What is IPSec and how does this VPN protocol secure your device?
IPSec is a set of network transfer protocols used by many VPNs. These internet data privacy rules establish secure connections by enforcing encryption that guards against eavesdroppers and hackers. Read on to learn what IPSec is, how IPSec tunneling works, and how Norton VPN can secure your internet traffic with cutting-edge protocols.

What is IPSec (IP Security)?
IPSec (Internet Protocol Security) is a protocol framework designed to ensure data transmitted across public networks remains secure. Frequently used as a VPN protocol, IPSec safeguards information against tampering or unauthorized access by encrypting data packets and verifying the authenticity of their source.
The term "IPSec" is a combination of "Internet Protocol" (IP) — the standard internet data routing protocol using IP addresses — with "Security" (Sec). IPSec builds on IP by integrating encryption and authentication, establishing a secure system for transmitting sensitive data across the internet or between networks.
Despite being developed in the early 1990s, it’s still considered robust and remains widely used in both site-to-site and remote-access VPNs. However, top VPN services also use newer protocols such as OpenVPN and WireGuard.
How does IPSec work?
IPSec works by establishing a secure connection or tunnel through which data can be privately shared across networks — even on public Wi-Fi. The process for securely sending and receiving data via IPSec protocols helps ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of IP packets, and it’s broken down into six steps:
- Key Exchange: IPSec first facilitates secure communication by enabling devices to exchange cryptographic keys — random character strings that "lock" (encrypt) and "unlock" (decrypt) data.
- Packet Headers and Trailers: Network data is divided into packets, each containing a data payload and metadata. IPSec adds additional security metadata in the form of “headers” and “trailers.”
- Authentication: IPSec authenticates each packet to verify its source, acting like a digital seal that confirms its legitimacy and prevents tampering.
- Encryption: Data is then secured by encrypting packet payloads and, in tunnel mode, their IP headers as well. This ensures data remains private and protected during transmission.
- Transmission: Encrypted IPSec packets traverse networks using a transport protocol, usually UDP as this helps packets to pass through firewalls more effectively.
- Decryption: Upon reaching their destination, the encrypted packets are decrypted, making the data readable by applications, and ensuring seamless and secure communication.
IPSec tunnel mode vs transport mode
IPSec can operate in two modes with different characteristics and levels of security. The so-called “tunnel mode” encrypts the entire IP packet, whereas “transport mode” encrypts only the packet’s payload. Here’s a closer look at the IPSec tunnel and transport modes:
- Tunnel mode encrypts the IP packet headers and trailers, as well as the data packet payload. This requires more bandwidth but enables more secure network-to-network communication.
- Transport mode encrypts the packet payload only, exposing the header information. It’s typically only used for direct device-to-device communication within trusted networks.


What is an IPSec VPN?
IPSec VPNs are virtual private networks that operate using IPSec protocols to create secure connection tunnels for transmitting and receiving internet data. By encrypting all your network traffic with IPSec, and routing it via a secure VPN server, you enjoy all the benefits of using a VPN, including data protection, anonymized online activity, and IP address masking.
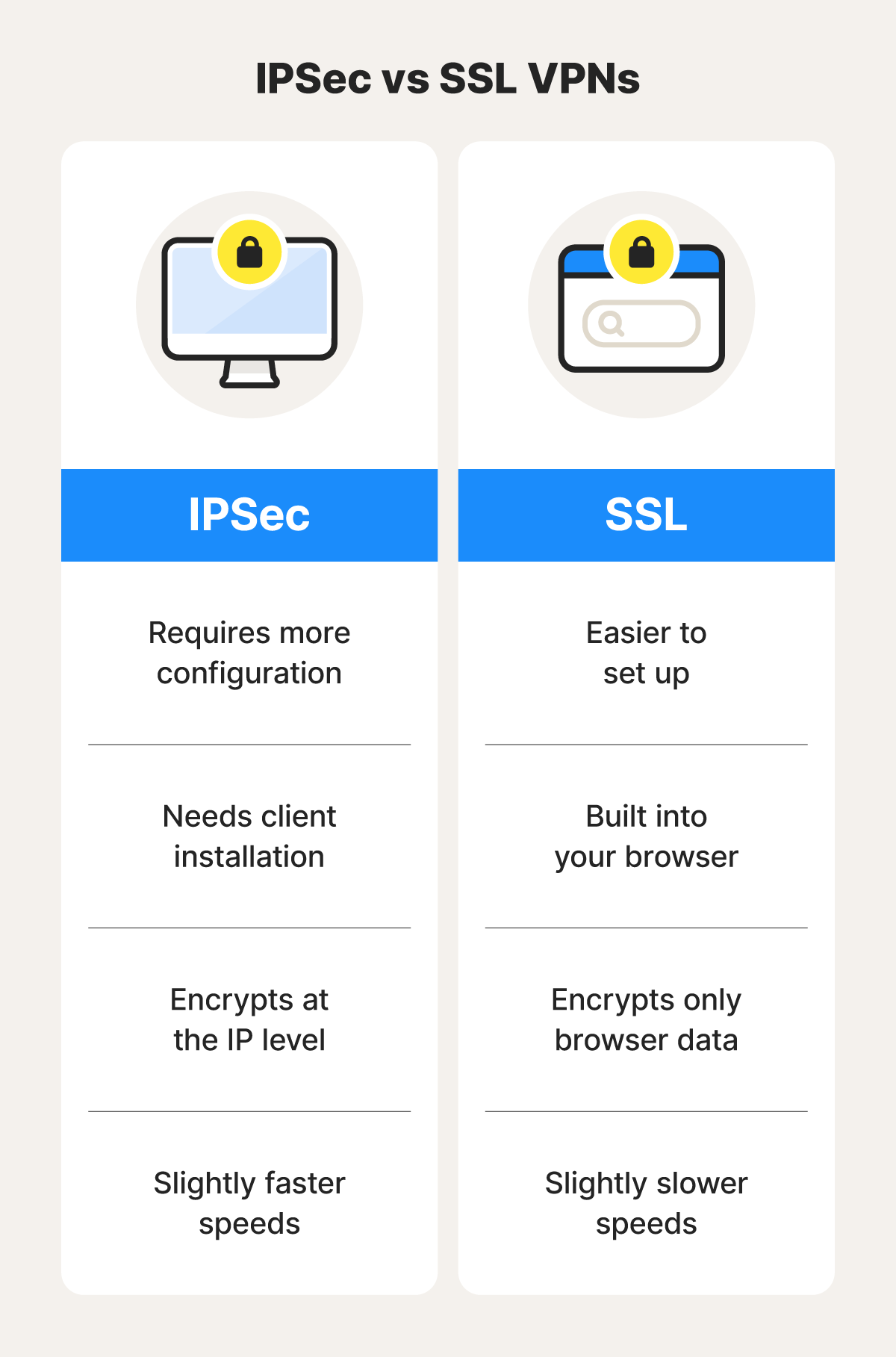
IPSec vs SSL VPNs
IPSec VPNs secure connections at the network layer to encrypt all internet data, and they typically require client software. SSL VPNs use Secure Socket Layer protocols to secure data just for specific applications — often a web browser.
While IPSec enables full network access, SSL VPNs are better suited for simpler, application-specific remote access, such as to a centralized corporate network via a VPN concentrator.
Here’s a breakdown of how IPSec and SSL VPNs operate and what use cases they suit best:
- Encryption: IPSec VPNs encrypt entire IP packets using robust algorithms like AES, but SSL VPNs encrypt data at the application layer using SSL/TLS.
- Client installation: IPSec VPNs usually require dedicated client software, whereas SSL VPNs are browser-based, requiring no special client installation.
- Ease of setup: SSL VPNs are generally simpler than their IPSec counterparts, with minimal setup required and easy remote access via standard web browsers.
- Speed: SSL VPNs may experience slower speeds due to the browser-based delivery method, which is less efficient than IPSec's direct network-level integration.

Different IPSec protocols
IPSec isn't a single protocol, but rather a collection of three protocols that sit on top of the basic IP infrastructure and work together to ensure the authenticity, integrity, and privacy of data in transit:
- Authentication Header (AH): The AH protocol provides data integrity and authentication by verifying the IP packet’s sender and ensuring it hasn’t been altered during transmission.
- Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP): This protocol encrypts both the IP header and the payload of each packet, except in transport mode, where only the payload is encrypted. It also adds a header and trailer to each packet.
- Security Association (SA): Various SA protocols, like IKEv2 and L2TP are used to establish a set of rules for secure communication between devices, defining encryption methods, authentication, and key management.
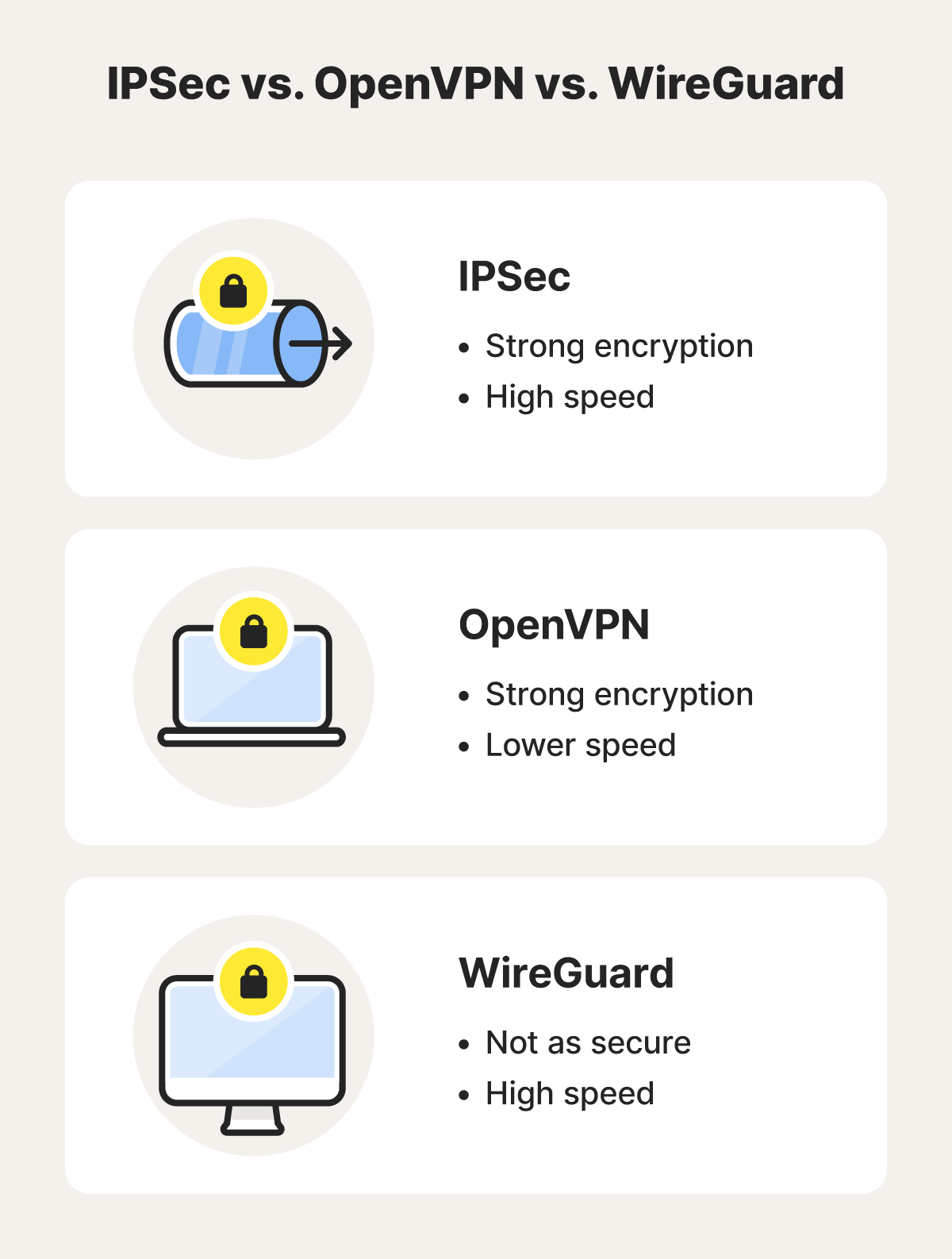
IPSec vs alternative VPN protocols
IPSec offers a good balance between data transfer speeds and robust encryption and authentication — and it’s been a viable VPN protocol for over 30 years. However, alternative methods like Open VPN and WireGuard can offer certain performance or security advantages.
Here’s a closer look at other VPN protocols:
- OpenVPN offers very strong security, flexibility, and cross-platform support, but performance lags behind simpler protocols.
- WireGuard boasts fast performance, simplicity, and modern cryptography, although it’s still under development and lacks some advanced features.
- PPTP (Point-to-Point Protocol) is a legacy protocol that’s still supported on some VPNs. However, due to security vulnerabilities, its use is no longer recommended.
- Mimic was developed by Norton as an ultra-private and secure protocol that masquerades as an HTTPS connection and is resistant to quantum attacks.

Keep your internet data private
The best VPNs offer users a variety of VPN protocols to tailor their connection to their security, privacy, and performance needs.
Norton VPN supports a versatile selection of privacy-focused VPN protocols — including IPSec/IKEv2, Wireguard, and Mimic — and it will protect all the data you send and receive online with bank-grade encryption. Get flexible, ironclad online privacy today.
FAQs
Does Norton support IPSec?
Norton VPN supports IPSec/IKEv2 as well as other VPN protocols including WireGuard, OpenVPN, and Mimic, Norton’s cutting-edge proprietary protocol.
Is IPSec the same as a VPN?
No, IPSec is not the same as a VPN. IPSec is a suite of protocols designed to encrypt and authenticate data at the network layer. VPNs are services that use protocols like IPSec to create secure tunnels for transmitting data over public networks.
Is IPSec still being used?
Yes, IPSec is still widely used and remains an important technology for secure network communications. Despite the emergence of newer protocols like WireGuard, IPSec's robust security, widespread adoption, and flexibility mean it’s still relevant and reliable.
What devices support IPSec?
IPSec is supported on Windows, macOS, and iOS devices, and it can also be used when you install a router VPN.
Can IPSec slow down network performance?
Yes, IPSec can slow down network performance due to the extra time needed for encrypting and decrypting data, authenticating packets, and managing secure connections. However, IPSec is one of the faster VPN protocols, and the impact on performance is often negligible.
Editorial note: Our articles provide educational information for you. Our offerings may not cover or protect against every type of crime, fraud, or threat we write about. Our goal is to increase awareness about Cyber Safety. Please review complete Terms during enrollment or setup. Remember that no one can prevent all identity theft or cybercrime, and that LifeLock does not monitor all transactions at all businesses. The Norton and LifeLock brands are part of Gen Digital Inc.






Want more?
Follow us for all the latest news, tips, and updates.