Malware: What it is, how it works, and how to get rid of it
Malware is malicious software designed to infiltrate or harm computers, networks, and other systems. Find out more about what malware is exactly, how this evolving threat works, and how you can use Norton 360 to identify and remove malware, and help prevent future infections.

Since the 1980s, security researchers have identified more than one billion malicious programs and potentially unwanted applications (PUAs). That’s a lot of dangerous software, and it highlights the importance of cybersecurity. Learn how malware works, the different varieties of malware, and malware attack prevention tips that can help keep your personal information and devices safer.
What is malware?
Malware is malicious software designed to infiltrate, disrupt, or damage a computer or network, usually without the owner’s knowledge. Cybercriminals or other bad actors use malware to hijack a device and damage or spy on its systems. This can result in your data being monitored, corrupted, stolen, or deleted.
Common types of malware
There are many different kinds of malware lurking online ranging from traditional computer viruses to more sophisticated worms, Trojans, and fileless malware. Here are some of the most common types of malware found in the wild:
- Viruses: Dangerous pieces of code designed to spread from one computer to another, damaging files or stealing data along the way, viruses are often triggered by opening an infected link, installing malicious software, or opening a PDF that contains a virus.
- Worms: This form of self-replicating malware spreads independently across devices and networks. Unlike viruses, worms don’t need to attach themselves to a host program to propagate.
- Rootkits: A rootkit is a stealthy kind of malware that grants cybercriminals remote access to your device, enabling them to manipulate your system, conceal malicious activities, and access your personal information.
- Spyware: This type of malware secretly tracks and records your activity to learn more about you. Spyware like keyloggers or Pegasus may grant hackers access to your financial accounts or other sensitive personal data.
- Adware: Malware that displays unwanted advertisements is known as adware. It can also collect data on your browsing habits to deliver targeted ads or sell it to third parties.
- Ransomware: This kind of malware can lock, encrypt, and hold your data hostage. Using ransomware, cybercrooks can threaten to destroy your personal files unless you pay them money.
- Fileless malware: By using legitimate system tools and processes, fileless malware executes attacks without leaving behind traditional files, making it harder to detect.
- Trojans: Disguised as a legitimate program or application, Trojans can spy on victims, steal data, or infect other programs.
- Scareware: Malware designed to frighten you with fake warnings and trick you into downloading bogus security software or sharing personal information is known as scareware.
- Keyloggers: By secretly tracking everything you type on your keyboard, keyloggers can harvest sensitive information such as passwords and account information.
How do you get malware?
Hackers infect devices with malware by exploiting technical vulnerabilities and using social engineering tricks to spread infected links, files, or email attachments. Often relying on phishing and similar techniques like smishing, malware spreads onto victims’ devices when they click on an infected asset.
While some people inadvertently download malware from the internet, hackers can also use flash drives or other removable storage devices to spread malware, a method that can bypass certain network-based security measures. To stay safer, never insert unfamiliar storage devices into your computer.
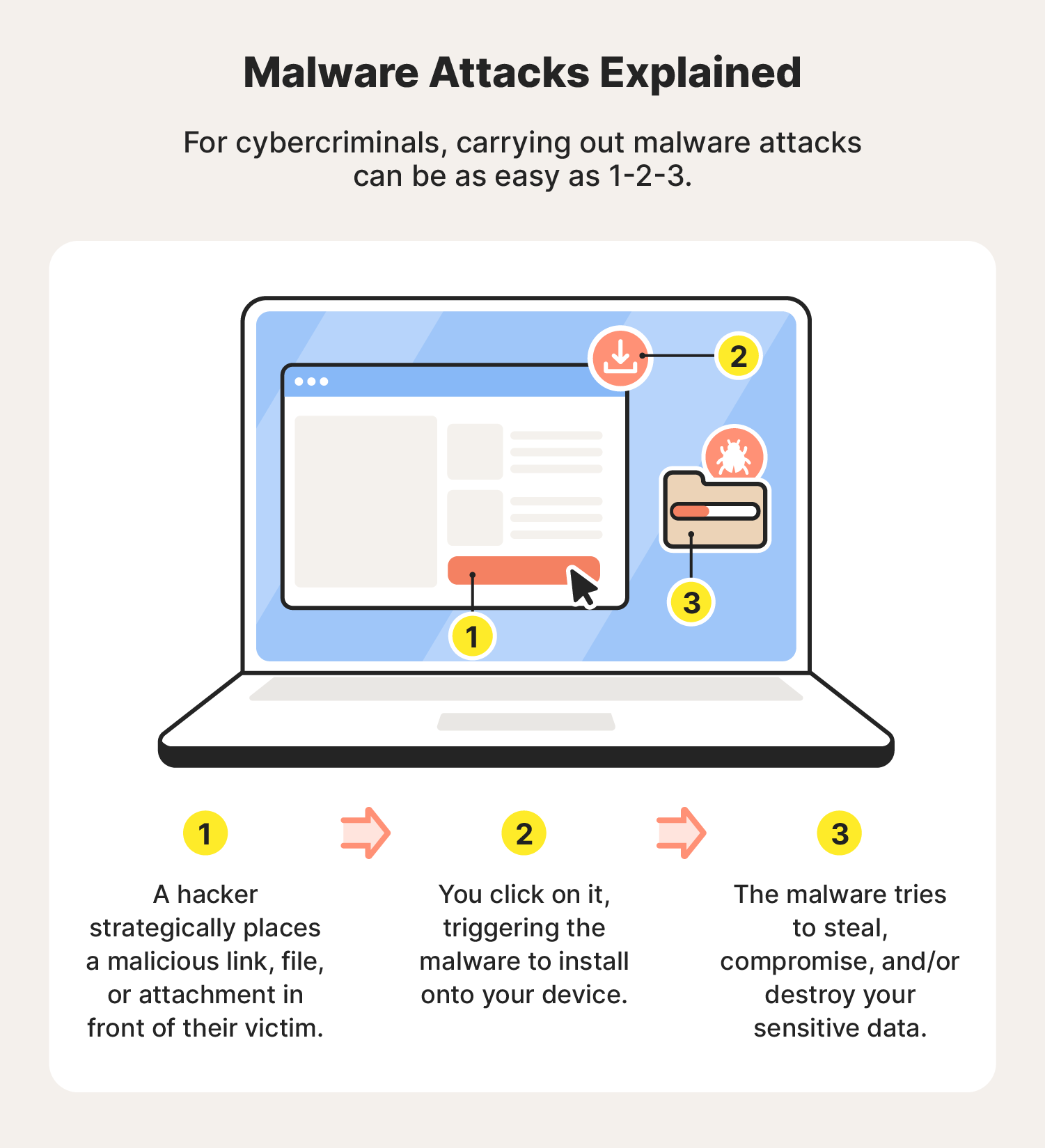

What is malware used for and why is it dangerous?
Malware is used by cybercriminals to harm, exploit, or infiltrate systems with the aim of stealing sensitive data, spying on individuals or organizations, disrupting operations, gaining unauthorized access, or holding systems hostage via various forms of ransomware.
Here’s a closer look at what malware can be used for:
- Stealing data: Hackers deploy malware to steal sensitive data, and then exploit it or sell it to the highest bidder.
- Extortion: After encrypting and keeping an individual’s data locked, hackers can ransom it, demanding payment in exchange for a decryption key.
- Corporate espionage: Some companies employ hackers to steal economic secrets, destroy research, or undermine their competitors.
- Sabotage: Whether for political or personal reasons, destroying data and compromising systems is a common way malware is used.
- Cryptojacking: Mining cryptocurrency requires a lot of processing power. Cryptojacking malware can siphon off processing power from other people’s devices without them ever knowing it.
- Cyberwarfare: Malware can be used to cripple government infrastructure, steal or corrupt intelligence, and even destroy physical infrastructure.
How to prevent malware attacks
Preventing malware attacks requires vigilance and proactive measures. Using antivirus software, avoiding suspicious links and downloads, and keeping your systems and applications current can dramatically reduce your attack surface, making it much harder for malware to successfully target you.
Here are the most important things you can do to help prevent malware from infecting your device.
- Update your operating system regularly. Check your devices for software updates at least once a week and install any updates immediately. Failing to do so can leave you exposed to zero-day exploits that can compromise your devices and network.
- Don’t click suspicious links or attachments. Never click on unknown links or download attachments from untrusted sources.
- Get an ad blocker. Cyberthieves may use pop-ups infected with spyware and/or adware to illegally track your network activity and install malware onto your device. Use an ad blocker to help get rid of pop-ups and prevent these kinds of malware attacks.
- Use a firewall. A firewall adds a barrier between your device and potential online threats by monitoring and blocking suspicious internet traffic.
- Be cautious on public Wi-Fi: Use a VPN when connecting to unsecured public Wi-Fi to encrypt your data and prevent hackers from intercepting it.
- Monitor your network activity. Regularly check your network for unusual activity, such as unknown devices or unfamiliar IP addresses using a lot of bandwidth. These could be signs of a malware infection or an attempted data breach.
- Download antivirus software. Trusted antivirus software, like Norton 360 Standard, helps provide your devices with 24/7 protection against malware attacks threatening your Cyber Safety.
How to check for and get rid of malware
The easiest way to find and remove malware from your device is to perform a malware scan with a dedicated malware removal tool like Norton 360 Standard. If you notice signs of malware, such as your computer crashing or a sudden uptick in spam emails, it’s time to check whether your device has been infected.
On a PC or Mac
The steps for removing malware on a computer are similar whether you’re using a PC or a Mac (yes, Macs can get malware too):
- Disconnect from the internet.
- Turn on Safe Mode.
- Look for malicious apps in the activity monitor.
- Use a malware scanner to find and remove these programs.
- Make sure your browser home page is correct.
- Clear the cache.
On an Android phone
To remove malware from an Android device, follow these steps:
- Disconnect from the internet.
- Turn off the device.
- Reboot in Safe Mode.
- Delete all suspicious apps.
On an iOS device
This is how you get rid of malware on an iPhone or iPad:
- Delete any suspicious apps.
- Clear your app and browsing caches.
- Restart your iPhone.
- Install the latest iOS.
- Restore your device from a backup.
If all else fails, you may need to reset your phone to factory settings, or wipe your computer’s hard drive.
Start protecting your devices today
Malware threats are evolving constantly. Thankfully, Norton uses powerful, heuristic malware-detection technology to help find and remove malware, blocking millions of cyberthreats every day.
Norton 360 provides comprehensive real-time protection against malware, ransomware, and hacking while helping to keep your online activity private with a powerful VPN. With multiple layers of robust protection, Norton’s suite of cyber safety tools helps keep you secure and in more control of your digital life.
Editorial note: Our articles provide educational information for you. Our offerings may not cover or protect against every type of crime, fraud, or threat we write about. Our goal is to increase awareness about Cyber Safety. Please review complete Terms during enrollment or setup. Remember that no one can prevent all identity theft or cybercrime, and that LifeLock does not monitor all transactions at all businesses. The Norton and LifeLock brands are part of Gen Digital Inc.





Want more?
Follow us for all the latest news, tips, and updates.