How to encrypt email in Gmail, Outlook, iOS, and Android
Email encryption safeguards your email contents and data to prevent unwanted access. Learn how to encrypt your email in Gmail and Outlook, and discover other email-security tips. Then get Norton 360 Deluxe with its built-in VPN to encrypt all your online communications and help protect your digital life.

The advent of emails allowed individuals to remain connected regardless of time or location differences. As time has passed, we’ve come to use our email accounts for much more than just messaging with friends and family. Banking, billing, and other types of sensitive information you should safeguard are likely sent to your inbox every day.
That’s why learning how to encrypt email messages is so important. It’s a prudent step to take if you need to send someone personal or sensitive information via email.
We’ve put together a step-by-step guide on how to send an encrypted email from different providers like Google and Outlook. We also provide guidance for iOS and Android mobile devices and some email security best practices.
What is email encryption?
Email encryption is a security measure that disguises the contents of an email to protect against sensitive data exposure and ensure only the intended recipient can read it. Email encryption encodes and scrambles the plain text of the email so that any hackers taking a peek will see only unrecognizable nonsense.
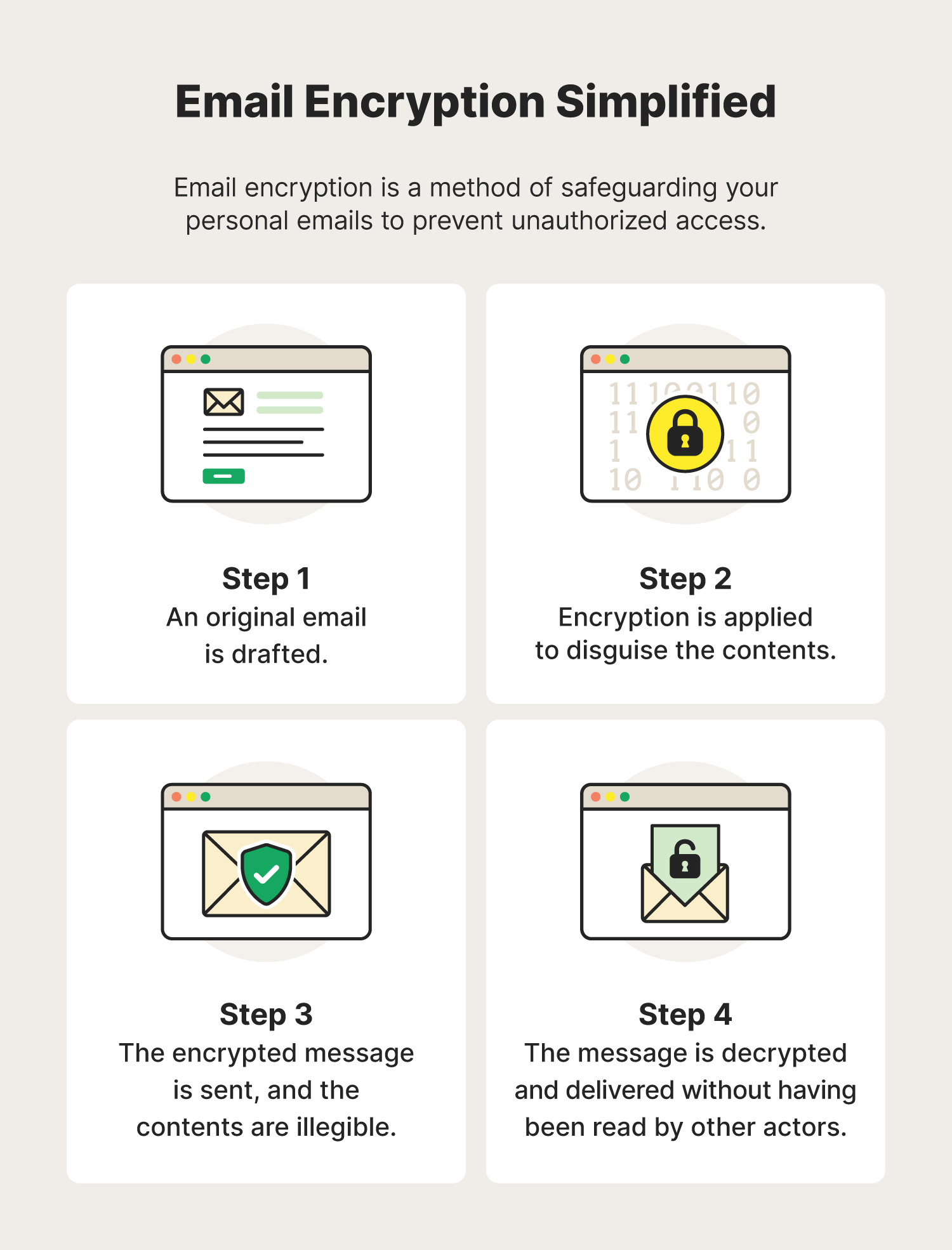
The importance of email encryption
Email encryption helps protect your personal information and communications from being exposed in data breaches and other cyberattacks. Protecting your personal information in emails can also help reduce the likelihood of identity theft.
If you send unencrypted emails, you risk hackers intercepting your messages. While a short email catching up with a friend may not have any information a scammer could use to break into your bank accounts or steal your identity, other messages could.
In 2022 alone, there were more than 21,000 business emails compromised. Using social engineering, scammers accessed business email accounts and used them to steal money, upload malware or spyware, and cause disruptions.
Types of email encryption
Understanding how email encryption works is important, and learning about the different types of protocols used for sending safer emails can help you choose the right encryption for them. Multiple email encryption protocols can protect information from unwanted online predators.
S/MIME (Secure/Multipurpose) encryption
Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extension (S/MIME) is an email encryption protocol often built into macOS devices and major web-based email providers like Outlook and Gmail. It uses public key encryption, involving digital certificates issued by a Certificate Authority for verification.
S/MIME encryption enables the sender to secure messages with these digital certificates. The recipient can then use the provided certificate to verify the safety of the message received, helping to keep their device secure.
PGP/MIME encryption
Pretty Good Privacy/Multipurpose Internet Extensions (PGP/MIME) is another encryption protocol that can send secure emails. While it provides the same protection as S/MIME, this protocol only uses the recipient’s private and public encryption keys, eliminating the need to use a Certificate Authority (CA), and instead relying on the “web of trust” model.
PGP/MIME provides more control and flexibility concerning how well you want your emails encrypted but sometimes requires a third-party extension.
SSL/TLS/STARTTLS encryption
Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security is a protocol that uses SSL and TLS (the successor to SSL) to encrypt communications between two devices, including email encryption. This type of encryption does not apply directly to messages and email contents, but to the connection between email servers.
The sending server signals the receiver to secure the connection during email transmission. This helps prevent snoops from seeing the contents of a message while it’s being sent.
How to encrypt an email in Gmail
Gmail supports Transport Layer Security (TLS) encryption tools like S/MIME to send encrypted email messages.
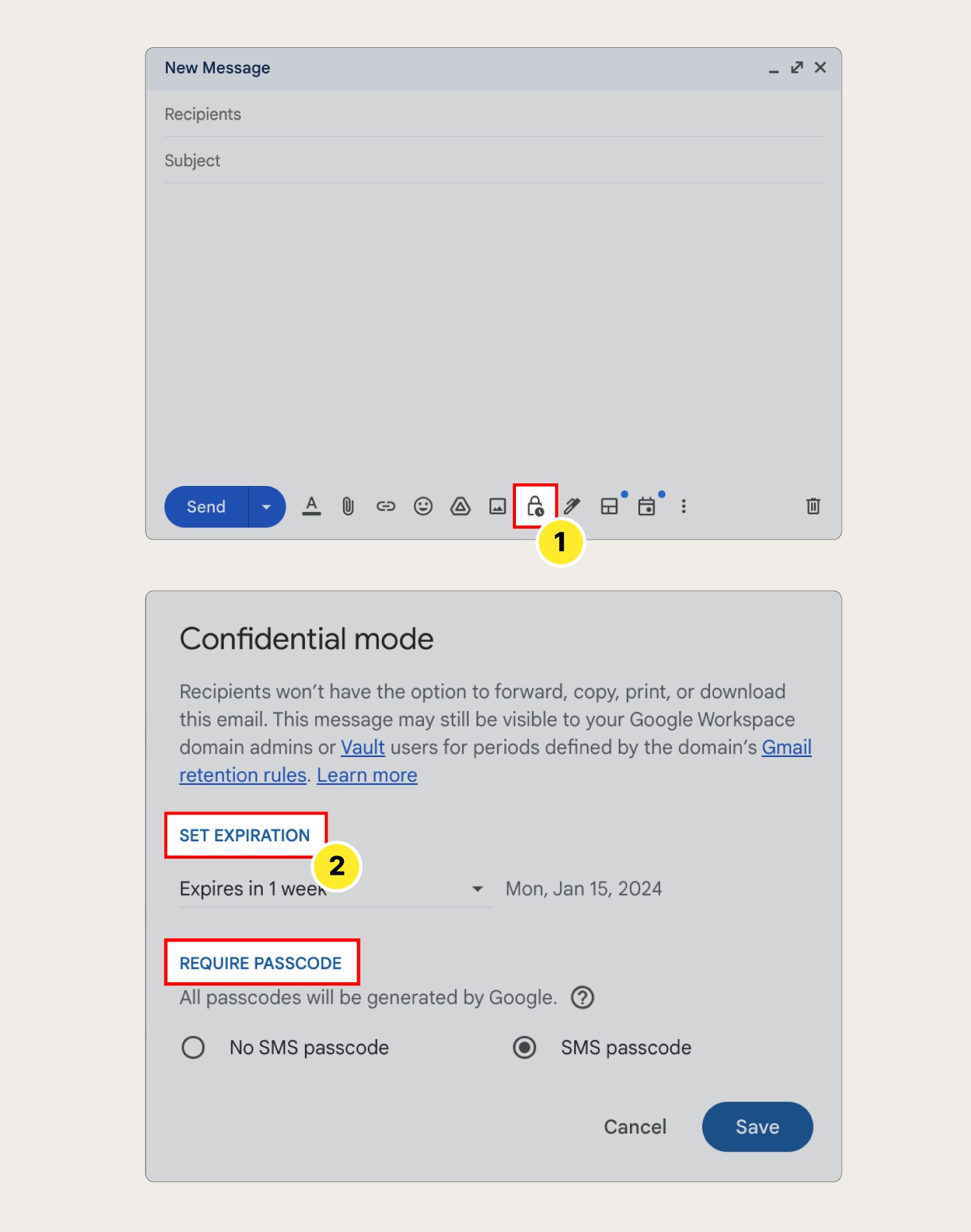
The “confidential mode” setting within Gmail lets you send secure emails. This adds an expiration date and password to an email, giving the recipient a specific window of time to view the message. The recipient will also need to have a unique passcode to gain access. This passcode will be sent by Google.
Here are the steps to encrypt an email in Gmail:
- Open Gmail and click Compose to draft a new email. Click the lock icon that says Toggle confidential mode to turn confidential mode on or tap More options on mobile (three vertical dots).
- Review the expiration date and passcode settings before hitting the Save button.
- Once the settings are saved, you can Send the email.
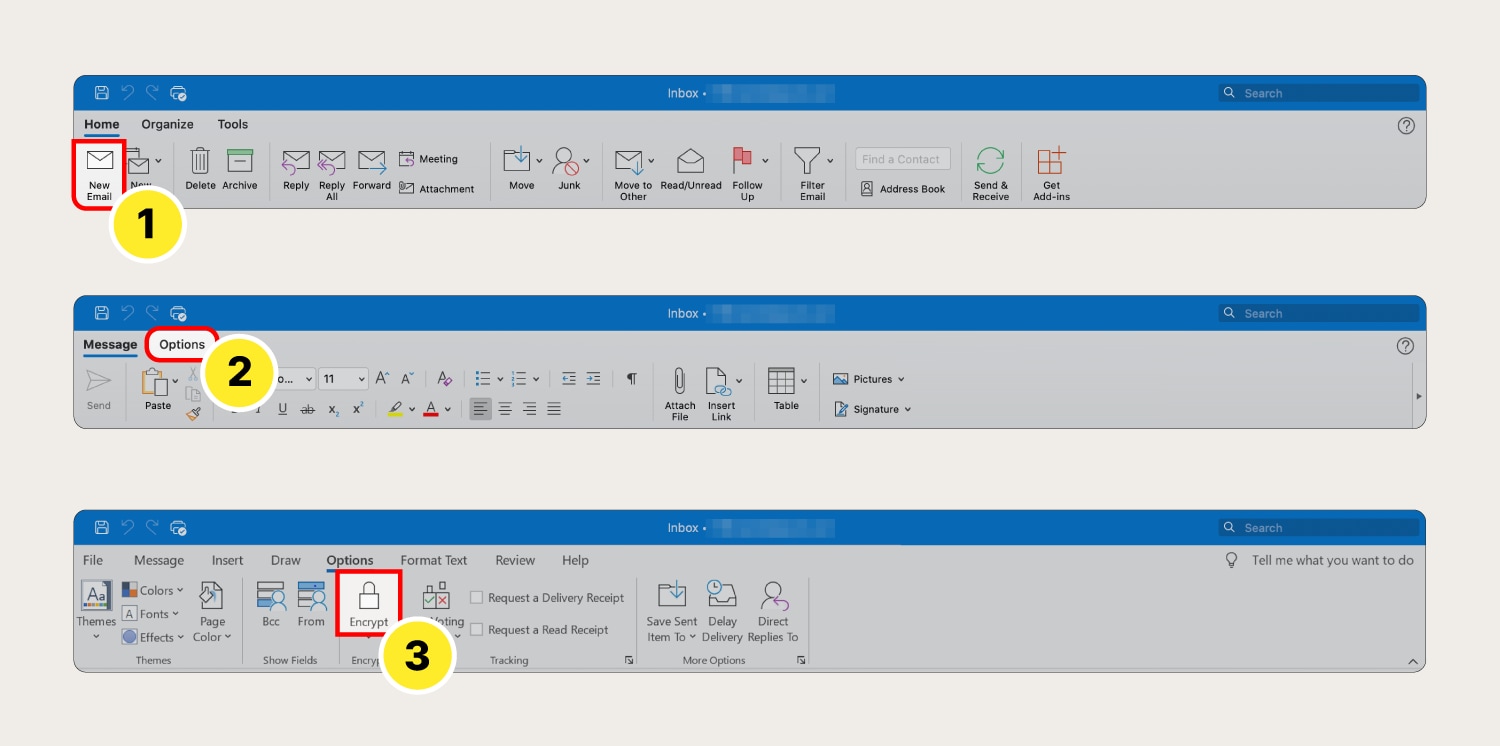
How to encrypt email in Outlook
Outlook makes it easy to send encrypted email messages as long as you have a paid Office 365 subscription. Here’s how:
- Open Outlook and press the New Email button.
- Select the Options tab.
- Click Encrypt (the lock icon), then compose and send the email as you normally would.
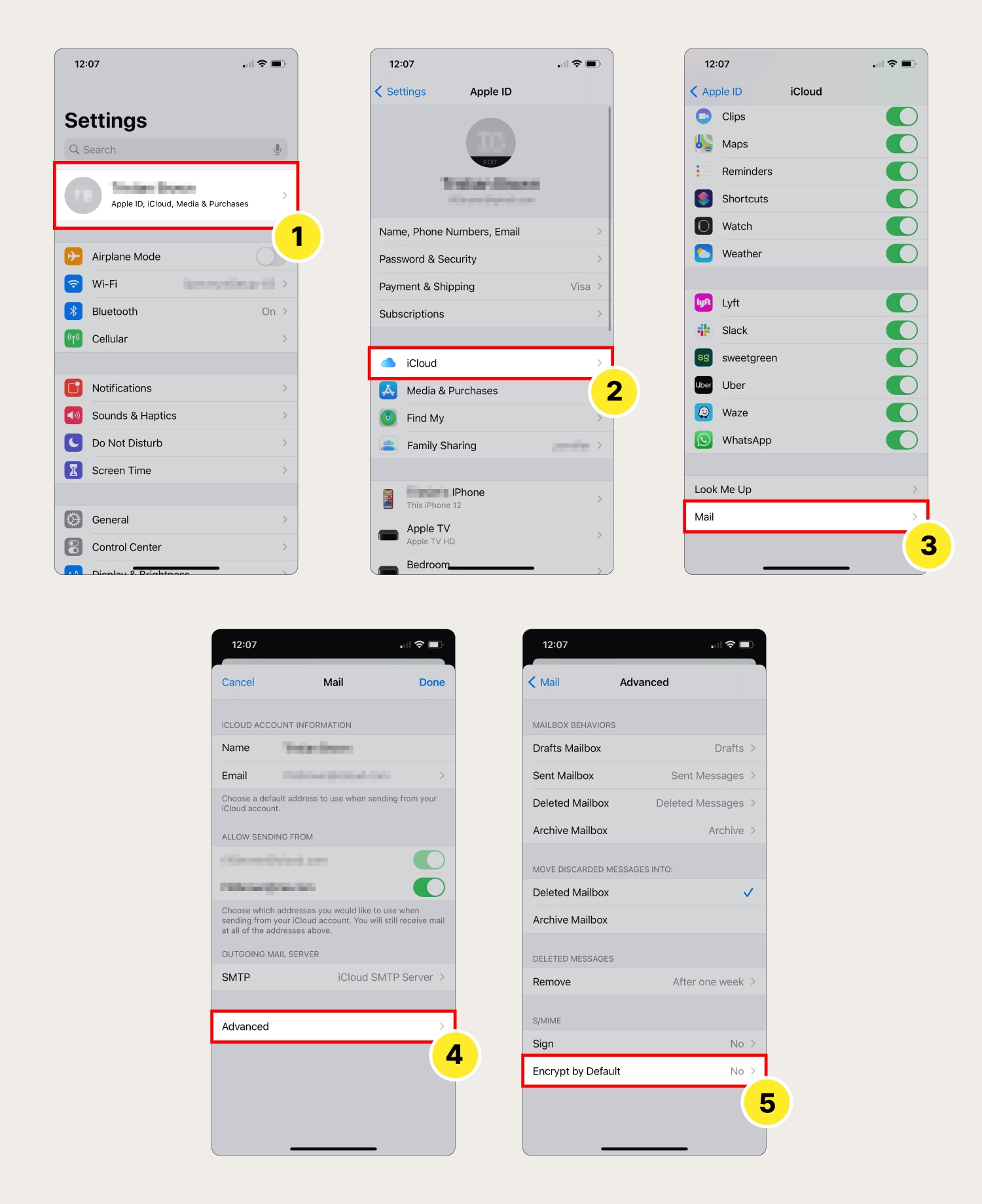
How to encrypt email on iPhone + other iOS devices
The security measures on iOS devices allow for S/MIME encryption. But you'll have to purchase and download an S/MIME certificate before successfully encrypting email messages. These steps may vary depending on the device you’re using.
- Open Settings and select your Apple ID account at the top of the screen.
- Select iCloud.
- Tap the Mail button.
- Scroll to the Advanced button at the bottom of the screen.
- Tap Encrypt by Default and make sure the S/MIME details are correct.
Email encryption for Android
Android devices are similar to iOS devices in that they can support an additional encryption extension to protect emails. However, these devices require the PGP/MIME protocol and third-party apps to send secure emails.
Email encryption tools/services
Because some email providers and device makers make it harder than others to send encrypted email messages, there are also some third-party tools you can use to help send secure emails.
A few of the free apps available to send and receive encrypted messages, along with a few anonymous email services, include:
- GPGTools
- Mailvelope
- GNU Privacy Guard
- AnonEmail
- Proton
How to read encrypted emails
These are the main methods for reading encrypted emails:
- If an email is encrypted and protected by a password, you must enter the password to decrypt the email and read it.
- If an email is encrypted and not protected by a password, you’ll need to have the encryption key before the message's contents are readable.
5 email security best practices
Knowing how to encrypt email messages is a great start to improving your email security. With the following steps, you’ll make it more difficult for hackers to get into your email. These practices and other identity management routines can help you better protect your information.

1. Create strong email passwords
Cyberattacks and data breaches are not only carried out using session hijacking or brute force attacks. Today’s cybercriminals also use strategic methods, like credential stuffing, to access sensitive information. Having a well-thought-out and unique password can lessen the likelihood of you falling victim to these kinds of cyberattacks.
Because remembering several unique and difficult passwords can be tough, you should consider using a password manager.
Norton 360 Deluxe comes with a built-in password manager that helps you create and securely store your passwords and access them whenever you need them.
2. Use two-factor authentication
Two-factor authentication (2FA), a type of multifactor authentication, adds another step to your login process to keep unauthorized users from gaining access to your account. Email providers like Gmail and Outlook are already using these tools.
Some 2FA uses biometrics, like a fingerprint or FaceID, and a password before logging in. Others will send a text message to your device with a code you’ll need to log in. These login requirements are usually inaccessible to everyday hackers, meaning your email will be more secure.
3. Beware of phishing emails
Hackers use phishing scams to access people's private information. One common type of phishing involves a scammer sending emails embedded with links leading to malicious websites designed to trick you into entering your login credentials. Those credentials are then saved and used to access your actual accounts.
Always verify that you're on a site’s proper URL, and try to avoid opening emails that appear to be suspicious.
4. Avoid accessing emails via public Wi-Fi
Whether you’re checking your account balances while in line for coffee or checking your email while at lunch, if you’re doing it on a public Wi-Fi network, your data is at risk. Public Wi-Fi networks make it easy for cybercriminals to hack and siphon off information from everyday people because they’re often unencrypted.
If you’re using public Wi-Fi, consider downloading a virtual private network (VPN) to put a protective shield over your device.
VPNs obscure the location of your device and encrypt your online traffic so no one can access your data. Norton VPN helps secure the data you send and receive online, even if you’re connected to public Wi-Fi.
5. Always log out when finished
You should always log out of your email account after you've finished using it. This applies to when you're on both unfamiliar and familiar devices. If a hacker enters a protected network, you don’t want them to have a clear pathway toward the information they’re looking for by leaving your accounts wide open.
Protect your personal communication and information
Protecting your data, privacy, and identity is undeniably important. And with all of the threats lurking online today, it pays to have help. With trusted security software like Norton 360 Deluxe, you’ll get help protecting your devices from malware, hackers, and scammers who want to compromise your devices and steal your data.
FAQs about encrypting email
Still have questions about encrypting email messages? We have answers.
How do I encrypt a document before emailing it?
Learning how to encrypt email attachments depends on the type of document, but some documents will allow you to save them in an encrypted format. For documents without built-in encryption, you can use a third-party program to encrypt your documents.
How do I password-protect an email attachment?
It depends. For some types of attachments, you can save them with a password requirement. Other types of attachments can be password-protected within an email system, though this feature is not available for all providers.
Is it a good idea to encrypt your email?
It is usually a good idea to encrypt your email, especially if you’re sharing any information you’d like to keep private. If somebody hacks your email, having certain types of email encryption can prevent the hacker from reading your messages.
What is the difference between encrypted email and secure email?
Encrypted emails are messages that are themselves encrypted, meaning that they are secure whether they’re in your sent messages or the inbox of the intended recipient. Secure email means that the data in an email account is secure within the system, but individual emails are not necessarily encrypted.
Editorial note: Our articles are designed to provide educational information for you. They may not cover or protect against every type of crime, fraud, or threat we write about. Our goal is to increase awareness about Cyber Safety. Please review the complete Terms during enrollment or setup. Remember that no one can prevent all identity theft or cybercrime, and that LifeLock does not monitor all transactions at all businesses. The Norton and LifeLock brands are part of Gen Digital Inc. For more details about how we create, review, and update content, please see our Editorial Policy.
- What is email encryption?
- The importance of email encryption
- Types of email encryption
- How to encrypt an email in Gmail
- How to encrypt email in Outlook
- How to encrypt email on iPhone + other iOS devices
- Email encryption for Android
- Email encryption tools/services
- How to read encrypted emails
- 5 email security best practices
- Protect your personal communication and information
- FAQs about encrypting email








Want more?
Follow us for all the latest news, tips, and updates.