Hardware acceleration: How to turn it on or off in Chrome and Firefox
If your browser feels slow and you’ve tried all the well-known methods to fix it, enabling hardware acceleration might be the answer to your problem. Hardware acceleration delegates specific tasks to certain computer components, which can help speed up a sluggish browser. Learn how to turn on hardware acceleration, and get a specialized optimization app to help revitalize your PC and keep it running like new.

What is hardware acceleration?
Hardware acceleration is the process of offloading specific tasks from the central processing unit (CPU) to specialized hardware components designed to handle them more efficiently. This allows the CPU to focus on other essential processes, improving overall system performance and efficiency.
The most common example of hardware used for acceleration is your computer’s graphics processing unit (GPU), often referred to as a graphics card. Particularly sophisticated machines may also use a tensor processing unit (TPU) or a neural processing unit (NPU), for tasks like machine learning and AI workloads.
When considering what hardware acceleration is and how it works, imagine the CPU is a Swiss Army knife. Both can handle a wide variety of tasks, but when you need precision cuts, you might prefer to use a chef’s knife. In the case of a PC, that chef’s knife might be a GPU.
Many different tasks benefit from hardware acceleration, including:
- Web performance optimization: When dealing with a slow internet connection, hardware acceleration can improve the responsiveness of web browsing by offloading rendering and video playback tasks to the GPU. This frees up the CPU to handle JavaScript execution and other logic, making sites feel faster.
- Audio processing: Audio-related tasks are usually delegated to a digital signal processor or a dedicated sound card to help with tasks like equalization, enabling a freer CPU workload.
- Video encoding and decoding: A codec (coder-decoder) processes millions of pixels per frame — intensive work for a CPU also handling other processes. Encoding and decoding may instead be delegated to a GPU or video processing unit (VPU) under hardware acceleration.
- AI data processing: AI data processing, drawing, and modeling can be demanding on a general-purpose CPU. These are ideally offloaded to a GPU, TPU, or NPU, depending on the setup.
How does hardware acceleration work?
Hardware acceleration enables programs to leverage hardware components designed for specific tasks. This offloads particularly heavy tasks to these specialized components, so the CPU is freed up to handle more basic computation.
For example, many video processing tasks (like texture rendering and lighting effects) are delegated to your GPU when you play a computer game. This lets the CPU handle things like overall game logic and interpreting player inputs, which can boost overall performance.
Hardware acceleration happens behind the scenes across diverse types of software, often without you realizing it. Once enabled, it typically works automatically. That’s why, when gaming, you generally don’t need to worry about which libraries your GPU is using or how its resources are being managed. You can just focus on playing while the game dispenses instructions to your hardware under the hood.
How to turn on hardware acceleration
Hardware acceleration is available in certain programs and most modern web browsers. Browsing has evolved a lot since the early days of the web when pages were mostly text based. Now, there are videos, animations, 3D graphics, and other rich media — hardware acceleration helps provide a smooth and responsive experience.
Here’s a quick guide to enabling hardware acceleration in some of the most popular browsers.
In Chrome
1. Click the three-dots in the top right-hand corner, then click Settings.
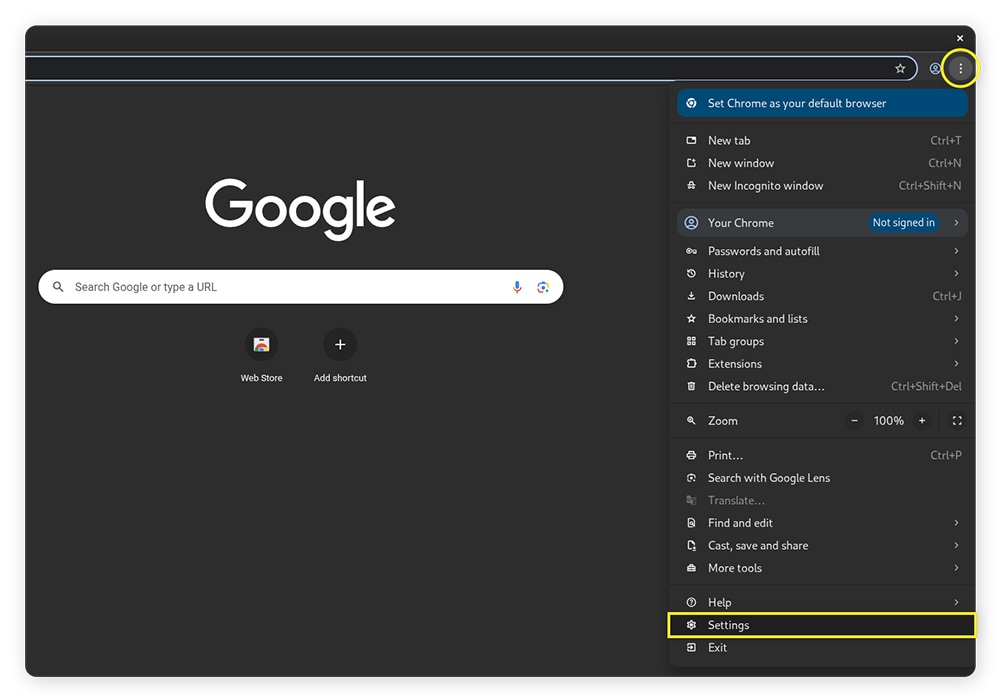

2. Click System on the left-hand side of the new screen, then toggle on Use graphics acceleration when available.
3. Restart the browser to apply the changes and enable hardware acceleration in Chrome.
In Firefox
1. Click the three lines in the top right, then click Settings.
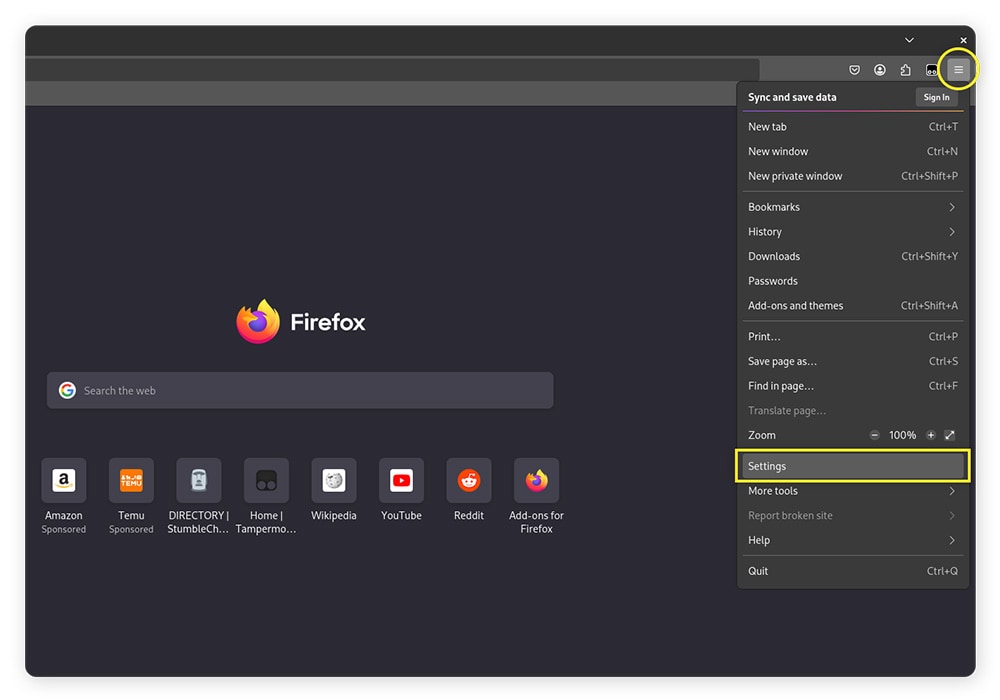

2. Scroll down until you find Performance, then check Use recommended performance settings and check Use hardware acceleration when available (if it’s not already checked).
3. Restart the browser to apply the changes and enable hardware acceleration in Firefox.
In Safari
There’s no need to worry about turning hardware acceleration on when using Safari on your Mac, as it has been automatically enabled since macOS Catalina was released in 2019, with no way to toggle the setting off.
How to turn off hardware acceleration
Turning hardware acceleration off on your internet browser is as simple as turning it on. Just find the relevant option in the settings menu and disable it.
There are several reasons you might want to turn off hardware acceleration. For example, if your PC has low-end hardware, you may actually see a performance decrease with hardware acceleration enabled. Also, if your GPU drivers are buggy, some elements may not function correctly with hardware acceleration enabled.
If you think it might be slowing down your computer, here’s how you can disable hardware acceleration in your browser.
In Chrome
- Click the three-dots in the top right-hand corner, then click Settings.
- Click System on the left-hand side of the new screen, then toggle off Use graphics acceleration when available.
- Restart the browser to apply the changes and disable hardware acceleration in Chrome.
In Firefox
- Click the three lines in the top right, then click Settings.
- Scroll down until you find Performance, then uncheck Use recommended performance settings and uncheck Use hardware acceleration when available.
- Restart the browser to apply the changes and disable hardware acceleration in Firefox.
Benefits of enabling hardware acceleration
Hardware acceleration is generally beneficial, allowing your computer to utilize each hardware component to its full potential for better browsing performance. By offloading tasks like rendering websites and media to components like the GPU, it frees your CPU up for other tasks, which can help speed up your computer.
Here are more details about the benefits of enabling hardware acceleration:
- Faster processing speeds: By delegating difficult tasks to components designed specifically to perform them, hardware acceleration leaves the CPU freer to process other tasks. This can result in faster overall performance.
- Improved energy efficiency: By assigning tasks to hardware like integrated GPUs, less overall power is consumed. This can help preserve battery when using a laptop or other battery-powered device.
- Reduced heat and noise: If your CPU is handling lots of difficult tasks at once, it can overheat. This could potentially result in thermal throttling and cooling fans spinning faster, reducing performance and creating noise. Delegating some tasks to other components can help keep temperatures and noise levels down.
- Enhanced visual quality: When watching videos or animations, giving the GPU tasks like processing or decoding can help generate a smoother playback experience with less jitter and frame loss.
Downsides of enabling hardware acceleration
Depending on your hardware setup, hardware acceleration can also result in performance decreases. While it usually results in a better experience, bugs or compatibility issues can degrade your experience.
Here are more details about the downsides of enabling hardware acceleration:
- Crashes and instability: If your hardware drivers are buggy or outdated, enabling hardware acceleration may mean you experience jitters or crashes when performing certain tasks.
- Software compatibility issues: If you’re using a browser to remotely control another desktop, hardware acceleration can be a hindrance. Offloading the frames to another component could cause scheduling delays that result in input lag.
- Higher resource contention: It can increase overall resource usage, including read/write operations. If your system has limited resources, this can result in a poorer user experience.
Keep your browser up to speed with Norton Utilities Ultimate
Hardware acceleration is a useful feature that can boost performance, but not always. Sometimes, it takes smarter tools to get the most out of your PC. Norton Utilities Ultimate can help revitalize your system in ways that manual fixes can’t or would otherwise take a considerable amount of time to achieve. It cleans browser data, removes system junk, turns off background programs, and more — so you can enjoy a clutter-free digital life and speeds you deserve.
FAQs
Is hardware acceleration necessary?
No. Although it’s useful, hardware acceleration isn’t necessary. Your CPU can typically handle all the computing tasks required to browse the internet, it just might not do them as quickly as when it’s supported by specialized components.
When should I use hardware acceleration?
Generally, it’s good to use hardware acceleration whenever it’s available. Leveraging specialized hardware, like a GPU for graphics processing, lets your computer handle specific tasks more efficiently.
Why is hardware acceleration causing issues on my browser?
This can come down to a number of issues, including buggy or outdated drivers, or high resource usage. If you’re experiencing issues, try turning hardware acceleration off and using a dedicated PC cleaning tool like Norton Utilities Ultimate to optimize your device and keep it performing at its best for longer.
Editorial note: Our articles provide educational information for you. Our offerings may not cover or protect against every type of crime, fraud, or threat we write about. Our goal is to increase awareness about Cyber Safety. Please review complete Terms during enrollment or setup. Remember that no one can prevent all identity theft or cybercrime, and that LifeLock does not monitor all transactions at all businesses. The Norton and LifeLock brands are part of Gen Digital Inc.






Want more?
Follow us for all the latest news, tips, and updates.