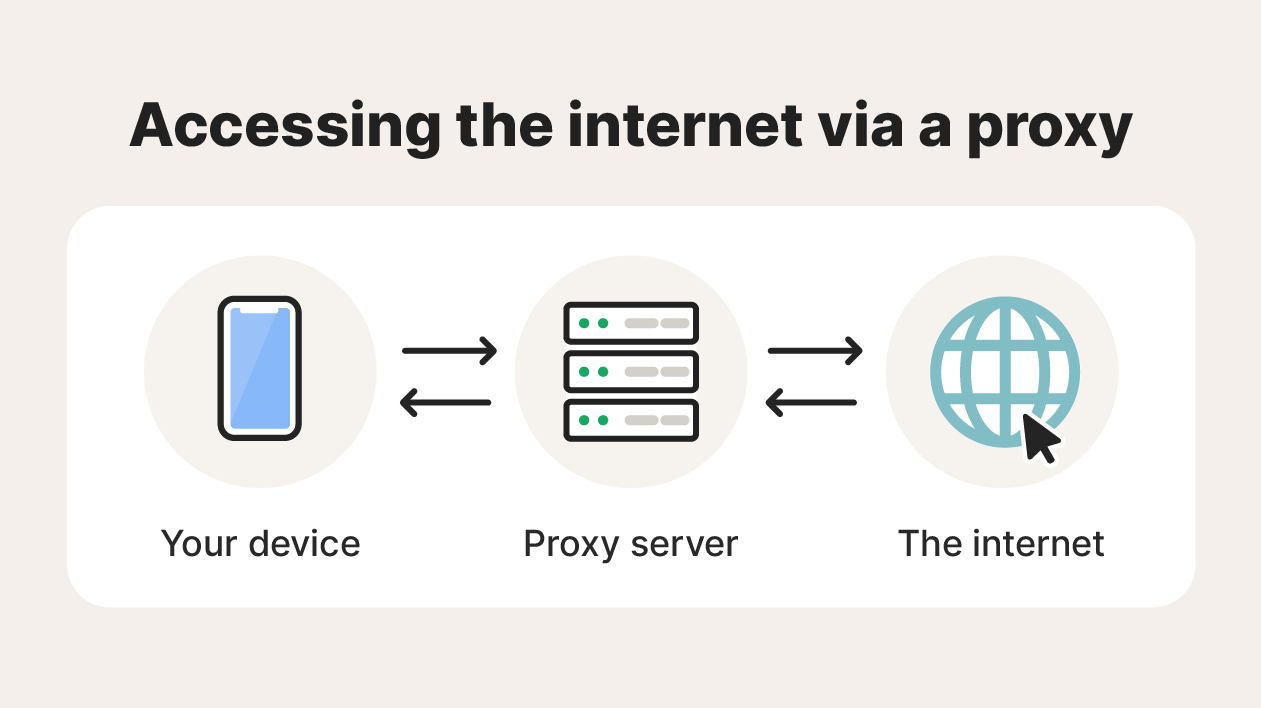
How do proxies work?
Proxy servers act as mediators between your device and the internet, forwarding requests for web content and returning responses from web servers.
Here’s a closer look at how this process works.
- Proxy connection: Your device establishes a connection to a proxy server.
- Request sent: Your data request is sent to the proxy instead of directly to the website server.
- Request forwarded by proxy: The proxy receives your request and sends an identical request to the intended web server.
- Server response: The web server responds to the proxy, which receives the data.
- Response forwarded by proxy: The proxy server routes the data back to your device.
By relaying data this way, proxies help hide your IP address, which can hide your identity and web activities from some third parties.

Proxy pros and cons
Proxies can add a layer of privacy to your browsing and help you reach blocked sites, but they’re far from a full security solution. Before using one, it’s worth weighing proxy server pros and cons.
|
|
|
|---|---|
Hides your IP address from websites, providing some anonymity |
Usually unencrypted, leaving data visible to ISPs, trackers, or attackers |
Helps bypass geo-blocked or restricted content |
Only covers traffic from specific apps or browsers, not your entire device |
Offers basic content filtering and traffic management for networks and organizations |
Free proxies often log user activity, compromising privacy and security |
May improve browsing speed by caching frequently accessed sites |
Proxies are a helpful tool for basic privacy and access needs, but their limited security and lack of full-device coverage leave users vulnerable to data interception, tracking, and other online threats.
What is a VPN?
A virtual private network (VPN) is an internet privacy tool that encrypts your internet connection and routes traffic through a secure server. This hides your IP address and online activity, securing your data even on public Wi-Fi.
VPNs are commonly used to:
- Secure public Wi-Fi connections.
- Maintain privacy and anonymity online.
- Access content restricted by location or network.
- Protect sensitive data from interception.
- Connect safely to work networks remotely.
- Bypass network or government censorship.
- Avoid bandwidth throttling or location-based restrictions.
Different VPNs handle traffic and security in distinct ways depending on the user and situation. Some focus on individual devices, others protect mobile connections, and some link entire networks.
Here are some of the main types of VPN:
- Remote-access VPNs securely connect individual users to a private network, encrypting traffic and hiding activity. They are common for personal use and working from home.
- Mobile VPNs are designed for devices that frequently switch networks or move between locations, keeping connections secure on the go.
- Site-to-site VPNs link entire networks, usually used by businesses to connect multiple offices securely.
How does a VPN work?
A VPN creates a secure, encrypted tunnel between your device and the internet, shielding your browsing, downloads, and other activity from hackers, advertisers, your internet provider, and other prying eyes. Unlike a proxy, which only masks your IP address, a VPN encrypts all the data you send and receive. This means your real location stays hidden and your online activity is much harder to track.
Here’s how a VPN works, step by step:
- VPN connection: A VPN protocol establishes a secure, encrypted tunnel between your device and the VPN server.
- Data encryption: All of your internet data is encrypted before it leaves your device, making it unreadable to anyone who tries to intercept it.
- VPN server routing: The encrypted data travels to the VPN server, where it’s decrypted before being forwarded to an internet server under a virtual IP address.
- Data response: Data is returned to the VPN server from the internet server, and is encrypted.
- Data decryption: The encrypted data is forwarded to your device, where your VPN unscrambles it.
While VPN technology sounds complex, the setup is simple. Just open the VPN app, choose a server, and hit connect. Once active, the VPN works in the background to safeguard your activity.
VPN pros and cons
VPNs provide privacy and security online, but they aren’t perfect. Here’s a look at VPN pros and cons.
|
|
|
|---|---|
Encrypts your internet connection, protecting data from hackers and ISPs |
Reduces internet speed due to encryption and server routing |
Hides your IP address and online activity, enhancing privacy and anonymity |
Varies in quality and security; free VPNs may log activity or display ads |
Secures public Wi-Fi and remote work connections |
Doesn’t protect against malware or phishing on its own |
Bypasses geo-restrictions and network censorship |
|
Prevents bandwidth throttling by ISPs |
|
Includes features like kill switches, split tunneling, and no-log policies |
VPNs provide strong privacy and security benefits, but users should choose a reliable provider and combine it with other safe browsing practices for maximum protection.
Top-quality VPN services like Norton VPN also include additional enhanced privacy and performance features such as kill switches, split tunneling, and no-log policies, to provide flexible yet watertight internet privacy. Get Norton VPN on all your favorite devices today so your online activity remains private, as it should.
VPN vs. proxy: 5 key differences
The main difference between a VPN and a proxy is how much protection they give you. A VPN sends all your internet traffic through an encrypted tunnel and hides your IP address across every app and website. A proxy only changes your IP for the specific app or site you set it up for and does not typically encrypt your data.
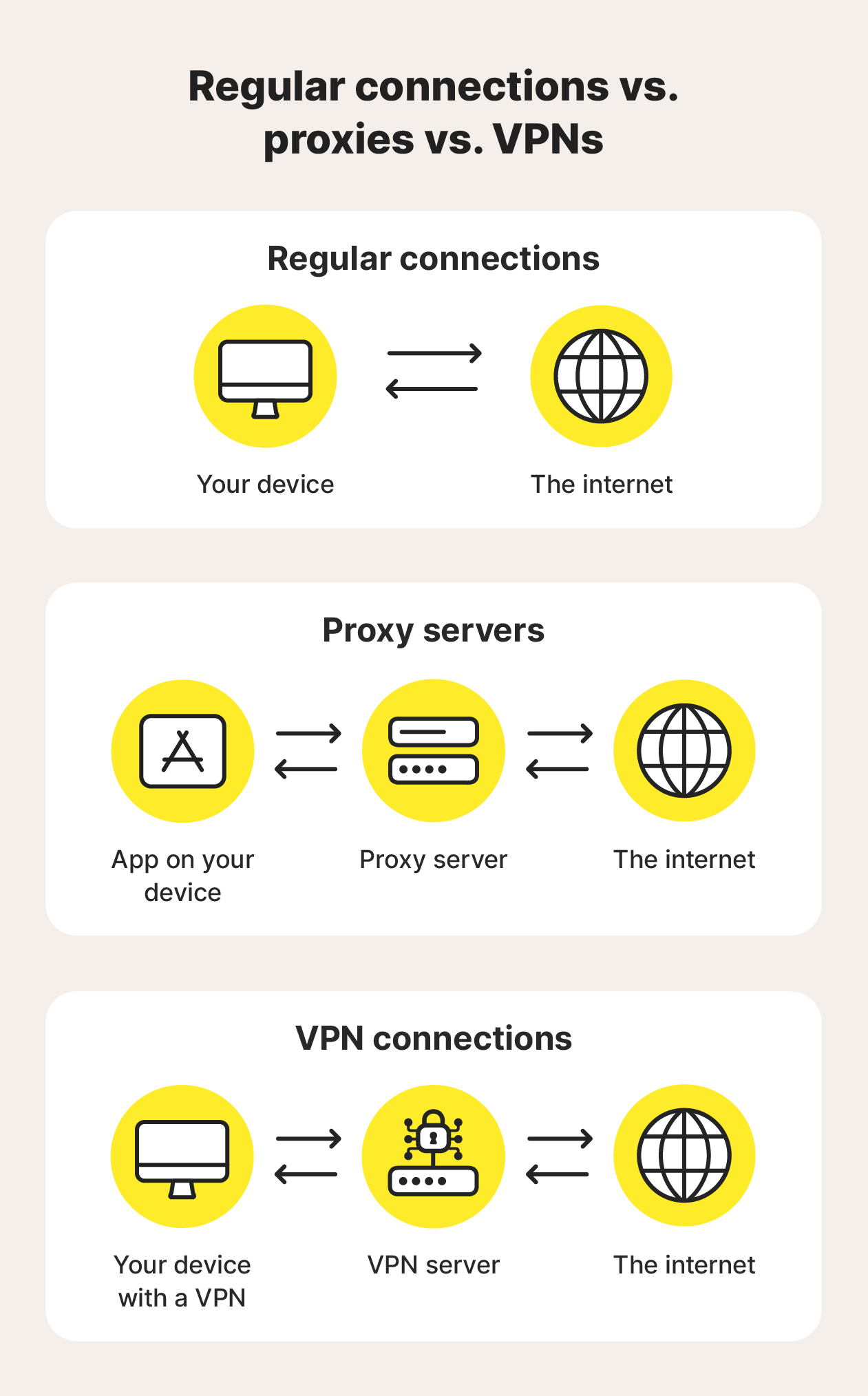

In short, VPNs provide stronger security and privacy, while proxies are mainly helpful for quick IP changes or bypassing simple location blocks. But proxies do have some advantages, and there are certain use cases they’re better suited to than a VPN.
Below, we explore five key differences: security, speed, encryption, privacy policies, and cost.
Feature |
VPN |
Proxy |
|---|---|---|
Data security |
Encrypts internet traffic, protecting data from hackers, ISPs, and trackers |
Usually doesn’t encrypt traffic, leaving data potentially visible |
Coverage |
Protects all device applications |
Protects only specific apps or browsers |
Connection speed |
Can be slower due to encryption overhead |
Often faster since traffic isn’t encrypted |
Online privacy |
High: hides IP, location, and activity |
Limited: hides IP, but activity may still be tracked |
Price |
Mostly paid: free versions have limits |
Many free options, but paid versions are more reliable |
1. Information security
VPNs encrypt all internet traffic, keeping data like passwords and financial info safe from hackers and network observers. Many VPNs also include extra protections, like kill switches, to prevent accidental exposure if the connection drops.
Proxies only hide your IP address and don’t encrypt your data. This leaves sensitive information vulnerable, so proxies aren’t safe for private activities like online banking unless paired with additional security tools.
2. Coverage
Proxies only protect traffic from specific apps or browsers, exposing other online activity, like email or messaging.
VPNs provide system-wide protection, encrypting all traffic across apps, browsers, and background services. They also support multiple devices, including phones, tablets, and routers, helping to keep your entire network secure.
3. Speed of connections
VPNs and proxies can slow your connection by adding extra data routing steps, but proxies are usually faster since they don’t encrypt data, making them quicker for simple browsing or streaming.
VPN speed depends on protocol, server load, and distance, but top VPNs offer nearly seamless performance. With an extensive global server network and speed-optimized protocols like WireGuard, Norton VPN delivers top-performing upload and download speeds.
And, thanks to our recent Data Channel Offload boost, Norton VPN unleashes the power of your hardware for more efficient processing, meaning it now runs even faster, with ultra-low latency.
4. Online privacy
Proxies offer basic online privacy by masking your IP address, making it harder to trace your location or identity. However, they generally don’t encrypt your internet traffic, leaving your online activities visible to your ISP and exposed to hackers, trackers, and other snoops.
VPNs, on the other hand, provide robust privacy protection by encrypting your entire internet connection. This helps stop anyone from monitoring your online activity and makes it harder to trace your virtual IP back to your real IP. And, unlike proxies, no-log VPNs offer additional privacy safeguards against data breaches and even law enforcement investigations.
5. Price
Most proxy servers are free to use. While some free VPNs are also available, they often have limited features, weaker privacy and security, bandwidth caps, and fewer server locations. They may also log or even sell user data. A premium VPN service costs extra but offers much stronger privacy, security, reliability, and functionality than free or lower-tier VPNs or proxies.
Should you choose a VPN or proxy server?
When deciding between a VPN and a proxy, the data encryption and more robust security protocols of VPNs make them the superior choice from a privacy and security perspective. But a proxy server can still be a useful tool if all you want to do is use it to change your virtual location and access non-sensitive data.
Here’s an at-a-glance comparison to help you decide whether a VPN or proxy is right for you:
VPN advantages |
Proxy server advantages |
|---|---|
More secure |
Faster |
Stronger privacy |
Usually free |
Easy app setup |
No software required |
For some use cases, a proxy may be the better option for its simplicity, faster setup, and lighter resource usage. But any time you connect to the internet to share sensitive information, or if you want to keep your identity or activity private, you should use a VPN from a trusted provider for maximum protection.
Secure your internet connection with a VPN
Almost anything a proxy can do, a VPN can do better. It not only hides your IP but also secures your data, anonymizes your online activity, and gives you more control over your privacy.
Whether you're browsing, streaming, or shopping, Norton VPN masks your IP address and encrypts your internet connection, keeping your data safer from hackers and trackers. Unlock ultimate internet privacy today, with a wide range of global server locations, kill-switch and split-tunneling features, and a strict no-logs policy.
FAQs
What is a residential proxy vs a VPN?
A residential proxy routes your traffic through a real residential IP address assigned by an ISP, effectively masking your actual IP address for specific apps or websites. A VPN encrypts all internet traffic and transmits it via a secure server, hiding your online activity and obscuring your IP across all device-level traffic for stronger, system-wide privacy and security.
Do you need a proxy if you have a VPN?
No, you don’t need a proxy if you already have a VPN. On top of the many security and privacy benefits of using a VPN, your IP address is hidden from web servers, and you can customize your virtual IP address location. Connecting to a proxy on top of a VPN wouldn’t offer additional advantages, but it would likely cause reduced download speeds.
Are free VPNs safe?
Some free VPNs are safe to use, but aren’t typically as secure as paid options. Many free VPNs lack strong encryption, have weak security protocols, and collect and sell your data. For better privacy and security, faster connection speeds, and a full range of server options, use a premium VPN service from a trusted brand.
Is a free proxy safe?
Many free public proxies are not safe to use. These “free” services often monetize your activity by logging your browsing activity and injecting ads into your web traffic. It's better to use a reliable paid proxy service or — better yet — a VPN for truly secure and private browsing.
Is a proxy server illegal?
A proxy server itself is not illegal. It’s simply a tool that reroutes internet traffic, often used for bypassing geo-restrictions. However, using a proxy server to engage in illicit activities, such as accessing banned content or committing other cybercrimes, is against the law. Always ensure you’re using proxies within legal boundaries.
Is a VPN better than a proxy server?
Yes, a VPN is generally better than a proxy server. While both can mask your IP address, a VPN offers stronger security by encrypting all your internet traffic, protecting your data from hackers and surveillance. A proxy server, on the other hand, only reroutes specific traffic, leaving your connection vulnerable. For comprehensive privacy and security, a VPN is the best choice.
Editorial note: Our articles provide educational information for you. Our offerings may not cover or protect against every type of crime, fraud, or threat we write about. Our goal is to increase awareness about Cyber Safety. Please review complete Terms during enrollment or setup. Remember that no one can prevent all identity theft or cybercrime, and that LifeLock does not monitor all transactions at all businesses. The Norton and LifeLock brands are part of Gen Digital Inc.







Want more?
Follow us for all the latest news, tips, and updates.