What is a chatbot? Explanation, uses, and security tips
Chatbots are software that can respond to written or verbal inputs. You've likely heard about or even interacted with them before, such as ChatGPT—but you might not be entirely sure what they are, how they work, or if they’re even safe to use. Read on to understand just what a chatbot is, and explore how a tool like Norton 360 Deluxe can help address potential cybersecurity threats associated with them.

How do chatbots work?
Chatbots can respond to our questions and comments. For example, if someone visits a clothing website, clicks on the chat widget, and asks, “How can I return a shirt?” The chatbot may then respond with a link to that site’s “shipping & returns” page. As you can see, chatbots can lead you on quite a journey—so it’s important to make sure that you’re interacting with them on a safe website.
The earliest chatbots relied on scripts or rules to function—they could only respond to a set of strictly defined prompts or keywords. Now, modern chatbots like ChatGPT rely on machine learning methods to process information. Some of these methods include:
- Natural language processing (NLP), which helps chatbots interpret written and verbal information.
- Neural networks, which rely on algorithms to “think” similarly to a human being.
- Deep learning, which refers to an advanced neural network that is more layered and adaptable than a regular neural network.
- Artificial intelligence (AI), which encompasses various machine learning (ML) methods.
AI chatbots may use a combination of the previous methods as well others. Chatbots can range in complexity, but one common thread links them all—human input. Chatbots work based on the information we provide them. Specificity is also important: A chatbot on a tax-prepping site won’t answer questions about donuts or sports teams, for instance.
6 different types of chatbots
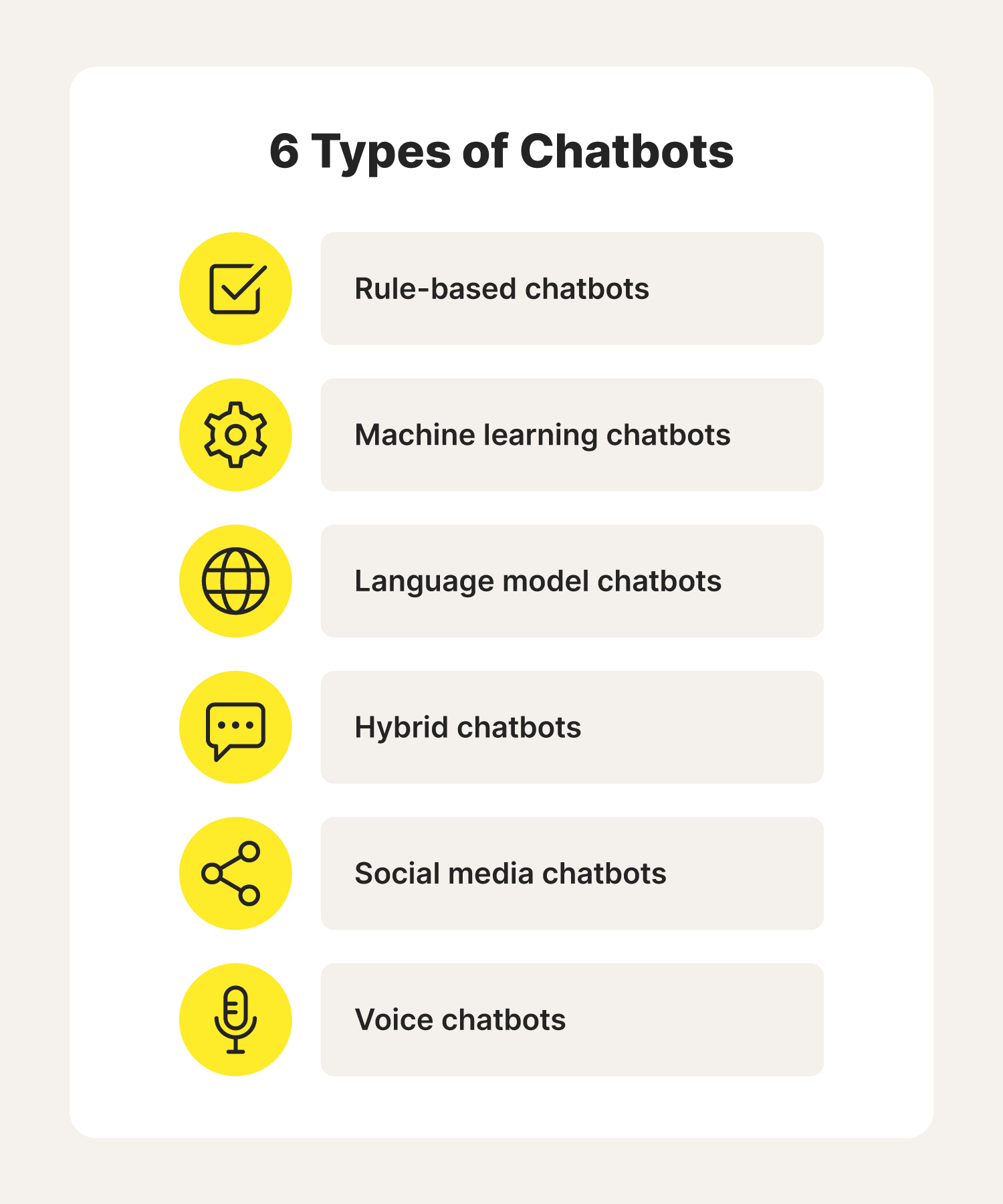
There are various types of chatbots that each suit different needs and niches. Here are five common programs you may encounter online or over the phone.
1. Rule-based chatbots
Also known as “Scripted chatbots,” these simple programs excel at offering specific answers to a limited set of user keywords or phrases. Rule-based chatbots are incredibly prominent in instant messaging services and have paved the way for more complex software over the years.
2. Machine learning chatbots
These programs can utilize machine learning methods to hold conversations with users—or at least do an excellent job mimicking a conversation. AI chatbots like Apple’s Siri and Amazon’s Alexa fall into this category; depending on your phone settings, these programs can listen to your conversations and learn more about you.
3. Language model chatbots
Language model chatbots are incredibly advanced programs that use data and context to respond to questions. ChatGPT, developed by the Open AI research group, is the most notable example of a language model chatbot. The prevalence of this software raises many ethical, legal, cultural, and safety concerns that contrast with its potential benefits for society.
4. Hybrid chatbots
Hybrid chatbots combine live service representatives with a chatbot (which is typically rule-based) to expedite customer-facing processes. Hybrid bots will formally introduce themselves and answer basic questions. If your queries fall out of their wheelhouse, they’ll call in a live service rep for a more in-depth conversation.
5. Social media chatbots
Have you ever received a strangely worded message from a total stranger while scrolling through your social media feed? Well, that stranger might’ve been one of these programs. Social media bots pretend to be people and message users to promote businesses—or, on occasion, siphon sensitive info.
6. Voice bots
As the name implies, these chatbots can understand and respond to human vocal prompts. The IRS employs voice bots to whittle down the onslaught of incoming calls it receives daily.
How do chatbots help businesses and customers?
Chatbots can potentially benefit businesses and customers in multiple ways.
They can streamline customer service for businesses and expedite customer service interactions for customers. Professionals in various fields already use chatbots to boost their productivity and day-to-day efficiency. Potential uses for chatbots include:
- 24-hour assistance: Chatbots can offer support long after a customer service center has closed for the day. This also applies to weekends and holidays.
- Shorter wait times: Customers can instantly speak with chatbots to resolve basic issues. Conversely, live service agents can place more effort into solving complex questions.
- Increasing sales: Chatbots can bolster customer outreach strategies by contacting and qualifying potential sales leads. Bots can also contact customers to promote sales and referral initiatives.
- Boosting productivity: Language model tools like ChatGPT can generate first drafts for various types of outlines, emails, and reports. Professionals can then use their expertise and judgment to fine-tune these generated drafts. Microsoft Office and G Suite already offer tools like these to users.
Are chatbots safe to use?
Chatbots used by government agencies and enterprises are generally safe by and large as they use data encryption to protect sensitive information. However, issues can arise if bad actors misuse chatbots to harass targets or commit crimes.
Recent cyber safety reports have shown that generative tools like ChatGPT can pose several risks such as deepfake content, phishing scams, and malware attacks. For more context:
- ChatGPT deepfakes can produce high-quality misinformation content.
- Generative tools can imitate legitimate sources to phish sensitive info.
- Criminals can use ChatGPT to create malicious code.
There are also concerns about chatbots sharing inappropriate material with children. A Washington Post reporter famously received unsavory advice from Snapchat’s My AI program during an experiment where he posed as a teenager. In another instance, New York Times reporter Kevin Roose had an “unsettling” experience when speaking with a Bing chatbot.
Chatbots can also be susceptible to misinformation and algorithmic bias, especially concerning matters requiring judgment and context. A chatbot might incorrectly draw conclusions about a certain group of people based on the data it receives. This ties into long-standing concerns about racial bias that can surface when interacting with chatbots, including certain algorithms used in hospitals.
5 cybersecurity tips when talking to a chatbot
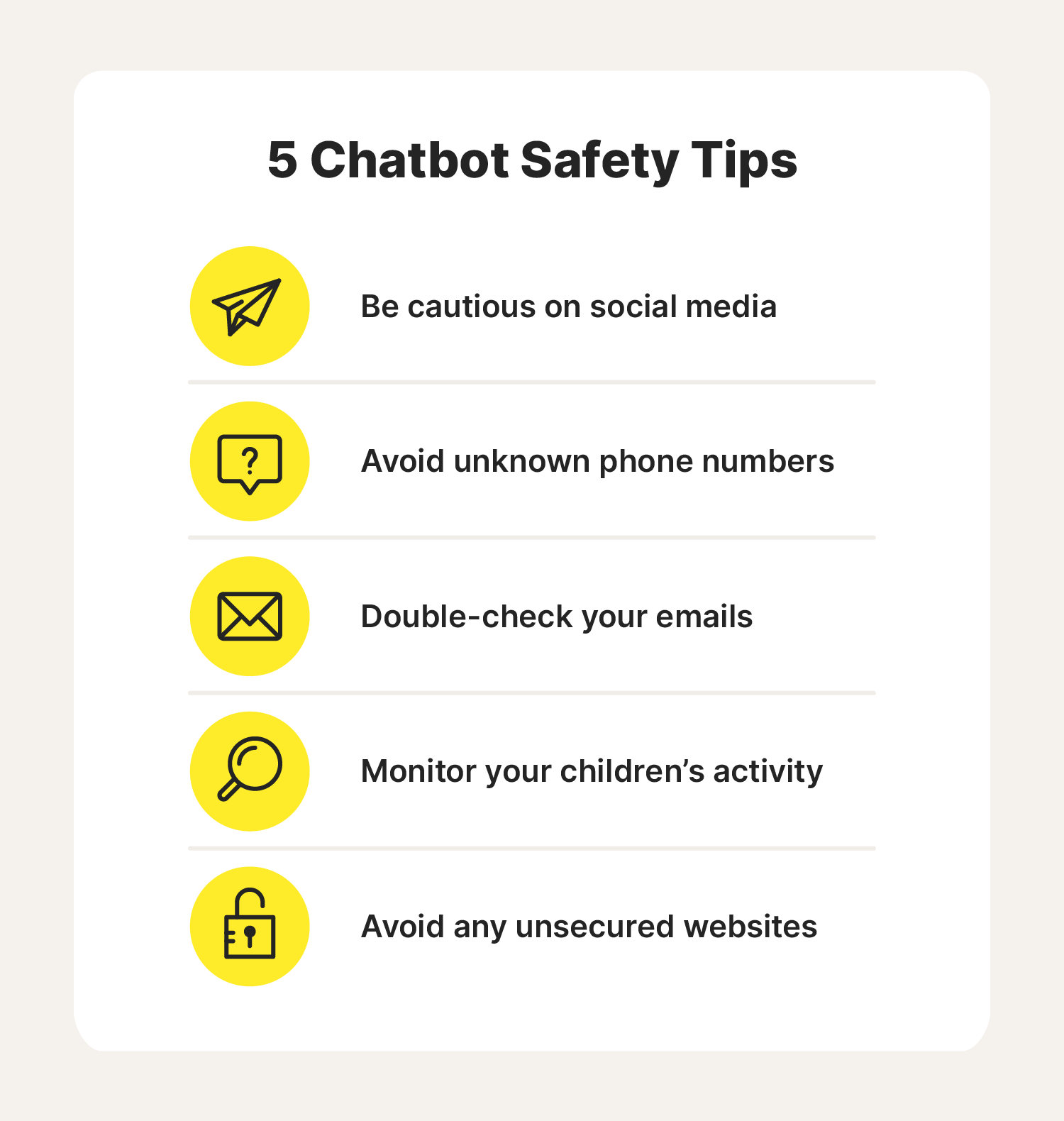
Chatbots are tools by the end of the day. Like a smartphone or a hammer, they work best when you know how to use them safely. The following five safety tips are general guidelines for any programs you may encounter online.
- Don’t share private info with chatbots.
- Don’t respond to texts or calls from unknown numbers.
- Be wary of emails from unfamiliar people/companies.
- Monitor your children if you let them interact with a chatbot.
- Avoid chatbots on unencrypted/unsecured websites altogether.
Use chatbots more safely with Norton 360 Deluxe
Chatbots have many fantastic applications that can benefit companies and customers in nearly every business sector. However, they’re not immune to cybersecurity risks or misuse via malware, deepfakes, and phishing scams. Consider turning to an antivirus solution like Norton 360 Deluxe to maintain peace of mind the next time you interact with a chatbot.
Editorial note: Our articles are designed to provide educational information for you. They may not cover or protect against every type of crime, fraud, or threat we write about. Our goal is to increase awareness about Cyber Safety. Please review the complete Terms during enrollment or setup. Remember that no one can prevent all identity theft or cybercrime, and that LifeLock does not monitor all transactions at all businesses. The Norton and LifeLock brands are part of Gen Digital Inc. For more details about how we create, review, and update content, please see our Editorial Policy.




Want more?
Follow us for all the latest news, tips, and updates.