13 different types of AI you should know about
There isn’t just one form of artificial intelligence, or AI, and understanding the various types can help improve your ability to take advantage of it and stay safer against AI risks. Discover the main types of AI and what they do. Then, boost your protection in the AI age with powerful security software.

Just a few years ago, the concept of artificial intelligence was most associated with science fiction. Today, it seems almost ubiquitous — from the workplace to our social media feeds.
In a recent survey, nearly 80% of respondents reported their organizations were using AI in some form, up from about 55% in 2023. And over half of Americans say they interact with AI at least once a day.
But when people talk about AI, what do they mean? AI can take many different forms. Large language models (LLMs), the “generative AI” technology that powers ChatGPT and other AI chatbots, are one type. But AI is also involved in self-driving cars, facial recognition tech, and even your Netflix recommendations.
Keep reading to learn more about the different types of AI and how they’re used in daily life, so you can use this emerging technology effectively and safely.
Capability-based AI
One of the most common ways to classify AI is based on its capacity to perform tasks, or its practical capabilities. In other words, this means categorizing types of AI by what they can do.
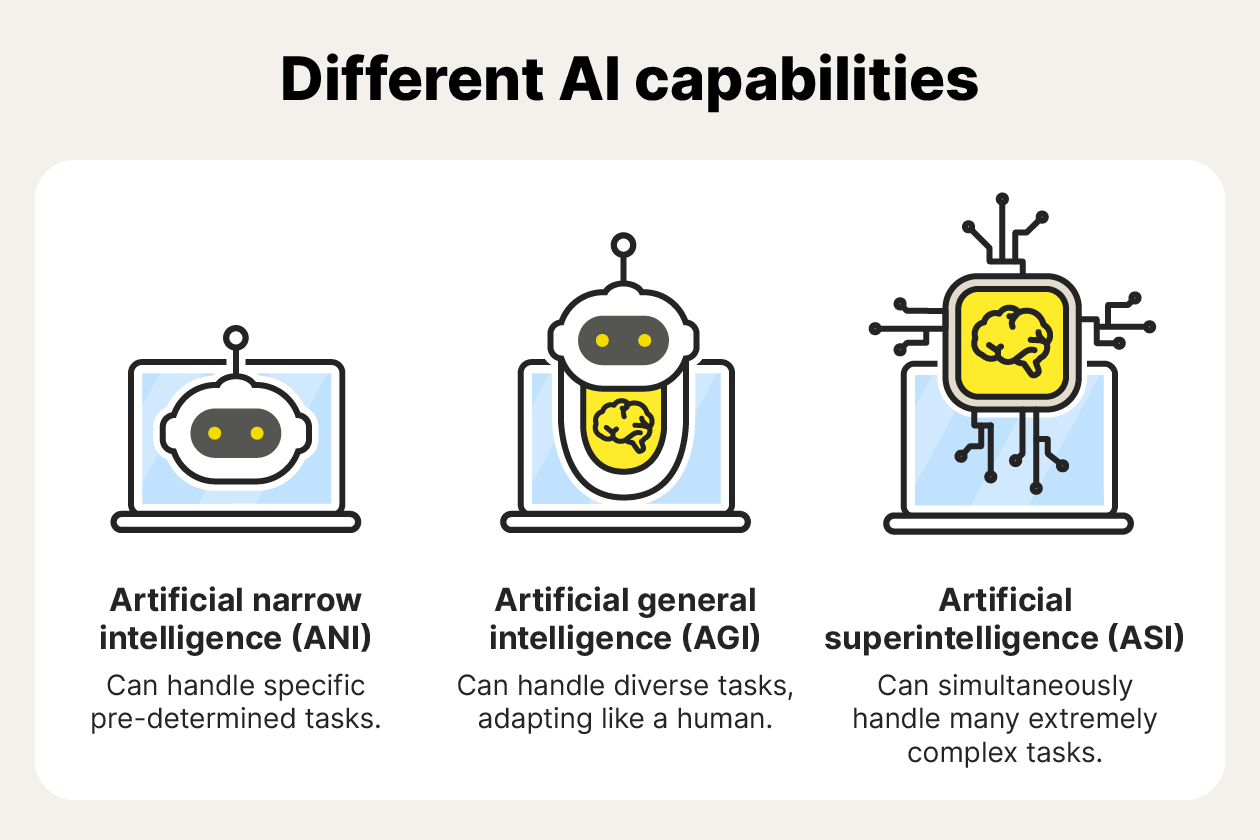

1. Narrow AI (ANI)
Artificial narrow intelligence (ANI) is designed and developed to complete simple, predefined tasks, like recognizing faces or generating text. This type of AI is trained on large sets of data that its algorithm uses to make predictions.
For example, a self-driving car’s AI is trained on millions of driving scenarios, helping it recognize traffic signs, detect pedestrians, and predict other drivers’ behavior. Then, when deployed in real-world situations, the AI-driven car refers to this training data to react to inputs gathered from cameras or sensors.
Narrow AI is not really intelligent or aware. Think of it like a very powerful calculator that predicts the right answer to a given question (whether that’s an actual text-based question or a set of inputs sourced from other data) based on its training and context.
Some of the most common capabilities of ANI include:
- Routine tasks (spam filtering, customer service replies).
- Data analysis (finding patterns in spreadsheets, identifying trends).
- Predictions within specific contexts (recommending content on streaming apps).
- Image and speech recognition (facial ID, voice assistants).
- Language processing (translation, text generation).
- Autonomous control (self-driving vehicles).
- Anomaly detection (fraud detection).
- Personalization (targeted ads, curated social media feeds).
Despite the fact that some modern AI tools, like ChatGPT, seem adaptable to different types of tasks, all of the models available in early 2025 are examples of ANI. Some tools combine multiple narrow AI models in one platform, giving the illusion of more general capabilities.
2. Artificial general intelligence (AGI)
Artificial general intelligence (AGI) is a hypothetical type of AI that could use its training to accomplish a diverse range of tasks (compared to ANI, which can only handle single tasks) and learn from experience to continuously teach itself to perform new tasks.
For now, AGI is theoretical. It doesn’t exist yet, but it’s the current target on the horizon for companies developing AI models, like OpenAI. Some experts predict AGI will be achieved within the next decade, while others argue it’s further away, or not possible at all.
The best comparison to an AGI’s capabilities would be a human being. Like a human, an AGI would be able to learn from its environment and make independent decisions. However, AGI would likely be much more capable than any human in its ability to both process data and learn from it.
Here are a few capabilities we can expect from AGI:
- Performance of human-level cognitive tasks (reasoning, problem-solving).
- Adaptability to real-life situations (adjusting behavior based on the environment).
- Usefulness across multiple domains (a single AI would be effective in science, law, healthcare, etc.).
- Self-directed learning (acquiring new skills without new programming).
- Abstract thinking and creativity (generating new ideas).
- Emotional and social intelligence (understanding human emotions and social cues).
- Generalization of knowledge (applying learning from one area to solve problems in another).
If and when AGI is achieved, it will likely be able to do almost anything a human can — and in many cases, much better than any human. These complex AI tools could contribute to or replace virtually all human jobs, including doctors, lawyers, and CEOs.
3. Artificial superintelligence (ASI)
An artificial superintelligence (ASI), also known as a super AI, is another hypothetical type of AI that would greatly exceed human intelligence and reasoning capabilities. This AI would be self-aware, independent, and many times smarter than human beings.
ASI is theoretical and unlikely to be achieved any time soon, but some start-ups are trying.
Some of the potential capabilities of ASI include:
- Advanced reasoning.
- Solving millions of complex problems simultaneously.
- Inventing new advanced technologies.
- Improving and rewriting its own programming.
- Predicting long-term outcomes.
- Understanding human behavior on a massive scale.
ASI, should it be realized, could be powerful enough to govern entire nations or coordinate processes across the globe, such as resource management or healthcare.
Cognitive functionality-based AI
AI is sometimes classified by how “smart” it is. For example, simple AI tools have no memory and generate a predictable output, much like a calculator. Advanced theoretical AIs, on the other hand, may be able to self-analyze and adapt to situations similarly to humans. Classifying AI based on cognitive functionality helps us understand how deeply different types can analyze information, learn, and interact.
4. Reactive machine AI
Reactive AI programs are the least cognitively functional type of AI. They don’t have memory, learning, or awareness; instead, they simply react to inputs based on their training. This means they will theoretically always respond the same way to the same inputs, making them more predictable than even modern GenAI tools.
Chess bots are a good example of reactive AI: they are programmed to evaluate their opponents’ moves and react based on the lay of the board. It took decades for a chess AI to beat a pro human player, because these programs do not learn from experience and often make predictable moves.
Here are some capabilities of reactive AI:
- Solving basic math problems and reasoning (calculators).
- Streaming recommendations.
- Playing chess or other games.
- Filtering spam.
5. Limited memory AI
Limited memory AI is a level above reactive machine AI. These programs use deep learning to make predictions, but they can improve their decision-making in short, limited periods by “remembering” recent inputs. This improves the AI’s accuracy and allows it to adapt to context.
Self-driving cars and LLMs like ChatGPT are examples of limited memory AI. They remember inputs (such as road conditions or messages) and adapt their responses accordingly. However, this memory isn’t permanent: it may only last for a single journey or conversation. The memory resets when you begin a new session.
Some examples of limited memory AI include:
- Self-driving cars.
- LLM-powered chatbots.
- Virtual assistants.
- Fraud detection systems.
6. Theory of mind AI
Theory of mind AI is a theoretical level of artificial intelligence that doesn’t yet exist but could understand human thoughts and emotions, allowing it to interact with humans more naturally and intuitively.
Theory of mind AI would be a type of AGI, so it could handle complex interpersonal situations. That potentially means it could convincingly act as a therapist, friend, HR rep, or customer support agent. While these AIs may not necessarily be self-aware, humans would not be able to distinguish conversations with them from real human interactions.
Some potential uses of theory of mind AI include:
- Social interactions.
- Customer service.
- Virtual companions.
- Teachers and tutoring.
- Conflict resolution.
7. Self-aware AI
Self-aware AI is the highest possible level of AI cognitive functionality. This hypothetical type of AI would possess something that appears identical to consciousness, with an understanding of its own existence and personality much like humans. However, it would likely be far more intelligent and capable than any human.
These AI programs would likely have their own, self-governed lives and not be compelled to serve human needs, though they would interact autonomously with humans.
Capabilities of self-aware AI may include:
- Independent decision making.
- Creative problem solving.
- Self-improvement.
- Long-term planning.
- Emotional support.
- Leadership.
AI based on how it’s trained
Another way to classify AI is based on the techniques used to build and train its systems. This classification focuses on the inner workings of AI, not what it does or how smart it is.
8. Rule-based AI
Rule-based AI was one of the earliest AI techniques to be developed. Rule-based AI programs are built around predefined rules and logic. Their training is often based on simple “if-then” conditions.
For example, imagine a simple customer service bot that asks pre-determined questions such as “Did you forget your password?” A rule-based AI would be programmed to respond to a limited selection of answers, like “No” or “Yes”. If the reply is “Yes,” then the AI would send a password reset link.
Rule-based AI has no real intelligence or memory, and it does not engage in deep learning.
Rule-based AI is often used in:
- Automated customer service decision trees.
- Spam filters.
- Basic medical diagnosis systems.
- Workflow automations.
- Basic fraud detection.
Rule-based AI is effective in predictable, structured environments, but it cannot adapt or learn from context. Still, it’s widely used for repetitive tasks.
Some complex rule-based AIs are called “expert systems.” They are designed to mimic human expert decision-making when the parameters are fixed, such as in medical contexts. A medical expert AI system might be capable of suggesting possible conditions when the user inputs symptoms.
9. Machine learning AI
Machine learning isn’t a distinct type of AI, but rather a capability that some AI systems use. These systems are developed through repeated training cycles, which gradually improve their performance and lead to more sophisticated behavior.
The machine learning process uses complicated algorithms to evaluate outputs in the training process and adjust the internal weighting of different factors in the model. Over many rounds, this helps reduce errors and increase accuracy.
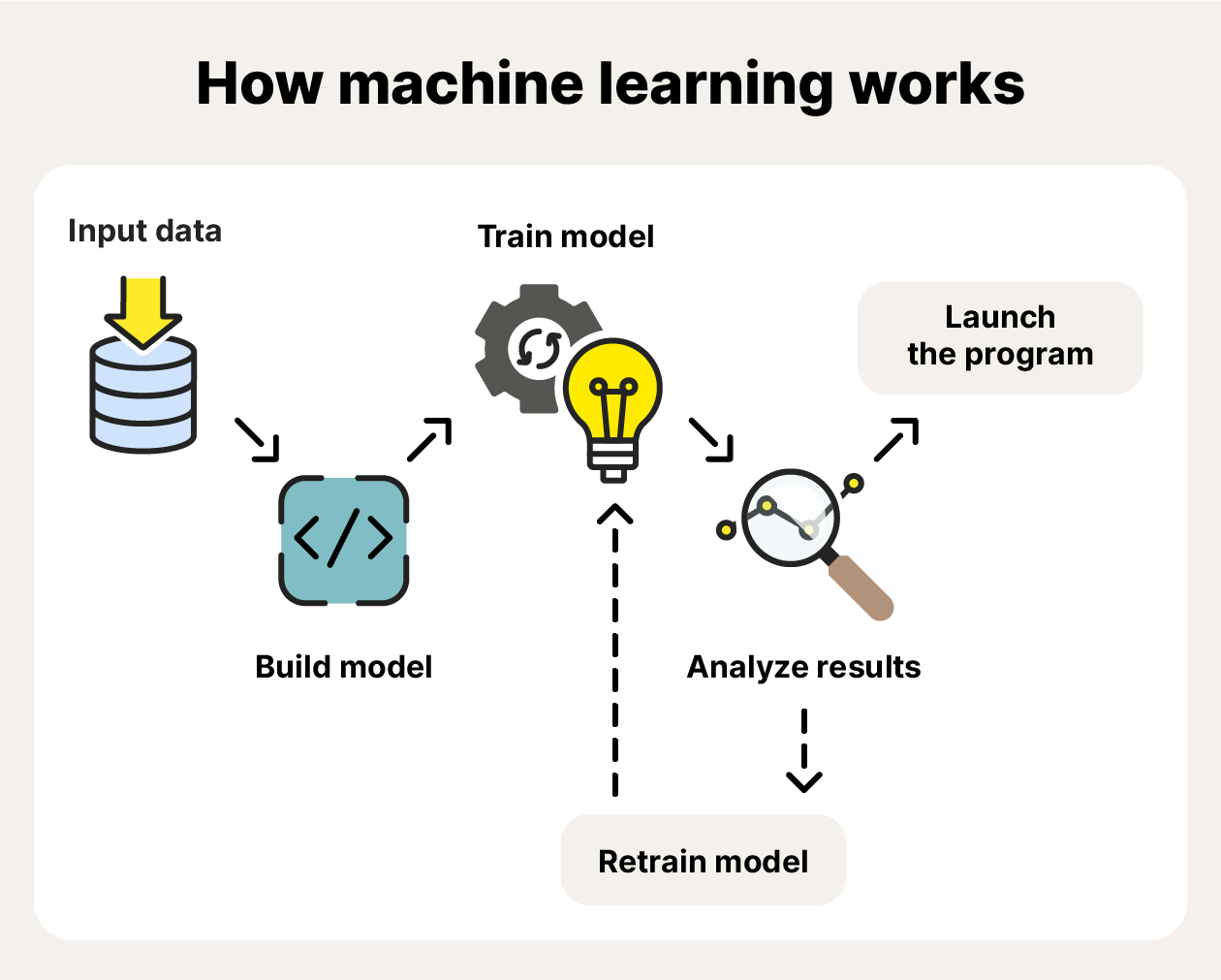

Here are some use cases of machine learning AI:
- Data security.
- Financial trading.
- Healthcare diagnostics.
- Speech and image recognition.
- Predictive maintenance in manufacturing.
- Behavioral analysis.
Norton Genie is another example of AI that’s capable of machine learning. It is designed to identify scam emails, texts, and images. The more scams Genie detects, the more it learns about fraudsters’ techniques, helping it grow smarter and more capable.
Get Norton 360 Deluxe to benefit from Genie’s capabilities, along with a range of other security and privacy features. Our suite of tools helps you boost your data privacy, enhance device security, and identify potential risks, like scam messages or unsafe websites.
10. Generative AI
Generative AI (GenAI) is a type of AI that can create new content, including audio, code, images, text, simulations, videos, and 3D models. These are the AI tools that many people interact with daily, such as ChatGPT, Google Gemini, Grok, and Claude.
Modern GenAI tools use transformer models, which essentially predict what output will effectively meet the intent behind a “prompt.” For example, if you ask a GenAI chatbot what colour the sky is, it might respond “blue.” This is not because it actually knows the sky is blue, but instead because it knows from its training data that “blue” is the most likely answer to that question.
Other GenAI tools, like image generators, are powered by generative adversarial networks (GANs). This approach pits two neural networks against each other. One creates content, and the other criticizes it, which leads to the first model improving the output. These tools create images based on text input. They can also be used to generate AI deepfakes and scams.
Some examples of GenAI uses include:
- Content production.
- Image generation.
- Customer service bots.
- Code generation.
- Tutoring and training.
- Data analysis.
AI by application domain
This classification groups AI according to what it’s used for, from creating text to driving cars. Since AI is used in many different industries, it’s often useful to categorize it by its application.
11. Natural language processing
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is an AI application that involves training computers to understand, interpret, and generate human language. It makes it possible for tools like ChatGPT to communicate in a natural, human way.
Many AI processes and technologies are involved in NLP, including transformers (the tech that powers ChatGPT and other modern LLMs), tokenization (breaking down text into smaller parts), language modeling, and more.
Some examples of how NLP is used include:
- Chatbots and LLMs.
- Machine translation.
- Sentiment analysis.
- Text summarization.
- Text-to-speech.
12. Computer vision AI
Computer vision AI is a field of artificial intelligence that enables systems to recognize images, videos, and other visual inputs. It can analyze and understand what it “sees,” and use what it learns to take actions or make recommendations.
The AI programs behind self-driving cars are a good example of computer vision. It interprets the world around the vehicle in the form of data inputs from cameras and sensors, and then reacts to it in real-time. Self-driving cars can identify objects, detect patterns, and track movement, responding intelligently to various forms of data to keep you safe on the road.
More uses of computer vision AI include:
- Image recognition and classification.
- Object detection and tracking.
- Medical imaging analysis.
- Facial recognition.
- Augmented reality (AR).
13. Robotics and autonomous systems
Robotics and autonomous systems are what you might refer to as robots. This category includes AI-powered machines like Roombas, food delivery robots, and autonomous drones. These AIs interact with humans in the real world instead of on a computer screen.
Examples of robotics and autonomous systems include:
- Self-driving cars.
- Robotic vacuum cleaners.
- Drone delivery systems.
- Factory automation robots.
- Hospital delivery robots.
These autonomous systems often combine several AI types, such as computer vision and machine learning. This helps them interact seamlessly with humans.
Experts expect that AI robots will soon play greater roles in many industries, such as food service, agriculture, and finance.
Use AI to protect yourself from scams
There are many types of AI in use today, and more are coming. It’s important to remember that today’s AI tools do not possess true human intelligence and are not self-aware. Their uses are determined by the people who control them.
This means many AI tools are beneficial. However, others can be used by scammers and hackers for harm. Protect yourself from the dark side of AI with Norton 360 Deluxe. It provides comprehensive malware protection and a suite of digital privacy tools, including AI-powered features that can help you detect the latest AI threats.
FAQs
What’s the most common type of AI?
The most common type of AI is artificial narrow intelligence (ANI). In fact, all AI tools in use today are different forms of ANI, including LLMs like ChatGPT, self-driving cars, and spam filters.
What type of AI is ChatGPT?
ChatGPT is a type of AI called a large language model (LLM). It uses complex algorithms and vast amounts of training data to predict an effective output based on input prompts. ChatGPT is a form of artificial narrow intelligence (ANI), meaning it was designed to perform a specific set of tasks. It is also a natural language processing (NLP) system designed to replicate human language.
What type of AI is Siri?
Siri is an artificial narrow intelligence (ANI) and a basic natural language processing (NLP) system. It uses speech recognition and rule-based AI systems to help users with simple tasks, like setting an alarm or opening an app. Siri is much less advanced than modern LLMs like ChatGPT. However, Apple is reportedly rebuilding Siri as an LLM.
Which AI has the highest IQ?
Currently, ChatGPT’s o3 model has the highest IQ among LLMs. It scored a 136 on the Mensa IQ test, while competitors are still struggling to break 100. However, AI technology is evolving rapidly, so the smartest and most capable AIs are constantly changing.
Editorial note: Our articles are designed to provide educational information for you. They may not cover or protect against every type of crime, fraud, or threat we write about. Our goal is to increase awareness about Cyber Safety. Please review the complete Terms during enrollment or setup. Remember that no one can prevent all identity theft or cybercrime, and that LifeLock does not monitor all transactions at all businesses. The Norton and LifeLock brands are part of Gen Digital Inc. For more details about how we create, review, and update content, please see our Editorial Policy.








Want more?
Follow us for all the latest news, tips, and updates.