Email security: A definition + email protection tips
Use this email security guide to learn about the importance of email protection, how to make your email more secure, and how to help yourself avoid common email security threats.

Email security encompasses the methods and procedures used to avoid different forms of email intrusion — whether at home or in the workplace. Today’s digital landscape, unfortunately, allows different types of hackers to use private emails as a means of delivering malware that can compromise either corporate or personal information. They can then leverage that stolen data to make a profit or commit other cybercrimes.
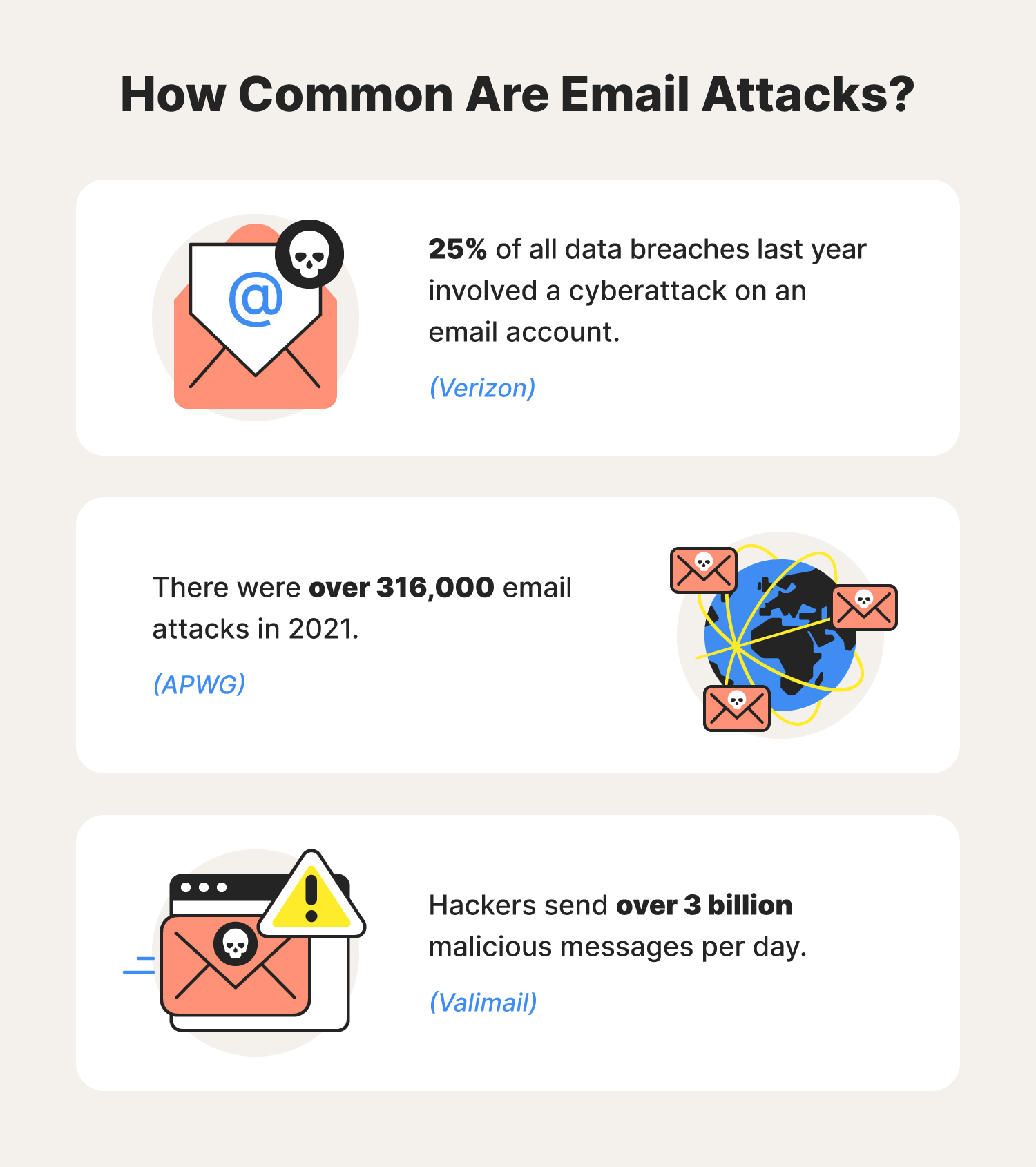
To that end, there’s no better time than now to start taking email safety seriously. After all, cybercriminals send more than 3 billion malicious emails every day. Our email security guide overviews the importance of email security, common email security threats paired with email protection tips, and best practices to help secure your email accounts and elevate your overall online privacy.
Let’s dive in.
Are emails secure?
Spoiler alert: Emails are not the most secure means of communication.
Although their design matches that of a mailbox you’d have at home to receive messages and letters from businesses and loved ones, they’re unlike a regular mailbox because hackers can embed messages with malicious files and/or software that can compromise your devices and network.
Hackers learned to use this open line of communication to their benefit, combining the evolution of hacking with modern-day technology to birth new email attacks. But lucky for us, email threats like website spoofing and phishing all have the same giveaways.
The components of an email that hackers usually target and compromise include:
- Sender’s email address
- Body of the email message
- Links, files, and downloadable attachments
Delete an email if you suspect someone falsified any of these parts of a message.
Types of email attacks

Below, you’ll find examples of email attacks used by hackers to break into vulnerable email accounts.
Spear phishing
Spear phishing is a type of cyberattack that sends customized but counterfeit email messages from people and/or places you’re associated with to get you to expose sensitive data. Hackers often try to impersonate institutions that you already trust — like a bank or credit card company, to increase the odds of you clicking on the malicious link or attachment included in the email.
Spear phishers often make urgent requests for money and/or account details to resolve a supposed account issue. These emails, though seemingly legitimate, are false. And failing to recognize them could lead to headaches such as banking fraud and identity theft.
Email security protection tip: Know the signs of a potential phishing message.
DDoS attacks
DDoS attacks and botnets are what cybercriminals use when they want to send an overwhelming amount of traffic to the servers email providers use. By targeting servers that keep systems running properly, these attacks can help disable the security features used to keep hackers out of email networks, providing uninterrupted access to private information in need of protection.
Email security protection tip: Consider increasing your Wi-Fi bandwidth.
Malware attacks
Getting malware installed onto your device is one of the first steps for hackers trying to expose your private data. For this reason, you should always suspect the presence of malware if you come across spam or any other kind of suspicious email. After downloading hacking tools such as adware, shareware, and spyware, hackers can sift through and disable computer systems as they see fit.
Email security protection tip: Beware of suspicious links, websites, and attachments that could be hosting viruses.
Social engineering attacks
Put in simple terms, social engineering occurs when a hacker tries to con you into divulging sensitive information by impersonating a person or company you trust. They could be using emails, like in phishing attacks, or illegitimate websites from well-known companies known as website spoofing. Sure they take longer to set up, but if successful, the cybercriminal gains direct access to the exact information they were looking for.
Email security protection tip: Enable two-factor authentication whenever possible.
Spoofing attacks
Spoofing is when a hacker creates and mimics a legitimate website. They generally try to trick users into exposing personal data, using viruses such as spyware to record information typed onto the website. Though sometimes difficult to spot, you’ll most likely find an element that is different from what you’re used to seeing, for example, a slightly different URL or website layout.
Email security protection tip: Lookout for suspicious URLs. Secure websites will have “https://” at the head of your search bar instead of “http://”.
Ransomware attacks
Ransomware is one of the scarier types of malware, as it can disable systems and encrypt files until you pay the ransom demanded by the hacker. Using tricks such as social engineering and phishing, they install their form of ransomware onto your device, identifying personal files of any value.
Email security protection tip: Download antivirus software.
Email security best practices

Email security starts with how you use and protect your email account. Consider these best practices to help secure your email from hackers.
Beware of phishing
Online users reported over 315,000 phishing attacks in 2021—the most since their discovery in 2004. Thankfully, there are warning signs that can help you spot these potential scams and avoid becoming a part of an unfortunate statistic.
Typical warning signs of a phishing email include:
- Grammatical errors
- Unfamiliar email addresses and domain names
- Urgent requests
- Requests for money
- Requests for login credentials
If you come across an email featuring any of these warning signs, delete it and leave those hackers in your trash.
Never download attachments from suspicious messages
Cybercriminals love attaching malicious files and attachments to phishing emails to trick users into downloading dangerous types of malware. That’s why you should always be cautious of the files sent to you via email on personal and work accounts. And if you don’t recognize the sender, simply delete the message.
Turn on spam filters
Email providers took on the challenge of trying to outthink hackers looking for system vulnerabilities in their services. One tool created to help protect email accounts is spam filters. Spam filters work to automatically send potentially dangerous and/or irrelevant advertising messages to a folder where you can choose to delete or open them as you please.
Create strong passwords
As with any online account, passwords are your main defense against ill-willed hackers—this is especially true when it comes to your email. Creating strong, reliable passwords helps keep you from falling victim to credential stuffing and password spraying—cyberattacks frequently used to break into email accounts with less complex or previously exposed passwords.
Enable two-factor authentication
Hackers may have a few different email attacks up their sleeves, but many of those become useless with the help of two-factor authentication, also known as multi-factor authentication. This cybersecurity tool requires you to validate your identity by answering specific security questions, entering a PIN, or using facial recognition and/or fingerprint scanning technology. This makes it next to impossible to replicate your identity during the login process.
Download antivirus software
Antivirus software could be the warrior you’ve been looking for in your fight against common email security issues like spear phishing and ransomware. Advanced malware detection and removal features allow you to know if and/or when a potential threat comes into your inbox, destroying it once verified.
Now that you know the importance of email security—for yourself or maybe some employees and customers—you can go forward with a bit more confidence in terms of how you protect your data against these emerging threats.
Email security FAQs
Have a few unanswered email security questions? We’ve likely got the answers. Take a look below.
What are the types of email security?
Some common types of email security tools include:
- Antivirus software
- Spam filters
- Data encryption
How do you keep your email secure?
Some best practices for helping keep your email secure include:
- Never downloading attachments from suspicious messages
- Avoiding phishing scams
- Turning on spam filters
- Creating reliable passwords
- Enabling two-factor authentication
- Downloading antivirus software
Why do we need email security?
We need email security to help stop hackers from easily intercepting and decoding information that could lead to crimes such as identity theft and/or bank fraud.
What can a hacker do with your email address?
If a hacker gains access to your email, they could use it to reset passwords to other online accounts, gain access to medical and banking information, and manipulate social media profiles.
How can I tell if someone is using my email?
The best way to check if someone accessed your account without access is by checking your account’s last login time, typically labeled as “Last account activity.”
Can I get hacked by opening an email?
No, you can’t get hacked by just opening an email. But you can get hacked if you open an email and click on a malicious link in that email.

Cyber threats have evolved, and so have we.
Norton 360™ with LifeLock™, all-in-one, comprehensive protection against viruses, malware, identity theft, online tracking and much, much more.
Try Norton 360 with Lifelock.
Editorial note: Our articles are designed to provide educational information for you. They may not cover or protect against every type of crime, fraud, or threat we write about. Our goal is to increase awareness about Cyber Safety. Please review the complete Terms during enrollment or setup. Remember that no one can prevent all identity theft or cybercrime, and that LifeLock does not monitor all transactions at all businesses. The Norton and LifeLock brands are part of Gen Digital Inc. For more details about how we create, review, and update content, please see our Editorial Policy.





Want more?
Follow us for all the latest news, tips, and updates.