Why is my computer so slow all of a sudden, and how can I fix it?
If you notice signs of a slow computer, including the spinning wheel of death, long loading bars, delayed typing, or frozen screens, it’s time to learn what could be causing the issue. Specialized optimization software like Norton Utilities Ultimate can help clean up your device and make it faster.

When your computer suddenly slows down, it can get in the way of work, video calls, games, and file saves, turning a minor issue into a major inconvenience. These problems typically stem from malware, low storage, outdated software, and other resource hogs.
A quick reboot might resolve simple issues, like too many open applications or a minor software glitch. However, if the underlying problem is more severe, it will require more intensive troubleshooting. Here’s how to identify the cause of a laggy desktop or laptop.
High resource usage
High resource usage can slow down a computer if its processing power and memory become overwhelmed by intensive tasks like video editing, gaming, or running multiple apps simultaneously. When you spread your computer’s resources too thin, the operating system has to work harder, which can lead to sluggish performance and crashes.
Maxed out CPU from background programs
Programs that launch automatically or run in the background can hog system resources, particularly the CPU, which carries out the instructions and calculations that make your computer work. If the CPU is tied up with non-essential tasks, it can lead to noticeable delays and unresponsiveness when you need it most.
- How to diagnose it on a Mac: Check your Activity Monitor to see what’s running, and look for any apps consuming a high percentage of your CPU.
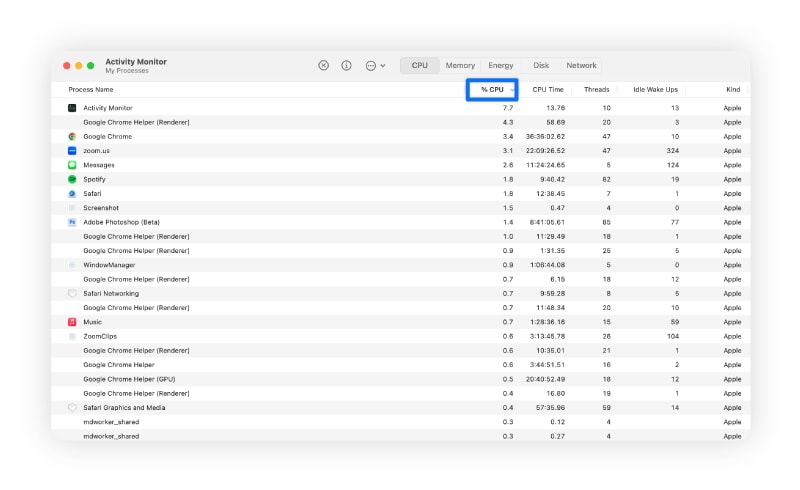

- How to fix it on Mac: Quit active resource-intensive processes. Also, limit apps that run in the background by navigating to System Settings > General > Login Items & Extensions, and disable programs you don’t need running when you’re not using them.
- How to diagnose it on Windows: Open Task Manager and go to the Processes tab. Look for apps and background processes using a high percentage of CPU.
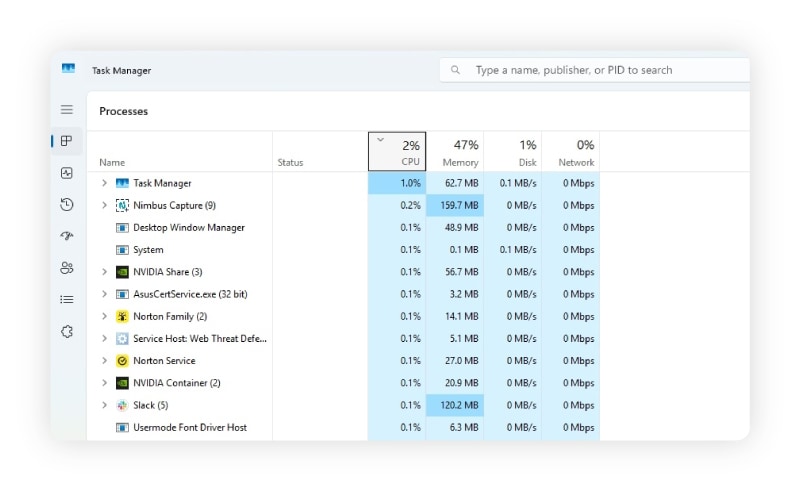

- How to fix it on Windows: Still in the Processes tab, select a resource-intensive task or program and click End Task to quit it. Then, disable programs that don’t need to launch automatically by going to the Startup apps tab, selecting an app, and choosing Disable.
Insufficient RAM
RAM (Random Access Memory) is your computer’s short-term memory. When it fills up — typically because you have too many applications open or are running demanding programs — your computer uses virtual memory instead. This means temporarily storing data on the hard drive that would normally sit in RAM.
When your computer needs that data again, it has to be swapped back into RAM. This back-and-forth process, known as “paging” or “thrashing,” is much slower than accessing RAM directly. It consumes valuable processing power, leading to delays and unresponsiveness.
- How to diagnose it on Mac: Open the Activity Monitor and go to the Memory tab. At the bottom, you’ll see a graph. If it’s yellow or red, you may need to increase or free up RAM. Compare Memory Used to Physical Memory (total available) to confirm if you’re nearing RAM capacity.
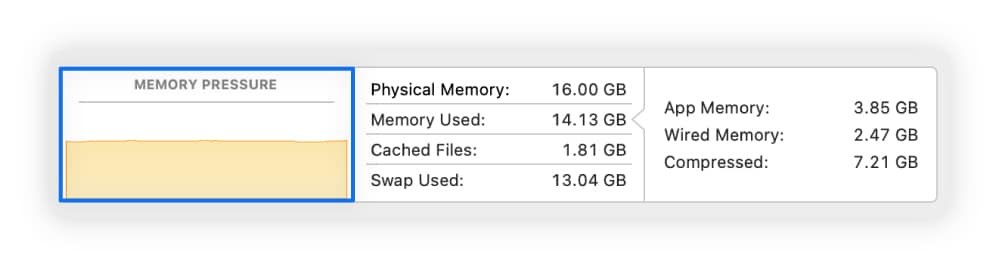

- How to fix it on Mac: Still in the Memory tab, close apps that are using the most memory by clicking on the process name and selecting Quit.
- How to diagnose it on Windows: Open Task Manager > Performance > Memory to check usage.
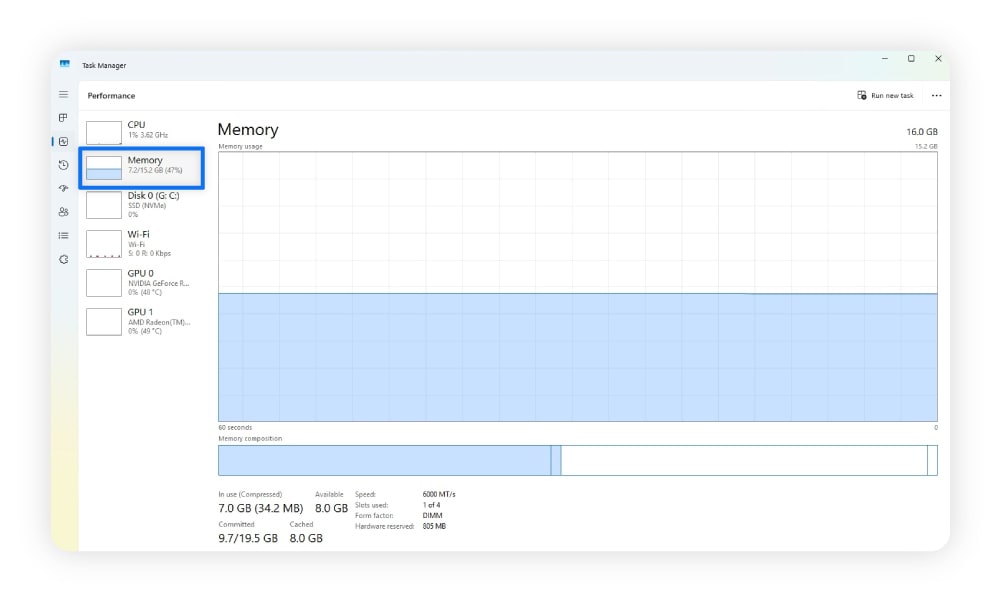

- How to fix it on Windows: In the Processes tab within Task Manager, select any memory-hungry apps, then click End task.
Open browser tabs
Too many open tabs can drain memory, which slows load times and potentially crashes your computer. This is especially true if the pages contain media or constantly refresh, because these activities require more resources.
- How to diagnose it on Safari: Check the CPU and Memory tabs in the Activity Monitor for web-related processes like “Safari” or “Safari Web Content.” If these processes consume a lot of CPU, open tabs or media-heavy pages may be responsible for slow load speeds.
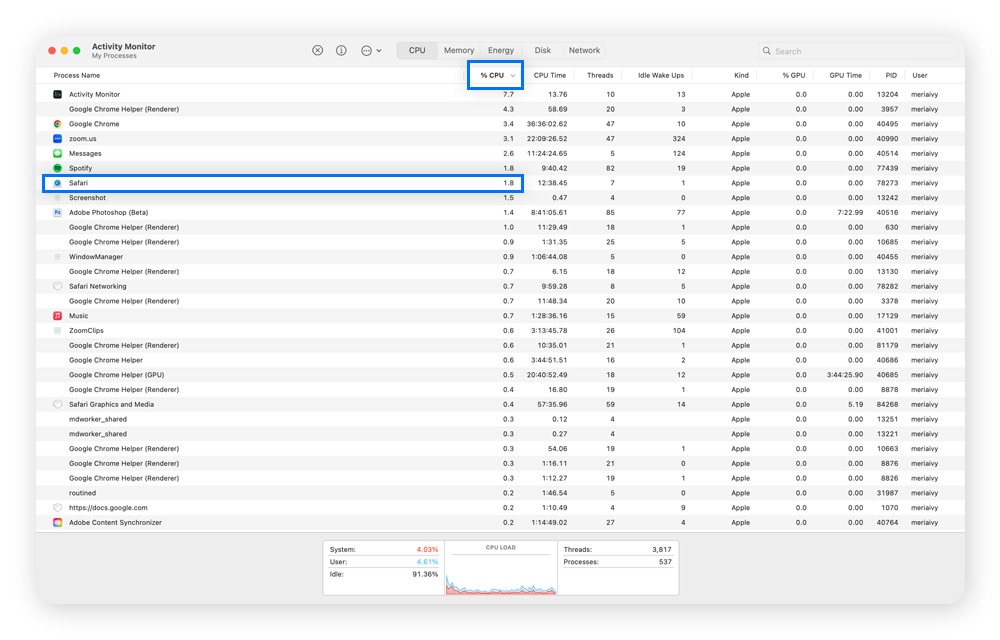

- How to fix it on Safari: Close unused tabs, especially those playing video or running ads.
- How to diagnose it on Chrome: If you’re using Chrome, click the three-dot menu > More Tools > Task Manager. Identify which tabs are using the most memory.
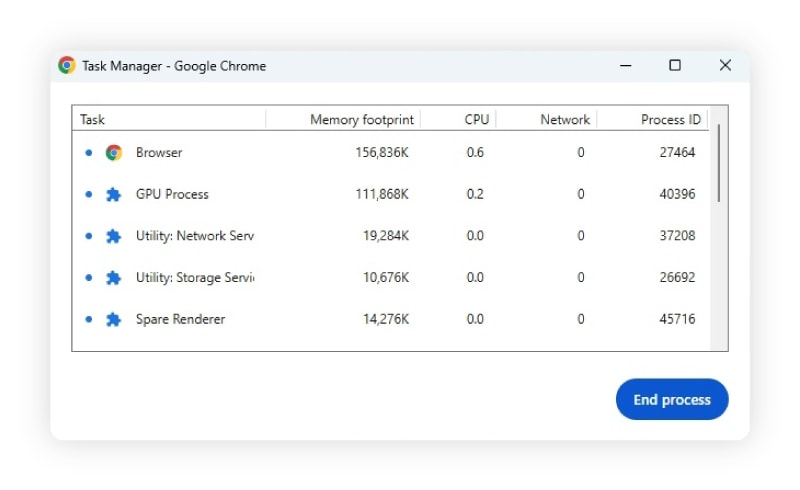

- How to fix it on Chrome: Close unused tabs and tabs using the most memory.
Excessive cache and cookies
Cached data and cookies usually help sites load faster by storing bits of site information locally on your device. However, when too much builds up, it can make your browser slower, as it has to sift through more data to load pages. An outdated or corrupted cache can also cause loading issues if the data conflicts with newer site content.
- How to diagnose it: There’s no definitive way to confirm if your cache is full. You just have to look out for warning signs like webpages loading incorrectly, freezing, or taking longer than usual to open.
- How to fix it on Safari: To clear Mac cache and cookies in Safari, go to the Safari menu > Settings > Privacy > Manage Website Data > Remove All.
- How to fix it on Chrome: Click the three-dot menu > Delete browsing data > choose the time range and types of data you want to delete > click Delete data.
Overheating issues
Heat can throttle your processor and force your system to slow down to prevent damage. Most commonly, this heat is caused by dust buildup, poor ventilation, or heavy use in hot environments.
- How to diagnose it: The easiest way to tell if your computer is overheating is if you hear loud fan noises, your device is hot to the touch, and you’re experiencing sudden shutdowns.
- How to fix it: Clear vents, place your device in a cool and well-ventilated area, keep your resource usage in check, avoid placing your device on soft surfaces, and consider using a cooling pad.
Low storage space or fragmented hard drive
Your hard drive is responsible for permanently storing your files, programs, and operating system. When it’s nearly full, your computer may slow down because the operating system doesn’t have enough space to store or swap data and files.
Fragmentation is another possible issue with hard drives. This is when files are broken up and scattered across the drive. This slows down read and write speeds on Hard Disk Drives (HDDs), which causes delays when opening files, launching apps, or saving data. However, this mostly affects Windows computers, since macOS automatically manages file storage.
Most modern computers — including newer Macs and many Windows PCs — use Solid State Drives (SSDs). These drives don’t experience slowdowns due to fragmentation, and defragmenting them can actually damage them and reduce their lifespan. If your computer has an SSD, you shouldn’t defrag it, regardless of your operating system.
- How to diagnose it on Mac: Check your storage space by going to System Settings > General > Storage. The bar at the top will show how much storage space you have left.
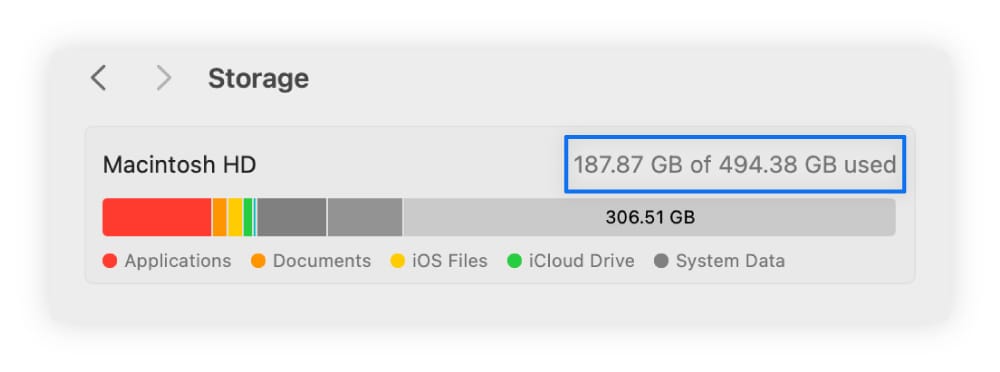

- How to fix it on Mac: If you’re nearly out of storage space, you can back up your data in iCloud or delete large files and applications you no longer need.
- How to diagnose it on Windows: Check your storage space by going to Settings > System > Storage.
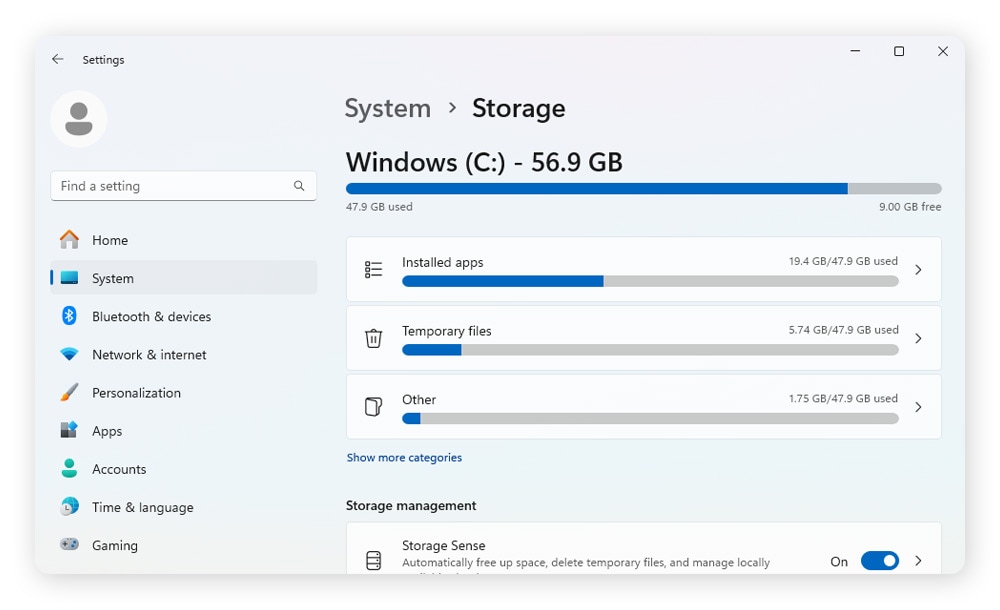

- How to fix it on Windows: If you’re nearly out of storage, back up large files to the cloud or delete large files or apps you no longer need. If you have an HDD, you may need to defrag the hard disk drive too.
Free up storage for more space
Cleaning up your device manually can be time-consuming and quite a hassle. That’s where automated optimization software comes in. Norton Utilities Ultimate will identify unused apps and unnecessary programs that you can shut down or remove, helping you organize your machine and reclaim valuable space.
Hidden malware
Security threats like hidden malware can slow down your computer by consuming system resources to generate ads and pop-ups, spy on you, corrupt or encrypt files, modify system settings, mine crypto, or communicate with the attacker’s servers.
- How to diagnose it: Search your device for new programs you didn’t install or unusual activity like spikes in CPU use. You should also run a fully automated malware scan using a reputable antivirus.
- How to fix it: Use a malware removal tool and remove any threats the software detects.
Network connectivity
You might have a poor internet connection for several reasons: a weak signal, an overloaded network, or issues with your internet service provider. This can lead to computer slowdowns, as numerous applications and operating system functions depend on a stable, fast internet connection to load data, sync files, and perform updates efficiently.
Weak connection
A weak network connection slows down your computer because it stops data from transferring efficiently between your device and the internet.
- How to diagnose it on Mac: Go to System Settings > Wi-Fi. There, you should see a green circle (indicating you’re connected) and a Wi-Fi signal icon with full bars. If not, your device may have a connectivity problem.
- How to fix it on Mac: Restart your router and computer to resolve bugs and improve connectivity. If this doesn’t help, it could be due to poor router placement, ISP throttling, insufficient internet plan speed, or damaged hardware or cables.
- How to diagnose it on Windows: Go to Settings > Network & internet > Wi-Fi, and review your connection information.
- How to fix it on Windows: Restart your router and computer. If this doesn’t help, it could be due to poor router placement, ISP throttling, insufficient internet plan speed, or damaged hardware or cables.
Software and system updates
If your computer is running old software, it could slow down due to bugs, hardware incompatibility, or poor resource management.
Outdated browser
Older versions of browsers may not handle modern web standards efficiently, causing freezing or lag when loading content-heavy sites.
- How to diagnose and fix it: Find your browser’s About section, usually located in Settings or Help. It will show your current version and whether an update is available. If a newer version is available, install it.
Outdated operating system
An outdated operating system can cause your computer to slow down, as it may lack essential performance optimizations, remain vulnerable to unresolved bugs, or struggle to keep up with the demands of modern applications.
Installing an update can help speed things up again by providing performance enhancements, bug fixes, improved resource management, and better compatibility with current software and hardware.
- How to diagnose and fix it on Mac: Check for system updates by going to System Settings > General > Software Update. If an update is available, install it.
- How to diagnose and fix it on Windows: Check for system updates by going to Settings > Windows Update. If an update is available, install it.
Outdated or corrupt drivers
Drivers enable your operating system to communicate with and control your computer’s hardware components (like graphics cards, printers, and network adapters). If they’re outdated or become corrupted, they can cause sluggish performance, crashes, or glitches.
- How to diagnose it on Mac: Since macOS handles driver updates automatically with system updates, the primary way to diagnose potential driver-related issues is to observe the system for crashes, glitches, or unresponsive hardware.
- How to fix it on Mac: Make sure you’re running the latest version of macOS.
- How to diagnose it on Windows: Open Device Manager and look for yellow exclamation marks or red “X” symbols next to device names — these indicate problems with a driver.
- How to fix it on Windows: Right-click problematic devices and choose Update driver, then follow the instructions to install the latest version. You can also use a dedicated tool, like Norton Driver Updater, to update all of them at once and ensure drivers are kept up to date going forward.
Optimize your computer for faster performance
If your computer is still slow after trying these fixes, don’t worry — Norton Utilities Ultimate can help rid your device of unneeded junk, delete browser data, and turn off resource-hogging processes. After cleanup, your device will be more lightweight, and you should start to notice speed improvements almost immediately.
FAQs
Why is my new computer so slow?
New devices can be slow due to pre-installed bloatware, startup programs, background processes, system updates, or cloud syncing running in the background.
Why is my computer downloading so slowly?
Slow download speeds can be caused by a poor internet connection, outdated network drivers, open browser tabs, VPN or firewall usage, limited storage space, or background downloads.
Can background antivirus scans reduce my computer’s responsiveness?
Yes, full antivirus scans can use significant system resources and temporarily cause poor responsiveness. However, automatic updates and background monitoring typically use minimal resources. They’re designed to run during idle times or at low priority, so they’re less likely to interfere with performance.
Editorial note: Our articles are designed to provide educational information for you. They may not cover or protect against every type of crime, fraud, or threat we write about. Our goal is to increase awareness about Cyber Safety. Please review the complete Terms during enrollment or setup. Remember that no one can prevent all identity theft or cybercrime, and that LifeLock does not monitor all transactions at all businesses. The Norton and LifeLock brands are part of Gen Digital Inc. For more details about how we create, review, and update content, please see our Editorial Policy.








Want more?
Follow us for all the latest news, tips, and updates.