Ransomware statistics: Facts and trends
Ransomware is an ever-growing threat to businesses, organizations, and individuals everywhere. The more you know about this cyber-menace, the better protected you are. Learn about some of the most alarming ransomware statistics, and defend against ransomware attacks and other digital threats with a state-of-the-art Cyber Safety tool.

Ransomware is an insidious variety of malware that cybercriminals use to encrypt their targets’ essential system data and effectively lock users out of their software. The attackers then threaten to further restrict access or leak sensitive information unless their victims pay up. Ransomware attacks frequently target large organizations like schools, hospitals, and corporations.
With so many organizations reliant on IT infrastructure, ransomware attacks can have a devastating impact. Keep reading for the latest statistics and trends in ransomware, and learn what you can do to protect yourself and your organization.
Key ransomware statistics
- According to a Gen Threat Report, ransomware attacks surged by 50% in the final three months of 2024, building on the 100% increase that had already happened in the three months prior.
- In 2023, 66% of organizations reported experiencing a ransomware attack according to a 2024 Sophos survey. But ransomware attacks are likely to be grossly underreported.
- In fact, Black Fog estimated that in June 2024 the ratio of unreported attacks was at 774% — meaning at least seven times more attacks occurred than were reported. This is despite improvements in reporting in recent years, highlighting the sheer scale of the ransomware problem.
- According to an ExtraHop survey, 91% of ransomware victims paid at least one ransom within the last year, despite 88% of surveyed organizations reporting that they’re confident in their organizations’ ability to manage cyber threats.
- Small businesses are among the most vulnerable to lasting damage. A University of Maryland study found that following a ransomware attack, 60% of small businesses folded within six months due to the financial repercussions, as many of them did not have the resources to resist effectively.
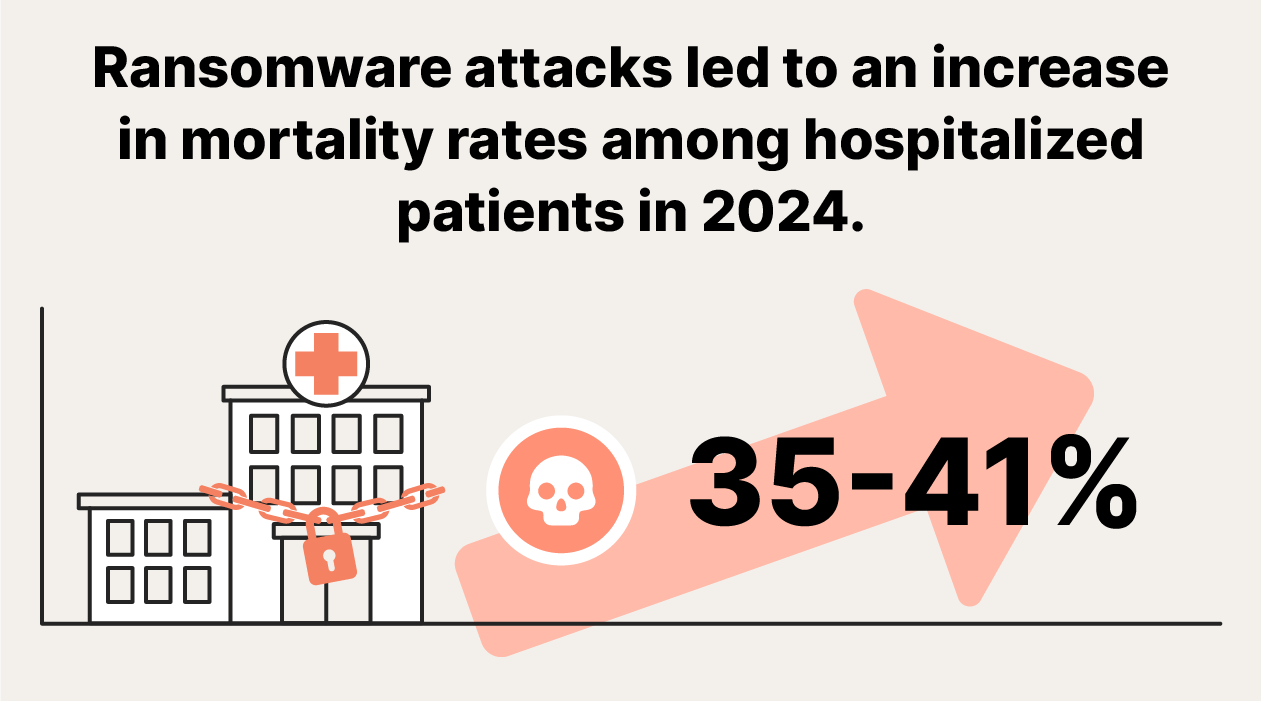
- When vital institutions like hospitals are targeted, ransomware attacks can be deadly. A study conducted by the University of Minnesota found that among patients already admitted when an attack begins, ransomware attacks on hospitals result in 35% to 41% increases in in-hospital mortality rates. This is because ransomware disrupts critical care, jeopardizing the lives of patients in critical conditions.

How frequent are ransomware attacks?
In the first half of 2024 alone, more than 2,500 attacks were reported, amounting to 14 per day, but those attacks are just the ones that got reported. According to another study, the number of reported ransomware attacks — both failed and successful — in 2023 amounted to about 10 attempts per second.
What the experts say
“For the third consecutive quarter, ransomware has continued its alarming upward trend... highlighting an ongoing, escalating threat to both individuals and organizations globally.” - Gen 2024 Threat Report
Luis Corrons, Security Evangelist
Semperis, an expert Active Directory security company, even updated their general philosophy to “assume constant breach” in their 2024 Ransomware Risk Report, which found that 74% of survey respondents reported being targeted by ransomware multiple times within the previous 12 months.
Ransomware trends
It’s easier than ever to launch a ransomware attack, thanks to the spread of Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) and the accessibility of hacking tools. RaaS is now available for purchase on the dark web, meaning hackers don’t have to create their own ransomware to carry out attacks.
LockBit is one of the most popular RaaS providers, responsible for 24% of ransomware attacks worldwide in 2023. In fact, the top five ransomware variants are all RaaS:
- Lockbit
- ALPHv/BlackCat
- Cl0p
- Play
- Black Basta
Among the different kinds of ransomware attacks, supply-chain attacks are gaining prominence. Of the data breaches that occurred in 2023, 15% involved a third party or supplier. Meanwhile, one of the most notable ransomware attacks of 2024 targeted Blue Yonder, a supply chain software company, resulting in widespread fallout with two of its biggest clients: Starbucks and Morrisons, a supermarket chain.
Supply-chain ransomware attacks are especially effective as they have ripple effects not only across the targeted organization, but throughout the industry the target serves. As organizations become more interconnected and rely on centralized systems, they’re increasingly vulnerable to ransomware attacks. This vulnerability is often exacerbated by victims’ urgent need to prevent disruptions in their operations, which can lead to hasty decisions regarding payments.
Law enforcement steps up, but so do threats
At the end of 2023, a major bust-up of the ALPHv/Black Cat gang’s ransomware operation scored a big win for law enforcement. This helped around 500 victims avoid paying $68 million in ransom demands collectively. By the time the FBI acquired ALPHv’s encryption keys, the gang had already exploited over 1,000 victims and accepted $300 million worth of ransom payments.
However, with every cybercriminal operation that gets busted, another one sprouts up to take its place, and the newcomers are often even more formidable. For example, the LockBit ransomware group got in touch with ALPHv’s affiliates, convincing them to switch over and continue negotiations with victims.
As a result, 2024 was LockBit’s biggest year ever — until the FBI got ahold of 7,000 encryption keys. This is good news for law-abiding netizens, but it won’t be long before another ransomware gang crops up to take its place.
Types of ransomware
There are many types of ransomware out there, as well as multiple ransomware groups. Ransomware-as-a-Service is by far the most popular type of ransomware, with the top five attackers in the United States being RaaS.
Lockbit, APLHv, and Cl0p are among the most notorious ransomware strains of the past year, with relative newcomer Play, which first appeared in 2022, also proving to be a formidable threat. In 2023, Play attacked IT service provider Xplain and published 65,000 files relating to the Swiss government on the dark web.
Other types of ransomware specifically target individual users and small businesses, demanding thousands of dollars rather than millions. Here are the top ransomware strains of 2024:
- RansomHub
- LockBit
- Medusa
- Play
- INC
Common ransomware targets
Ransomware attackers go where the money is. This means industries and high-income countries, rather than consumers and lower-income countries, are more likely to be attacked. Here’s the breakdown of the most common ransomware targets.
Businesses
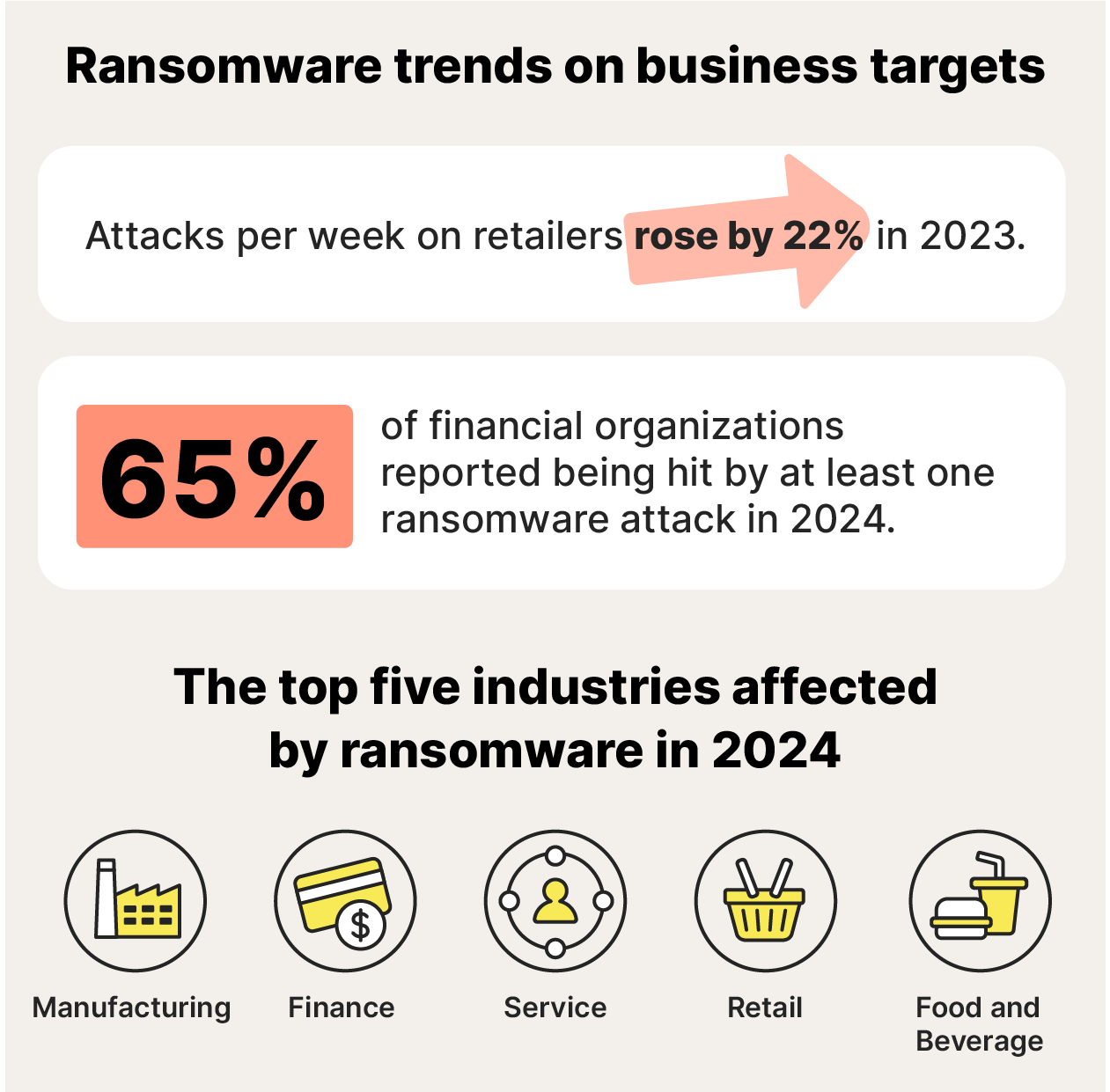
Retailers saw the biggest increase in ransomware attacks, experiencing a 22% rise in attacks per week. Financial service providers are also targeted more frequently. By the end of 2024, 65% of financial organizations worldwide had reported being hit by at least one ransomware attack.
Healthcare and public health organizations, including hospitals, are also among the most likely to be targeted. Critical infrastructure sectors and organizations are popular targets because they’re more likely to pay a ransom to restore access quickly to critical services.
The top five industries with the most reported ransomware attacks in 2024 were:
- Manufacturing
- Finance
- Service
- Retail
- Food and Beverage
The education sector is also increasingly targeted by ransomware. In 2023, attacks against K-12 schools increased 105%, while attacks on higher education increased 70%.

Individuals
While ransomware attacks primarily target large organizations that can presumably afford a hefty ransom, some attacks are pure extortion against customers and end users. In 2023, the Cl0p ransomware gang hacked MOVEit transfer — a secure managed file transfer software — and held the data of nearly 18 million individuals hostage.
More broadly, one-third of American consumers reportedly had their data stolen in 2023, totaling 6 terabytes. Personal identity and health information were the most likely information to be stolen.
Specific countries
The United States experienced more ransomware attacks than any other country in the last few months of 2024, with half of all attacks targeting it. Meanwhile, France experienced the highest rate of attacks throughout 2024, with 74% of organizations reporting they had been hit within the last year.
Who carries out ransomware attacks?
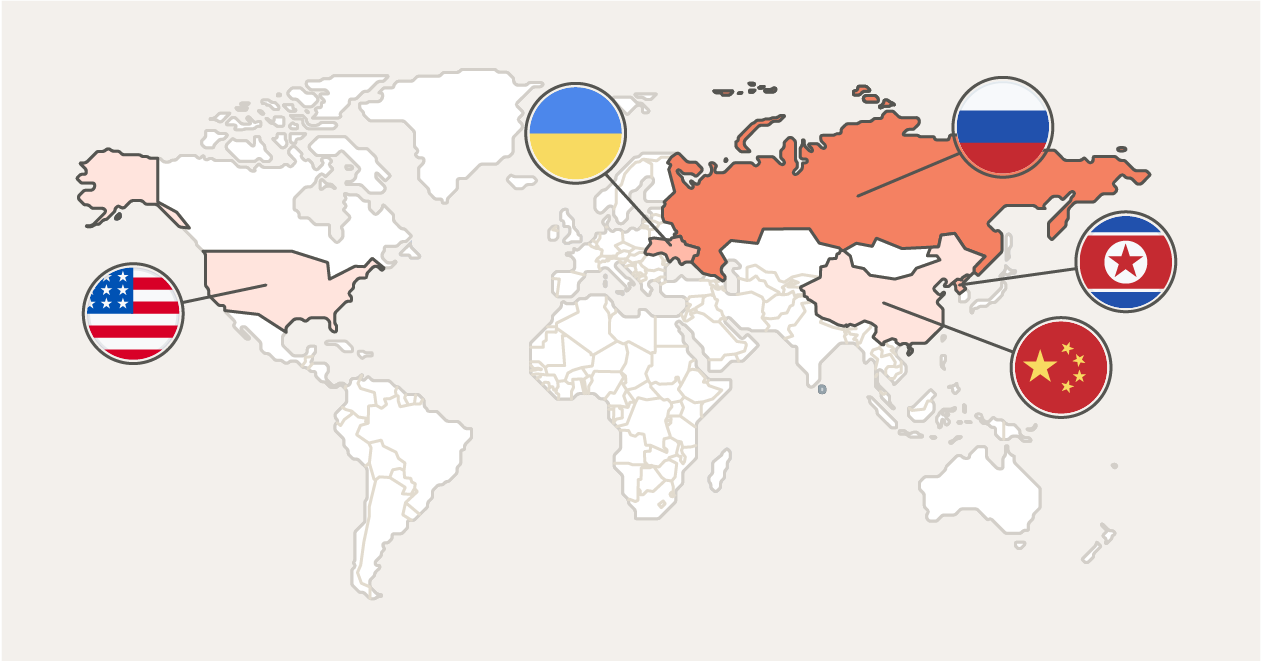
The World Cybercrime Index, which compiles cybercrime data from all over the world (including data on ransomware attacks), found that most cyberattacks originate from a small number of countries. Here are the top five, with Russia being the originator of the most cyberattacks.
- Russia
- Ukraine
- North Korea
- China
- United States
These countries top the list due to several factors: they have a highly educated populace, relatively few opportunities to profit (in some cases), and geopolitical significance.

While cyberattacks may be part of an international conflict, most ransomware attacks are carried out by individual criminals using RaaS or organized cybercriminal gangs working independently of state influence. A relatively small number of gangs are responsible for most ransomware attacks.
In the healthcare industry, more than half of all ransomware attacks are carried out by one of five ransomware gangs. Of course, there are always new ransomware gangs popping up. By the second quarter of 2024 alone, there were 27 new ransomware groups on the scene.
The financial impact of ransomware
In 2023, ransomware payments surpassed $1 billion for the first time ever, and the average cost of a ransomware attack is now $4.91 million. Notably, ransomware can have a devastating financial impact on businesses even when they don’t pay up. Meanwhile, the financial impacts of downtime, lost productivity, and reputation damage can be difficult to quantify.
Cryptocurrency is by far the most popular payment currency for ransomware attackers, due in part to its greater anonymity. By mid-2024, almost $460 million in ransoms had already been paid in cryptocurrency. 2024 was also a record-breaking year for ransomware payments in general, with the largest ever payment, amounting to about $75 million, paid to the Dark Angels ransomware group.
In the 2024 State of Ransomware study, published by ActualTech, researchers found that 29% of queried organizations have a strict no-payment policy for ransomware, which ensures they have a clear procedure to follow if they fall victim. However, there’s still a long way to go, as another 29% of organizations have no ransomware policy at all.
Insurance can help mitigate financial losses: in 2023, insurance was used to pay for about one-quarter of the amount demanded for ransom. While insurance is a boon to victims, it does little to address the underlying problems that incentivize ransomware attackers.
It’s been shown time and time again that paying the ransom doesn’t pay off. Only one-third of organizations that paid ransom in 2023 got data access fully restored, and 13% of those who paid didn’t get access restored at all and had to retrieve their data another way.
Even if data access is fully restored, breached data often ends up on the dark web, where cybercriminals can buy and sell information for future attacks or schemes to commit identity theft.
The amount of data available on the dark web is massive. While exact figures are hard to come by, known data leaks help reveal the scale of the problem. In a single data breach of AT&T in 2024, more than 70 million customers’ data appeared on the dark web.
Downtime resulting from lost access to valuable data also has financial repercussions. Businesses average 56 hours of downtime following a security incident. In heavy industry, the median cost of downtime averages around $125,000 per hour; thus, 56 hours of downtime would amount to over $7 million in losses per security breach.
Ransomware attack methods
The most “traditional” ransomware attack method remains the most prevalent; the majority of ransomware attacks businesses observed in 2023 were carried out through data encrypted for ransom, at 55%.
However, for many organizations, data encryption attacks are accompanied by other attack vectors too, especially when they fail to invest in proper cybersecurity.
Double extortion is another increasingly popular ransomware attack method: ransomware attackers not only encrypt sensitive data, they also exfiltrate (steal it) and threaten to sell or leak the data on the dark web. According to Rapid7 Labs, an average of 24 ransomware groups posted on leak sites per month in the first half of 2023, and the number increased to 40 groups in the same period of 2024 — a roughly 66% increase in ransomware groups posting to data leak sites.
Another increasingly common ransomware method is posting the data to leak sites. In 2023, there was a 75% spike in posts to data leak sites compared to 2022. Combined, ransomware attacks that occurred through exploited vulnerabilities and compromised credentials accounted for 65% of attacks in 2023.
Some ransomware also gets through to a device directly through phishing emails, but this only accounts for around 5% of cases. Most ransomware attacks are made through stolen credentials obtained on the dark web. Stolen data can be obtained through phishing scams on social media or other communication methods, indirectly connecting phishing to ransomware attacks.
Ransomware predictions and prevention
Ransomware attacks are expected to become more frequent and financially damaging. By 2031, it’s predicted that a ransomware attack will occur every 2 seconds, which translates to a mind-boggling 43,200 attacks per day. Globally, quantifiable losses attributed to ransomware are estimated to reach $265 billion by 2031.
Ransomware attacks are also more likely to be linked to state actors, with governments making use of hackers and RaaS to fund military operations or advance political agendas.
Despite the predictions and current prevalence of ransomware, many organizations lack proper preventative strategies against ransomware attacks.
Many are woefully unprepared. According to Ransomware.org’s 2024 State of Ransomware report, just under half (48%) of survey respondents felt their organization was ready for a ransomware attack. A similar proportion of organizations (46%) had small incident response teams, of 5 people or less.
Many ransomware attacks occur in part due to sensitive data obtained from data breaches. A Ponemon study found that 60% of data breaches occurred due to an unpatched known vulnerability that could have been fixed before the data breach. In the same survey, 52% of respondents said they used manual processes to respond to vulnerabilities, putting them at a disadvantage.
AI may change the impact of future vulnerabilities, with AI tools being used for patch management. Microsoft found that using AI allowed the company to predict the vulnerabilities most likely to be exploited within 30 days of their disclosure.
End-user employees outside IT departments are often the weakest link in organizations’ defenses. However, cybersecurity training can reduce the risk of cyberattacks from 60% to as low as 10%.
Using cybersecurity software that includes ransomware protection, such as Norton 360, can help avoid ransomware and other preventable online threats.
Help defend against ransomware attacks
Ransomware attacks aren’t going away. New threats are constantly appearing and evolving, and it’s up to you to stay one step ahead of attackers.
Norton 360 Deluxe can help you stay on top of evolving threats and keep your data safer. In addition to protection against ransomware, viruses, and other malware, Norton 360 Deluxe helps block fake websites that attempt to steal your passwords. It also comes with a secure VPN so you can browse the internet more privately. Get award-winning cyberdefenses to help secure your digital life.
Editorial note: Our articles provide educational information for you. Our offerings may not cover or protect against every type of crime, fraud, or threat we write about. Our goal is to increase awareness about Cyber Safety. Please review complete Terms during enrollment or setup. Remember that no one can prevent all identity theft or cybercrime, and that LifeLock does not monitor all transactions at all businesses. The Norton and LifeLock brands are part of Gen Digital Inc.








Want more?
Follow us for all the latest news, tips, and updates.