What is a tailgating attack + how to protect yourself
What is a tailgating attack?
A tailgating attack is a social engineering tactic where an attacker follows someone with authorized access into a restricted area to steal private information, install malware, or damage property.

Imagine you start working at a new company and are asked to deliver paperwork to your company’s warehouse.
Eager to make a solid first impression, you gladly take on the task and make your way to the warehouse. As you round the corner toward the entrance, you see someone waiting outside the warehouse door with their hands full of boxes.
Clearly struggling to support the weight of the boxes, they ask if you could get the door for them. Without thinking twice, you swipe your card and let the person in behind you.
While this might seem like an innocent act of kindness, you may have accidentally assisted with a tailgating attack. Tailgating is a social engineering technique where an attacker gains access to a restricted area by following an authorized employee.
So how exactly do tailgating attacks work, and how can you protect yourself? Read along to learn more about tailgating attacks and what you can do to help keep yourself and your company safe.
How tailgating attacks work
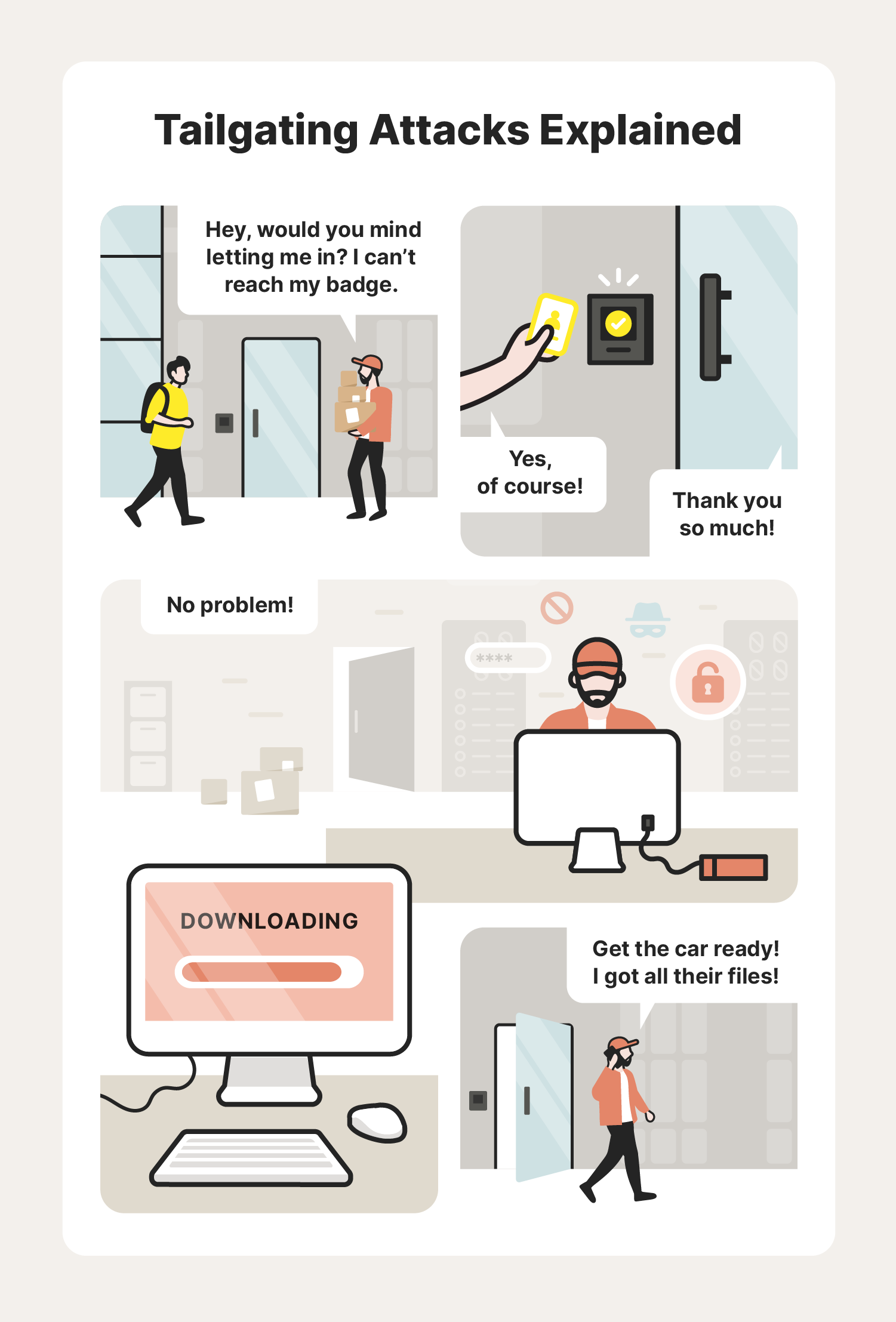
Unlike social engineering scams on social media, tailgating attacks revolve around gaining physical access to a building or area that contains sensitive information. Attackers may do this by waiting around a secure exit and then sneaking in once someone with authorized access unlocks the entry point or by impersonating someone with proper access.
No matter the technique, tailgating attacks are any time an intruder gains physical access into a location they do not have permission to be in by taking advantage of someone with access in order to steal, compromise, or damage sensitive data.
Companies are often the most at risk for tailgating attacks as opposed to individuals. Criminals may specifically target businesses with lots of employees and multiple access points, as it can be easier for the attacker to blend in compared to small businesses.
On top of that, companies that have subcontractors working for them or frequently receive deliveries may be more at risk, as an attacker can attempt to impersonate a subcontractor or delivery worker.
Tailgating in social engineering attacks can look different on a case-by-case basis.
Common tailgating methods include:
- Hiding near a locked entrance
- Claiming to have forgotten their entrance credentials (key, pass, etc.)
- Impersonating a delivery person or subcontractor
- Asking someone to hold the door for them
- Simply following someone with access into the area
Because tailgating is the practice of taking advantage of employees and low-security entrances, businesses that already have strong physical and cybersecurity measures may be less at risk for these types of attacks. But it doesn’t protect them entirely, as a clever thief may be able to get an employee to let them in without ever thinking twice.
Tailgating vs. piggybacking: What’s the difference?

There's one main difference between tailgating and piggybacking. Tailgating is when an unauthorized person gains access to a physical location by following an authorized employee into the location without their knowledge, whereas a piggybacking attack is when an authorized person knowingly grants access to the attacker.
To put it simply, tailgating describes an attack that involves taking advantage of the authorized individual, and piggybacking is a coordinated attack where an authorized person helps the attacker gain access to an otherwise off-limits area and assists in the data breach.
How to help protect yourself from tailgating attacks: 7 protection tips
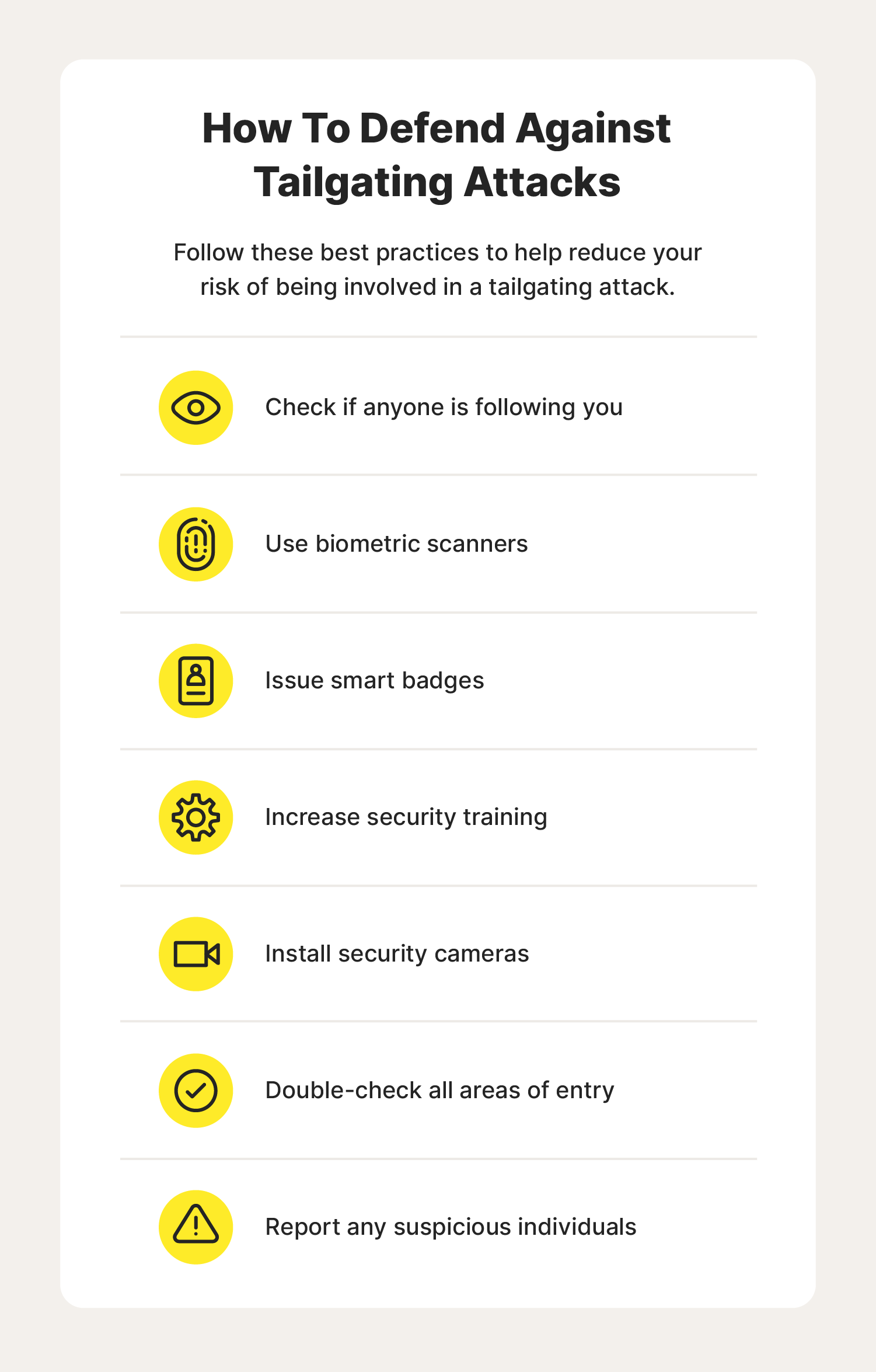
Now that you know what a tailgating social engineering attack is, you’re probably wondering what you can do to keep yourself safe and to prevent accidentally letting a tailgater into your place of work. Fortunately, there are safety measures you can follow to reduce the chances of a tailgating attack.
Check if anyone is following you
One of the easiest ways to better protect yourself from being taken advantage of in a tailgating attack is to be aware of your surroundings when entering a restricted area. You can do this by looking around before unlocking the entrance, closing the door behind you, and ensuring nobody tries to sneak through.
Use biometric scanners
Another tailgating security measure that can help stop tailgating attacks is the use of biometric scanners.
Examples of biometric security scanners include:
- Fingerprint scanners
- Facial recognition
- Heart rate sensors
- Voice recognition
- Iris recognition
Because biometric scanners work by scanning a unique physical feature of an authorized employee, they are much more secure than PINs or password security.
Issue smart badges
Smart badges or cards are another way that you can help increase physical security. These badges often use RFID technology and you can configure them to allow access to different locations, often by scanning or swiping them at the entrance.
That way, you can easily decide who is granted access to specific areas without needing to give out or retrieve a key whenever they want to make a change. By requiring smart badges or cards to enter restricted areas, you can help prevent unauthorized individuals from easily gaining access.
Increase security training
While many businesses now train their employees on the importance of cybersecurity and how to deter cyberthreats such as phishing or malware, many businesses lack the proper training related to physical cybersecurity attacks and tailgating security awareness.
By educating employees about tailgating in security trainings, you can reduce the risk of someone accidentally giving an unauthorized person access to sensitive information. On top of that, creating a specific security policy and a culture of cybersecurity can ensure everyone is on the same page when it comes to keeping restricted areas and information secure.
Install security cameras
In addition to tailgating cybersecurity training, installing security cameras is a great way to prevent a tailgating attack. Video surveillance can deter an attacker from breaching the premises and help catch them if they do so.
Some advanced video surveillance systems even use artificial intelligence and facial recognition to scan the faces of those on camera and compare them to an employee database of headshots, which can help flag unknown visitors and increase tailgate security.
Double-check all areas of entry
Because tailgating attackers rely on gaining access to an otherwise off-limits area, it’s important to always double-check all areas of entry to make sure they are secure. Something as simple as an unlocked window or a door that doesn’t latch on its own could be the reason an attacker gains access to a restricted area.
Report any suspicious individuals
If you ever come across a stranger or any suspicious behavior in your day-to-day activities, it's best to report the individual to the appropriate team members. That way, you can carry out your work knowing that you’ve taken the proper precautions to help keep your workplace secure and prevent tailgating attacks.
While the goal of a tailgating attack is often to get a hold of valuable data, it’s crucial that you do whatever you can to increase both your physical and data security. By prioritizing data protection and using good cyber hygiene habits, you can help stay cyber safe and reduce the risk of security threats, whether physical or digital.
FAQs about tailgating attacks
Continue reading to learn the answers to some commonly asked questions about tailgating attacks.
Why is it called tailgating?
Tailgating attacks earned their name due to their resemblance to “tailgating” when driving. In driving, tailgating is when a driver follows closely behind another vehicle. In a tailgating attack, an attacker may gain unauthorized access by following closely behind someone that has access to a restricted area.
What are the dangers of a tailgating attack?
Tailgating attacks are dangerous because once the attacker breaches the restricted area, they may be able to steal confidential information, damage private property, or install different types of malware onto devices.
Who is at risk of tailgating attacks?
Large businesses with physical locations are most at risk of tailgating attacks, especially if they have multiple employees and entrance points. Attackers may also take advantage of companies that hire subcontractors or frequently receive shipments by impersonating a subcontractor or delivery driver to sneak in.
Editorial note: Our articles are designed to provide educational information for you. They may not cover or protect against every type of crime, fraud, or threat we write about. Our goal is to increase awareness about Cyber Safety. Please review the complete Terms during enrollment or setup. Remember that no one can prevent all identity theft or cybercrime, and that LifeLock does not monitor all transactions at all businesses. The Norton and LifeLock brands are part of Gen Digital Inc. For more details about how we create, review, and update content, please see our Editorial Policy.





Want more?
Follow us for all the latest news, tips, and updates.