Why is my browser so slow? 12 tips to speed it up
Are you waiting 30 seconds for a site that should load in 3? Read on to learn why your browser might be slow and how to fix it. Then, try Norton Utilities Ultimate to help speed up your browser, and your overall PC, without the need for manual troubleshooting.

If you feel like you’re slugging through social media and the quality of everything you stream is barely watchable despite paying for fast internet, your browser might be the problem. Thankfully, you can start with some relatively easy fixes to boost your browser’s speed.
In this article, we’ll provide tips for Chrome, Edge, Safari, and Firefox. Then we’ll explain how software optimized to boost your PC’s performance can help protect your precious time.
Why is my web browser so slow?
If your web browser is slow but your internet is fast, you may be using too much of your computer’s limited resources. Multiple extensions, background processes, or software bugs could also consume your computer’s resources.
Here are some additional causes for a slow browser:
- Internet issues: Sometimes, the problem isn’t your browser but an unstable or slow internet connection. Run an internet speed test to find out if your internet is the problem. If it is, jump down to our tips on what to do if your internet speed is slowing down your browser.
- Full cache and cookies: Your browser stores temporary files and cookies in its cache to speed up repeat website visits. Sometimes, however, the cache gets too full, slowing down your browser as it sifts through outdated or unnecessary files.
- Too many extensions: Each browser extension you install uses memory (RAM) and processing power (CPU), even when you aren’t actively using it. Browser extensions run in the background and can increase your CPU and RAM usage, leading to sluggish performance.
- Outdated browser or operating system: An out-of-date browser or operating system is missing out on the latest speed improvements and security patches. Regular software updates help browsers and operating systems work better with current software and web pages.
- Background processes: Device programs and browser tabs compete for your computer’s resources. Use your browser’s built-in Task Manager to spot and close resource-hungry processes.
- Malware: Malicious software (malware) can run hidden processes, steal your data, and drain your system’s performance. A 2025 Gen Threat Report saw a 300% increase in malicious browser push notifications, which re-target users with fake system alerts and continuous system slowdowns.
- Software bugs: Glitches in your browser, extensions, or the websites you visit can cause memory leaks that consume your RAM, even after these processes are closed. Software updates can often resolve these bugs.
- Old computer: Older computers might not have the processing power to handle modern browsing. If your computer can’t handle Windows 11, consider replacing it, as Microsoft will no longer support Windows 10 as of October 14, 2025. However, there is an option to pay a fee for Extended Security Updates for those who want to keep using their Windows 10 devices until October 13, 2026.
12 tips to speed up your browser
You can speed up your browser by stopping unnecessary processes, removing browser extensions, updating your browser, or using your system’s built-in tools.
Speeding up your browser starts with closing unnecessary processes and changing your performance-based settings. Below, we’ll cover the steps in Chrome, Edge, Safari, and Firefox.
1. Close tabs
Even on powerful computers, having too many tabs open can eat up your memory and processing power. Closing tabs you aren’t currently using means your computer’s resources get allocated to what you’re actively doing.
Here are some ways you can close tabs in Chrome, Edge, Safari, and Firefox:
- Click the X button on the tab.
- Press Ctrl + W (on Windows) or Command + W (on Mac).
- Right-click your active tab and select Close all other tabs (not available on Safari).
To conserve resources, Chrome, Firefox, Edge, and Safari all have the capability to put tabs to sleep after a period of inactivity, whether by using extensions or being an automatic browser feature. When you click on the sleeping tab, it reactivates, rejoining other tabs in consuming resources.
Each extension you install runs code in the background, using your memory and processing power. While many extensions are lightweight, bulkier extensions result in slower page load speeds. If you have too many extensions, you could also experience slowdowns.
Here’s how to remove browser extensions on Chrome and Edge:
- Click the three-dot menu in the top-right corner.
- Select Extensions and then Manage Extensions.
- Select Remove next to unwanted extensions.
You can also type chrome://extensions (if you’re using Chrome) or edge://extensions (if you’re using Edge) in your address bar to get to the extensions page faster.
Here’s how to remove browser extensions on Firefox:
- Click the puzzle icon in the top-right corner.
- Select the three-dot menu next to an extension.
- Click Remove.
Here’s how to remove browser extensions from Safari:
- Select the Apple menu in the top-left corner and click Safari Extensions.
- Click your profile icon in the bottom-left corner.
- Select the three-dot menu next to any extensions and click Delete App.
3. Update your browser
Keeping your web browser up to date helps resolve bugs and slowdowns present in the code of older browser versions. Most modern browsers update automatically in the background. Still, it’s good to check for updates manually every so often.
On Chrome, Firefox, and Edge, you’ll usually see an “Update Browser” pop-up or button on the browser itself. Safari updates your browser alongside its regular operating system updates.
Here’s how to check for updates on Chrome:
- Select the three-dot menu and click Settings.
- Click Privacy and security.
- Check the box under Safety at a glance for updates.
Here’s how to check for updates on Edge:
- Select the three-dot menu.
- Click Settings near the bottom.
- Select About Microsoft Edge and see if it’s up to date.
On Firefox for Mac, clicking Firefox in the upper-left corner and About Firefox tells you if any updates are available. Here’s how to check for updates on Firefox for Windows:
- Select the three-line menu.
- Click Help.
- Select About Firefox and review potential updates.
On Safari, your browser updates alongside your Mac’s operating system. Here’s how to get there:
- Click the Apple menu and select System Settings.
- Choose General and then Software Update.
- The system will check for updates for you, which you can click to install.
4. Clear your cache
When your cache gets too full or contains outdated data, it can slow down your browser and cause websites to display incorrectly. Clearing your cache can fix these issues, free up storage, and get your browser running smoothly again.
To save time and use a shortcut, clear your Chrome, Edge, or Firefox caches by holding Ctrl + Shift + Del on Windows or Cmd + Shift + Del on Mac. There is no cache-clearing shortcut on Safari, but you can hold Cmd + Comma to open your Settings.
Here’s how to clear your cache on Chrome, Firefox, and Edge:
- Select the three-dot menu (three-line menu on Firefox) then click Settings.
- Click Privacy and security (Privacy, search, and services on Edge).
- Select Delete browsing data (Clear browsing data on Edge).
- Select the Time range (next to When on Firefox) and then Delete data (Clear now on Edge).
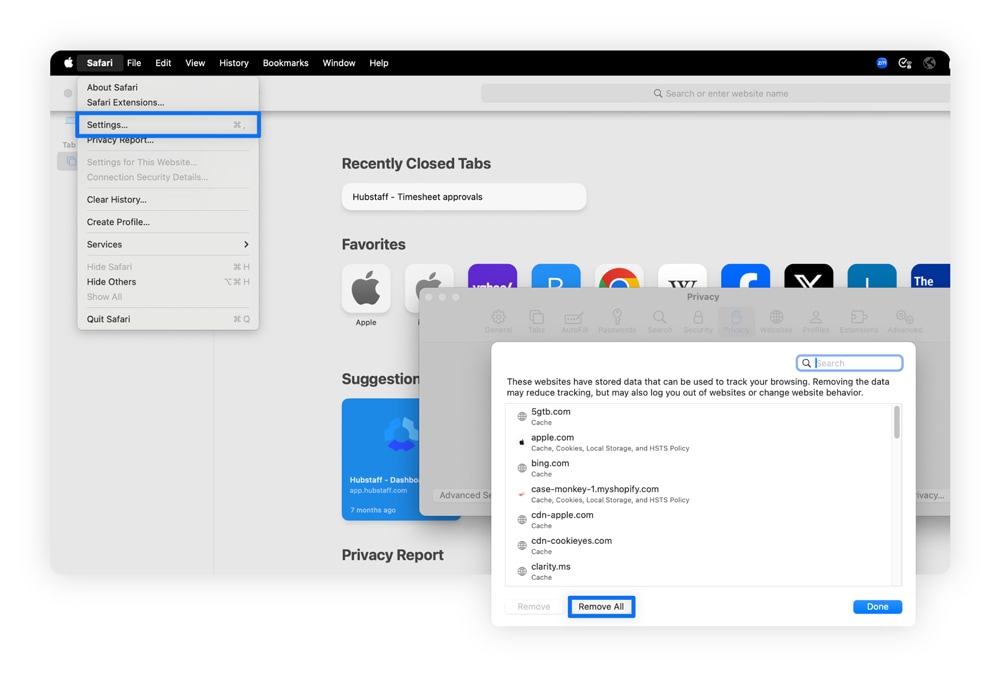
Here’s how to clear your Safari cache:
- Select the Safari menu in the top-left corner and then Settings.
- Click the Privacy tab and then Manage Website Data.
- Select Remove All to clear all cache and cookies, or click the sites you want to remove.

5. Consider hardware acceleration
Enabling hardware acceleration speeds up your browser by offloading graphically-intensive tasks from the CPU (central processing unit) to the GPU (graphics processing unit). However, hardware acceleration can slow you down if you have a weaker or outdated GPU.
Most browsers enable hardware acceleration by default. Here’s how to disable or enable it on Chrome and Edge:
- Under Settings, click System (System and performance on Edge).
- Toggle on or off Use graphics acceleration when available.
- Click Relaunch to restart your browser (on Chrome).
Here’s how to enable or disable hardware acceleration on Firefox:
- Select the three-line menu and click Settings.
- Scroll down until you see the Performance header.
- Uncheck Use recommended performance settings.
- When it appears, uncheck (or check) Use hardware acceleration when available.
You cannot disable hardware acceleration on Macs because this option was removed in macOS Catalina (version 10.15). Instead, it’s managed automatically by the system. If your browser is running slow, consider alternatives for more control over your settings.
6. Scan for malware
Malware and viruses steal your information and RAM processing power. One type of malware, adware, can hide on your computer and collect your information to sell to online advertisers.
Norton AntiVirus Plus can help you spot these background viruses. Features like real-time detection can stop malware, ransomware, hacking attempts, and new malware before it steals your computer resources (or worse).
7. End browser processes
Browser processes consume system resources similar to tabs, but differ in that they manage a browser’s overall functions. If you don’t need these functions, you can disable them to lower your CPU usage.
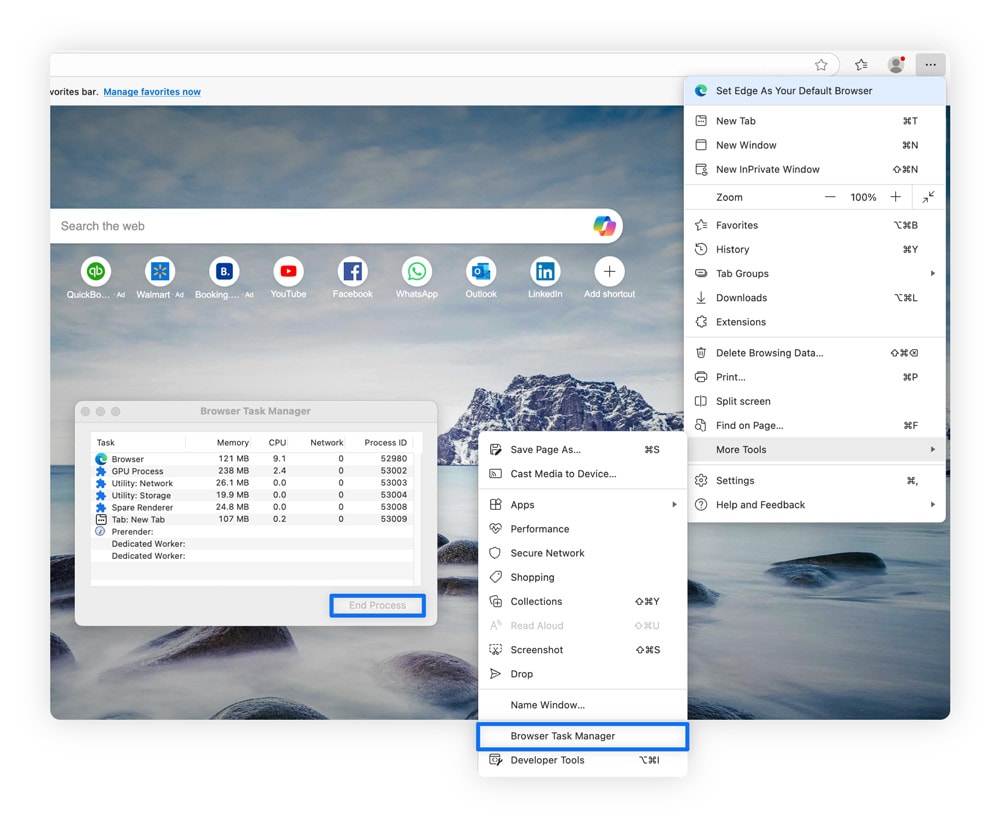
You can disable browser resources by opening the browser’s Task Manager. The instructions for doing so are the same for Chrome, Firefox, and Edge:
- Select the three-dot menu (or three-line menu) and More Tools near the bottom.
- Select Task Manager from the submenu.
- Click the process and select End Task to close it.
You can also hold down Shift + Esc to open the Browser Task Manager on either Windows or macOS for Chrome, Firefox, and Edge.

Safari doesn’t have a browser-based task manager. Instead, you can disable processes by using Activity Monitor:
- Select Launchpad at the bottom and click Activity Monitor.
- Click the Memory header to sort by RAM usage.
- Select a process and click the X button at the top to close the process.
You can also get to Activity Monitor by pressing Cmd + Space, typing “Activity Monitor,” and pressing Enter.
8. Get an ad blocker
Online ads and trackers lead to slower browser performance, but you can block these using an ad blocker. Recent research shows that browsers with integrated ad-blockers reduce power consumption by up to 44%. Some ad blockers can even block sites that host entire ad networks.
Norton’s new Neo browser includes ad- and tracker-blocking functionality, which helps prevent third-party trackers and ads from appearing on your computer. This helps improve your browser’s performance while also protecting your data.
9. Reset your browser settings
If your browser is still running slowly after trying other optimization tips, returning your settings to their default state can speed up your browser. Consider this a fresh start to fix settings that can cause performance issues over time.
Here’s how to reset Chrome’s or Edge’s settings:
- Select the three-dot menu and click Settings.
- Click Reset settings in the left-hand menu near the bottom.
- Confirm your decision by clicking the Reset settings button.
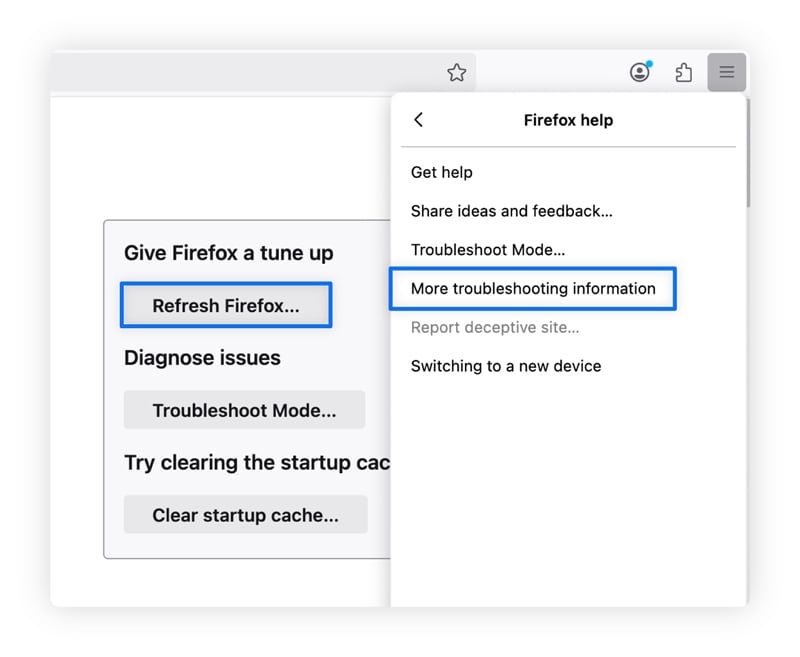
Meanwhile, Firefox follows a different process:
- Select the three-lines menu and click Help.
- Select More Troubleshooting Information.
- Click Refresh Firefox and confirm your choice.

Safari has no easy way to reset your browser settings. Instead, you can manually remove your extensions, change your settings, and delete your history. You can also choose to factory reset your entire Mac or iPhone, but this will remove more than just your browser settings, meaning you’ll want to back up your data.
10. Reinstall your browser
Reinstalling your browser can clear old data and corrupted files that could be contributing to a slow browser. It also resets your settings and removes extensions, but may not remove your bookmarks and passwords if you use the same Google, Apple, Firefox, or Microsoft account between browsers.
Here’s how to uninstall any browser on a Windows computer:
- Open Settings and click Apps in the left-hand menu.
- Select Installed apps from the right-hand menu and search for Edge.
- Click the three dots next to the browser and select Uninstall.
Some apps are part of your operating system and cannot be uninstalled, such as Edge for Windows and Safari for Macs. You can force these to uninstall through the Command Prompt on Windows by copying and pasting “setup.exe --uninstall --system-level --verbose-logging --force-uninstall”. On Macs, you cannot uninstall and reinstall the Safari browser.
11. Disable IPv6
Disabling IPv6, the latest IP address standard, may speed up your browser if your network configuration is causing issues. Disabling IPv6 forces it to rely on IPv4, potentially overcoming issues that may lead to slower connection speeds.
While disabling IPv6 can lead to improved speed, it can also negatively impact performance and cause compatibility issues. IPv4 is an older protocol, meaning it might not work with sites that only accept IPv6 connections. Reenabling it may be necessary if you run into broken websites or browser slowdowns.
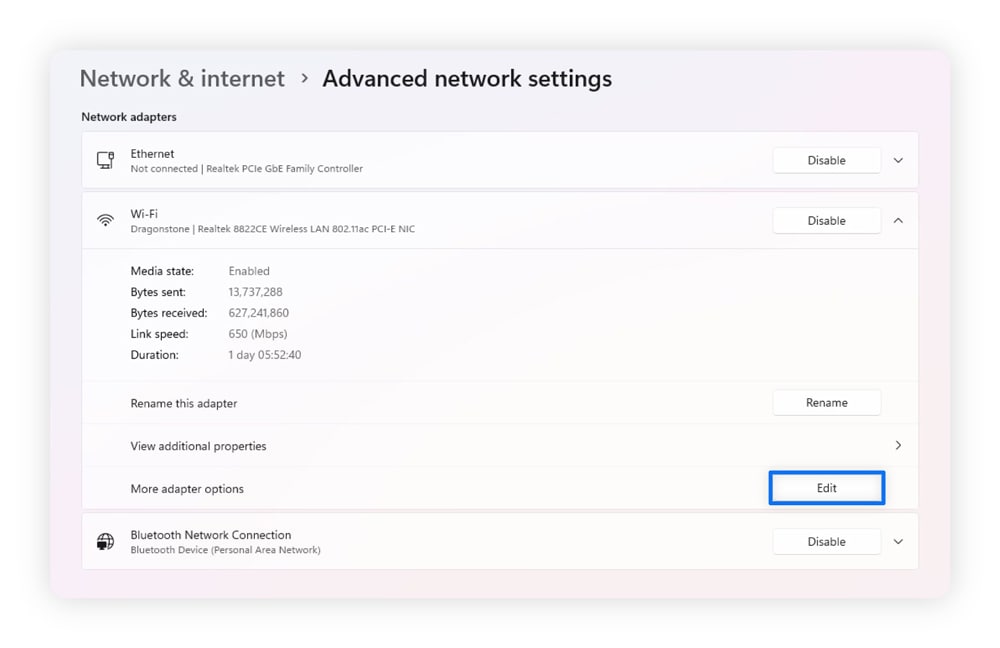
Here’s how to disable IPv6 on Windows:
- Open your Start menu and select Settings.
- Click Network & internet and then Wi-Fi (if your connection is wireless) or Ethernet (if wired).
- Select Edit next to More adapter options.
- Right-click your active network connection and select Properties.
- Uncheck the box next to Internet Protocol Version 6 (TCP/IPv6).

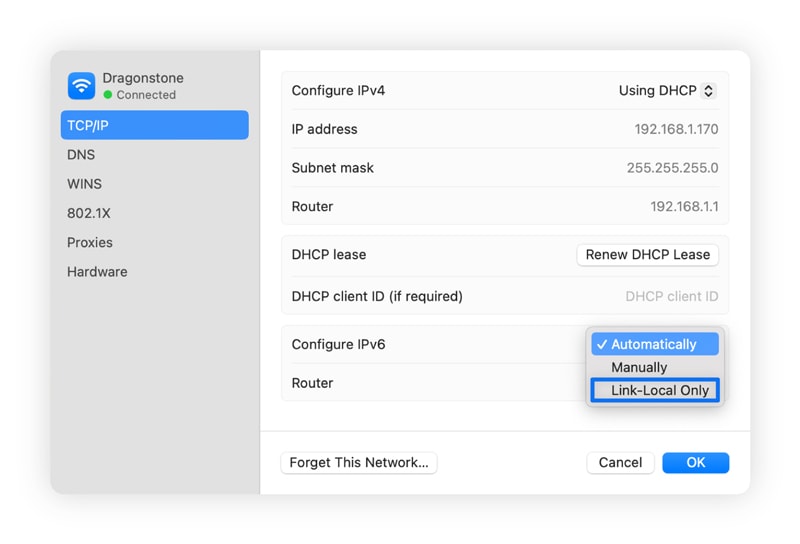
Here’s how to disable IPv6 on Mac:
- Click the Apple icon in the top-left corner and select System Settings.
- Select Network, choose your active network, and click Details.
- Click the TCP/IP tab and select Off or Link-local only from the Configure IPv6 dropdown.

You can also disable IPv6 on your router:
- Access your router’s web interface by typing the router IP in your browser’s address bar.
- Enter your router’s administrative username and password (found on the side of the router if you never changed it).
- Navigate to your advanced network settings.
- Locate and disable your IPv6 settings, typically under connection type information.
12. Use an optimization tool
Third-party optimization tools clear your cache and disable processes to speed up your entire computer, not just your browser. Using one of these tools involves some of the steps we suggested earlier, but all from one program, saving you time.
Norton Utilities Ultimate uninstalls programs, disables processes, and cleans junk from a single program on Windows, macOS, and Android devices. You can schedule this cleaning to be automatic, saving you time typically spent on computer maintenance tasks.
Here’s a video showing you how to use Norton Utilities Ultimate to speed up your device:
What to do if your internet is slowing down your browser
Sometimes, slowdowns aren’t actually your browser’s fault; instead, they come from slow internet. If you notice that streaming apps, online games, or other internet-dependent services are sluggish, your internet speed is the more likely culprit.
Here’s how to fix slow internet issues affecting your browser:
- Use a wired connection: Wired ethernet connections deliver higher speeds, have less signal loss, and result in lower latency (ping) than wireless connections.
- Move your device closer: It almost sounds too simple, but just moving your device closer to your router or extending your Wi-Fi can improve your signal strength and network performance.
- Move your router to a clear space: Place your router in a central, elevated, and open location away from thick walls, metal objects, and electronics that can cause interference.
- Change your Wi-Fi band: A 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi band reaches farther and penetrates through walls better than a 5 GHz band, which you can change in your router’s settings.
- Remove unnecessary devices: Check your device list and ask yourself if you need all of them connected, as too many devices — especially excessive IoT devices — can slow your network down.
- Reset your router: Unplug your router for 30 seconds or hold down the reset button to return it to factory defaults, resulting in potentially faster speeds due to different settings.
- Update your router: New firmware improves your router’s performance with new, more efficient code that works better with newer web pages.
Speed up your browser and your device
Web browser slowdowns are often caused by poor computer performance, so a solution that fixes both can help. Get Norton Utilities Ultimate to help automate device performance improvements through scheduled cleanings, uninstallation of bloatware, and disabling startup programs. Enhancing your entire computer’s performance can help you avoid frustrating slowdowns.
FAQs
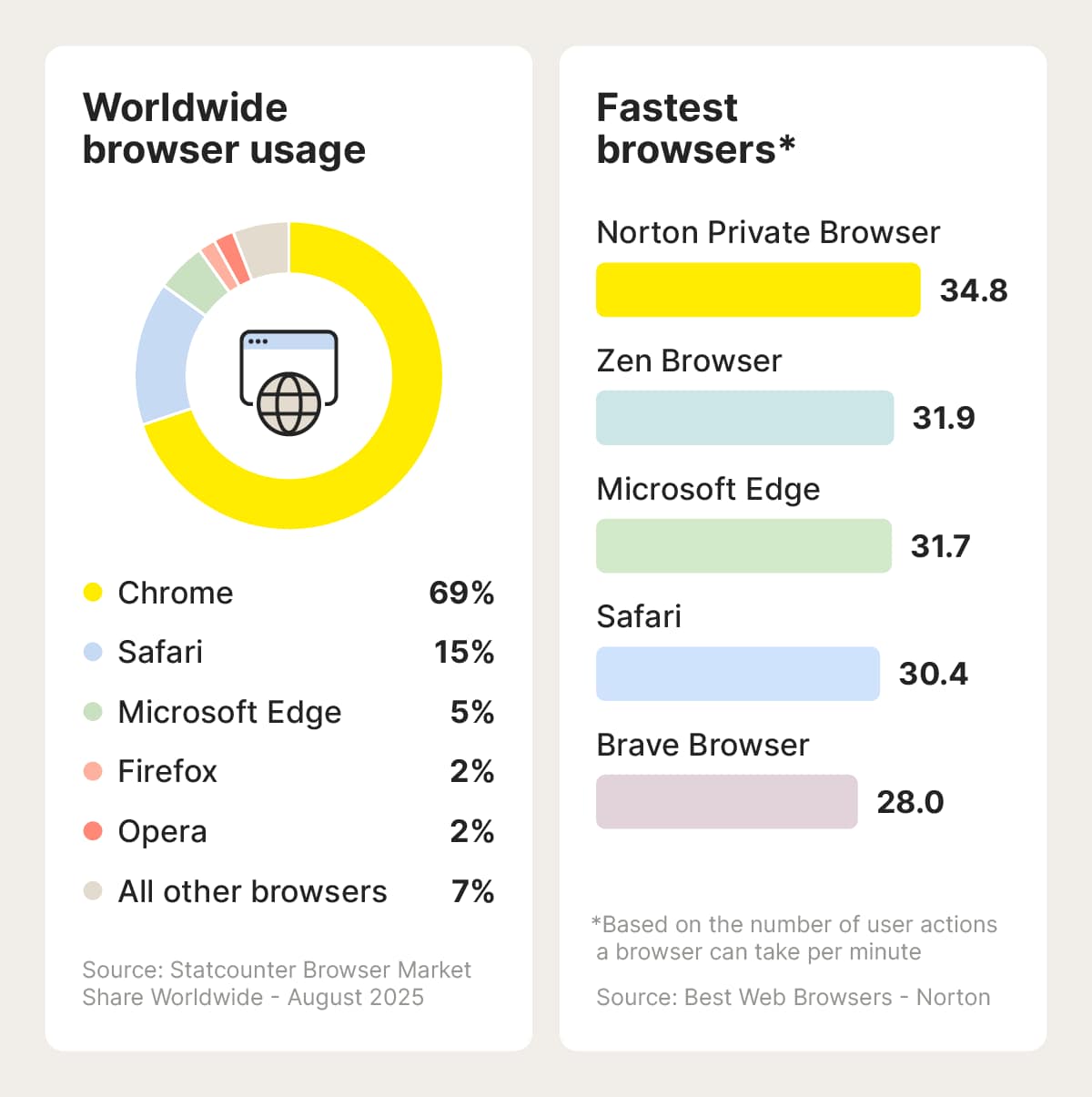
What’s the fastest browser?
Based on our tests during the best browser review, the fastest browser is Norton Private Browser. Other fast browsers include Edge, Chrome, and Zen. Apple users may also find Safari to be the fastest browser for them.
How many tabs is too many?
Older machines can typically experience slowdowns when opening 10 or more tabs, while newer machines can typically support 20 or more tabs. Some browsers, like Edge, put their tabs to sleep after some time has passed, allowing users to open more tabs with fewer performance drops.
How does hardware acceleration speed up my browser?
Hardware acceleration speeds up your browser by offloading graphically intense tasks like video playback to your GPU, reducing the load on your CPU. However, this might not work if your GPU is outdated or doesn’t have enough power to handle video rendering tasks.
Can an outdated computer slow down my browser?
Outdated computers slow down your browser due to compatibility issues with some websites, limited RAM or processing speeds, or just not having the latest performance improvements. Older computers tend to collect more software that can slow your computer, so it might be time to consider a factory reset.
Editorial note: Our articles provide educational information for you. Our offerings may not cover or protect against every type of crime, fraud, or threat we write about. Our goal is to increase awareness about Cyber Safety. Please review complete Terms during enrollment or setup. Remember that no one can prevent all identity theft or cybercrime, and that LifeLock does not monitor all transactions at all businesses. The Norton and LifeLock brands are part of Gen Digital Inc.








Want more?
Follow us for all the latest news, tips, and updates.