What is the Internet of Things? Learn what it means, examples, and more
The Internet of Things (IoT) is changing the way the world works, bringing the benefits of internet connectivity to countless new areas, from fridges and cars to cities and farms. Learn what IoT actually means, how it works, and what risks you need to know about. Then, get Norton 360 Deluxe to help boost your cybersecurity in an increasingly connected world.

The days of the internet being limited to computers and smartphones are long gone. The Internet of Things is a rapidly developing innovation that brings the web into practically every element of daily life. It lets you check your home’s security remotely, track your heart rate while you sleep, stream Netflix on your TV, stay in your lane while driving, and much more.
The IoT revolves around adding internet connectivity to everyday objects, or “things,” allowing them to interact with each other. It has countless potential benefits for both individuals and organizations, but, as with all new technologies, it also introduces new risks.
As the Internet of Things continues to grow, it’s essential that you know what it is, how it works, and what precautions you might need to take to help protect against the new types of threats that are emerging in our hyper-connected world.
IoT meaning: What is the Internet of Things?
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a network of internet-connected devices or objects equipped with sensors and software that allow them to collect data and wirelessly communicate with one another. Common IoT devices include smart wearables, digital household appliances, and commercial inventory management systems.
IoT compatibility upgrades the functionality of typically “unconnected” devices by enabling seamless information exchange. An IoT refrigerator, for example, could be connected to your smartphone to automatically update your shopping list when you’re running low on groceries.
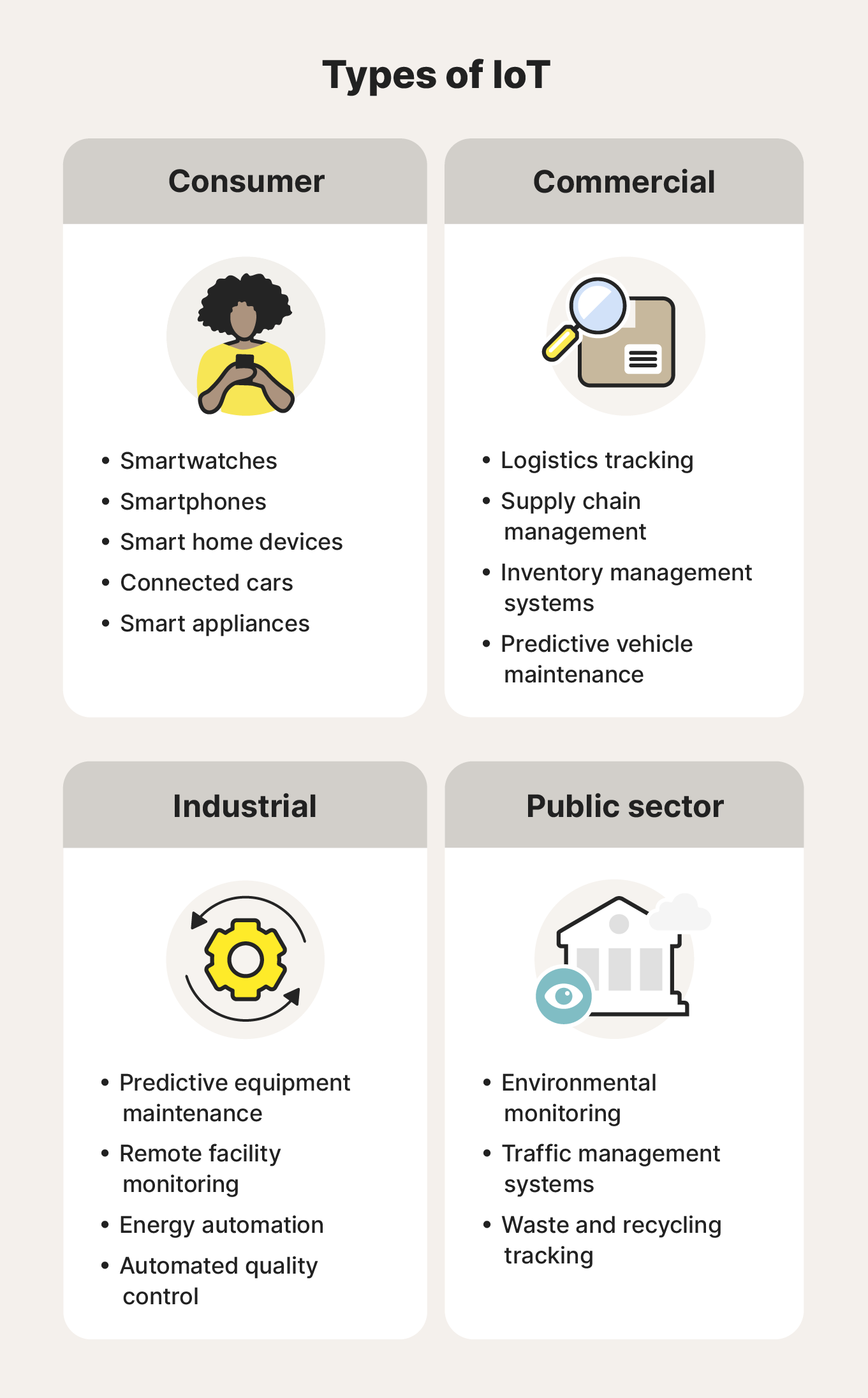
There are four main categories of IoT devices:
- Consumer IoT: Brings the web to everyday items, like smart home devices, wearables, digital appliances, and connected cars. Consumer IoT functionality is typically designed to boost convenience, increase security, or help with health monitoring.
- Commercial IoT: Optimizes commercial operations, improves customer experiences, and provides valuable insights in industries like healthcare and retail. Examples include devices for intelligent logistics tracking and inventory management.
- Industrial IoT: Focuses on the application of IoT in industrial settings like manufacturing and energy. Examples include devices that oversee automated processes or remotely monitor equipment to make predictive maintenance recommendations.
- Public sector IoT: Optimizes public infrastructure, safety, and environmental monitoring. Governments and public organizations often use vast networks of IoT devices to create “smart cities” or monitor environmental factors like air quality.

Regardless of how or where they’re applied, IoT devices leverage device-specific data to help automate processes, improve decision-making, or maximize resource use.
How does the IoT work?
IoT devices feature sensors that collect data. Software installed on the device processes and analyzes this data in real-time, or sends it to the cloud for online storage. Depending on the results of the analysis, IoT devices will take specific pre-programmed actions or send relevant information to other devices on the network.
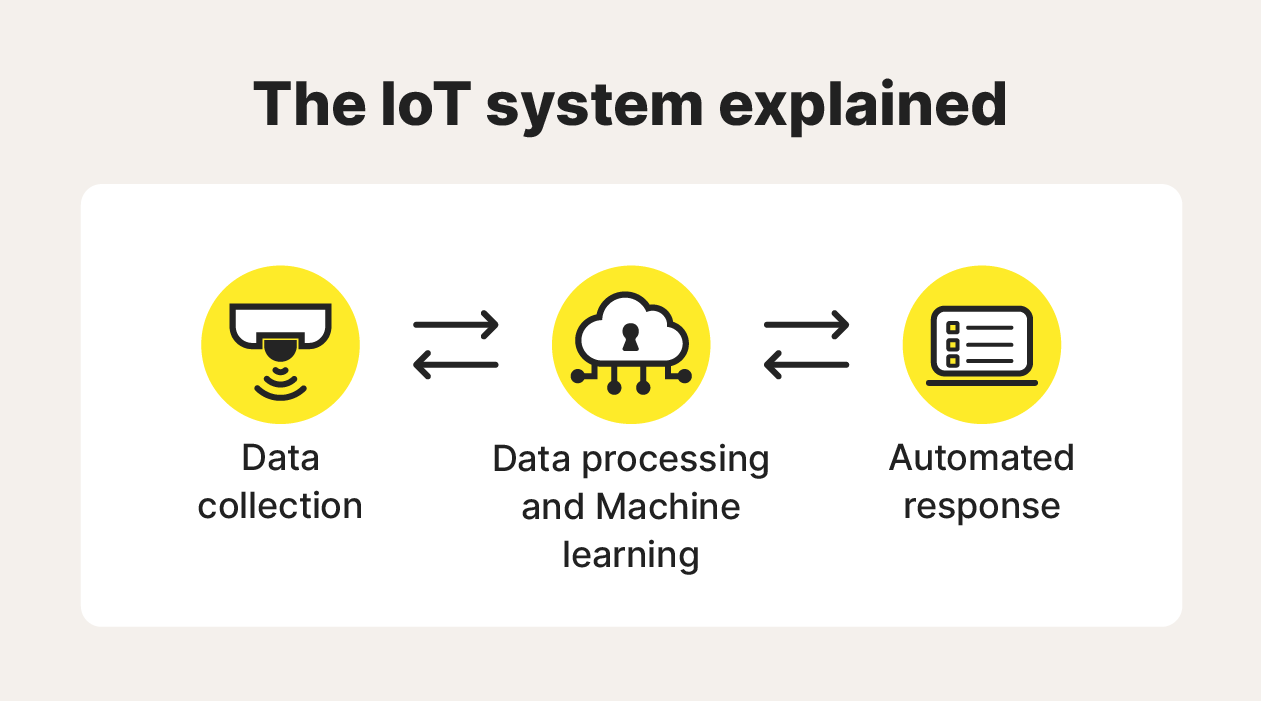

Here’s a more detailed look at the Internet of Things process, broken down into its four main steps:
- Data collection: IoT devices use hardware sensors to collect various types of data from their surroundings, such as temperature, weight, or motion.
- Data processing: Software installed on the device processes this data locally or sends it to a cloud-based server for remote processing and storage.
- Data analysis: Algorithms analyze the data to identify insights, patterns, or trends, with machine learning technology often allowing IoT devices to “learn” from the analysis and deliver better insights over time.
- Automated response: Based on the results of the analysis, IoT devices take automated actions like adjusting a thermostat, triggering another device or process, displaying information on a built-in screen, or sending an alert to the user’s smartphone.
Why is the IoT important?
The IoT offers diverse potential benefits that all stem from its ability to automate processes. This automation can be as simple as seamless data transfer between two connected devices, enabling better decision-making by boosting information visibility. It can also be complex, with some industrial IoT applications significantly increasing efficiency and reducing costs.
It’s likely that IoT is already improving your life without you realizing it, even if you don’t use smart devices at home. In healthcare, for example, IoT devices help doctors monitor vital signs remotely and catch potential health issues early so they can intervene more quickly.
In agriculture, IoT technology helps farmers monitor crop conditions and manage automated tools, helping them generate higher yields and decrease their environmental impact. It can also reduce their costs, making the end products more affordable for consumers.
And, in manufacturing, IoT devices help companies optimize processes throughout the supply chain and in production, while also improving product quality. This also benefits consumers by minimizing defects and lowering costs over the long term.
The risks and challenges of IoT
Although IoT technology offers lots of benefits, it also comes with some risks and challenges. Most notably, it introduces new digital security vulnerabilities and data privacy concerns that can affect both individual users and organizations.
Just like computers and smartphones, IoT devices are likely to contain sensitive or personal information that could be valuable to hackers or cybercriminals. However, unlike these more established personal devices, they might not always feature robust security.
These are some of the main IoT vulnerabilities that pose a risk to your digital safety:
- IoT devices are part of a wireless network which means they’re vulnerable to hackers, putting additional data at risk of being compromised in the event of a network security breach.
- IoT devices and applications don’t tend to receive software patches as frequently as more widespread digital devices like computers and smartphones, leaving them more exposed to new attack vectors.
- IoT devices all collect and store data in different ways, sometimes making it difficult to determine how safe your data is and what you can do to protect it from cyberthreats.
Although some IoT devices might not feature built-in security software, there are other ways to help safeguard them against risks. Exercising good cybersecurity practices, like ensuring that your wireless network has a strong password, can keep all of your devices safer.
You can also use Norton 360 Deluxe to get powerful malware and virus protection for up to five computers, smartphones, or tablets. Norton will help you identify potential security threats so you can take action to prevent them from spreading across your network and compromising data from connected IoT devices.
Internet of Things examples
There are countless examples of IoT devices in commercial and industrial fields, from inventory tracking tags to remote monitoring devices used on farms. To many people, though, personal or home IoT devices are the most relevant innovations.
These are some common types of IoT devices that can help you leverage internet connectivity to make your life easier:
Smart wearables
IoT wearables like smartwatches and fitness trackers can help you monitor your health and track fitness goals. These devices typically use sensors to monitor heart rate, blood oxygen levels, sleep patterns, or activity levels. The data is then shared with a smartphone or computer app, providing insights you can use to inform your exercise regimen or sleep schedule.
Smart appliances
IoT-connected home appliances bring new functionality to standard household items like washing machines, refrigerators, and robot vacuums. They typically come with an associated app that allows you to control them remotely, but they can also send data to you, alerting you that a wash cycle has ended or your fridge temperature has risen, for example.
Smart cars
Smart cars use IoT technology to create better driving experiences and help keep people safer on the roads. The applications of IoT in vehicles range from simple features like connectivity with music streaming services to full autonomous driving capabilities powered by IoT sensors and cameras.
Smart homes
IoT technology can help create “smart homes,” with devices offering features that can help you automate tasks, improve energy efficiency, and boost your home’s security. Doorbells equipped with video cameras and microphones that you can access remotely and thermostats controlled through your phone are particularly popular examples.
The history and future of IoT
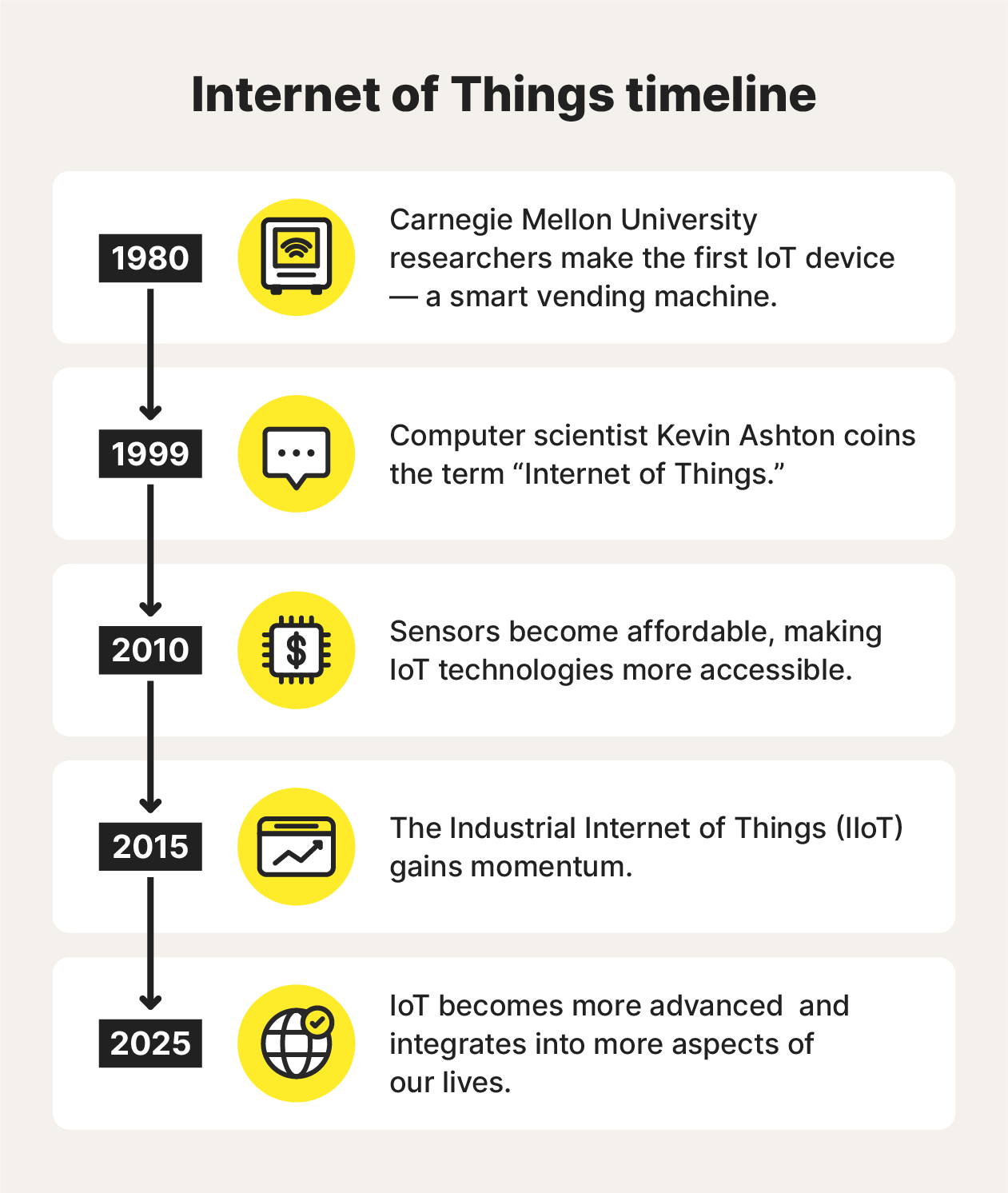
The concept of connecting physical objects to the internet dates back to the 1980s, but the term “Internet of Things” was coined in 1999. Since then, IoT technology has advanced rapidly, and experts predict continued growth.
Here’s a timeline of where IoT technology started and how it’s developed over time:
- 1980: Carnegie Mellon University researchers made the first IoT Coca-Cola vending machine. Connected to the school’s network, it could track inventory, temperature, and operation status.
- 1999: Computer scientist Kevin Ashton, who’s also credited with helping develop a global standard for the Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) sensors that power many IoT devices, coined the term “Internet of Things.”
- 2010: The smartphone revolution and the rise of affordable sensors led to the rapid adoption of IoT technologies, including the emergence of consumer-grade smart wearables.
- 2015: The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) gained momentum, focusing on connecting industrial equipment and systems to improve efficiency and productivity.
- Now: IoT is becoming increasingly integrated into more and more aspects of our lives, from smart homes and cities to industrial automation and healthcare.

A lot of progress has been made in a relatively short period, but there’s much more to come in the future of IoT. Several other technologies are developing in tandem with the IoT, each one creating new possibilities for unique and innovative applications.
The growth of 5G coverage means that more IoT devices will be able to transmit larger volumes of data, leading to smoother experiences in and out of the home. Continued development in artificial intelligence (AI) will help boost machine learning capabilities, helping IoT devices get increasingly “smart” over time.
In the future, everything from your toothbrush to your shoes might be connected to the internet. And while each technology might only make a small difference individually, together they have the potential to significantly improve our quality of life.
Keep all your devices more secure
In an increasingly connected world, it’s more important than ever to take precautions against the threats posed by hackers, viruses, and malware. Norton 360 Deluxe offers protection for up to five personal devices, including smartphones, computers, and tablets, which can help you keep your home network and any connected IoT devices safer.
Combining antivirus features, a secure VPN, and additional privacy features, you’ll be able to embrace the future of technology with greater peace of mind.
Editorial note: Our articles are designed to provide educational information for you. They may not cover or protect against every type of crime, fraud, or threat we write about. Our goal is to increase awareness about Cyber Safety. Please review the complete Terms during enrollment or setup. Remember that no one can prevent all identity theft or cybercrime, and that LifeLock does not monitor all transactions at all businesses. The Norton and LifeLock brands are part of Gen Digital Inc. For more details about how we create, review, and update content, please see our Editorial Policy.









Want more?
Follow us for all the latest news, tips, and updates.