What is cloud security? Benefits & best practices
Cloud security helps back up, store, and secure photos, documents, and other files in the cloud. Learn about different types of cloud security and the benefits and risks. Then get Norton 360 Deluxe with built-in Cloud Backup1 to help store and protect the critical files and data you need to keep safe.

As our lives move online, more and more of our important information gets stored in cloud-based storage systems like Dropbox, iCloud, and Google Drive. This includes everything from cherished family videos to critical work documents. While cloud storage offers convenience and accessibility, it's natural to wonder how secure this data is. That’s where cloud security comes in.
But what is cloud security exactly? We’ve created this comprehensive guide to answer that question and deepen your understanding of how to protect your cloud data.
We’ll discuss the importance of cloud security, how companies secure your data in the cloud, common cloud security risks, and cloud security best practices you can use to take control of your Cyber Safety.
After all, there’s no better time than the present to learn how to safeguard your data, protect your privacy, and prevent files that aren’t stored properly from being compromised, which can lead to identity theft.
What is cloud security?
Cloud security refers to the safety guidelines, technology, and best practices that help prevent unauthorized access to data stored on cloud-based platforms. When you store data in the cloud, it’s stored on the servers of the cloud service provider (CSP) rather than locally on your device.
The CSP offering the cloud service is responsible for monitoring and responding to security risks that threaten its cloud infrastructure. However, it’s a shared responsibility.
This means it’s up to users—whether they’re businesses or individuals using a cloud-based service—to follow best practices to protect their data in case of data leakage or theft.
Types of cloud computing
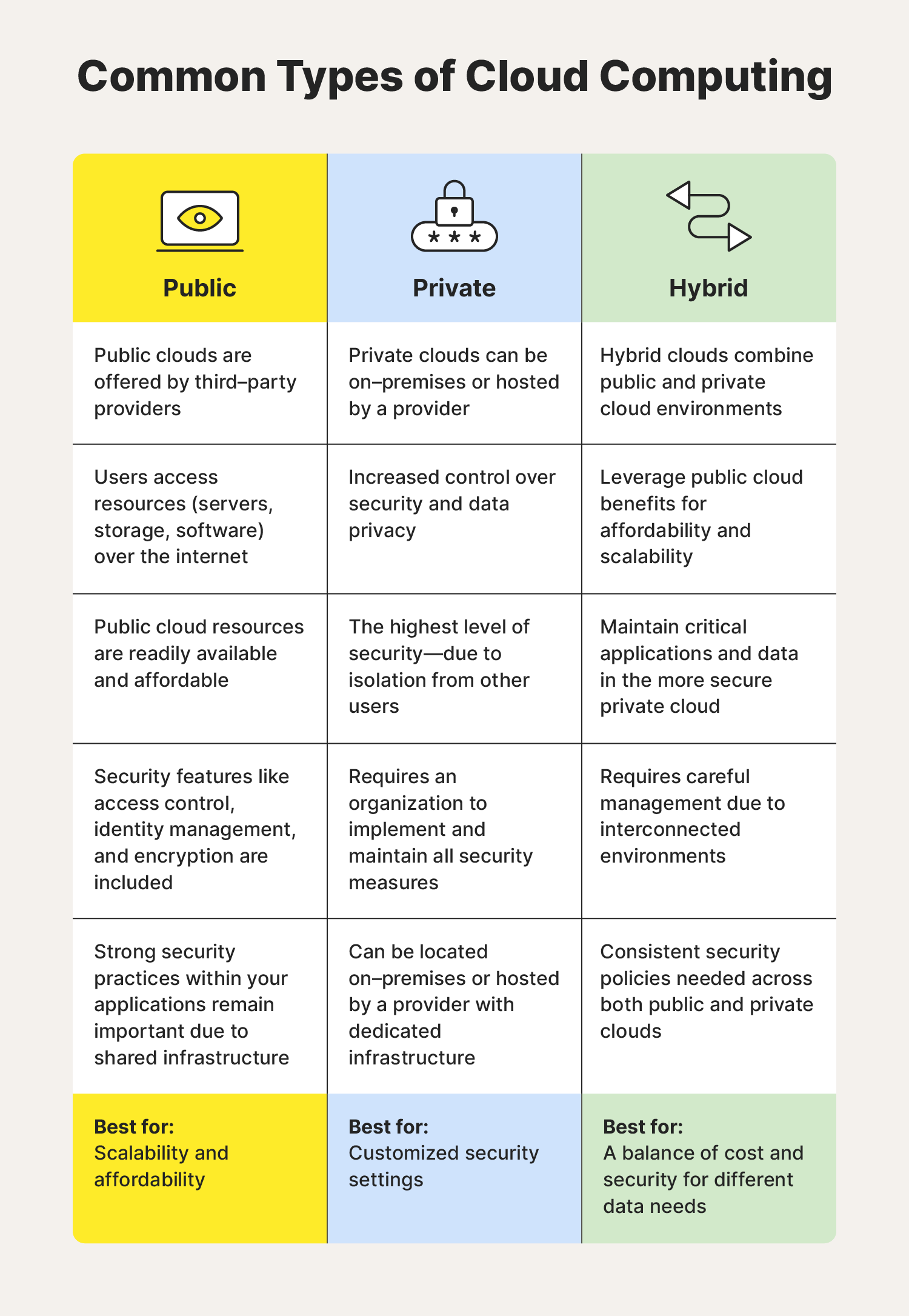
There are three distinct types of cloud computing: public, private, and hybrid clouds. Some of the main differences between the cloud environments are accessibility, cost, and where the servers are located.
Here’s a closer look at the main options available:
You may have also come across references to the multi-cloud approach. That’s probably because 89% of companies use this method, which refers to organizations using services from at least two cloud providers. The mult-cloud approach is often used to take advantage of different cloud providers’ strengths for specific workloads, and it can embrace a mix of public, private, and hybrid clouds.
Let’s examine in more detail public, private, and hybrid environments.
Public clouds
Public clouds are owned and operated by third-party providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). Users access resources like servers, storage, and software over the internet. These are readily available and affordable.
Public cloud providers often adhere to strict compliance standards, which can enhance security measures, so choosing the right service for your organization is key. Features can include access control, identity management, and encryption. However, you’re still responsible for securing your data and apps, while the service looks after the infrastructure.
Best for: Scalability and affordability.
Private clouds
Private clouds are dedicated to a single organization. They can be located on-premises or hosted by a provider with dedicated infrastructure. This isolation offers greater control over security and online data privacy.
Private clouds can offer the highest level of security, as long as a robust security strategy is in place. However, this also means organizations are responsible for implementing and maintaining all security measures.
Best for: Greater control and customized security settings.
Hybrid clouds
Hybrid clouds combine public and private cloud environments. This allows organizations to leverage the cost-effectiveness and scalability of public clouds while keeping critical applications and data on the private cloud where they can tailor security settings to their needs.
Due to its interconnected nature, security in a hybrid cloud requires careful management. Organizations must ensure consistent security policies across both environments and have measures in place to control data flow between them.
Best for: Balancing cost and security for different data needs.
Why is cloud security important?
Cloud security is important for protecting data stored in the cloud so that it’s safe and accessible when needed. For individuals, poor cloud security could mean losing everything from sensitive work files to irreplaceable photos. For businesses, the repercussions could be reputational, financial, or legal.
Cloud security is important to:
- Protect data stored in the cloud.
- Ensure businesses comply with data regulations.
- Ensure resources are accessible at all times.
- Help businesses maintain the trust of their customers.

Cloud security benefits
As you might expect, cloud security offers several advantages for individuals and businesses.
- Protects sensitive data: Cloud security safeguards personal information and critical documents from unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Enhances security and compliance: Cloud providers invest heavily in advanced security infrastructure and follow strict data privacy regulations, ensuring data management meets industry compliance standards.
- Offers continuity and reliability: Cloud storage offers redundancy and disaster recovery features, minimizing downtime and ensuring data remains accessible even during outages or disruptions.
- Manages reputations: By prioritizing cloud security, businesses demonstrate a commitment to protecting customer data and building trust.
How secure is cloud storage?
The security measures undertaken by larger companies providing cloud services to individuals will likely be more robust and powerful than what you have protecting your home computer and devices.
But remember, hackers can use malware and phishing emails to steal your personal information. So always be vigilant about your online safety and use two-factor authentication and a strong password to secure your cloud storage account.
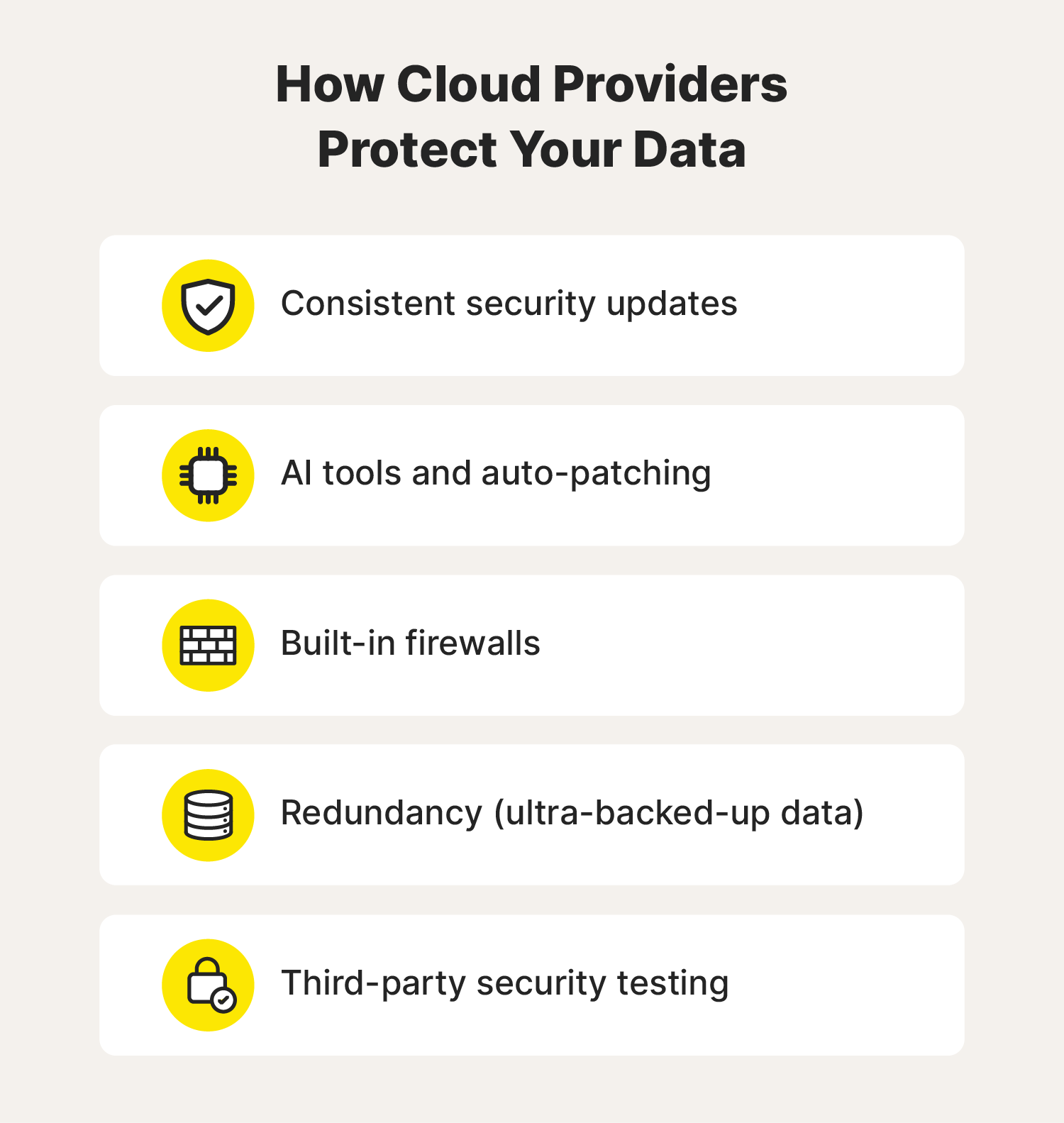
Cloud service providers typically have strong security measures in place, including:
- Proactive security measures: Cloud providers constantly update their systems, utilize AI for threat detection, and implement firewalls.
- Redundancy and backups: Your data is replicated across multiple servers, ensuring accessibility even during outages or hardware failures.
- Third-party security testing: Cloud providers regularly undergo security audits by third parties to identify and address any threats, including viruses.
By employing these measures, cloud storage providers can offer a high level of security for your data.
Cloud security risks and concerns
While cloud providers implement many security measures to protect your data, that doesn’t mean there aren’t risks of cyberattacks. 46% of organizations have experienced a data breach in their cloud environment. The best defense against these attacks is preventing them in the first place.
To understand data security, let’s explore common cloud security risks and concerns for individuals and businesses.

Common cloud security threats
Cloud security faces threats from various forces. Here are some common cloud security risks to be aware of:
- External or insider threats: While hackers are a concern, human error or negligence from authorized users can also compromise data security. This could result from inadequate training, weak passwords, or accidentally sharing sensitive information.
- Cloud-native breaches: Attackers specifically target vulnerabilities within cloud platforms to gain access, steal data, and exploit it.
- Limited visibility and control: Depending on the service model, CSPs may have full control over the cloud system’s design and infrastructure, leaving the users or client almost entirely out of the loop. This may also include a lack of visibility around security measures.
- Privacy and data protection: While CSPs follow strict guidelines on protecting data, some may share users’ data with third parties, such as subcontractors involved in providing the cloud service. The terms of service and privacy policies will vary with each CSP.
Cloud security tips
Follow these security tips to protect your data within the cloud.
- Follow strong security measures: To safeguard your data, use antivirus software, two-factor authentication, and strong passwords.
- Make informed decisions: Before committing to a cloud service, understand its security features and the level of control you have over your data.
- Review user agreements: Carefully read user agreements to understand data privacy practices and whether your data could be shared with third parties.
Cloud security best practices
Now that you understand how different cloud security risks could compromise data stored in the cloud, let’s look at how to mitigate threats. First, we’ll share cloud security best practices for individuals, and then businesses.

1. Back up your data
One way to prevent information loss or misplacement is to perform data backups. Tools like external hard drives and flash drives can help you be prepared in an emergency, but hardware isn’t infallible.
Norton PC Cloud Backup1 is a valuable solution that allows you to securely safeguard copies of your computer files, ensuring you won’t lose them if your computer is misplaced, damaged, or subjected to ransomware attacks. Having copies on a computer or physical storage device as well as the cloud gives you extra protection.
2. Practice password hygiene
Creating strong unique passwords is imperative for your cloud security and the Cyber Safety of all your devices, accounts, and networks. Unique passwords can help protect against cyberattacks like password spraying and credential stuffing. Use a password manager to create strong passwords and keep track of them all.
Norton Password Manager has a built-in password generator to help you create new, hard-to-break passwords with a single click. It also helps to secure logins in your private, online vault. And you can access your vault quickly with Touch ID/Face ID or Android biometrics on your mobile devices.
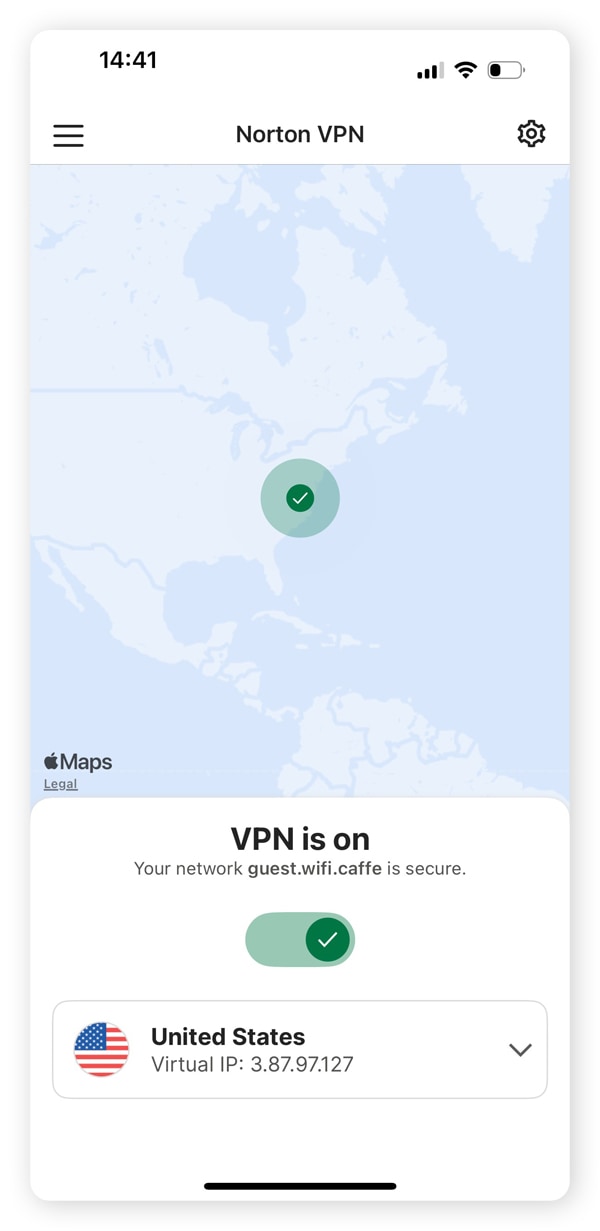
3. Use a VPN to encrypt your data
VPNs encrypt the data you send over the internet and to cloud storage. Norton VPN allows you to mask your IP address to hide your cloud traffic and network activity, which is especially important on public Wi-Fi.
4. Monitor your network regularly
You can monitor your network using network monitoring software or manually. You should regularly check the list of connected devices and make sure you recognize them all. Some routers let you set up alerts to notify you when unknown devices connect to your network so you don’t have to do this manually.
5. Enable two-factor authentication
When given the option, enable two-factor authentication for an extra layer of security on your accounts, devices, and connected cloud platforms like Dropbox. Using biometrics like fingerprint scans and facial recognition makes forging your identity incredibly difficult.
6. Download antivirus software
Antivirus software like Norton 360 Deluxe helps protect against malware, ransomware, and hackers. You should always use an antivirus on all your devices, no matter how secure your cloud service or passwords are. After all, just clicking a malicious link can infect your device and leave your data vulnerable.

7. Regulate access to data
Use data security policies to limit who can access cloud data and help protect against potential unauthorized users. It also lessens the risk of insider threats compromising valuable data.
8. Perform risk assessments
Businesses should use risk assessments to identify areas vulnerable to cyberthreats. To improve cloud security, update these assessments to include the cloud service used and evaluate how workers operate the system. This will give you a deep understanding of the potential risk factors threatening the cybersecurity of your cloud environment.
9. Incorporate application programming interfaces (APIs)
APIs can help businesses automate security operations and enable security tools and services to work together. Another function in relation to cloud security is access control and ensuring that authorized users can perform only the tasks they need to.
APIs can also help businesses understand who’s accessing data and when, along with where users download and share that information.
10. Modify security permissions
Modifying default security permissions like sharing capabilities and access controls set by CSPs can help configure your cloud network to your security needs as a business. It’s best to set restrictions regarding who can download and view cloud data and where.
11. Comply with regulations
Before committing to a CSP as a business, it’s imperative to ensure the cloud service adheres to government and industry standards to avoid legal troubles. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the U.S. and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe are just two examples.
12. Automate cloud security monitoring
Businesses should invest in cloud security solutions that autonomously identify and remedy security risks, allowing them to focus on other critical business operations. There are many tools and monitoring services that can be leveraged, from automated incident alerts to using artificial intelligence to predict anomalies and detect threats.
Help keep your data secure
Norton 360 Deluxe provides multiple layers of protection for your connected devices and online privacy. It comes with Cloud Backup1 to give you 50 GB of secure cloud storage. Plus, it includes a built-in VPN, Password Manager, and other security tools to help block hackers and malware. Download Norton 360 Deluxe and use it on up to five devices with just one account.
1Only available on Windows systems (but not in S mode or on ARM processors).
Editorial note: Our articles provide educational information for you. Our offerings may not cover or protect against every type of crime, fraud, or threat we write about. Our goal is to increase awareness about Cyber Safety. Please review complete Terms during enrollment or setup. Remember that no one can prevent all identity theft or cybercrime, and that LifeLock does not monitor all transactions at all businesses. The Norton and LifeLock brands are part of Gen Digital Inc.








Want more?
Follow us for all the latest news, tips, and updates.