Public vs. private IP address: Understanding the differences
IP addresses locate devices on the internet, guiding data to and from the right destination. But to help you connect securely and efficiently, some IP addresses are public while others are private. Discover the differences between public vs. private IP addresses, and how even your public IP can be kept private with the help of a VPN.

What is a public IP address?
A public IP address is a unique identifier assigned by an Internet Service Provider (ISP) to a device, such as a router or server, allowing it to communicate over the internet. These IP addresses are globally unique and publicly accessible, enabling data exchange between your network and external systems via TCP/IP protocols.
But because public IP addresses are visible on the internet, they can be used to trace a device's approximate geographic location. To help protect the privacy of individual network users, multiple devices within a local network often share a single public IP address hosted by the router, utilizing private IP addresses to communicate internally within the local network.
What is a private IP address?
A private IP address, also known as a local IP address, is assigned by a router to devices within a home, office, or public Wi-Fi network. Unlike public IP addresses, which are exposed on the internet, private IPs function only within the local network. Since they don’t need to be globally unique, the same private IP ranges can be used across different networks without conflict.
However, each device on a network receives a distinct private IP, allowing the router to manage data transfers effectively. This enables LAN connections between network devices and ensures that external traffic arriving via the public IP address is forwarded to the correct individual computer, phone, or IoT device.
5 key differences between a public and private IP address
The difference between public and private IP addresses isn’t just their visibility. While both types play a role in data transmission, they serve distinct purposes, operate in different environments, and have different technical parameters.
Public IP address |
Private IP address |
|---|---|
Connects to the global internet |
Connects to your local network |
Enables website access and communication across networks |
Enables communication between devices on the same network |
Wide range of numerical addresses |
Narrow range of addresses |
Traceable to user or ISP |
Limited traceability |
Low security |
Higher security |
Here’s a deeper dive into the five main differences between public and private IP addresses:
1. Scope
Public IP addresses are global in scope, allowing you to connect directly to other public IP addresses across the entire internet, including websites and cloud resources. Private IP addresses, on the other hand, are limited to local networks and are only visible within that network. While anyone can see your public IP address, only those connected to your local network can see your private IP address.
2. Purpose
Public and private IP addresses serve different networking purposes. A public IP is globally unique and enables devices to communicate over the internet, directing internet traffic to the correct server or local network. In contrast, a private IP is used within local networks, ensuring secure internal communication while preventing direct exposure to the wider internet. This separation helps manage security, routing, and network efficiency.
3. Range
To avoid conflicts, public and private IP addresses use different address ranges — continuous blocks of IP addresses that can be assigned to devices within a network. ISPs receive large batches of public IP addresses from regional organizations such as the American Registry for Internet Numbers (ARIN). They allocate these public IP addresses to customers (such as homes, businesses, or data centers) for their internet-facing devices.
Private IP ranges reserved for local networks are assigned by your router from a limited range set by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) and can be reused across multiple networks without conflict, as they aren’t visible beyond the local network. Private IPs can be distributed dynamically via DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol), ensuring each network device receives a unique address while optimizing address space usage.
Here’s what the specific IP address ranges mean for a private IP address:
10.0.0.0 – 10.255.255.255
This range allows for over 16 million IP addresses and is often used in enterprise networks or large organizations that have thousands of devices used in their local network.
172.16.0.0 – 172.31.255.255
Known as the 172.16/12 block, this range offers about 1 million unique addresses and is typically used in medium-sized networks such as schools, universities, and businesses.
192.168.0.0 – 192.168.255.255
This range supports about 65,000 IP addresses and is primarily used in home and small office networks, since they don’t require access to a wide range of unique addresses.
4. Traceability
Because public IP addresses are globally unique and accessible across the entire internet, they are traceable to a specific user or organization that has been assigned them. This can reveal information like your geographic location, identity, and associated online activity unless you take steps to hide your IP address.
In contrast, private IP addresses do not appear publicly, offering a higher level of privacy by making it more difficult to identify or track devices or individual users on a local network by third parties. However, activity linked to private IP addresses can still be tracked from within the local network
One of the many benefits of using a VPN like Norton VPN is that it helps limit your traceability on any network by routing all of your internet traffic through a VPN server via an encrypted tunnel, hiding your online activity, and obscuring your public IP address.
5. Security
Because devices assigned a public IP address are directly accessible from the internet, they’re more exposed to security risks such as malware, packet sniffing, and session hijacking. In contrast, unless they’re exposed to the internet via port forwarding, private IP addresses are typically shielded by software firewalls installed on routers, making them much more difficult for hackers to target.
How to check your IP address to see what type you’re using
To find your public IP address, simply search “What is my IP address?” on Google, and it will display your public IP in an info box toward the top of the results page. But to confirm that your device is also using a private IP address, you’ll need to dig into your device settings.
If the local IP address you see listed is different from the IP visible to Google and other web services, you’ll know that your device is partly obscured behind a private IP address. But if you’re looking for ironclad online privacy, and want to mask your public IP address too, you’ll need a VPN.
Here’s how to check your IP address on Windows and Mac computers:
Checking your IP address on Windows
Windows 11:
1. Open Windows Settings and select Network & internet, then Wi-Fi.
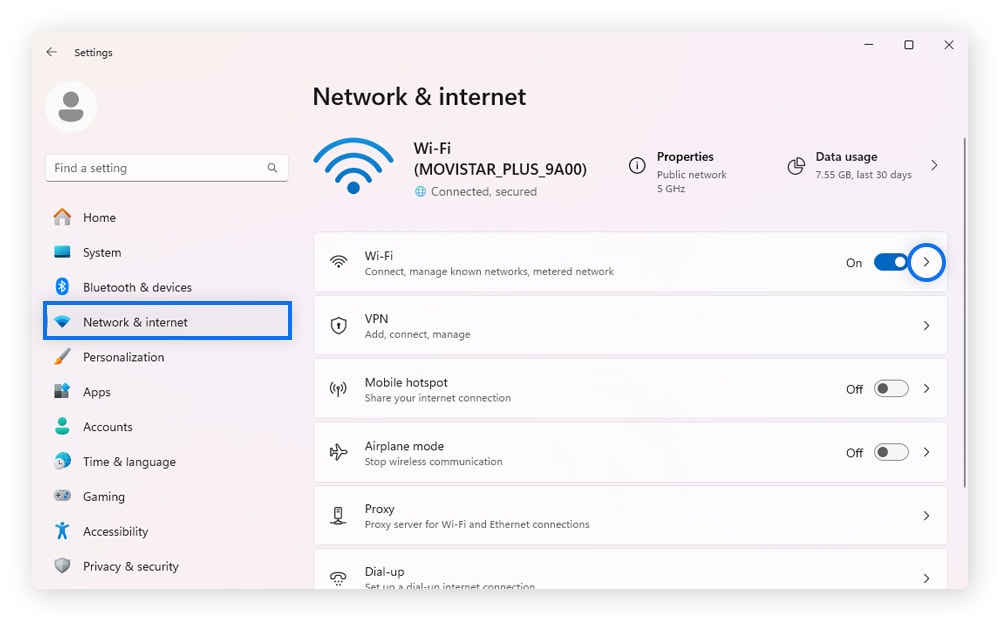

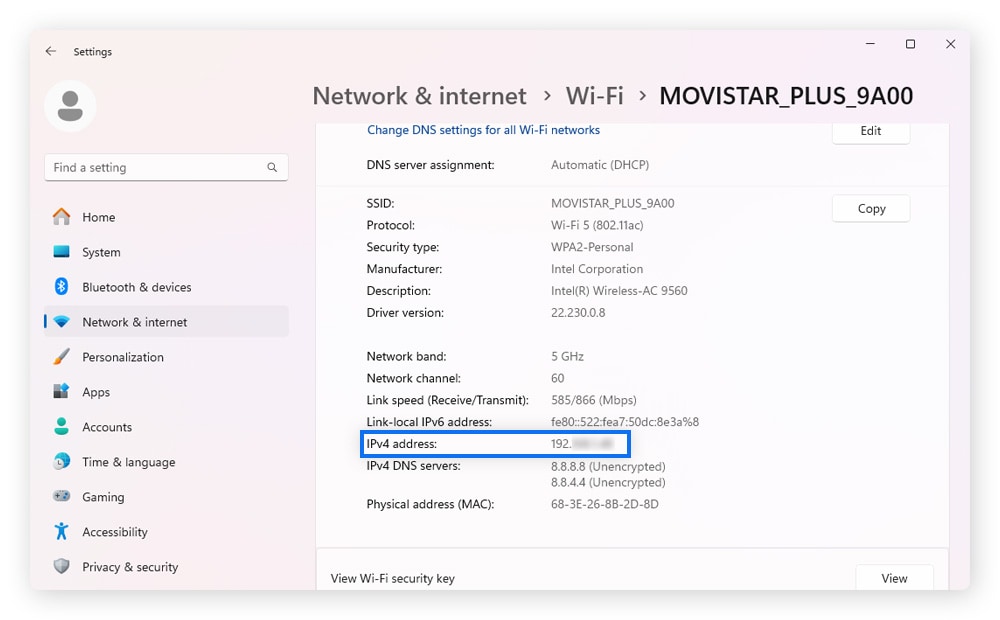
2. Choose your network, then scroll down and find your IPv4 address.

Windows 10:
1. Open Windows Settings and select Network & internet.
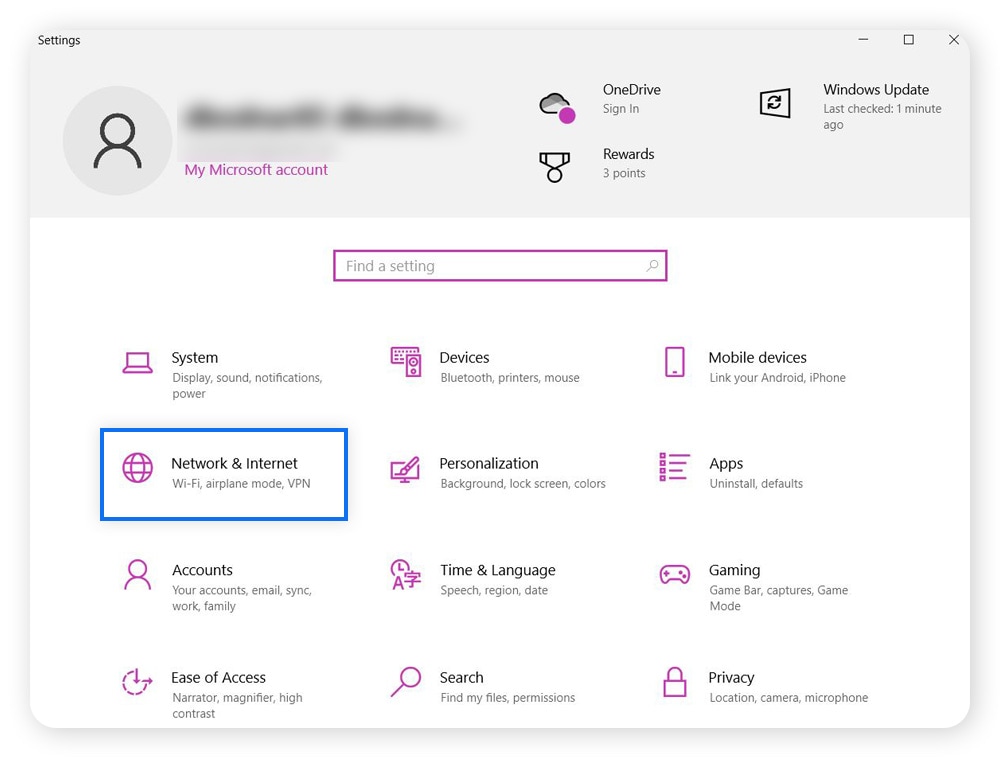

2. Go to Wi-Fi and choose your network
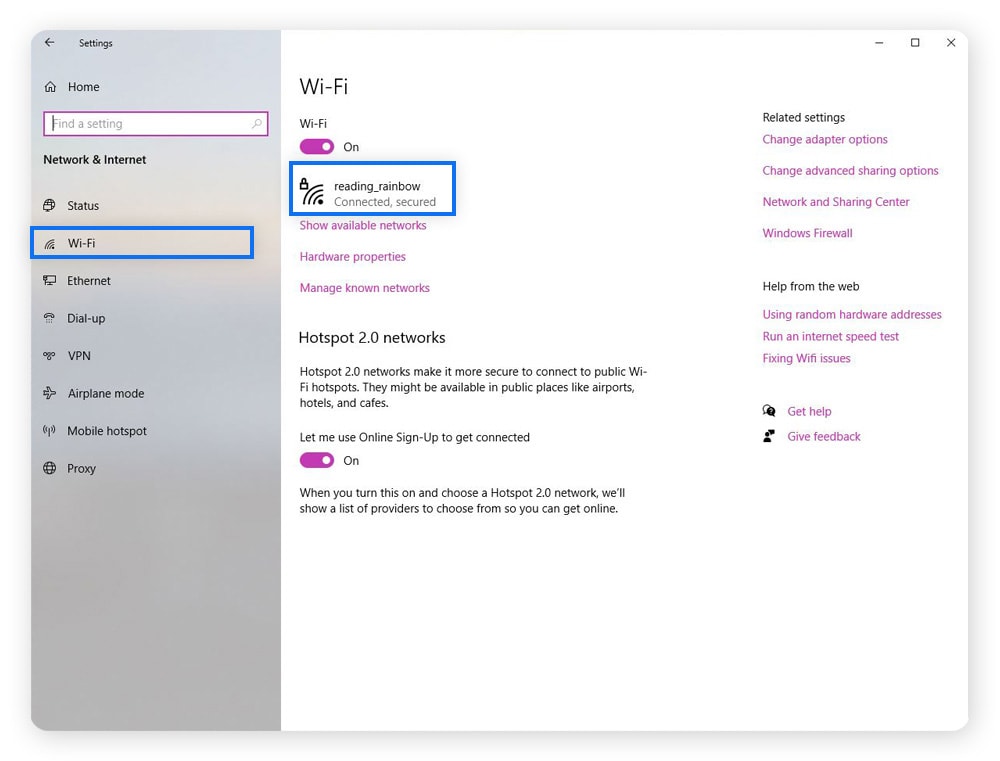

3. Scroll down to Properties, where you’ll find your local IP address listed under IPv4 address.
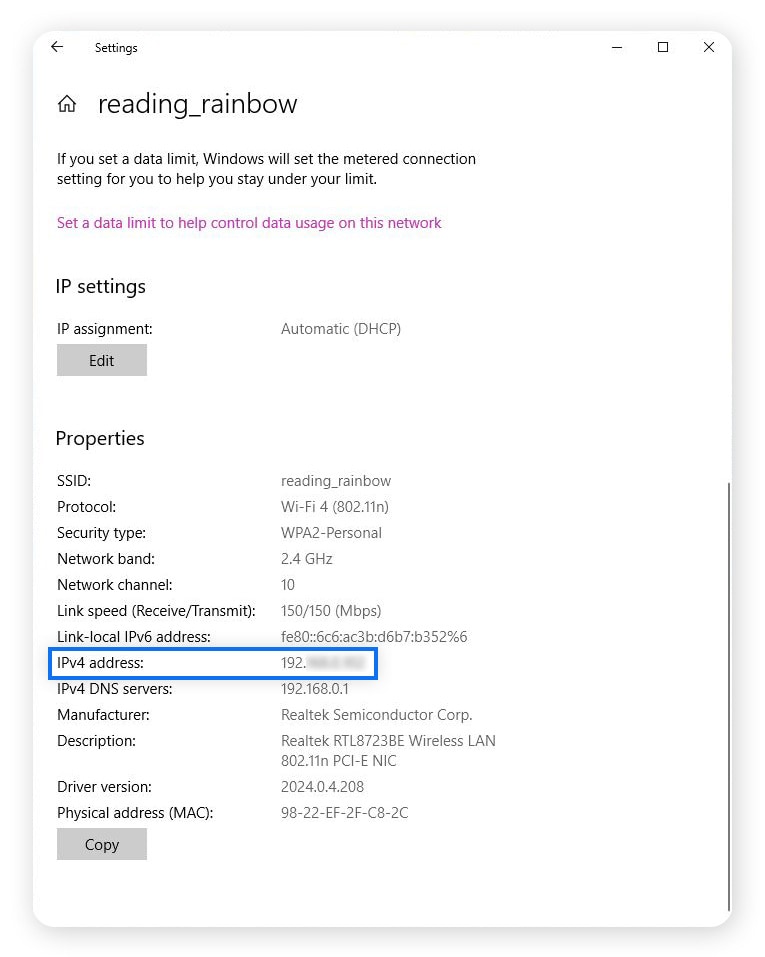

Checking your IP address on Mac
- Go to System Settings, then Wi-Fi, and ensure your network is correct
- Select Details and scroll down to view your IP address.
Hide your IP address with Norton VPN
Worried about your every move being tracked online? Hiding your public IP address with a trusted VPN like Norton is one of the best ways to help protect your internet privacy.
Norton VPN helps secure your internet connection with bank-grade encryption and obscures your IP address, stopping third parties from tracking your activity or eavesdropping on sensitive information. And with thousands of global VPN servers spread across five continents, you can customize your virtual IP location for maximum privacy, performance, and accessibility.
FAQs
Can you have both a public and a private IP address?
Yes, you can have both a public and a private IP address, and if you’re connected to a local private network, you almost certainly already do. The public IP address connects your network to the internet, while private IP addresses are used by devices within your local network.
How much does a public IP address cost?
The cost of a public IP address depends on your Internet Service Provider (ISP) and the type of service you need. Typically, dynamic public IP addresses are included in most internet plans at no extra cost. However, static public IP addresses can incur an additional fee, usually ranging from $5 to $30 per month, but they can cost a little less or considerably more.
Is there a difference between a public and an external IP address?
There is no difference between a public and an external IP address; they are two different terms for the same thing. Both refer to the unique IP address assigned by an ISP to a router or server, allowing it to communicate directly with other devices over the internet.
Editorial note: Our articles provide educational information for you. Our offerings may not cover or protect against every type of crime, fraud, or threat we write about. Our goal is to increase awareness about Cyber Safety. Please review complete Terms during enrollment or setup. Remember that no one can prevent all identity theft or cybercrime, and that LifeLock does not monitor all transactions at all businesses. The Norton and LifeLock brands are part of Gen Digital Inc.








Want more?
Follow us for all the latest news, tips, and updates.