GPS spoofing: What it is and why it can be dangerous
GPS spoofing is a form of digital deception that manipulates location data—with potentially catastrophic consequences. We'll go over what GPS spoofing is, how it's used, and how comprehensive online security software like Norton 360 Deluxe can help protect your digital life.

What is GPS spoofing?
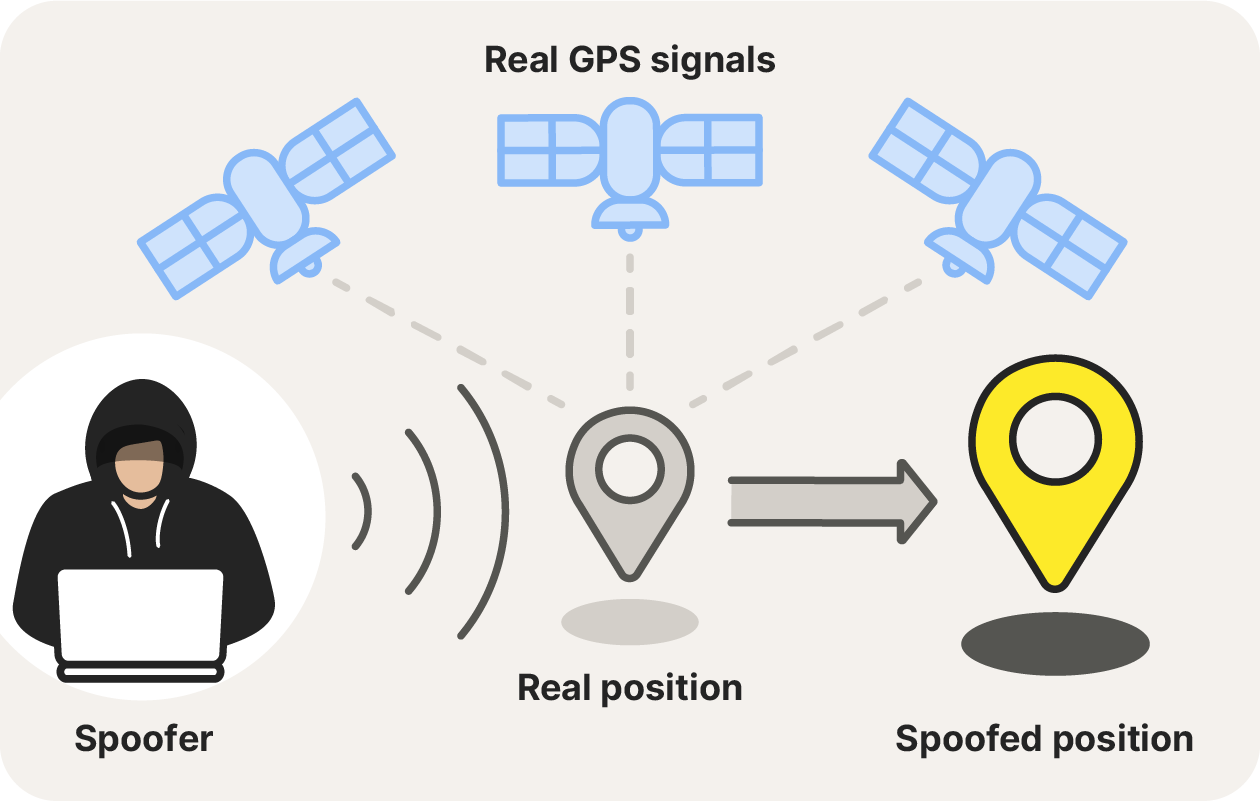
GPS spoofing uses bogus radio signals to imitate legitimate Global Positioning System (GPS) signals, misdirecting GPS-receiving devices about their actual location. This can result in incorrect navigation data and potentially life-threatening situations, especially in systems that rely heavily on precise location information.
A “spoofing attack” is a broad category of cyberattack where fake data is disguised as originating from a trusted source to deceive systems or users. Other kinds of spoofing include IP spoofing—often used to avoid detection while performing DDoS attacks—as well as SMS spoofing and caller ID spoofing, where messages or calls appear to be from another number or caller ID.
Is GPS spoofing illegal?
GPS spoofing is often considered illegal, particularly when used to deceive or harm others. Legal penalties for GPS spoofing can be severe, especially in life-threatening circumstances. However, there are some specific uses of GPS spoofing that are legal. It all depends on the context and intent.
How GPS spoofing works
GPS spoofing works by broadcasting fake GPS signals that mimic and override real ones because they’re intentionally stronger. Because most devices “trust” whichever GPS is strongest, the receiver locks onto these fake signals, causing it to calculate an incorrect position. This weakness in the way GPS works allows adversaries to exploit it and cause harm.

The technology behind spoofing GPS
There are two main types of GPS spoofing, each relying on different technological means:
- External spoofing: This is typically what is referred to as GPS spoofing and is where fake GPS signals are transmitted from hardware devices that can broadcast emulated signals for GPS-enabled devices to pick up on.
- Software-based spoofing: This is where software apps dupe the location services on the devices they’re installed on. This form of spoofing is more likely to be legal because it doesn’t transmit false signals or interfere with other devices.
How fake GPS signals are created
In external spoofing, fake GPS signals are created with specialized GPS signal generator hardware, using advanced radio technology. These transmitters broadcast signals that are carefully designed to mimic real GPS data and fool the receiver.
Software-based GPS spoofing doesn’t require a fake input signal. Instead, an app is used to alter GPS data internally. This is fairly simple to do on an Android phone, due to the relatively open nature of the Android ecosystem. But GPS spoofing with an iPhone requires jailbreaking, which can expose you to security risks and stability issues.
What is the difference between a VPN and GPS spoofing?
While GPS spoofing impacts GPS-enabled location services by manipulating data, a VPN hides your IP address, making it appear like your location is wherever the VPN server you're connected to is.
So while a VPN can help you obscure your location when using applications like Netflix or YouTube that rely on internet data, you’d need a GPS spoofing app to fool applications like Uber or Pokemon Go that use GPS location services.
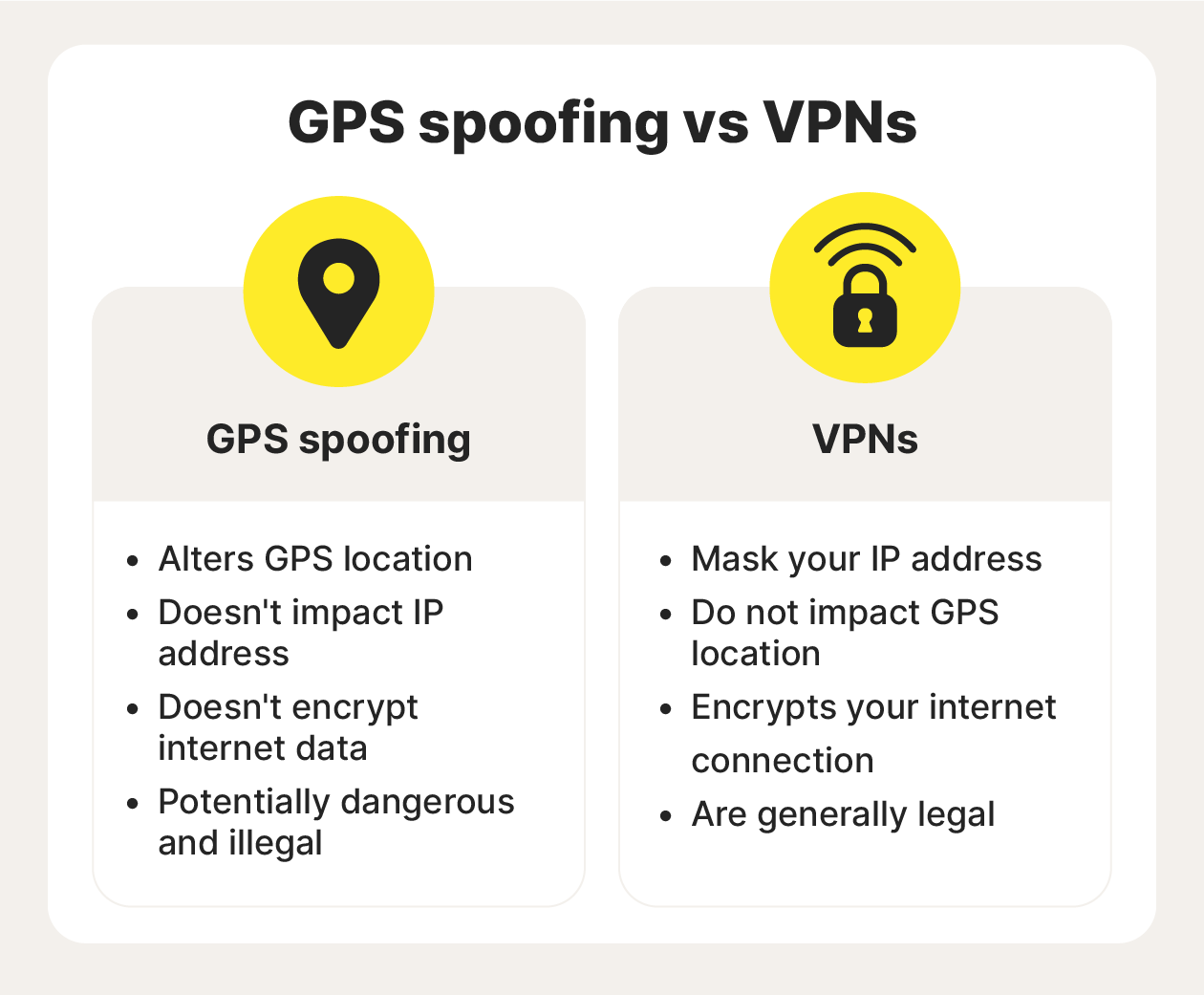
Here are some of the key distinguishing features of GPS spoofing and VPNs:
GPS spoofing
- Alters GPS-enabled location services
- Keeps your IP address the same
- Doesn’t encrypt the data you send and receive
- Is potentially dangerous and illegal
VPNs
- Alter your public IP address
- Do not impact location services using GPS data
- Encrypt your your online connection
- Are generally legal
The privacy and security benefits of a VPN extend beyond just masking your location; VPNs also encrypt your connection, keeping your online activity and the data you send and receive private.

What GPS spoofing is used for
GPS spoofing can be used for malicious and legitimate purposes. It’s used to enable a wide range of criminal activities that require obfuscating location data. Smugglers and poachers may create false location data to hide their movements from law enforcement. Fraudsters might also manipulate GPS-based tracking systems to falsify the whereabouts of valuable stolen assets to evade detection.
Although primarily associated with malicious actors, GPS spoofing has legitimate applications too. For instance, militaries use GPS spoofing to mislead their adversaries and defend against drones and GPS-guided weapons. Researchers also use GPS spoofing in controlled testing environments to improve the security of navigation systems and help thwart potential GPS spoofing attacks.
Individuals may use legitimate software-based GPS spoofing on their phones to take advantage of location-based features. For instance, spoofing your location on a dating app could allow you to arrange a local meetup at a destination you’re traveling to. Or, if you’re a mobile gamer, maybe you just want to catch some Pokemon from the comfort of your living room.
The dangers of GPS spoofing
The dangers of GPS spoofing pose significant risks to public safety and national security. Vehicles reliant on accurate GPS could be diverted, leading to accidents, hijackings, or thefts. Airports, power stations, and other infrastructure dependent on GPS time data could fail, causing widespread disruption and outages.
To highlight the clear and present dangers they represent, here are some of the most prominent GPS spoofing attack examples:
- Iran reportedly captured a US drone using GPS spoofing technologies in 2011. Since then Iran has also claimed or been accused of other military-related GPS spoofing attacks.
- Researchers used GPS spoofing to steer a yacht off-course in a proof-of-concept test in 2013.
- Russia has been using GPS spoofing and jamming to defend the Kremlin and other strategically important sites, resulting in disruptions to civilian aviation.
How to protect against GPS spoofing
While the US military can encrypt GPS signals (which are still vulnerable to certain attacks), most civilians can’t. But there are other ways to defend against GPS spoofing attacks—mostly with the help of software designed to detect sudden anomalies in GPS data and filter out malicious signals.
Here are some other defenses to help protect against GPS spoofing:
- Placing receiver antennas outside of the direct line of sight.
- Using decoy antennas to “spoof” potential spoofers.
- Practicing good cyber hygiene by staying up to date on cybersecurity basics.
- Using robust cybersecurity tools to defend against software-based GPS spoofing malware.
Get better protection for your devices
The diverse risks of GPS spoofing highlight the importance of safeguarding your digital life and privacy, but spoofed GPS signals are just one of many online threats. That’s why you need a comprehensive online security app on all your devices—to help protect against the unexpected.
Subscribing to Norton 360 Deluxe lets you join millions of others who benefit from the powerful combination of advanced malware detection that helps block hackers and a VPN that keeps your online activity private. Get greater peace of mind with Norton on your side.
FAQs about GPS spoofing
Got more questions about GPS spoofing? We’ve got the answers.
Can GPS spoofing be detected?
Yes, GPS spoofing can be detected, but it can be challenging. Detection methods typically involve monitoring for anomalies in the GPS signals or using additional technologies such as multi-receiver systems and sensor cross-referencing to verify the authenticity of the signals.
How would you know if someone is spoofing you?
Without dedicated anti-spoofing technology, it can be difficult to tell if someone is manipulating your GPS location services. But there are some signs to watch out for which could indicate you’re being targeted including inconsistent location data, unusual behavior in navigation systems, time discrepancies, and unexpected signal loss.
Why would someone use fake GPS?
As well as the obvious malicious use cases, people may use fake GPS to protect their privacy or access geo-specific resources in certain mobile games or apps.
Editorial note: Our articles provide educational information for you. Our offerings may not cover or protect against every type of crime, fraud, or threat we write about. Our goal is to increase awareness about Cyber Safety. Please review complete Terms during enrollment or setup. Remember that no one can prevent all identity theft or cybercrime, and that LifeLock does not monitor all transactions at all businesses. The Norton and LifeLock brands are part of Gen Digital Inc.






Want more?
Follow us for all the latest news, tips, and updates.