Why is my internet so slow? 11 common causes and how to speed it up
Fed up with web pages freezing, sluggish downloads, and the endlessly spinning loading icon? Learn what causes a slow internet connection and get tips to help fix each issue. Or, save yourself the hassle and let Norton experts help get your internet running smoothly again.

If you’re frustrated with a slow internet connection, you’re not alone. According to a recent report, 20% of Americans are unhappy with the speed of their internet connection.
If you’re among them, this guide explains 11 common reasons for a slow internet connection and offers practical tips to get your connection running at full speed. We've got you covered, from optimizing router placement to managing network congestion.
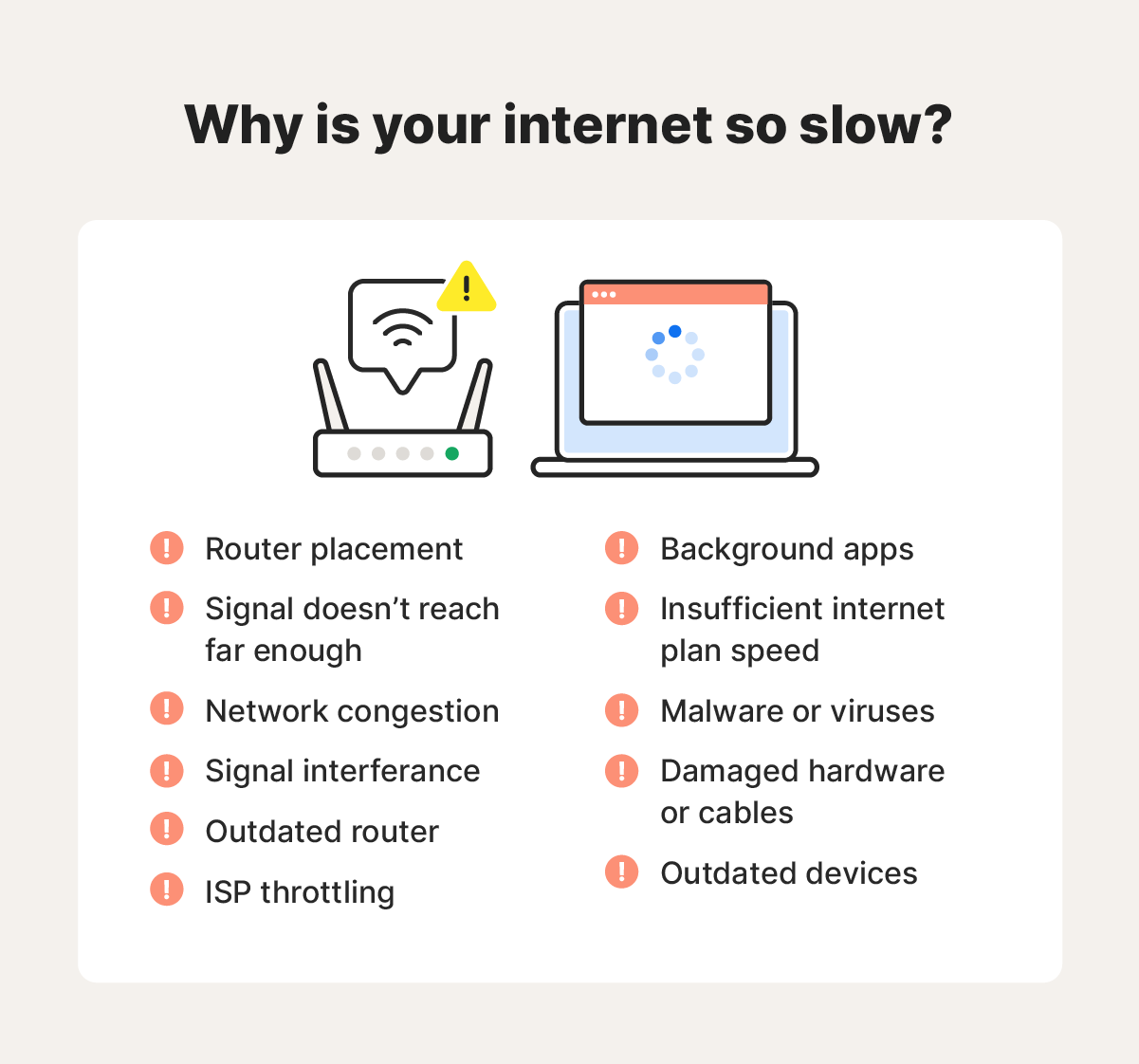

1. Router placement
Router placement is critical for ensuring your Wi-Fi signal is strong and consistent throughout your home. For example, placing your router too low to the ground or between thick walls can interfere with the signal and lead to slow internet speeds.
2. The signal doesn’t reach far enough
If your home is large, you might experience slower internet speeds or a weak connection in rooms farther from the router. Moving the router to a more central location or moving the affected device closer to the router can help, but these aren’t always practical solutions.
A Wi-Fi extender (or repeater) can help solve this issue by increasing the range of your Wi-Fi network. Wi-Fi extenders work by receiving Wi-Fi signals from your router and then re-transmitting them to cover hard-to-reach places around your home.
3. Network congestion
Network congestion occurs when data packet traffic exceeds your network's capacity, resulting in a slower connection. Think of it like a traffic jam — when too many cars are on the road, everyone must slow down.
Multiple devices connected to a network can cause network congestion and slow data, especially if they’re using a lot of bandwidth. Streaming, video calls, Internet of Things (IoT) smart devices, and online gaming are often the worst offenders for bandwidth usage.
4. Signal interference
Signal interference can be caused by other devices disrupting your W-Fi network, which can slow down the speed. For example, electronics like microwaves and Bluetooth devices can interfere because they operate at a similar frequency to many W-Fi networks.
5. Outdated router
Wi-Fi routers age over time, leading to reduced performance and slower speeds. Many experts recommend replacing your Wi-Fi router every three to five years to ensure optimal performance.
These are some key signs your Wi-Fi router is outdated and may need to be replaced:
- Firmware updates have stopped: Manufacturers eventually discontinue firmware updates for older routers, which can negatively impact router security and performance.
- Overheating: While some warmth is normal, a router that feels hot to the touch could signal that the internal components are overheating, affecting your connection.
- Frequent disconnections: If your devices randomly disconnect from Wi-Fi and disrupt your connection, you may need a newer router.
- Random rebooting: Frequent, unexpected reboots are another sign of an outdated router.
6. ISP throttling
ISP throttling is when your internet service provider (ISP) deliberately slows your internet speed to manage total network bandwidth usage. ISP providers do this for various reasons, including to regulate traffic, enforce data caps, and deal with network congestion.
In lots of cases, ISP throttling isn’t noticeable. However, at times, you may experience performance issues like buffering and lagging when your network is being throttled.
7. Background apps
Apps or programs left running in the background can affect network performance even when you’re not actively using them. These apps continue to execute processes — like receiving notifications, installing software updates, or tracking location — even while not in use. This can use up bandwidth and slow your internet speed.
8. Insufficient internet speed
If your internet plan’s guaranteed speed isn’t fast enough for your online activities, you may experience performance issues, especially during data-intensive tasks such as streaming or gaming.
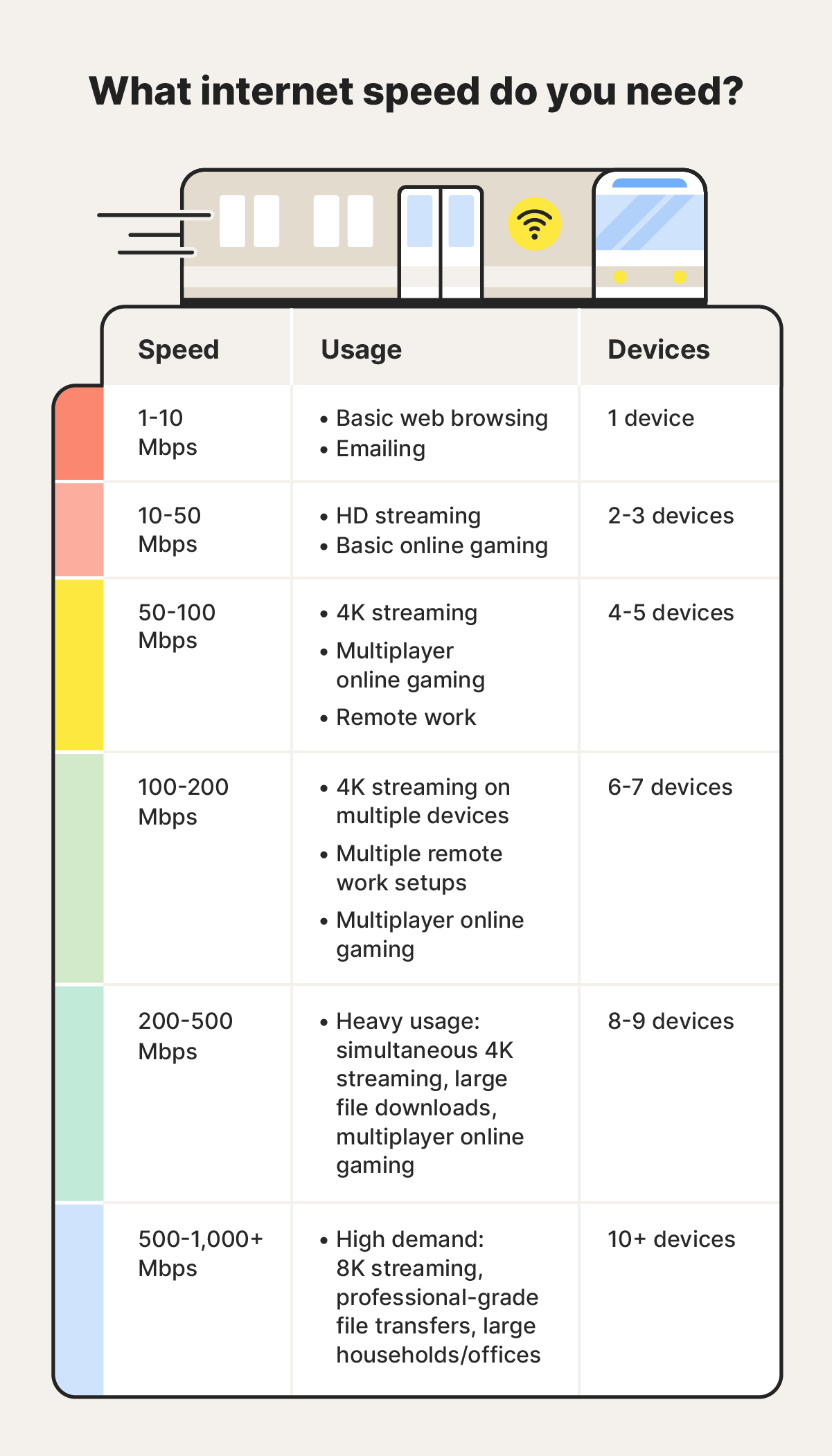
Internet speed is measured in megabits per second (Mbps). The most popular fiber internet speed in 2024 was 200 Mbps, which should theoretically allow for heavy usage on simultaneous devices. However, the ideal speed for you depends on how many users are on the network, the total number of connected devices, and what the network is used for.

9. Malware or viruses
If you’re experiencing persistently slow internet, it might be a sign of malware or viruses on your connected devices. These malicious programs often consume a significant amount of bandwidth as they transmit data, potentially causing noticeably slower speeds.
If your router has malware, it can affect the internet speed of all connected devices. To check if your router may be infected, log in to your router’s administrative interface and review the list of connected devices. If you notice any unfamiliar device names, disconnect them from your network immediately.
10. Damaged hardware or cables
Faulty hardware, cables, or other equipment can impact your internet speed. For example, a bent or frayed Ethernet cable can disrupt your connection, while a damaged modem or router may hamper network performance.
11. Outdated devices
Outdated devices actively using your network can slow down internet speeds for other connected devices. While they don’t take up more bandwidth, older devices may struggle to handle modern internet speeds and create a bottleneck.
How to increase internet speed
In addition to troubleshooting specific issues, there are other ways to boost your internet speed by optimizing both your router and the devices connected to your network.
Here’s what you can do:
1. Disconnect devices you’re not using
Disconnect from your network devices that you’re not currently using, especially those running background apps. This prevents unnecessary bandwidth consumption, allowing faster speeds for the devices in use.
2. Use an Ethernet cable
If your Wi-Fi is slow, plug your device directly into the router using an Ethernet cable. A wired connection typically offers faster speeds since it removes any interference caused by wireless signal transmission. Use a short, high-quality cable for the best performance.
While an Ethernet cable is beneficial for stationary devices like computers and game consoles, it won’t solve connectivity issues for mobile devices like phones.
3. Set up a guest network for visitors
Creating a guest network allows you to manage bandwidth to ensure your primary devices maintain optimal performance. It also helps secure your Wi-Fi and limits how many devices use your main password, boosting your network and device security.
4. Restart your router
Sometimes, restarting your router is all you need to get your internet running smoothly again. While it doesn’t directly increase speed, rebooting clears the cache and refreshes the connection, allowing the router to select a less congested channel, potentially boosting performance. Make sure you unplug it for at least 30 seconds to allow it to reboot.
5. Get a VPN
If you suspect that your slow internet is due to bandwidth throttling by your ISP, a VPN can help. By hiding your online activity, a VPN helps stop your ISP from monitoring and throttling your connection.
6. Clear your browsing history and cache
Clearing your browsing history and cache on your devices can help improve both internet speed and overall performance. Cached data can take up significant storage space, slowing down web page loading times.
7. Try a different ISP provider
If none of these tips improve your internet speed, it may be time to consider switching to a different ISP provider. Since different providers vary in speed and reliability, finding an alternative may improve your connection. And if you haven’t switched to fiber-optic internet, that can significantly increase speeds.
Help increase your internet speed
Use the above tips to determine why your internet is slow and take steps to improve it. If you’re still having trouble, consider using Norton Ultimate Help Desk to tackle tech issues like slow internet speeds.
Whether you need help with your network or a specific device, expert Norton technicians are available 24/7* to help get your internet and devices running smoothly again.
FAQs
How do I find out what's slowing down my internet?
To troubleshoot a slow internet connection, use an online tool like Speedtest.net, which measures the speed being delivered by your network and compares it to your ISP plan. You can also use an Ethernet cable to rule out Wi-Fi connection issues or a Wi-Fi heat map to identify dead zones.
If problems persist, check with your ISP provider for any outages, maintenance, or throttling that may be affecting your connection.
Why is my internet so slow on my phone?
If your internet is only slow on your phone, the issue could be due to poor signal strength, too many apps running in the background, a malware infection, or outdated software.
What internet plan do I need?
The internet plan you need depends on your intended usage. For intensive online activities like streaming, gaming, or video conferencing, especially if multiple devices are connected, 100Mbps minimum is a good starting point. You may need a faster plan if you have lots of devices that engage in high-bandwidth activities.
Why does my VPN slow down my internet speed?
A VPN can slow down your internet speed because it routes your connection through a VPN server and encrypts your data, which adds extra steps to the connection process.
Can a browser affect my internet speed?
A slow browser could be outdated or have a full cache, leading to internet slowdowns. You can fix this by updating your browser and clearing the cache in your settings.
* 24/7 Support is available in English only. Learn more at norton.com/globalsupport.
Editorial note: Our articles provide educational information for you. Our offerings may not cover or protect against every type of crime, fraud, or threat we write about. Our goal is to increase awareness about Cyber Safety. Please review complete Terms during enrollment or setup. Remember that no one can prevent all identity theft or cybercrime, and that LifeLock does not monitor all transactions at all businesses. The Norton and LifeLock brands are part of Gen Digital Inc.
- 1. Router placement
- 2. The signal doesn’t reach far enough
- 3. Network congestion
- 4. Signal interference
- 5. Outdated router
- 6. ISP throttling
- 7. Background apps
- 8. Insufficient internet speed
- 9. Malware or viruses
- 10. Damaged hardware or cables
- 11. Outdated devices
- How to increase internet speed
- Help increase your internet speed
- FAQs









Want more?
Follow us for all the latest news, tips, and updates.