VPN protocols: 7 types and comparisons
There are many types of VPN protocols—each with varying degrees of speed, security, reliability, and device compatibility. Read on to learn more about VPN protocols, how they work, and which of the several options available through the Norton VPN app you should use.
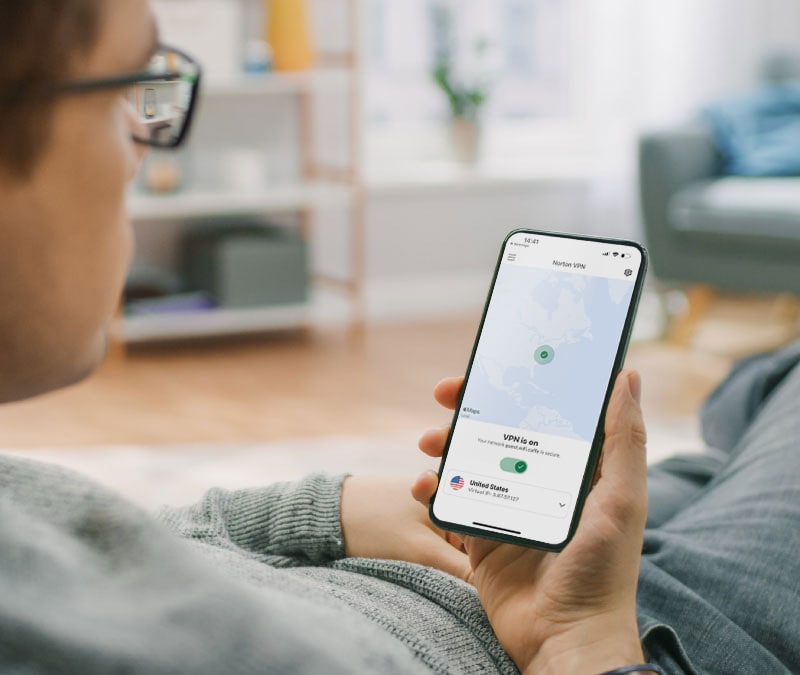

Virtual private networks (VPNs) enable users to send and receive data securely using data packet encryption. This serves the dual purpose of keeping your online activity and the data you transmit private, while enabling you to access content freely at home and on the move. But VPNs wouldn’t be able to do all of that without the right protocols in place.
VPN providers typically use different combinations of protocols to deliver robust security over their networks. As a bonus, more flexible VPN apps even let you choose which protocol to use based on your preferences. That means you can decide whether to prioritize security, speed, customization, or usability.
Learn more about some of the top VPN protocols, how they work, and what makes them stand out:
What are VPN protocols?
VPN protocols are a set of rules that dictate how data is encrypted and transmitted between a virtual private network server and your device. VPNs use these protocols to help establish secure online connections, protecting in-transit data from interception, manipulation, surveillance, and unauthorized access.
How do VPN protocols work?
VPN protocols work by using predetermined rules to encrypt, transmit, and authenticate data, ensuring private communication between the device and VPN server. Once a connection is established, all in-transit data travels through a secure tunnel, protecting it from eavesdropping, tampering, and other cybersecurity threats. However, even with a VPN, your online activity might still leave traces.
Here’s a closer look at how VPN protocols protect your online privacy:
- Initiation: The user activates their VPN via the client on their device, which sends a connection request to the VPN server.
- Authentication: The VPN client software and server verify the other’s identity by exchanging passwords, encryption keys, or other credentials.
- Encryption: Once the secure connection is established, the cryptographic encryption algorithm encrypts the data, making it unreadable to those without a decryption key.
- Tunneling: The encrypted data is nested inside the protocol’s data packets, which contain routing information to help the secured data make its way through VPN tunnels across networks.
- Transmission: The encapsulated and encrypted data is transmitted across the internet to the VPN server.
- Decryption and routing: The VPN server strips off the outer layer to access the encrypted data inside using a decryption key.
- Response: When the response from the destination is ready to be returned, it’s encrypted, encapsulated, and sent back through the secure tunnel to the VPN client.
Now that you understand how VPN protocols work, let’s explore the types of VPN protocols you can use and when it makes sense to use them.
7 types of VPN protocols
There are several types of VPN protocols, including the Internet Key Exchange version 2 (IKEv2), Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP), Lightway, Mimic, OpenVPN, Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol (SSTP), and WireGuard. The best VPN for you depends on which features it offers and how well it suits your needs
| VPN type | Operating system compatibility | Security and encryption | Speed |
| IKEv2 | Android, iOS, Linux, macOS, Windows, and routers | High | High |
| L2TP | Android, iOS, Linux, macOS, Windows, and routers | Moderate | Moderate |
| Lightway | Android, iOS, Linux, macOS, Windows, and routers | High | High |
| Mimic | Android, iOS, macOS, and Windows | High | High |
| OpenVPN | Android, BSD, iOS, Linux, macOS, Solaris, and Windows (server must be installed on Linux OS) | High | Moderate |
| SSTP | Windows | Moderate | Moderate |
| WireGuard | Android, BSD, iOS, macOS, and Windows | High | High |
1. Internet Key Exchange version 2 (IKEv2)
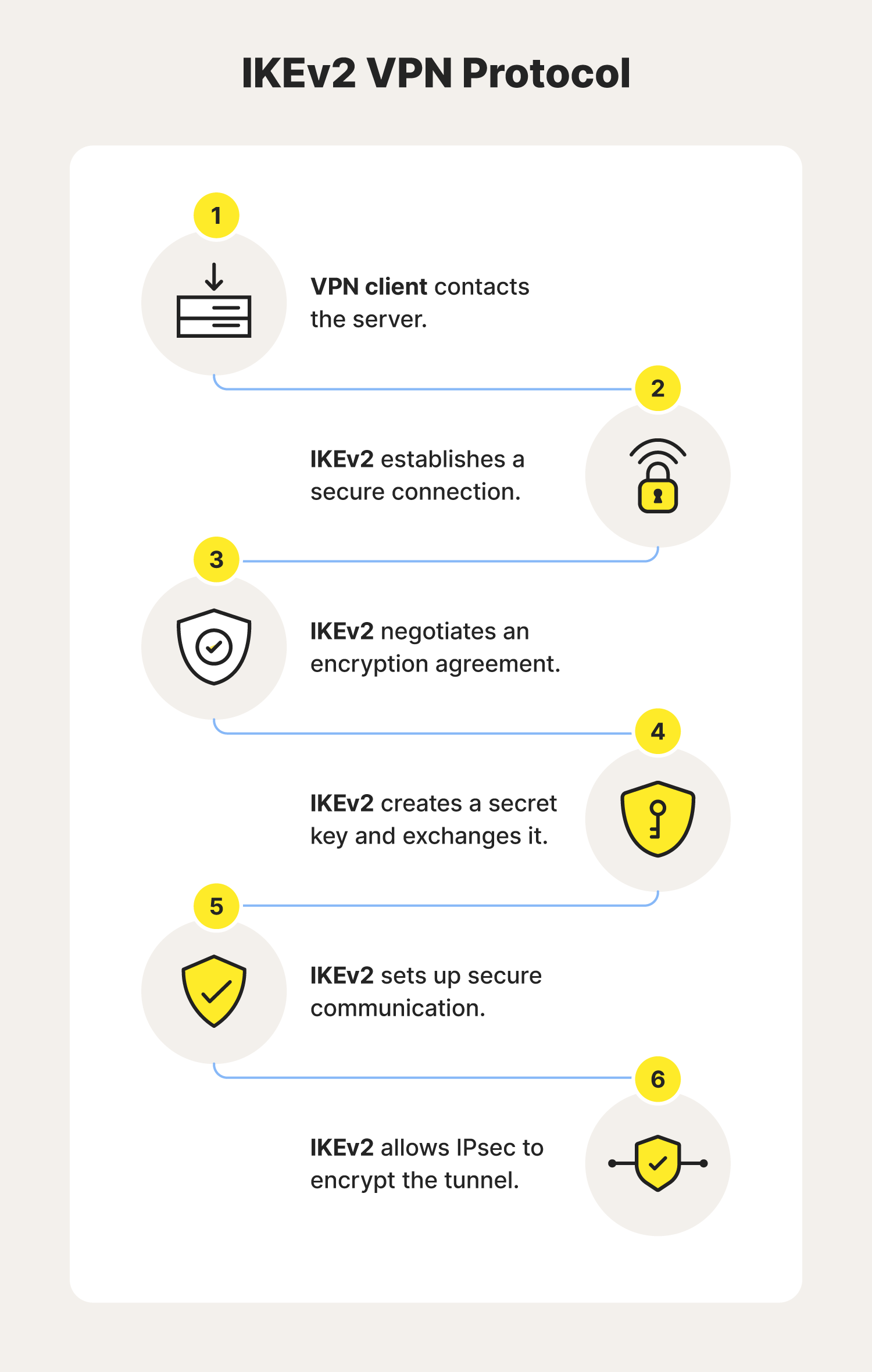
IKEv2 is a VPN key exchange protocol that creates a tunnel between the VPN client and server to help guard data during transmission. However, it can’t perform encryption without a helper protocol like IPsec (Internet Protocol Security).
Using the protocol’s pre-determined settings, IKEv2 negotiates an encryption agreement, and IPsec scrambles the data, making it unreadable. Together, these protocols are referred to as IKEv2/IPsec and can create a secure tunnel.
- Developer(s): IBM
- Compatible with: Android, iOS, Linux, macOS, Windows, and routers
- Pros: Secure connections, fast, reliable, and automatic reconnection
- Cons: Limited customizability, sometimes restricted by firewalls, and slower than other protocols
2. Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP)
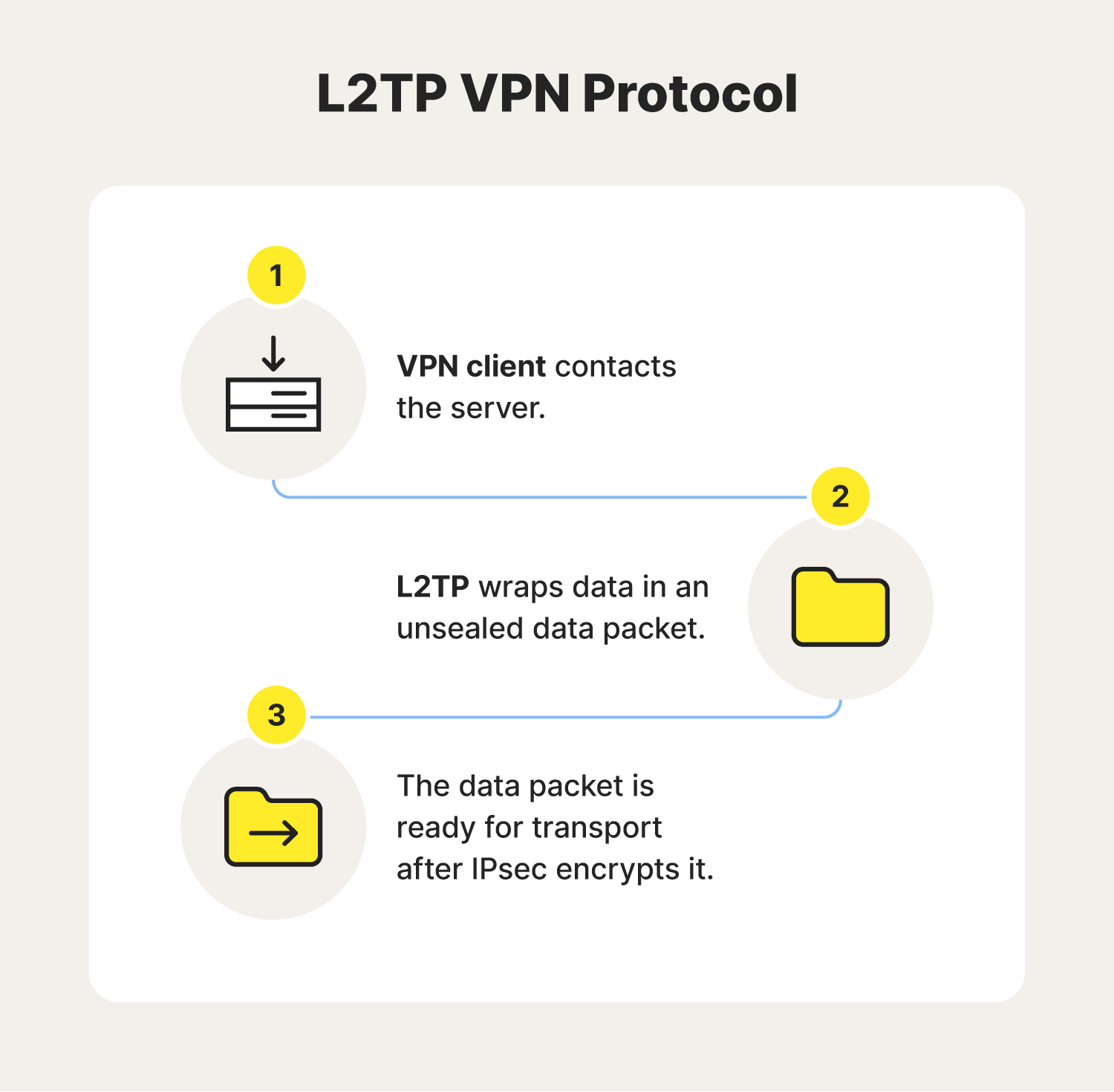
L2TP is a VPN protocol often used with IPsec to deliver AES-256 encryption, which is used to create secure connections between devices and VPN servers over internet networks. On its own, L2TP doesn’t have encryption or authentication capabilities. However, when used with other protocols like IPsec, VPN providers can create secure tunnels allowing data to pass securely over public networks.
- Developer(s): Cisco and Microsoft
- Compatible with: Android, iOS, Linux, macOS, Windows, and routers
- Pros: Straightforward setup and firewall-friendly
- Cons: No built-in encryption, and an older protocol
3. Lightway
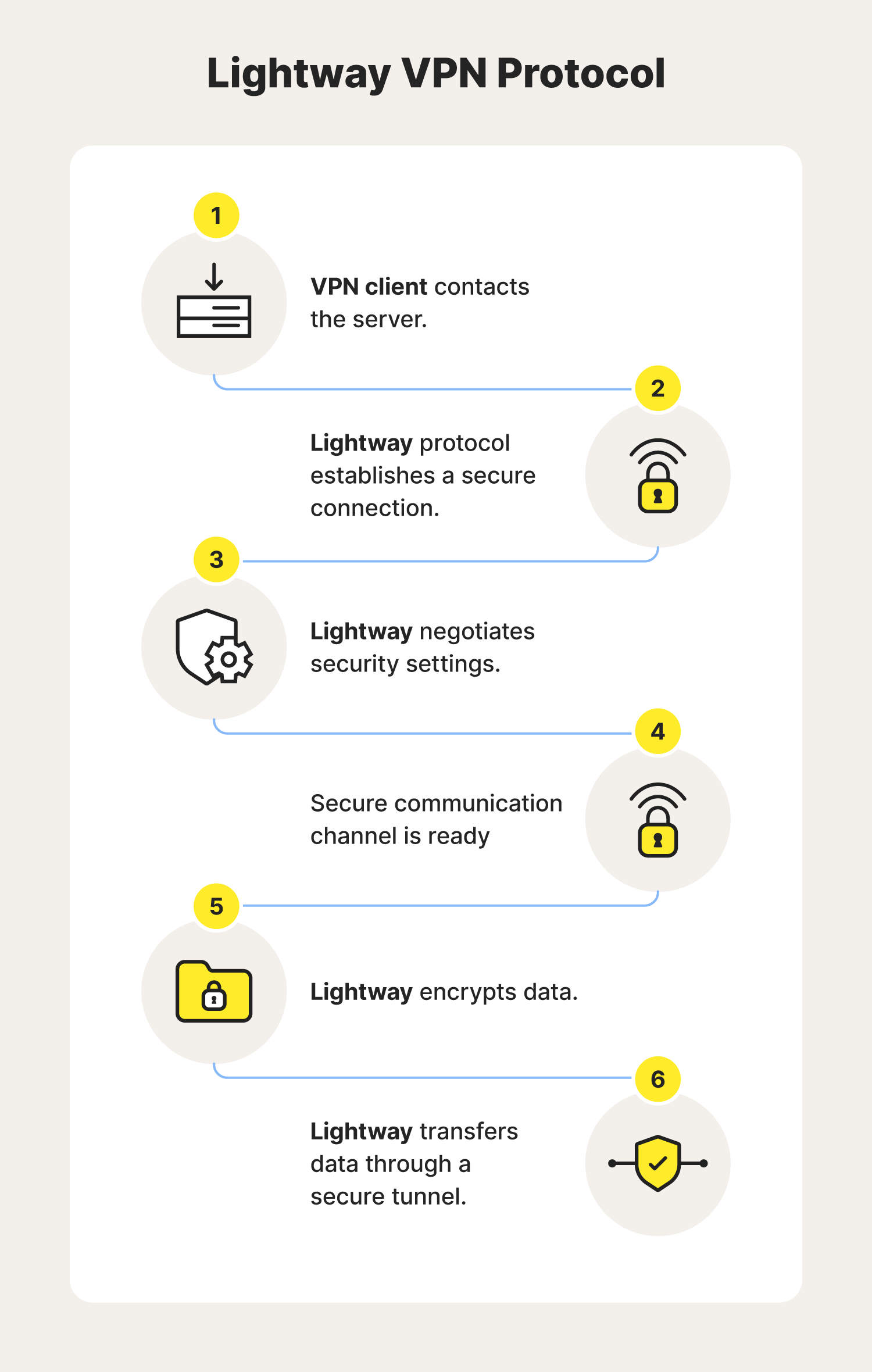
Lightway is a lightweight VPN protocol that delivers reliable internet security. Unlike some alternatives, Lightway can handle security negotiation and data encryption without sacrificing quality. This VPN protocol is often used for video streaming and gaming security, because its speed contributes to a smoother overall experience.
- Developer(s): ExpressVPN
- Compatible with: Android, iOS, Linux, macOS, Windows, and routers
- Pros: Fast, secure encryption and authentication protocols, minimal battery consumption, automatic reconnection, and VPN traffic concealment
- Cons: Only available through ExpressVPN and development is dependent on them
4. Mimic
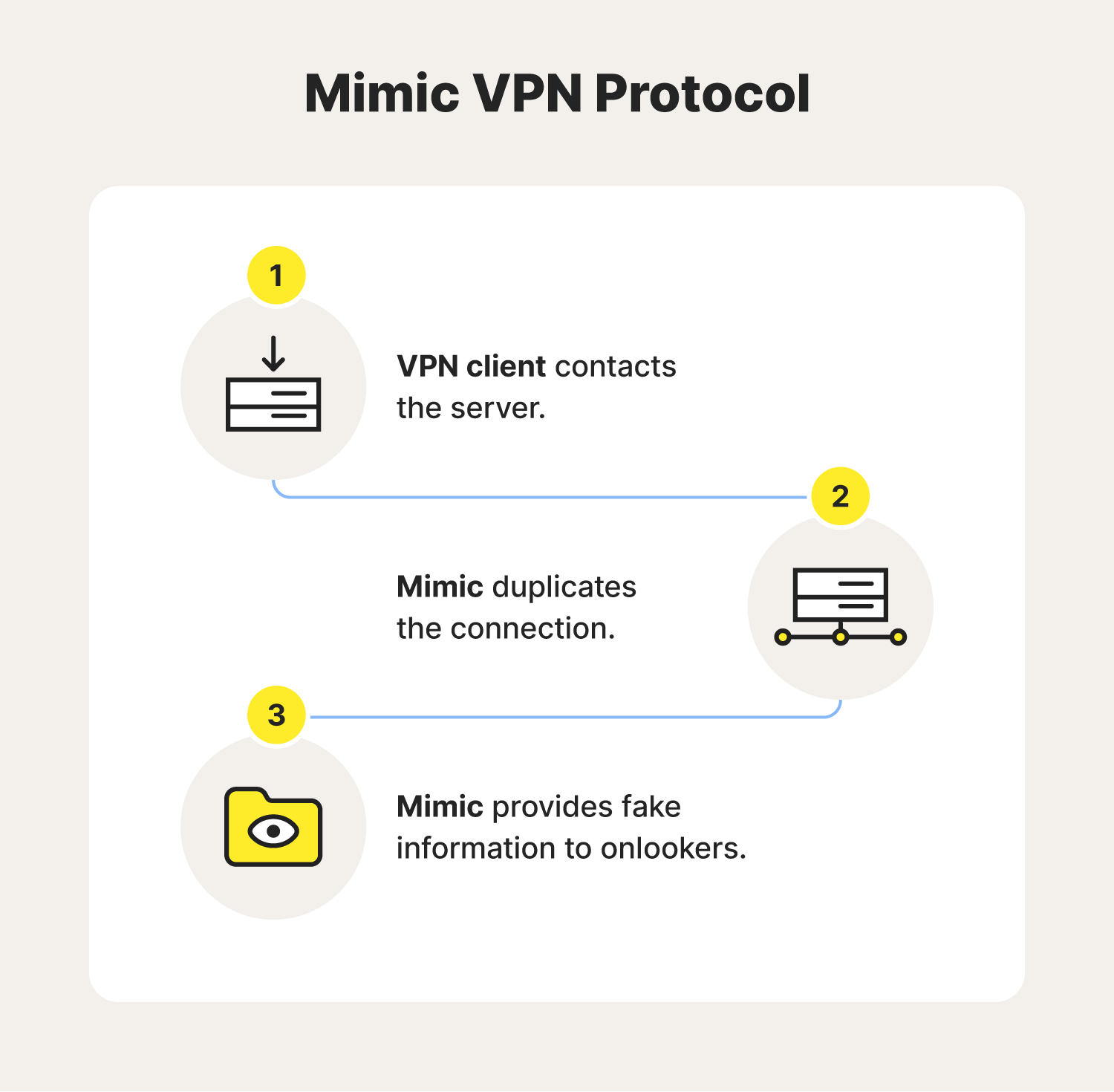
Mimic is a newer VPN protocol that stands apart from other options by masking itself as an unassuming HTTPS connection that you might use to check your email, stream your favorite show, or look up a dinner recipe. Aside from its encryption capabilities, Mimic doesn’t require additional configuration, uses less power, is eco-friendly, and is capable of establishing high-speed connections and transfers.
Mimic also has an impressive resistance to quantum attacks, which can ultimately help protect users from emerging computing threats. This proprietary protocol is one of the types you can choose from within the Norton VPN application, and it’s a strong option. With it, Norton can offer you core VPN capabilities like bank-grade encryption, anonymous browsing, and split tunneling.
- Developer(s): Gen Digital Inc.
- Compatible with: Android, iOS, and Windows
- Pros: Establishes connections quickly, resists cryptographic attacks, and masks user location
- Cons: Limited configurations
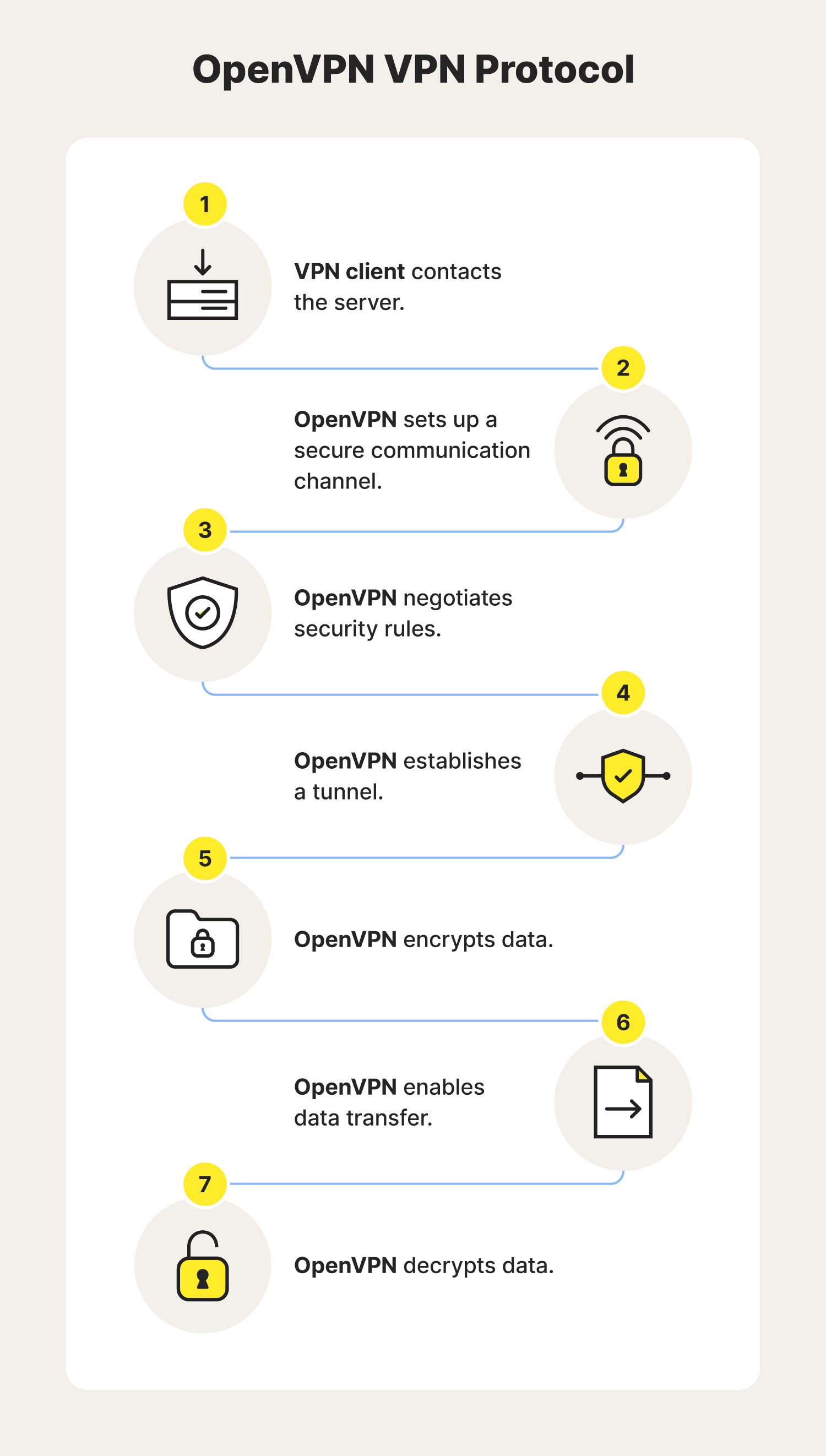
5. OpenVPN
OpenVPN supports both client and server applications, and allows peers to authenticate each other using various methods. It makes extensive use of the OpenSSL encryption library and the TLS protocol, offering many security and control features. Beyond that, this VPN protocol is highly customizable, allowing users to configure connection settings to their specifications.
- Developer(s): OpenVPN, Inc.
- Compatible with: Android, FreeBSD, iOS, Linux, macOS, NetBSD, OpenBSD, Solaris, and Windows (server must be installed on Linux OS)
- Pros: Industry-standard encryption, high customizability, and open-source
- Cons: Complex setup, slower connection speeds, and lacks native integration
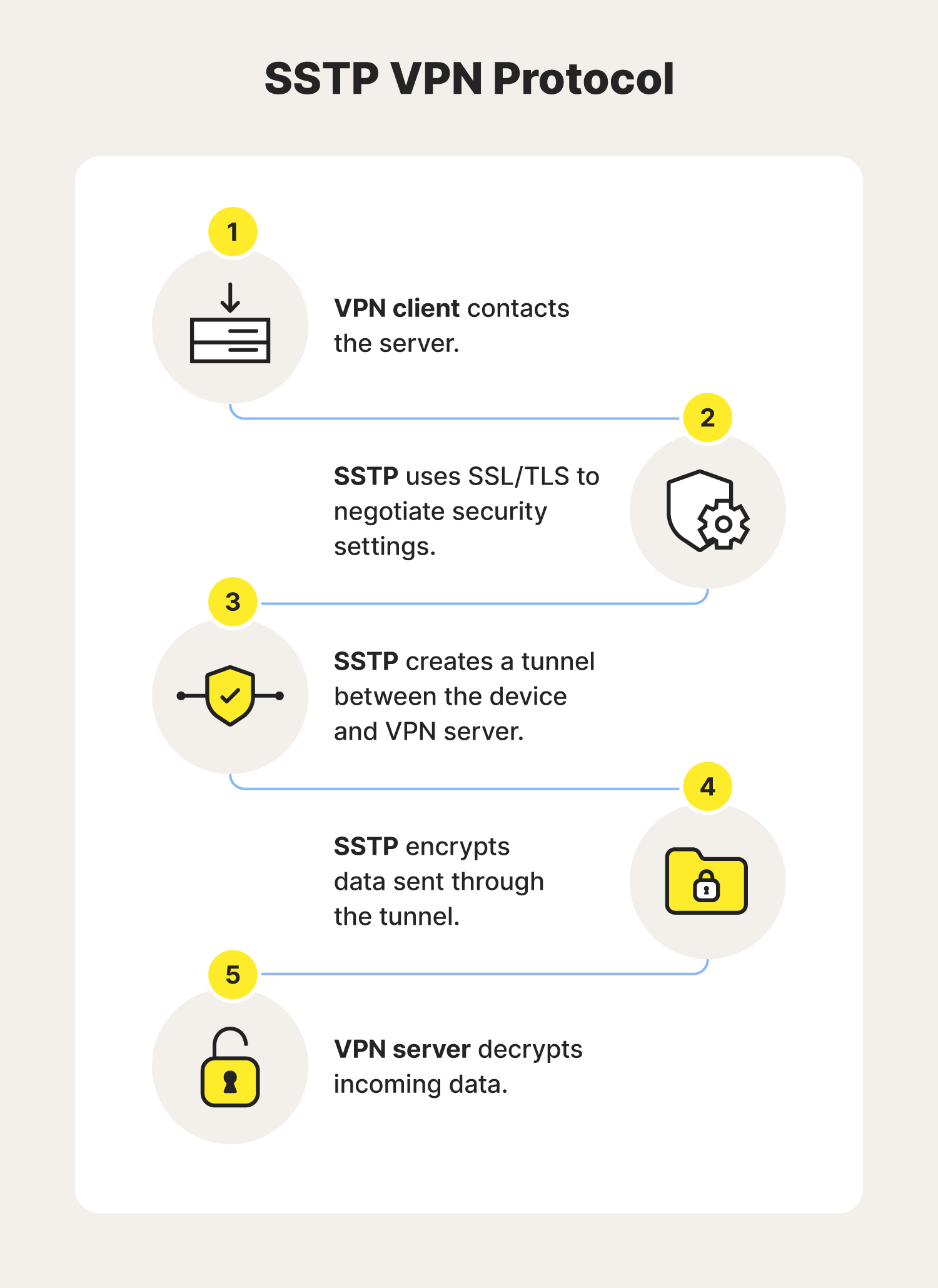
6. Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol (SSTP)
SSTP is a VPN protocol that leverages SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) technology to remotely access Windows devices and help encrypt internet traffic. While less cutting-edge than some alternatives, this VPN protocol is convenient, as most new Windows devices come with it built-in.
But to access enhanced security features, enjoy faster speeds, choose from more server locations, and strengthen anonymous browsing on Windows PCs, you’ll still need to download a third-party VPN.
- Developer(s): Microsoft
- Compatible with: Windows
- Pros: Easily accessible to Windows users and firewall-friendly
- Cons: Not compatible with non-Windows devices; closed-source and less robust security protocols than other encryption methods
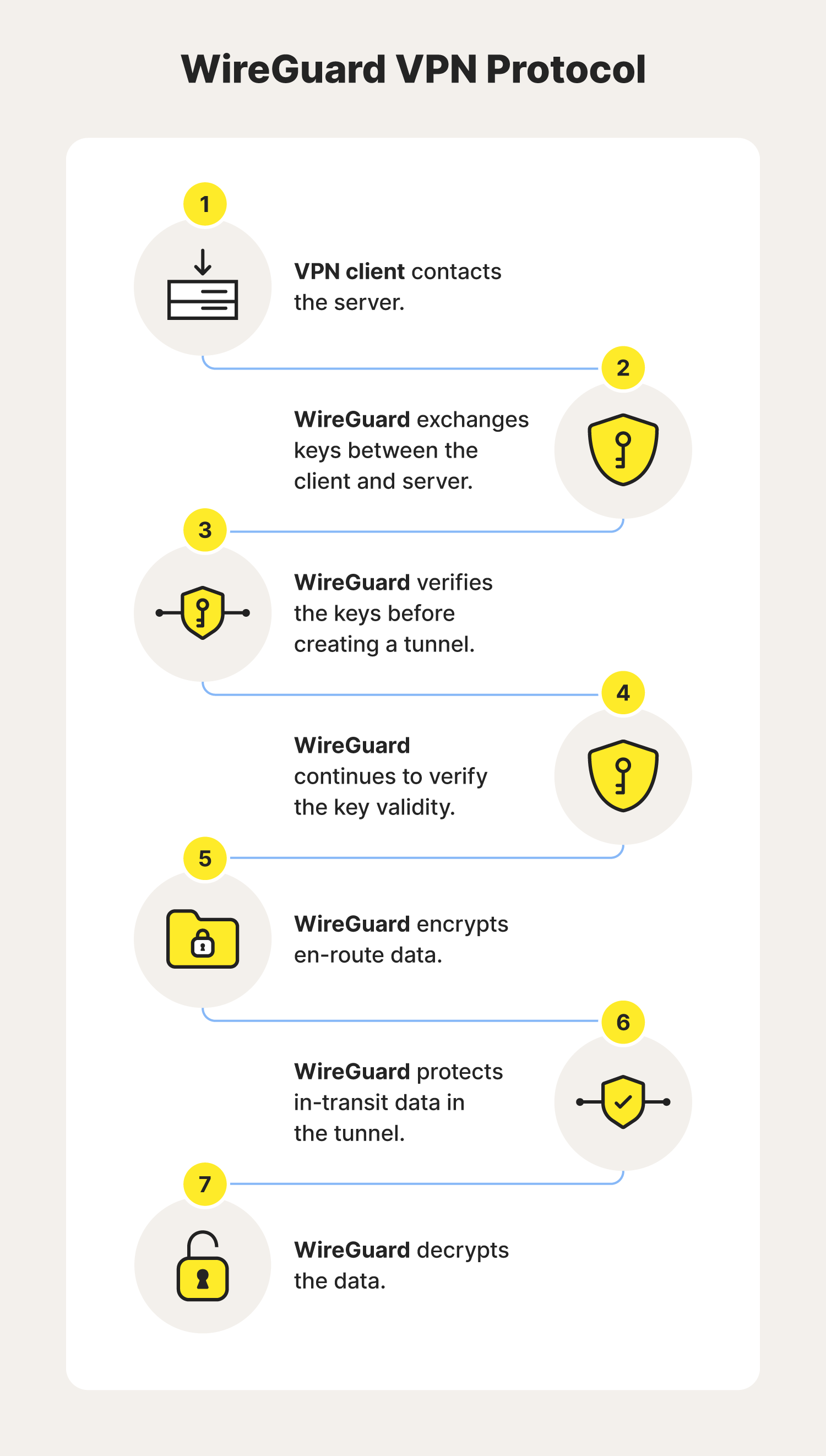
7. WireGuard
WireGuard is a cross-platform VPN protocol that uses cryptography to create secure tunnels, often for secure streaming and private browsing. This protocol hasn’t been around long but is already gaining popularity due to its speed and user-friendliness, and it’s now an option you can choose from in Norton VPN.
However, it’s important to note that though WireGuard is well-regarded in the cybersecurity industry, it’s still under development. While WireGuard hasn’t confirmed what they’re working on, they say they are working toward creating a faster, leaner, and more useful VPN protocol.
- Developer(s): WireGuard
- Compatible with: Android, BSD, iOS, macOS, and Windows
- Pros: Fast, easy configuration and state-of-the-art encryption
- Cons: Newer protocol that lacks key features like dynamic IP address assignment; configuration errors may compromise security
How to choose the best VPN protocol
Consider factors like security, device and operating system compatibility, user-friendliness, reliability, and log policy when selecting a VPN protocol. Here are some tips to help you make your decision:
- Security: Capabilities like encryption and authentication are important for scrambling your data, connecting to a trusted server, and enhancing online privacy.
- Compatibility: Ensure the protocols your VPN uses work seamlessly with your devices and operating systems.
- User-friendliness: Choose a personal VPN that is easy to set up and use. Or, at the very least, choose a solution that provides access to live customer support.
- Reliability: Look for a VPN that uses reliable protocols to ensure you have consistent coverage to help safeguard your online activities and data.
- Logging policy: Log policies directly impact your privacy and security by determining how your activity is recorded; use protocols that are compatible with no-log policy services to maximize privacy.
Keep your browsing private
The right combination of VPN protocols is at the heart of any good VPN. Norton VPN lets you choose between VPN protocols like WireGuard, OpenVPN, Mimic (Norton’s proprietary VPN protocol), or an automatic option to help give you the VPN experience you want.
Use Norton’s VPN to help keep private information like passwords, financial details, and other sensitive data from being intercepted or manipulated during transmission—especially when you’re on the go and using public Wi-Fi to stay connected.
FAQs about VPN tunneling protocols
Still have questions about VPN protocols? Here’s what you need to know.
What is a VPN connection?
A VPN connection is a secure tunnel that encrypts your internet traffic and hides your online identity. It's essentially an ultra-secure pathway that enables data to travel safely over private and public Wi-Fi networks.
Which VPN is the oldest and least secure of the VPN protocols?
Point-to-point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) is the oldest and least secure VPN protocol. Due to its weak encryption and known security vulnerabilities, PPTP is considered obsolete and isn’t typically used by reputable VPN providers.
What is the best protocol for a VPN?
The “best” VPN protocol depends on what you’re in the market for. For instance, Mimic is a leader in Security, WireGuard excels in speed, and OpenVPN is a leader in configuration flexibility.
Editorial note: Our articles are designed to provide educational information for you. They may not cover or protect against every type of crime, fraud, or threat we write about. Our goal is to increase awareness about Cyber Safety. Please review the complete Terms during enrollment or setup. Remember that no one can prevent all identity theft or cybercrime, and that LifeLock does not monitor all transactions at all businesses. The Norton and LifeLock brands are part of Gen Digital Inc. For more details about how we create, review, and update content, please see our Editorial Policy.






Want more?
Follow us for all the latest news, tips, and updates.