What is a honeypot and how does it work?
A honeypot is a decoy system or bait designed to trick a hacker into infiltrating a system so that security professionals can observe and study their behavior. The idea is that, like Winnie-the-Pooh, hackers will find it hard to resist the allure of a honeypot. Learn all about honeypots and how they work. Then, get Norton 360 Deluxe to help protect against cybercriminals and scams so you can stay safer online.

Honeypot definition
In cybersecurity, the meaning of a honeypot refers to a network intentionally designed to be compromised in hopes of attracting cybercriminals and luring them into revealing their methods. Broadly, the definition of honeypot stems from the world of espionage where enemy spies are seduced into compromising themselves.
What is a honeypot, exactly? It depends—on the application, who is beinglure in hackers targeted, and what kind of honeypot trap is used to target them. Honeypots can only be accessed illegitimately, so honeypot operators know that whoever is in a honeypot is a bad actor.
The specific trap laid differs depending on the type of threat involved. A more specific honeypot definition divides the term into low-interaction, mid-interaction, and high-interaction honeypots, depending on how much setup is involved and how much tracking and data collection the administrators want to do while the hackers are inside.
When there are multiple honeypots on one network designed to attract multiple types of attacks, that’s referred to as a honeynet. Honeynets are designed to dangle multiple “vulnerable” databases, systems, and processes at the same time to keep attackers occupied for longer. Leading hackers on a wild goose chase allows security experts to observe and study in detail how they launch attacks, coordinate, and interact with the network at large.
How do honeypots work?
A honeypot works by being a standalone, fake interface that’s enticing to hackers but isn’t too obvious. They’re populated with specific digital bait designed to attract unauthorized access—just like honey can be put out to attract bears. Legitimate traffic can’t access a honeypot, so anyone inside is likely hostile.
The initial lure is often a security vulnerability, while inside are fake digital assets, software applications, or data to keep the attacker occupied.
Here are some common bait tactics honeypots use to attract hackers:
- Weak passwords
- Open ports
- Fake IPs
- Fake emails
- Fake files
- Fake folders
- Fake URLs
After a hacker takes the bait, honeypot operators can usually see the usernames and privileges attackers access, the IP addresses being used, what data is being accessed or manipulated, and even the exact keystrokes attackers use.
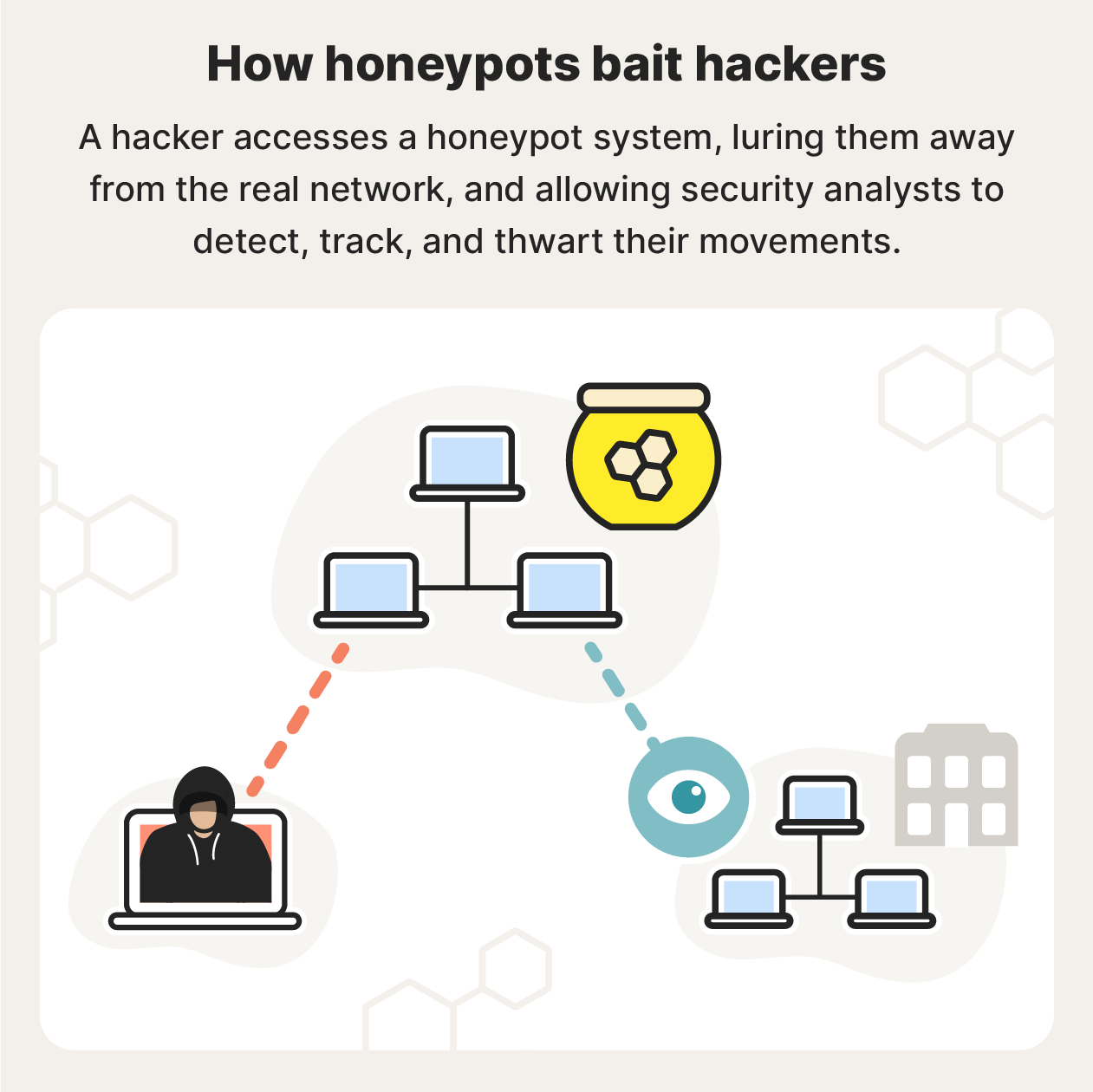

Honeypots also allow honeypot owners to:
- Divert malicious traffic: If hackers are stuck in a honeypot, such as a fake banking network, they are kept away from actual bank assets and infrastructure. If the honeypot is placed outside an external firewall, it can be used to attract, analyze, and deflect traffic.
- Track attacker movements: Honeypot operators can see where hackers enter, where they go, and what they do. This helps network administrators identify vulnerabilities in their own systems.
- Understand attacker motives: By seeing what hackers target inside the honeypot, honeypot operators also get an idea about what kinds of digital assets hackers find valuable.
- Improve security: Seeing how hackers break in allows security holes to be patched, and security protocols to be added. Honeypots can also attract malware that’s already on a network, which can then be blocked.
- Identify threats: Specific users can be detected and blocked, and threat types and levels can be better understood.
What is a honeypot used for?
Honeypots are primarily used by researchers to better understand security vulnerabilities in networks and as decoys for companies looking to protect their assets. Data from honeypot attacks can then be used to shore up security against watering hole attacks or other future cybersecurity threats. After learning all they can, honeypot owners can then block the attackers, and update their network.
Changing the bait also changes the types of hackers captured. For example, honeypot network security teams might create a network with open ports to see how infiltrators operate once inside, while law enforcement officials might create a fake back door to their files to catch crooks.
Meanwhile, cybercriminals may use honeypot attacks to target regular internet users, such as when they sit on dark web exit nodes waiting for personal information to pass through.
Research honeypots
Research honeypots are a specific type of honeypot that allow administrators to study the activity of hackers to learn how to protect against digital threats. Honeypots can also help expose system vulnerabilities that might not otherwise be detected.
For example, honeypots can be set up to receive only fake traffic. Then, if any real activity is detected, honeypot security teams know that cybercriminals may be active.
Production honeypots
Production honeypots are used by companies and institutions and are usually placed inside networks as a decoy to lessen the risk of real assets being infiltrated. These honeypots serve to distract hackers from legitimate targets inside a network. Honeypot security allows network administrators to identify threats, block attackers, and better protect their business.
If you own a small business, it's critical to keep all your digital assets protected. Norton Small Business helps safeguard up to 20 of your company’s devices, both mobile and desktop, with powerful protection to suit your needs. Norton Small Business also provides 24/7 support, so we’re there when you need us.
6 types of honeypots
What a honeypot is to one person might not be particularly attractive to another. A specific target usually requires a specific type of honeypot, such as in 2023, when cybersecurity researchers set up a honeypot for hackers of Microsoft’s Remote Desktop Protocol, or when video game company Valve caught 40,000 cheating Dota 2 players by patching a honeypot into the game.
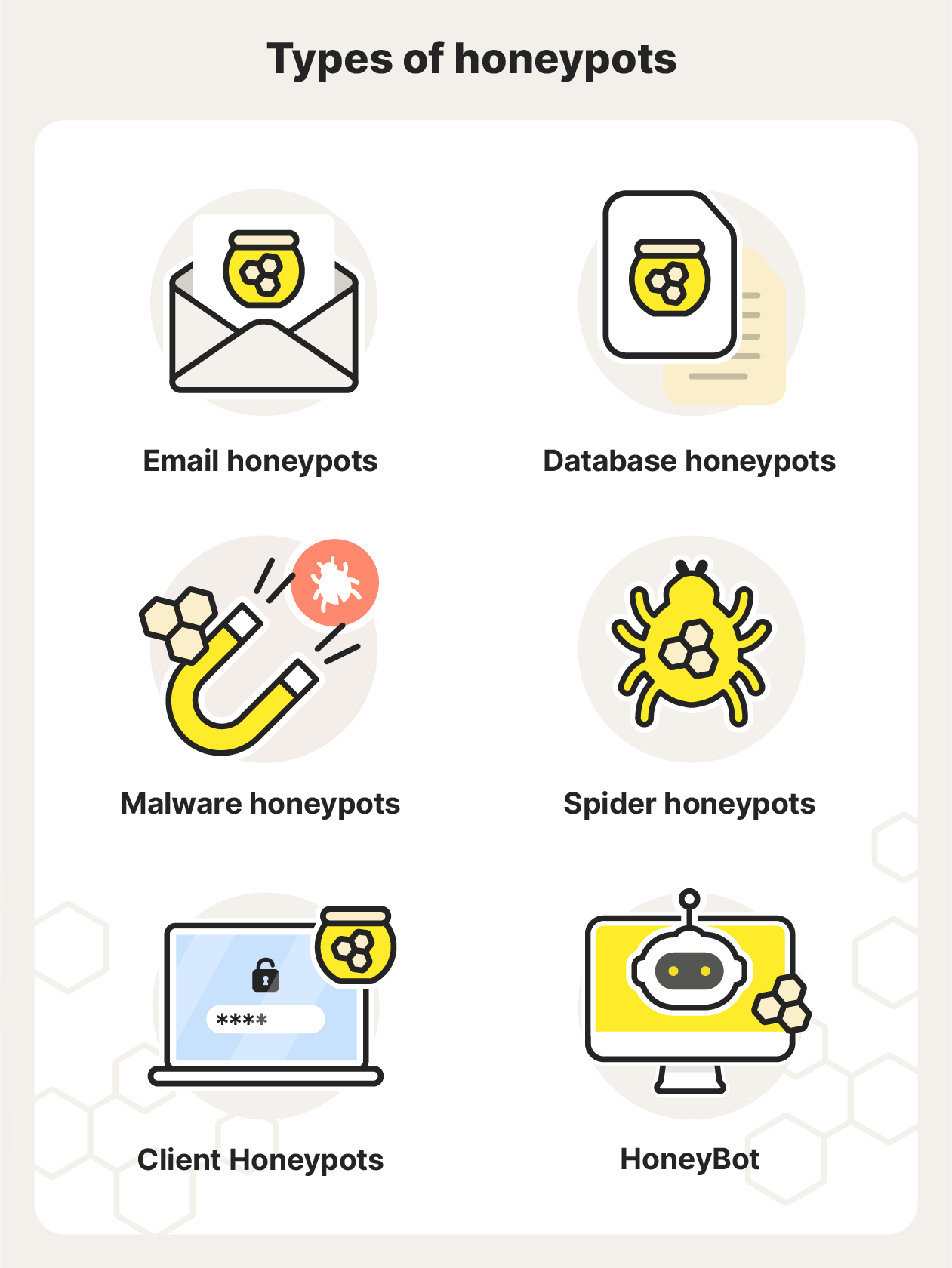
Here are six common types of honeypots:
- Email honeypots: Also known as “spam traps,” email honeypots are fake email addresses that are hidden and can only be accessed by email harvesters, so any emails sent to an email honeypot are likely spam emails. Email honeypots help block spammers from sending malicious emails to legitimate email addresses, and they’re used to study spamming activity.
- Database honeypots: These honeypots are also known as “decoy databases” and contain vulnerable and fake datasets to attract attackers who get through firewalls. These honeypots are used to monitor the type and number of attacks that occur in specific databases.
- Malware honeypots: These honeypots copy software apps and APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) to attract malware attacks. These can be used to find out what API weaknesses need to be addressed and allow developers to find and close zero-day exploits and create anti-malware programs.
- Spider honeypots: Spider honeypots target automated web crawlers and data scrapers by making web pages that can only be accessed by bots, signaling that malicious actors are at play instead of authentic users.
- Client Honeypots: Client honeypots pose as clients (any device or app that requests services from a server) to discover malicious servers that target real clients. Instead of passively waiting to be attacked, client honeypots actively search for malicious networks to expose them.
- HoneyBots: These are the newest type of honeypot, developed by university researchers. Unlike other honeypots, a HoneyBot can interact with hackers, mimicking legitimate systems to look even more convincing.

Pros and cons of honeypots
Honeypots allow network admins to learn tactics and techniques used by attackers, and identify potential points of attack on a network. At the same time, honeypots can also teach attackers about certain system vulnerabilities, helping them recognize honeypots in the future and potentially exploit real systems.
Benefits of using honeypots
Honeypots are effective threat detectors, luring hackers into a controlled environment so their activities can be monitored. Here are some main benefits of honeypots:
- They allow network admins to engage in real data collection about cyberattacks, including information on hacker behavior, tools, techniques, and new attack vectors.
- They make future attacks easier to avoid by revealing attack patterns, and lessen real attacks in the present by occupying a hacker’s time that could be spent elsewhere.
- They give fewer false positives when monitoring for cyberattacks, because hacker activities are their only genuine interactions.
- They typically run on their own with minimal monitoring, so honeypots are cost-effective and low maintenance.
- Honeypot infiltrators can usually safely be blocked.
Drawbacks of using honeypots
- They only collect attack data, limiting the scope of their usefulness to monitoring hacking potential and vulnerabilities in specific areas.
- They may allow hackers to more easily avoid honeypots in the future—there can be telling characteristics behind how a honeypot works that signal to savvy hackers that they’re about to enter a trap.
- They may actually increase the attack surface if the honeypot isn’t properly secured, providing hackers with another entry point into an organization’s system or network.
Help protect your devices against cyberattacks
Honeypots can be an effective cybersecurity mechanism for monitoring attacks and tracking hacker behavior. But most of us don’t have the need, resources, or skill to build honeypots to secure our own devices. That’s where powerful, automated cybersecurity software comes in.
Norton 360 Deluxe is a comprehensive cybersecurity suite that helps defend your device against hackers, as well as viruses, malware, and other online attacks. Plus, it features a built-in VPN to encrypt your connection and help keep your communications private.
FAQs about honeypots
Still have questions about honeypots? We’ve got some answers.
Are honeypots illegal?
While honeypots themselves are not illegal, there are some legal and ethical issues to consider when using a honeypot, because they collect and analyze personal data. Before employing a honeypot, consider all applicable privacy laws in your area, along with state and federal anti-hacking laws.
How do you set up a honeypot?
Ready-made honeypot software is available on the web. Popular examples are T-pot, Cowrie, OpenCanary, and Honeyd. After selecting a honeypot, you must create and activate your virtual environment, then install the appropriate honeypot inside. Finally, configure the honeypot to monitor the traffic you want. Third-party tools are also available to analyze honeypot traffic.
What’s the difference between a firewall and a honeypot?
Firewalls monitor traffic on real networks to authorize or deny access based on predetermined rules, while a honeypot monitors traffic on fake networks to determine their origin, behavior, and intent. While firewalls actively block unauthorized access, honeypots welcome it for the sake of research and detection.
Can hackers tell if you’re running a honeypot?
If a honeypot is set up properly, most hackers won’t be able to tell. But if experienced hackers discover known characteristics, configurations, or IP addresses associated with honeypots, they may become wise. Advanced hackers can “fingerprint” a system to try and identify a honeypot, so obvious vulnerabilities or irregularities in the honeypot may arouse suspicion.
Editorial note: Our articles are designed to provide educational information for you. They may not cover or protect against every type of crime, fraud, or threat we write about. Our goal is to increase awareness about Cyber Safety. Please review the complete Terms during enrollment or setup. Remember that no one can prevent all identity theft or cybercrime, and that LifeLock does not monitor all transactions at all businesses. The Norton and LifeLock brands are part of Gen Digital Inc. For more details about how we create, review, and update content, please see our Editorial Policy.







Want more?
Follow us for all the latest news, tips, and updates.