Why is my data so slow? 7 causes and 9 solutions
A slow mobile data connection is often the result of a simple issue that’s easy to fix. But it can also be a symptom of mobile malware, which represents a more serious problem. Find out how to troubleshoot slow mobile data and get Norton to help protect against mobile threats and keep your device running smoothly.

Why is the internet so slow on my phone?
Your phone’s internet could be slow because of a poor connection, network congestion, ISP throttling, a full browser cache, inefficient network settings, apps running in the background, or even a malware infection. Learn how to troubleshoot and fix the issue to get your mobile data running at top speed.
1. Poor connection
If your signal connection indicator only shows a couple of bars (or none), physical obstructions like tunnels or buildings could be interfering with your connection. Alternatively, you might be too far from a cell tower, which is most common in less populated areas or while camping.
To see your exact signal strength, measured in decibel-milliwatts (dBm) instead of a visual bar, check your connection in your phone's settings. Here's how:
- Android: You should be able to find your dBm under Network Type or SIM Status in the Network and Internet settings menu.
- iPhone: To find your dBm on an iOS device, enter Field Test Mode (FTM) by dialing *3001#12345#* and hitting the call button. When the FTM Dashboard appears, check the number next to RSRP (Reference Signal Received Power).
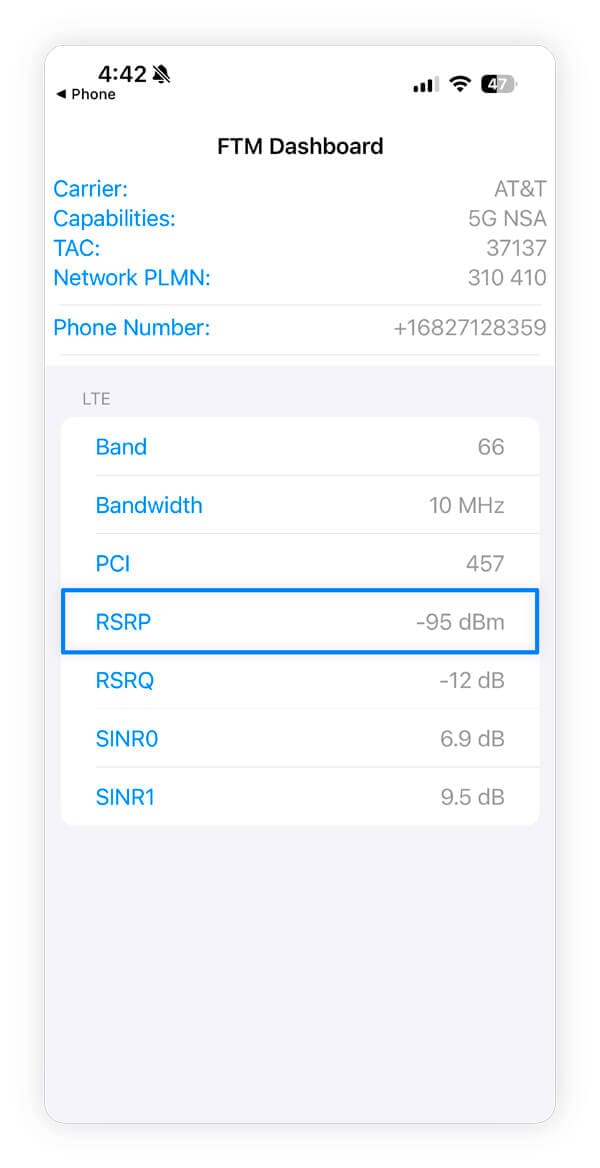

Then, refer to the dBm chart below to determine if you’re dealing with connectivity issues. Keep in mind these ranges vary slightly depending on the phone and network provider.
Connection quality |
Signal strength (dBm) |
|---|---|
Strong |
-50 to -79 |
Good |
-80 to -89 |
Average |
-90 to -107 |
Poor |
-108 to -114 |
Very poor or lost |
≤ -115 |
2. Network congestion
When too many people connect to the same cell tower, it can congest the network and slow down your internet connection. This is common during peak usage times, large-scale public events, and natural disasters when people are more likely to rely on mobile data rather than Wi-Fi or wired networks.
To manage excessive traffic during these times, internet service providers (ISPs) may use bandwidth throttling — intentionally slowing down internet speeds.
3. ISP throttling
Internet service providers may also throttle your mobile data connection if you’ve exceeded your monthly data cap or are on a budget plan without priority speeds. Even with an unlimited plan, you may experience throttling after reaching a certain threshold that represents a “soft” data cap.
When this happens, you’ll likely start noticing that videos start buffering, downloads take longer, and webpages take a while to load.
You can typically check your data limit, and how much of it you’ve used in the current billing cycle, under the cellular or mobile data sections in your phone’s settings.
4. Full browser cache
Browser caches store temporary files to make websites load faster when you revisit them. But when they’re full of outdated or unnecessary data, it can cause websites to load old content, render incorrectly, or take longer to load, leading to a slower browser. An overloaded cache can also lead to general lag, frequent crashes, and reduced storage space on your device.
5. Inefficient network settings
Your network settings impact how your phone connects to and uses the internet. If they’re set up incorrectly or unoptimized for your specific usage, they could contribute to connection problems.
Here are a few examples of key network settings that could be slowing down your mobile data:
- Data roaming affects your ability to use the internet outside of your network’s coverage area, like when you visit another country. When you travel, your data could slow down due to network compatibility differences or roaming agreement terms.
- Access Point Names (APNs) provide instructions for your phone to establish a connection with your mobile carrier’s network. If the APN uses the wrong protocol or server address, it could be difficult for your phone to establish a stable connection.
- Network mode settings determine which cellular network generation your phone uses. These technologies range from 2G, which is the oldest and works for basic talk and text, to 5G, which enables high-speed internet access. If your phone defaults to an older network mode, it could limit your data speeds, even if you have a strong signal.
6. Background apps
Some apps run even when you’re not actively using them. They may do this to send you notifications, scan for threats, sync data, or install updates. But if too many apps are working behind the scenes, they can drain bandwidth and processing power, slowing down your mobile data.
7. Malware infection
Even with Android and iOS security features, mobile devices can be infected with malware if you don’t take precautions. And like any other background app or process, hidden malware can slow down your data by consuming system or network resources.
However, these programs can also affect internet performance if they route your connection through malicious servers or intercept your data as it’s being transmitted. Similarly to network congestion, these issues can strain your network connection and reduce your internet speed.
How to make your mobile data faster
To speed up your mobile data, try re-establishing your internet connection, clearing your cache, closing background apps, checking that your SIM card isn’t faulty, upgrading your internet speeds and network settings, installing software updates, using a VPN, and removing any hidden malware.
Follow these steps to work through the process of troubleshooting a slow mobile data connection.
1. Restart your phone
Restarting your phone can resolve any system glitches that are slowing down your mobile data connection by clearing temporary files and rebooting background processes. It can also fix connectivity issues by reconnecting your device to the nearest cell tower.
2. Switch airplane mode on and off
Turning airplane mode on and off is another way to force your phone to search for the strongest available signal and re-establish a fresher, faster connection with the cell tower.
On iPhones, you can find airplane mode in your Control Center — the menu that shows utilities — by swiping down from the top-right corner of your screen. You can access the airplane mode toggle on Android phones in the notification panel that appears when you swipe down from the top of your screen.
3. Clear your browser cache
A full browser cache can worsen the effects of slow data and cause websites to load slowly or incorrectly. Clearing your cache removes temporary files that are taking up space and system resources, forcing the browser to fetch fresh, up-to-date data from the web, which can improve loading speeds and contribute to a smoother browsing experience.
Here’s how to clear the cache on your phone:
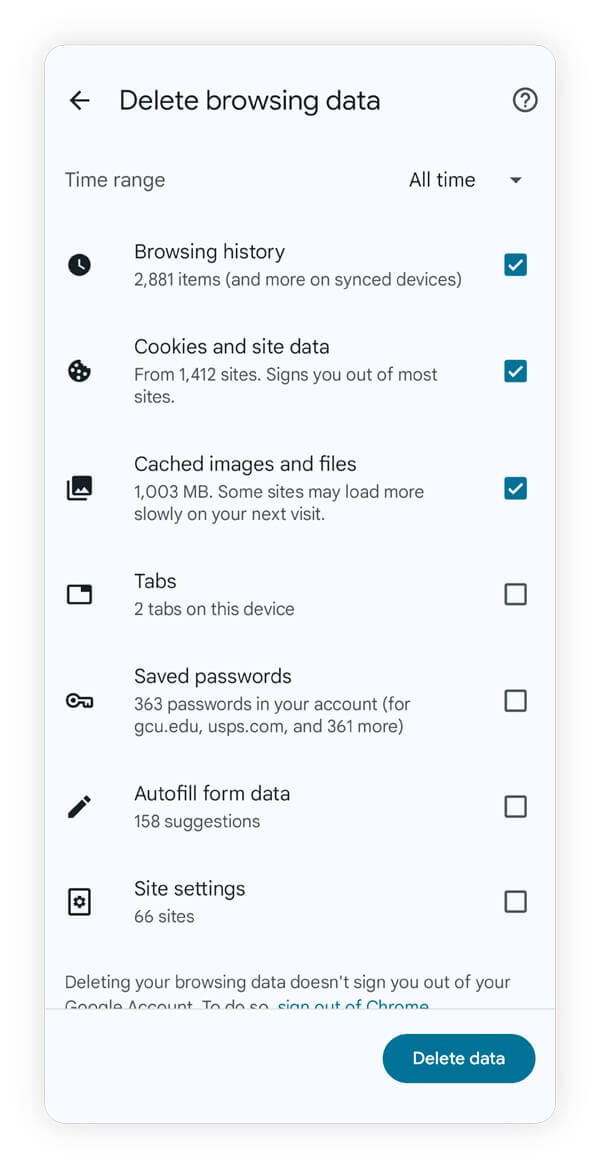
- Android: Open Chrome > tap the three dots in the top right corner > select Delete browsing data > tap More options > select your options > tap Delete data.

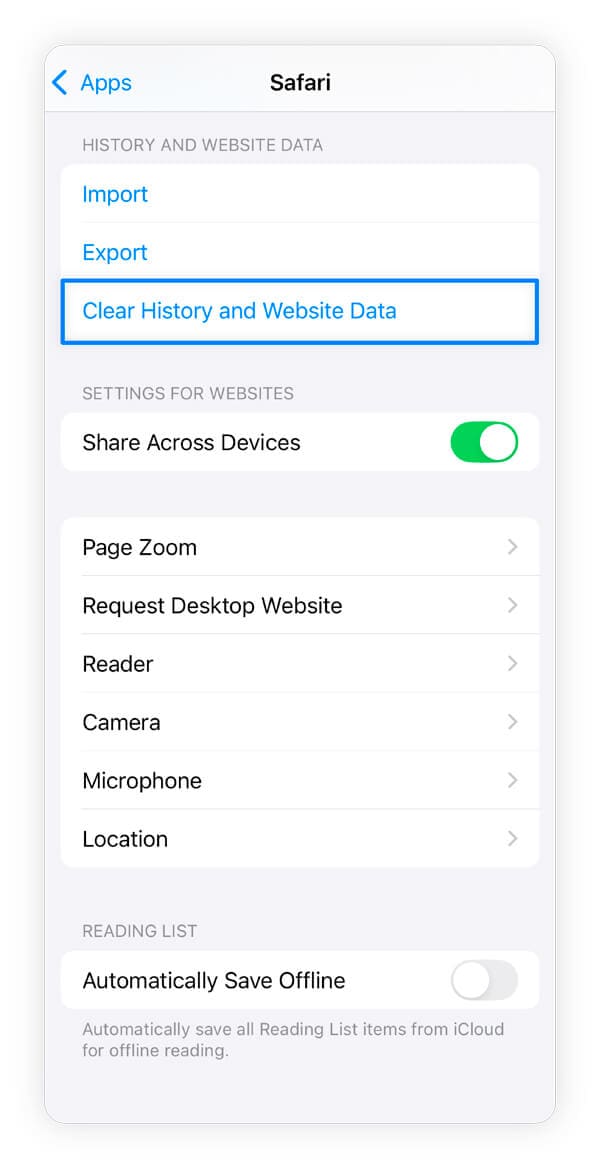
- iPhone: Open Settings > Apps > Safari > Clear History and Website Data > select a timeframe to erase > tap Clear History.

4. Close background apps
While some apps need to run continuously to function properly, you can close unnecessary apps to stop them from running in the background and using your bandwidth. This helps free up both system and network resources so the apps you’re actively using run faster and more smoothly.
To close background apps on an Android device or iPhone, swipe up from the bottom of your screen and flick the apps you want to close toward the top of the screen.
5. Assess your SIM card
If your SIM card is old or damaged, it could struggle to hold a stable signal which can lead to slower speeds and connectivity issues. To confirm if your SIM card is causing data slowdowns, you’ll need to take it out and inspect for signs of damage like scratches, cracks, or corrosion.
Look for a small rectangular SIM tray along the edge of your phone — there’s usually a tiny hole next to it. Insert a SIM ejector tool into the hole and press gently until the tray pops out so you can access the SIM card.
6. Use a VPN
If you suspect network congestion or throttling is behind your slow mobile data, try using a virtual private network (VPN) to mask your location. By routing your traffic through a remote VPN server, you can potentially bypass network congestion and prevent your service provider or other third parties from de-prioritizing your internet traffic based on your activity.
Try Norton VPN, available for both Android and iOS, to get on-the-go access to a broad selection of high-speed servers that offer bank grade encryption.
7. Upgrade your cellular network
Check your settings to determine if you’re on an older network like 2G or 3G. These networks have slower data transfer speeds, meaning you might notice higher latency or delays when browsing, streaming, or downloading. Switching to a faster network mode like 4G or 5G can improve speeds and reduce buffering.
If you’re not sure which network you’re on, follow these steps to figure it out:
- Android: Open Settings > Network & internet > Mobile network or SIM. Then, look for a label that says Preferred network type or Network mode. This will display the network you’re on, and you can select the fastest option that your phone and carrier support.
- iPhone: Open Settings > Cellular > Cellular Data Options > Voice & Data. Here, you can select the highest-grade network your phone can connect to.
8. Update network settings
Review and update your network settings to ensure your phone is optimized to connect to and use the internet efficiently. If you can reconfigure your Access Point Name (APN) it may establish a better internet connection. And with the right roaming settings, your device can connect to the most efficient available networks when you’re outside your usual coverage area.
To update your network settings:
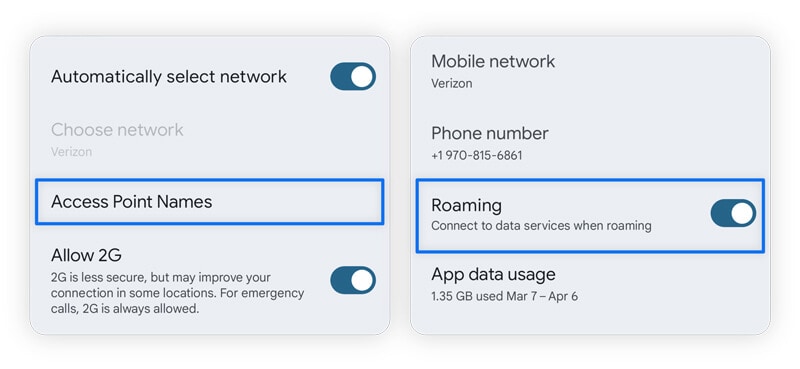
- Android: To review your APN and roaming settings, go to Settings > Network & Internet > Mobile Network or SIM > Access Point Names. To check your roaming settings, go to Settings > Cellular > Cellular Data Options > Roaming.

- iPhone: If your carrier allows you to view and edit your APN settings go to Settings > Cellular > Cellular Data Network. You’ll find roaming in Settings > Cellular > Cellular Data Options.
9. Update your software
Older software can sometimes cause connection issues due to bugs, outdated protocols, or a lack of compatibility with newer network standards. Many software updates offer patches to these issues and can resolve connection interruptions.
To determine if you’re due for a system update, follow these instructions:
- Android: Open Settings > tap System or About phone > select Software update or System update and follow the prompts.
- iPhone: Open Settings > General > Software Updates and follow the prompts.
Scan for data-slowing malware
If your phone data is running slowly and other fixes haven’t worked, use Norton AntiVirus Plus to find and remove any malware that may be hiding on your device, keeping it from eating up your bandwidth and slowing down your connection. You’ll also benefit from AI-powered scam detection that can help you protect against mobile threats across the internet.
Editorial note: Our articles are designed to provide educational information for you. They may not cover or protect against every type of crime, fraud, or threat we write about. Our goal is to increase awareness about Cyber Safety. Please review the complete Terms during enrollment or setup. Remember that no one can prevent all identity theft or cybercrime, and that LifeLock does not monitor all transactions at all businesses. The Norton and LifeLock brands are part of Gen Digital Inc. For more details about how we create, review, and update content, please see our Editorial Policy.









Want more?
Follow us for all the latest news, tips, and updates.