14 cryptocurrency scams to avoid
The excitement and gains in cryptocurrency values have led many people to invest in new types of currency. But that means scammers are waiting to take advantage. Explore the most common cryptocurrency scams to look out for, along with warning signs and tips to avoid these scams. And get Norton™ 360 with LifeLock™ Select to help safeguard your personal information and protect against identity theft.

Cryptocurrency and Bitcoin scams can jeopardize your finances and put your identity at risk if you aren’t aware of the ways that people can try to take advantage. Keep reading to learn more about these scams and tips to avoid cryptocurrency fraud.
Let's start by taking a closer look at 14 of the most common crypto scams to watch out for.
1. Investment or business opportunity scams
Investment or business opportunity scams often begin with an unsolicited offer, typically to become a cryptocurrency investor, that lures you to a fraudulent website to learn more about the apparent opportunity. Once on the site, you’re encouraged to invest and make money quickly. The website might even have celebrity endorsements or testimonials that are fake.
But once you complete your transaction, the offer never comes to fruition, and you don’t see your money again. You might equate these types of cryptocurrency scams to multi-level marketing schemes or Ponzi schemes. They’re called pig butchering scams because the butcher (the scammer) fattens up their account by getting you to invest more money over time before disappearing.
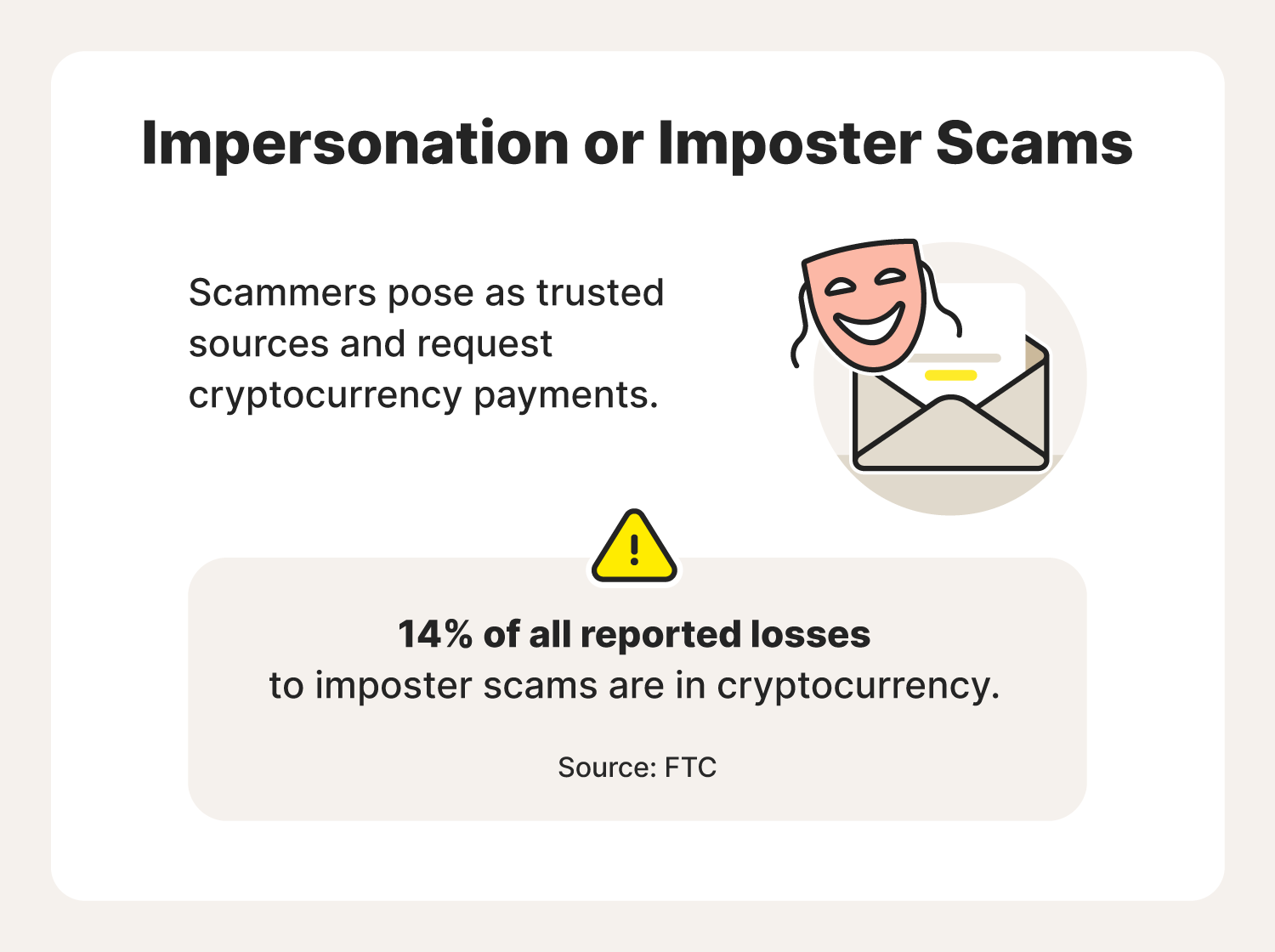
2. Imposter or impersonation scams
An imposter or impersonation scam is when a cybercriminal poses as a trusted source to convince victims to complete a cryptocurrency transaction. This might be under the disguise of government authorities, credit card providers, banks, a service provider, or even a fake celebrity, and they’ll often reach out via email and request you complete payment via cryptocurrency.
Remember, the government does not regulate cryptocurrency, and it’s also not yet widely accepted by businesses, so you should exercise caution whenever you receive email requests for crypto payments.
For safe measure, double-check with the source through a different communication channel and verify a website’s security before completing a transaction.
3. Blackmail or extortion scams
One of the oldest scamming approaches in the book, blackmail, or extortion, is when you receive a message that someone has compromising information about you—be it photos, videos, confidential data, etc.—and they request you pay them money or else they’ll release it.
This becomes a cryptocurrency scam when the scammer requests the payment in crypto, oftentimes because the victim can’t reverse the transactions and because of the anonymity cryptocurrency offers. That complexity and anonymity make it tough for law enforcement to track fraudulent payments. It’s best to delete these messages and report the sender to authorities.
4. Social media cryptocurrency scams
Social media cryptocurrency scams are just what they sound like: cryptocurrency scams that occur over social media. Oftentimes, this is via a false social media post or advertisement requesting payment in cryptocurrency. You might even see other users responding to the post or leaving reviews.
In reality, these could be bots trying to lure you into a social media scam. The post or message might be from a friend whose account got hacked. Alternatively, social media influencers might tout new and potentially fake crypto and encourage users to sign up or send them payments that they might multiply. In some cases, influencers merely pocket the payments. These are referred to as influencer cryptocurrency scams.
Bottom line: Recognize that cryptocurrency isn’t a widely used payment method, and any pushy requests to pay with crypto are likely a scam.
5. Giveaway cryptocurrency scams
Somewhat of a cross between impersonation and social media cryptocurrency scams, giveaway scams are when cybercriminals lure victims into sending them money while promising they’ll multiply the payment.
For example, this could occur if a fake celebrity social media account posts that if followers send them a certain amount of cryptocurrency, they will send back twice the amount. In fact, followers will send money directly to scammers, never to see their investment again.

6. Fake apps
As a digital payment method, different cryptocurrencies also have different apps, and cybercriminals can be skilled at replicating them. In 2021, there were over 300,000 downloads of a fake app that stole banking credentials from victims. Once users download these fake apps, they might begin sending payments directly to the crypto scammer.
7. Loader or load-up cryptocurrency scams
Believe it or not, some cryptocurrency scams will ask for your account logins outright. This is how a loader or load-up cryptocurrency scam works: Scammers might ask victims to borrow their account because they need higher limits. In return, the scammer promises to give them a portion of the proceeds from their investments.
But those returns never materialize. Instead, the scammers load up victims’ accounts and drain them, taking all of the cryptocurrency for themselves.
Remember: You should never provide your account logins to someone else, even if you think it’s someone you can trust.
8. Romance cryptocurrency scams
Romance scams pull on victims’ heartstrings by way of social engineering tactics. How does it work? Cybercriminals play the part of an online love interest and gain a victim’s trust before asking them to send money. Once the victim does, the cybercriminal pockets the funds and runs.
Romance cryptocurrency scams, like the Pig Butchering scam, follow the same approach, but the funds are requested in cryptocurrency and are much more difficult to reverse.

9. Phishing cryptocurrency scams
Another old-school cyberattack, phishing scams often occur over email and involve an ask for money. These messages are usually from cybercriminals posing as trusted sources, meaning phishing scams are similar to impersonation scams.
In the case of phishing cryptocurrency scams, the false request for payment is in the form of cryptocurrency. The messages might even be from a cybercriminal posing as a cryptocurrency company touting an initial coin offering (ICO) to appear authentic.
10. Employment scams
Similar to investment or business opportunity scams, employment scams involving cryptocurrency often begin with an unsolicited job offer that lures victims to a fraudulent website to learn more about the opportunity.
They will often ask victims to pay for training in cryptocurrency to become fully onboarded to a company. Once the victim makes the payment, the scammer will cut off all contact, having pocketed the money while never having had a real job to offer.
11. Flash loan attack scams
In a flash loan attack, a cybercriminal will take out an unsecured loan using a loan protocol to shift the market in favor of that cryptocurrency. These loan protocols work quickly, so scammers have to be able to take out these loans, siphon off the profits, and then dump the coin back into the market, lowering the value.

12. Bitcoin mining scams
In a bitcoin mining scam, also called a cloud cryptocurrency mining scam, someone offers to rent you computing power located at a data center that they claim is designed to mine cryptocurrency efficiently. In their sales pitch, they’ll say that the amount you earn from mining will pay for the rental several times over.
But that isn’t true. Either the rental will never earn you any money, or the criminal will use it to mine cryptocurrency for themselves.
13. Fraudulent initial coin offerings (ICOs)
Cryptocurrency is hot. Between August 2021 and August 2023, the number of cryptocurrencies available worldwide grew by over 3,000.
As these new currencies have gained mainstream recognition, scammers have found ways to make money by creating fake cryptocurrencies (or creating the illusion of a new currency) or hyping an existing currency by offering buyers a chance to get in on the ground floor of an ICO.
Once they have enough investors, they will disappear with all of the “invested” funds, leaving investors with nothing.
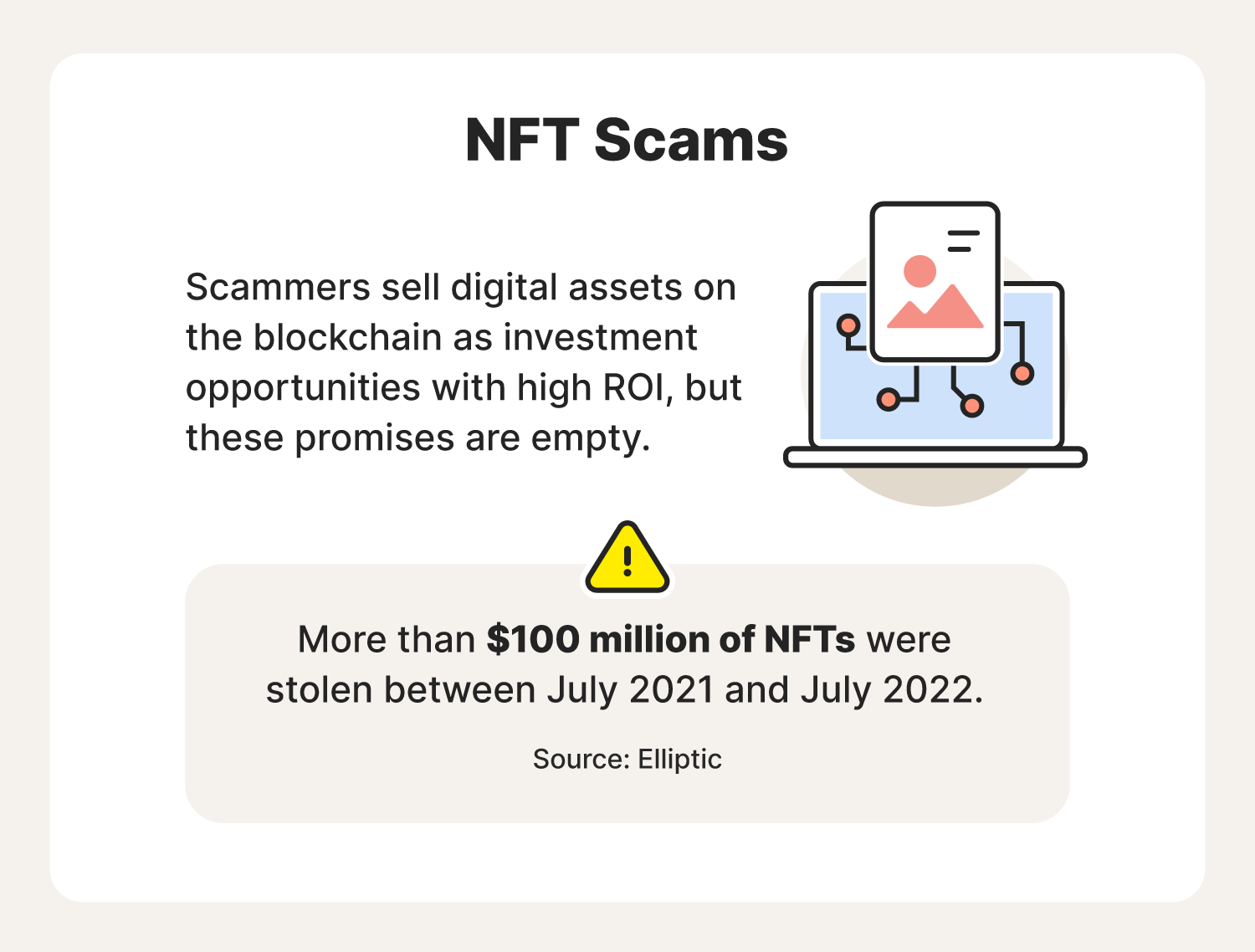
14. NFT scams
Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) are assets that can represent real or digital goods and whose ownership is recorded in a blockchain. In the last several years, there has been a huge explosion in the amount of NFTs created and sold.
Many of these NFTs are legitimate and allow people to buy unique artwork or other assets, but some scammers have used NFTs to take advantage of investors.
Be on the lookout for anyone offering NFTs with guaranteed growth—like any investment, there are no guarantees. Be sure to double-check the background of NFTs, as some people create elaborate stories about artists to increase sales and drive up prices artificially.
Warning signs of cryptocurrency fraud
Now that you’ve learned some background on the most common cryptocurrency scams, it’s time to learn how to spot them.
Here are the main cryptocurrency scam red flags to look out for:
- Too good to be true: The offer seems too good to be true
- “Get rich quick”: Alleged guarantees that you’ll get rich quick
- Sketchy website: A website’s address bar does not begin with “HTTPS”
- Urgency and threats: The payment request is urgent and/or includes threatening messages or unnatural urgency
- There’s no white paper: White papers show that proper due diligence has been completed
- Payment requested in cryptocurrency: Businesses and government agencies don’t ask for payment in crypto
- Influencer advertising: A social media user asks you to pay for something using cryptocurrency
- Overenthusiastic reviews: Reviews can be faked to present a better image of a company
- Your account logins are requested: Some scammers offer to pay you using your accounts but will instead steal your cryptocurrency
- Unsolicited offers: This could include job offers that require crypto payments for onboarding or offers of favors if you let someone use your cryptocurrency account
It's important to not underestimate crypto scammers and their devious tactics. Unfortunately, they’ve been able to see some success in recent years.

How to avoid cryptocurrency scams
If you know how to spot a cryptocurrency scam, you can stop a cryptocurrency scam. Financial investments are enough of a risk as it is. Dealing with scammers and their slew of cyberattacks shouldn’t be a part of the equation.
In the end, count on this: If something sounds too good to be true, it probably is. Play it safe and hold your money—cryptocurrency or otherwise—close. Bank on these pointers to invest with confidence and keep a Cyber Safety state of mind.
Crypto scam success rates and takeaways
Given that they’re not government-regulated, cryptocurrencies can sometimes feel like the Wild West of the web.
For further perspective, in early 2023, the International Monetary Fund found that trillions of dollars of value in cryptocurrencies have been lost following platform collapses.
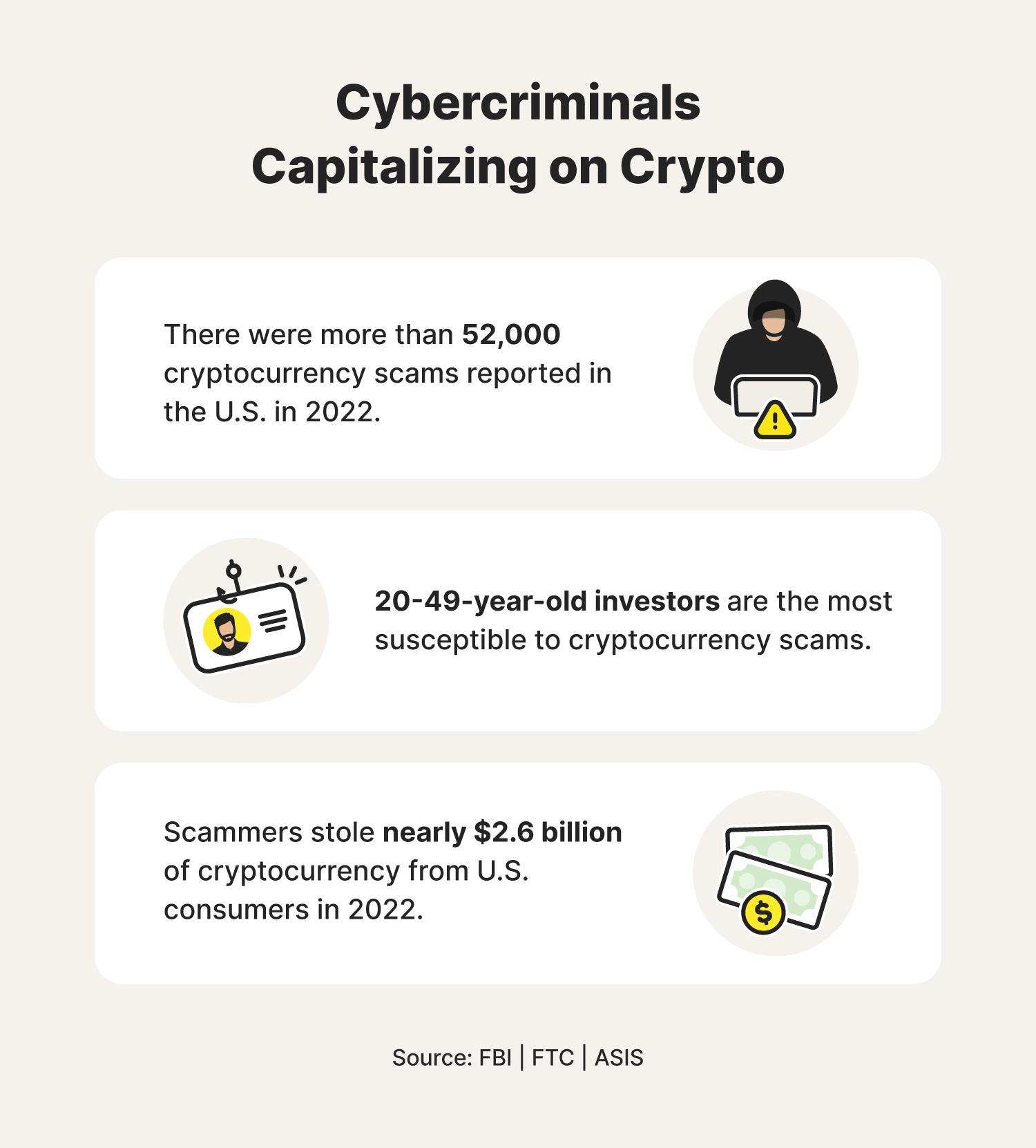
Between October 2021 and August 2022, nearly 46,000 people lost crypto assets totaling $1 billion. This amounted to a reported median loss of $2,600. Here are a few more trends indicated by data and some key takeaways about how these scams work.
Young investors are prime targets
Unsurprisingly, younger digital generations have embraced cryptocurrency quicker than most. As such, they’ve also become more susceptible to crypto fraud.
According to the FTC:
- People between the ages of 20 and 49 are more than five times more likely to lose money to cryptocurrency scams than older age groups.
- People in their 20s and 30s lose the most money to investment scams, more than half of which is in cryptocurrency losses.
Impersonation cryptocurrency scams work
It turns out that impersonations work when it comes to cryptocurrency scams—especially if you’re impersonating Elon Musk, once a big proponent of cryptocurrency. Cryptocurrency scam victims have sent over $2 million to Elon Musk impersonators. When looking at imposter scams as a whole, 14% of reported losses are in cryptocurrency.
It’s not just celebrity impersonations that work, though. Cybercriminals have also posed as
the Social Security Administration, resulting in the Office of the Inspector General issuing a warning.
Crypto scams rely on emotions
Romance scams have long been a successful cyberattack. Nowadays, scams that pull on people’s heartstrings involve pulling money out of their cryptocurrency wallets more than ever. Twenty percent of romance scam victims lose money through cryptocurrency.
Always research before investing
As new cryptocurrency types continue to emerge, it’s important to vet cryptocurrency exchanges before investing your time and money in them. This means:
- Questioning exchanges you haven’t heard of before
- Researching whether an exchange has been associated with scams or complaints
Investigate how transparent exchanges are about their liquidity and ICO rules—a sign of a reliable company. That might even mean reaching out to the exchange directly and asking. You should also verify if an exchange uses blockchain technology, which helps secure your transactions.
Remember: Nothing has to be paid in cryptocurrency
One of the biggest red flags of a cryptocurrency scam is receiving requests for cryptocurrency payments. Remember, cryptocurrency is not entirely government-regulated and is not yet widely accepted by businesses, so you should never have to pay in cryptocurrency. If someone, even a trusted online connection, insists you must, that’s a major warning sign of a scam.
Ignore urgent requests
Especially if they’re unsolicited, urgent payment requests are a major red flag of cryptocurrency scams. It’s best to delete these requests right when they hit your inbox or mark them as spam.
Be wary of get-rich-quick scams
It can be tempting to jump at a get-rich-quick opportunity. But when it comes to cryptocurrency, remember that cryptocurrency itself is an investment. Generally, any unsolicited opportunities that come to you with “guarantees” or “promises” for you to make money are a get-scammed-quick opportunity. It’s best to avoid these proposals at all costs.
Report suspicious activity immediately
If you think you’re being targeted by a cryptocurrency scam, reporting it can keep cryptocurrency exchanges safe for all users. There are a few places you can do this:
- Federal Trade Commission (FTC)
- Commodity Futures Trading Commission
- Securities and Exchange Commission
- Your cryptocurrency exchange

Start using security software
While there’s no way to completely eliminate the risk of falling for a cryptocurrency scam, taking the proactive measure of using security software like Norton 360 with LifeLock Select is one step that can help reduce the likelihood of being impacted by these scams.
Help keep your money and personal information safe
Norton 360 with LifeLock Select can help protect your devices and personal information from scammers and stop malicious software before it can do harm. And the built-in Dark Web Monitoring feature will alert you if your data appears on the dark web, where criminals can use or purchase it. Get Norton 360 with LifeLock to help protect your personal data against scams and keep your identity safer.
FAQs about cryptocurrency scams
Here are some answers to some common crypto scam and cryptocurrency questions.
Is cryptocurrency safe?
Kind of. If you buy from a trusted exchange, use a safe wallet, and do everything you can to spot and avoid scams, crypto is generally pretty safe. But because the industry is unregulated and the value of cryptocurrency changes so much, it’s not as safe an investment as you may be led to believe.
What is cryptocurrency?
Cryptocurrency is a digital currency designed to record and verify all transactions on a decentralized, unregulated system called a blockchain.
How is cryptocurrency different from the U.S. dollar?
Cryptocurrency differs from the U.S. dollar in that crypto is:
- Unregulated by governments
- Quite volatile in value
- A system that uses blockchain ledgers and cryptography to record and verify transactions
Can I recover scammed cryptocurrency?
While there are a few avenues to recover scammed cryptocurrency, the chance of actually recovering stolen or scammed cryptocurrency is extremely low. Those who lose crypto assets in a scam can report their case to the FTC. You could also contact the crypto exchange company you used to complete the transaction.
Can you get scammed if someone sends you crypto?
Yes. Someone sending you a crypto offer (especially if you don’t know them well) could send you to a site designed to phish your personal information or financial logins or install malware on your device.
Editorial note: Our articles provide educational information for you. Our offerings may not cover or protect against every type of crime, fraud, or threat we write about. Our goal is to increase awareness about Cyber Safety. Please review complete Terms during enrollment or setup. Remember that no one can prevent all identity theft or cybercrime, and that LifeLock does not monitor all transactions at all businesses. The Norton and LifeLock brands are part of Gen Digital Inc.
- 1. Investment or business opportunity scams
- 2. Imposter or impersonation scams
- 3. Blackmail or extortion scams
- 4. Social media cryptocurrency scams
- 5. Giveaway cryptocurrency scams
- 6. Fake apps
- 7. Loader or load-up cryptocurrency scams
- 8. Romance cryptocurrency scams
- 9. Phishing cryptocurrency scams
- 10. Employment scams
- 11. Flash loan attack scams
- 12. Bitcoin mining scams
- 13. Fraudulent initial coin offerings (ICOs)
- 14. NFT scams
- Warning signs of cryptocurrency fraud
- How to avoid cryptocurrency scams
- Crypto scam success rates and takeaways
- Help keep your money and personal information safe
- FAQs about cryptocurrency scams







Want more?
Follow us for all the latest news, tips, and updates.