Credential stuffing: Examples and 3 prevention tips
Do you have a favorite password you reuse across accounts? Maybe you think it’s uncrackable—and perhaps it nearly is—but there are ways hackers steal login details. Learn what credential stuffing is and how to help protect your accounts from these attacks. Then get Norton™ 360 with LifeLock™ Select to help secure your devices and identity.

According to the 2023 ITRC Consumer Impact Report, nearly 60% of U.S. consumers surveyed use the same password across multiple accounts. Does this leave them wide open to credential stuffing? What does an attack even look like? This guide will explore credential stuffing attacks and share strategies to help keep you safe.
What is a credential stuffing attack?
Credential stuffing, also called “password stuffing,” occurs when a criminal steals your login credentials for one account and tries them on your other accounts, hoping you’ve reused your username and password. Automated tools are typically used to try as many accounts as possible quickly.
What is an example of credential stuffing?
An example of what credential stuffing might look like could start with one of your account logins being leaked on the dark web. A cybercriminal buys the data and uses bots to test other possible accounts. One of the attempts is successful, and now the hacker has access to your other accounts, too.
If the account is a financial one, the hacker will likely drain it or make as many purchases as possible before you realize. If the account is on a social media platform, they could use social engineering tactics to try and scam your contacts by pretending to be you.
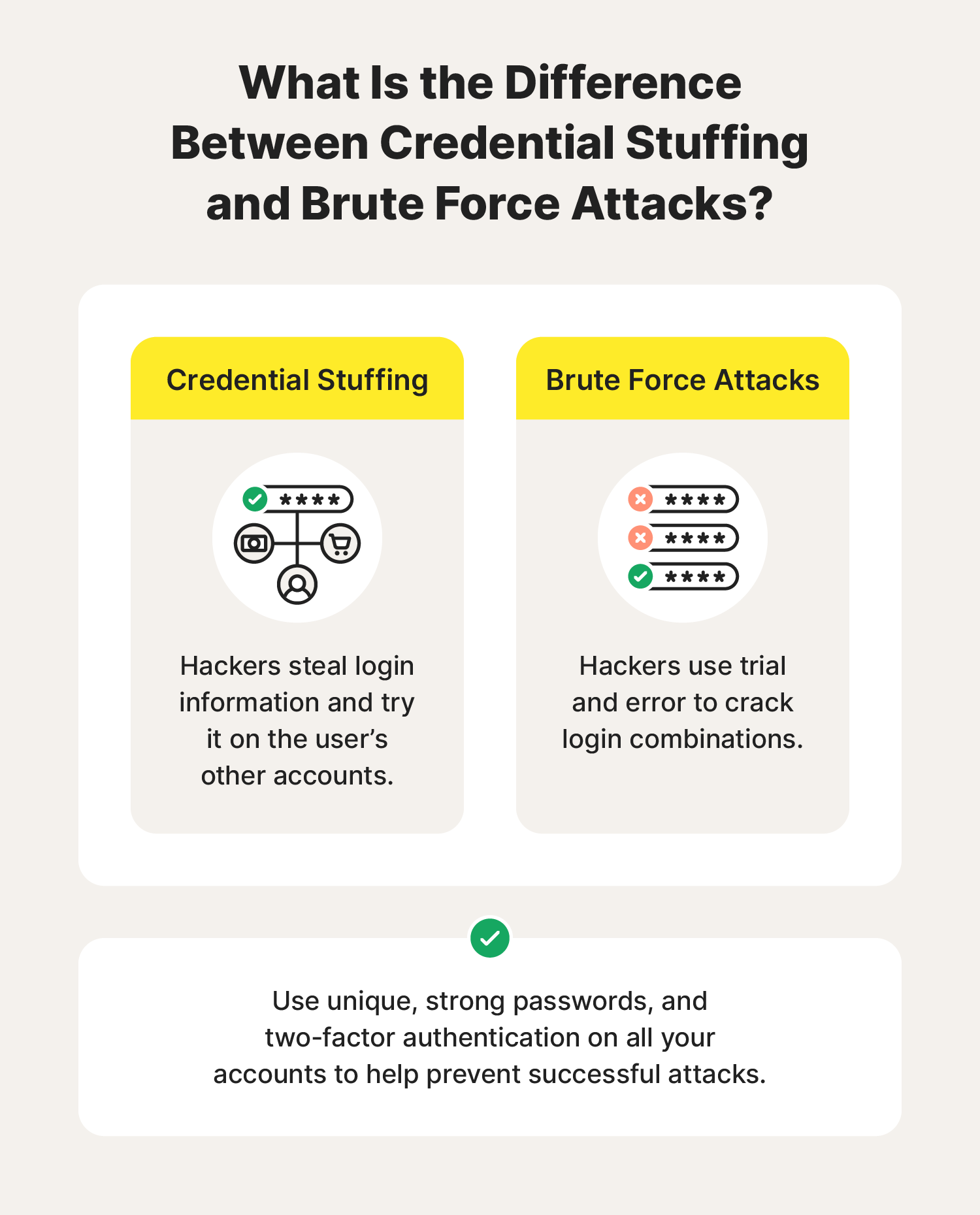
Credential stuffing vs. brute force attacks
In a brute force attack, hackers don’t know your login credentials; by contrast, in a credential stuffing attack, they do. Brute force attacks involve repeatedly testing different password combinations on an account until one of them succeeds.
- Brute force attack: Hackers use a network of connected computers (aka a botnet) to try out different password combinations until they successfully log into an account.
- Credential stuffing: Hackers already have their target’s password—which they may have got through a data breach, phishing, or malware like a keylogger—and they use it to try to break into other accounts.
To help prevent an attack from being successful, use unique, secure passwords on all your accounts and set up two-factor authentication (2FA).

How do credential stuffing attacks work?
Credential stuffing attacks work on the assumption that people often reuse login details across multiple accounts. If the assumption is true, then once a hacker gains access to one set of login credentials, they can more easily access other accounts using the same information.
Most credential stuffing attacks follow a similar process:
- Credential theft: Hackers can scour the dark web and password dump sites for stolen credentials obtained through a data breach or phishing scam.
- Credential testing: With the breached login details for one account, the attacker sets up an automation tool like a botnet to try and log into other accounts.
- Accounts exploited: Any accounts the attacker can access will be exploited. This could include an account takeover, transferring funds or making purchases, selling your personal information, or using data or the hacked account for further scams.
How to prevent credential stuffing
The easiest way to prevent credential stuffing is by using a unique password for each of your accounts, creating strong passwords with the help of a password manager, and enabling two-factor authentication.
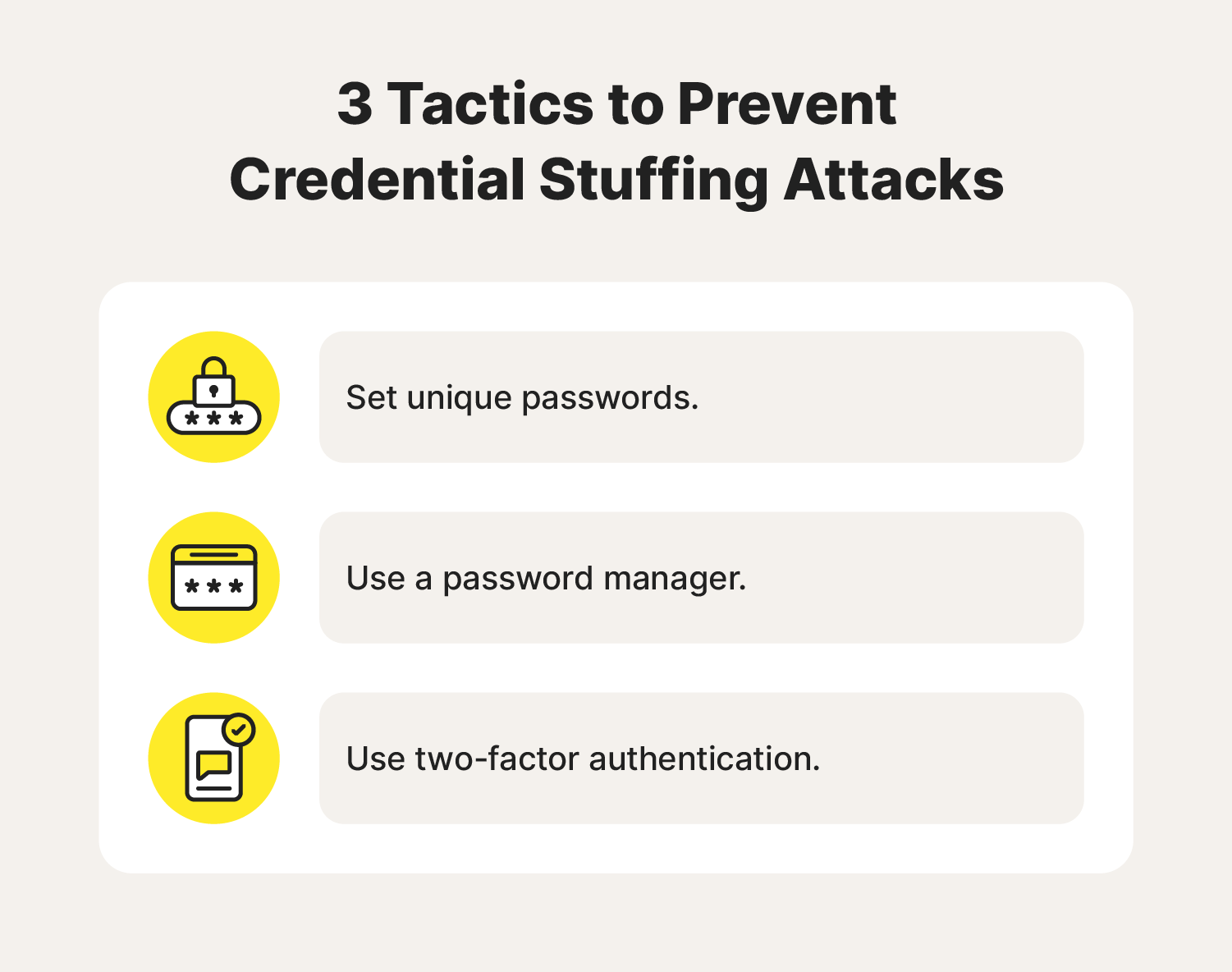

1. Set unique passwords
Using unique passwords on all your accounts is the only certain way to avoid credential stuffing. If you have a different password on every account, then a cybercriminal can’t use credential stuffing to hack into your other accounts.
2. Use a password manager
A good password manager will help you avoid credential stuffing attacks by creating unique, strong passwords for all your online accounts. It will also store your credentials safely behind one main account login, allowing you to quickly auto-fill your information while you browse. A strong password reduces the risk of someone guessing it correctly.
3. Use two-factor authentication (2FA)
Two-factor authentication is an effective strategy for protecting your personal information online. As well as a password, it requires a second verification method to access an account, like a biometric attribute or a one-time passcode sent via text message. 2FA can help keep hackers from accessing your accounts even if they obtain your password in a data breach.
Examples of businesses that have been affected by credential stuffing
Some of the first credential stuffing attacks were detected in 2014 when hackers were found selling customer login data on the dark web. Since then, attacks have impacted many businesses and their customers on a large scale.
- Netflix: Video streaming service Netflix experienced a credential stuffing attack in 2019. The hackers accessed the platform using credentials they stole in other data breaches and locked users out of their accounts.
- Nintendo: Credential stuffing hackers used breached data and crimeware to gain access to Nintendo user accounts in 2020. The account takeovers impacted 160,000 people and resulted in substantial financial loss.
- Spotify: In 2020, hackers stole records from a logger database and exploited the login credentials to target 300,000 Spotify accounts. To protect users, the Spotify team sent out links to help users quickly reset their passwords and began a campaign to take down the malicious database.
- Zoom: In 2020, hackers stole 500,000 Zoom login credentials from a database and placed them for sale on crime forums and dark web markets. They gave some passwords away for free and sold others for as little as a penny. This resulted in financial losses, operational deficits, and compliance breaches.
- PayPal: In 2022, around 35,000 PayPal accounts fell victim to a credential stuffing attack where personal data was exposed including names, addresses, and Social Security numbers. PayPal offered two years of identity monitoring from Equifax to impacted customers for free.
Businesses are legally required by the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) to responsibly manage user data. However, no security system is perfect, which is why it’s crucial to always take your own precautions.
How to mitigate damage from leaked credentials
While you can’t completely prevent your login details from being stolen in a wider data breach, you can use the tips above to help prevent credential stuffing. Additionally, there are ways to help protect yourself from other online threats resulting from leaked credentials.
Keeping your device’s software updated is essential for benefitting from security patches and keeping hackers at bay. And using antivirus software can help protect your devices against malware and online scams.
Identity theft protection services can also help prevent unwanted knock-on effects of a credential stuffing attack, helping to keep your identity secure in the future. Bundling an antivirus and identity theft monitoring service helps keep your devices and personal data more secure.
Help protect your devices and identity
If a data breach exposes your login credentials and other sensitive information, your accounts may be at risk of attack. That’s where a strong digital security tool that packs powerful identity theft protection comes in.
Norton 360 with LifeLock Select blocks online threats, helps you maintain best practices with your passwords, and scours the dark web and elsewhere to let you know if your information has potentially been exposed. And if identity theft does occur, you’ll have peace of mind knowing that a U.S.-based Personal Restoration Specialist is standing by to help you resolve your case.
FAQs about credential stuffing
Credential stuffing is just one of many cyberattacks you might encounter. Here are some answers to common questions about stolen login information.
How did hackers get my login information?
Hackers can gain access to your login info in many ways. Here are a few:
- Data breaches
- Password-cracking applications
- Malware that steals login credentials
- Guesswork, until they find the right login combination
- Compromised data purchased on the dark web
- Phishing attacks like smishing
How do I know if my information is compromised in a data breach?
The FTC requires companies targeted in a data breach to report the attack. But companies don’t always notify customers promptly or detect the breach soon enough. It helps to monitor your accounts for suspicious activity and use a data breach detection tool to check if your email has been found on the dark web.
You can also subscribe to Norton 360 with LifeLock Select, which will monitor the dark web for your personal information to help you protect against identity theft.
What is the goal of a credential-stuffing attack?
Hackers launch credential-stuffing attacks in the hopes that a target has reused the same login credentials on multiple accounts. That gives them easy access to accounts and the opportunity to commit financial fraud or further scams using the information they uncover.
Editor’s Note: No one can prevent all identity theft. Dark Web Monitoring is not available in all countries and varies based on region.
Editorial note: Our articles provide educational information for you. Our offerings may not cover or protect against every type of crime, fraud, or threat we write about. Our goal is to increase awareness about Cyber Safety. Please review complete Terms during enrollment or setup. Remember that no one can prevent all identity theft or cybercrime, and that LifeLock does not monitor all transactions at all businesses. The Norton and LifeLock brands are part of Gen Digital Inc.
- What is a credential stuffing attack?
- What is an example of credential stuffing?
- Credential stuffing vs. brute force attacks
- How do credential stuffing attacks work?
- How to prevent credential stuffing
- Examples of businesses that have been affected by credential stuffing
- Help protect your devices and identity
- FAQs about credential stuffing







Want more?
Follow us for all the latest news, tips, and updates.