Dictionary attack: A definition + 10 dictionary attack protection tips
Use this dictionary attack guide as an overview of how dictionary attacks work, real-life examples, and protection tips to help keep your data safe.

A dictionary attack is a brute force technique used to break into vulnerable online accounts. Dictionary hackers take advantage of people who may not know the importance of creating strong, hack-proof passwords for each of their profiles. And this likely played a role in how 330 million people fell victim to cybercrimes, including dictionary attacks, in 2021.
To that end, turn to this guide for an overview of what dictionary attacks are, how dictionary attacks work, and the difference between a dictionary attack vs. a brute force attack. You’ll also find real-life dictionary attack examples and protection tips to help keep your profiles and personal information safe.
How does a dictionary attack work?
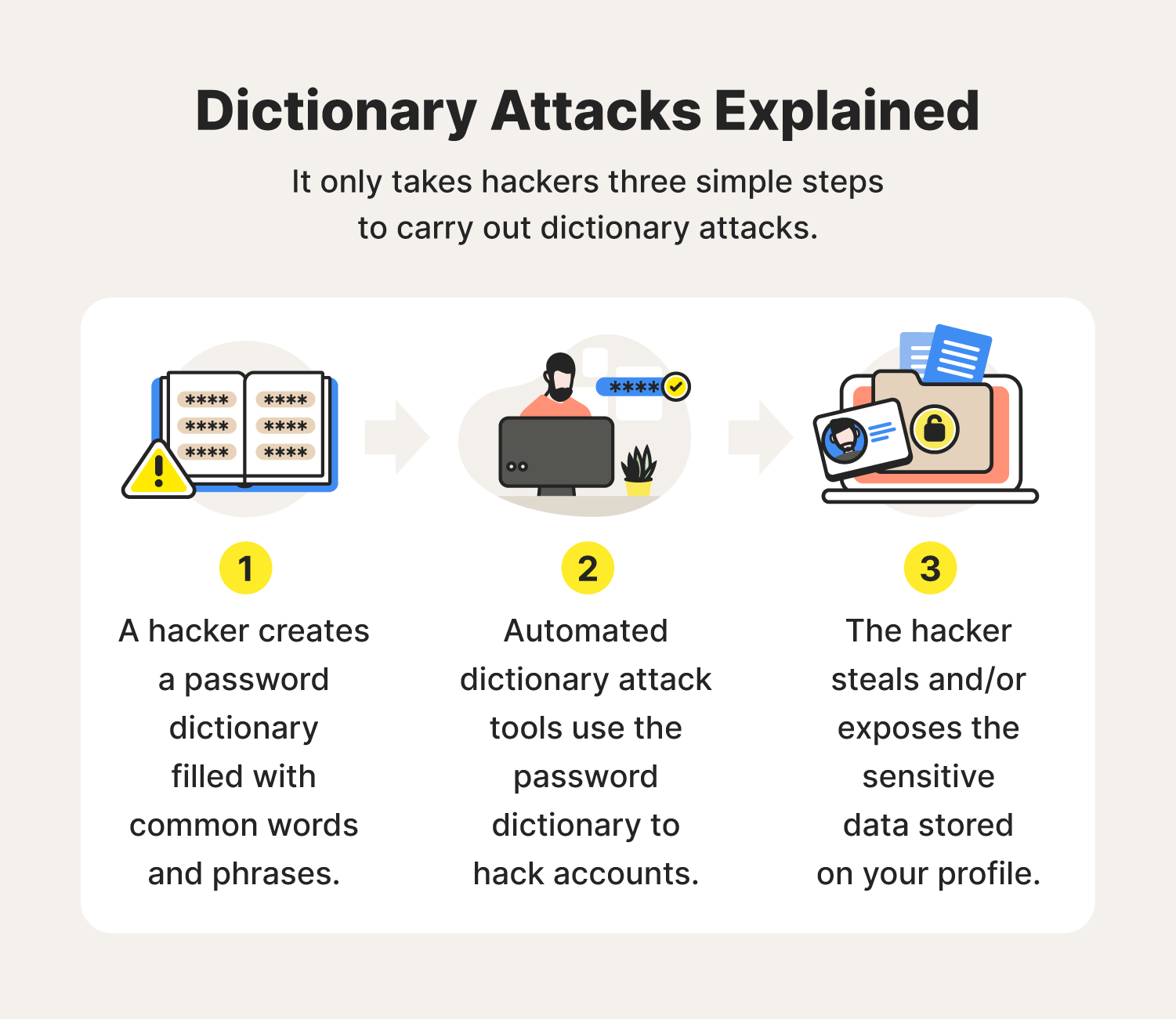
One of the first steps to beating any opponent is by getting in their head. Take a look at how hackers carry out their dictionary attacks so you can learn how to better your defense:
- A hacker creates a password dictionary filled with common words and phrases that may work as passwords.
- Automated dictionary attack tools use phrases in the password dictionary to break into vulnerable accounts.
- The hacker steals and/or exposes the sensitive data stored on your profile, potentially for financial gain or other malicious intent.
It’s nothing too complicated. But you should know there are important differences between a dictionary attack and its older, stronger cyberattack cousin that uses brute force.
Differences between dictionary attacks and brute force attacks
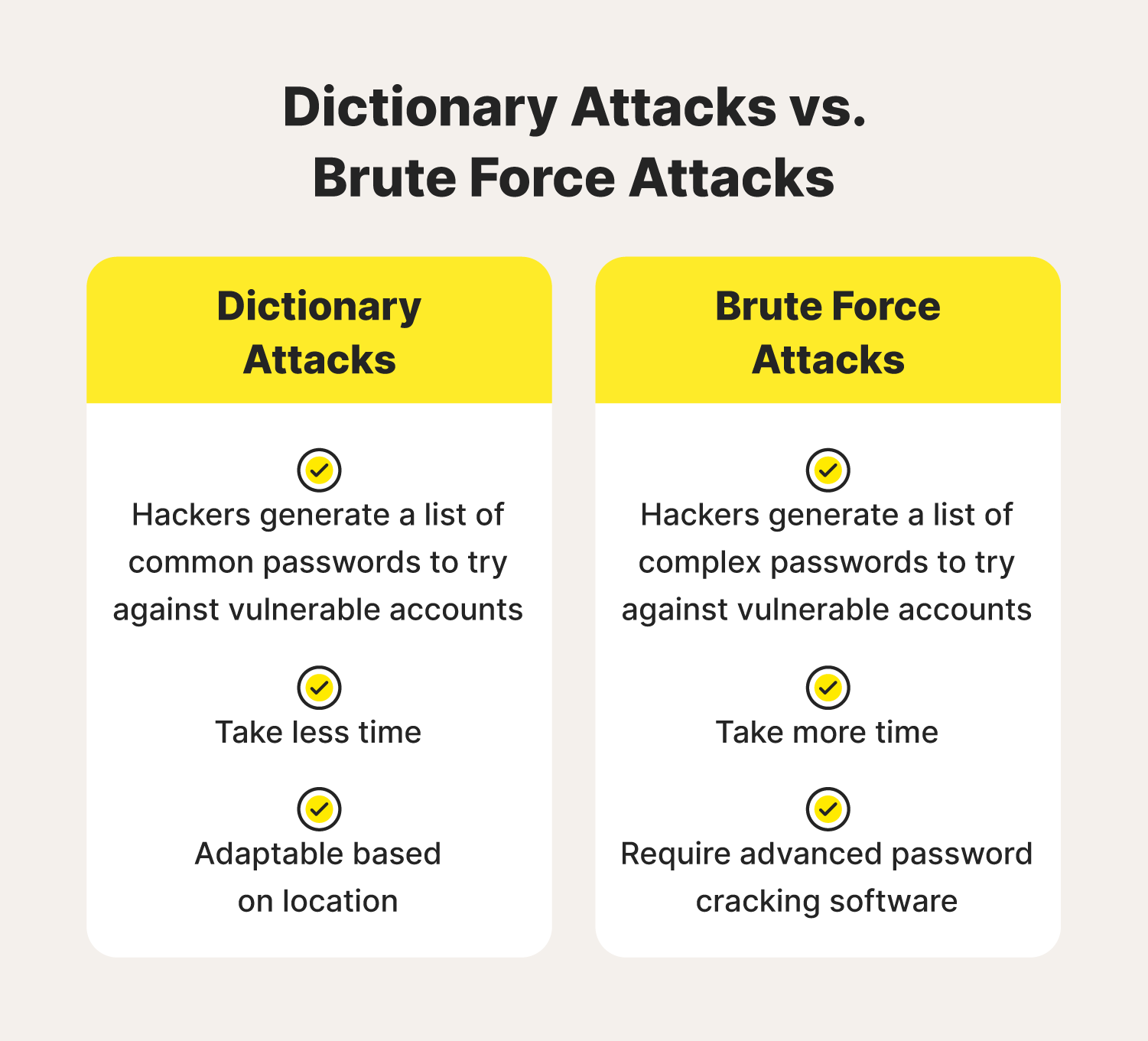
The difference between a dictionary attack vs. a brute force attack lies in the type of passwords tested against your accounts. Brute force attacks try short and random passwords containing various letters, numbers, and characters. This hacking method requires advanced software and often takes more time.
Dictionary hackers use what are known as password dictionaries. These are lists of common words and phrases that people may quickly think of when creating an account. They’ll include simple phrases like “qwerty” and combinations like “1234.” But some may consider location as well. For example, hackers in San Francisco may include phrases like “GoldenStateWarriors” or “AlcatrazIsland.”
Examples of successful dictionary attacks
To help you understand how relevant — and successful — this emerging cyberthreat is, here are some recent dictionary attacks carried out on digital citizens just like you in recent years:
- GMZ, 2009: A hacker known as GMZ used a dictionary attack to hack into a Twitter account belonging to an employee with administrative privileges, allowing them to access other high-profile accounts owned by celebrities such as President Barack Obama and singer Britney Spears.
- SolarWinds, 2020: Russian hackers used a dictionary attack to hack into SolarWinds company servers and embed malware capable of stealing sensitive and confidential data.
- Tel Aviv, 2021: An Israeli cybersecurity researcher was able to gain access to more than 3,500 Wi-Fi networks using dictionary attack software.
- TransUnion South Africa, 2022: A TransUnion representative reported a data breach that resulted from a dictionary attack and led to the company receiving a $15 million ransom note.
10 tips to avoid dictionary attacks
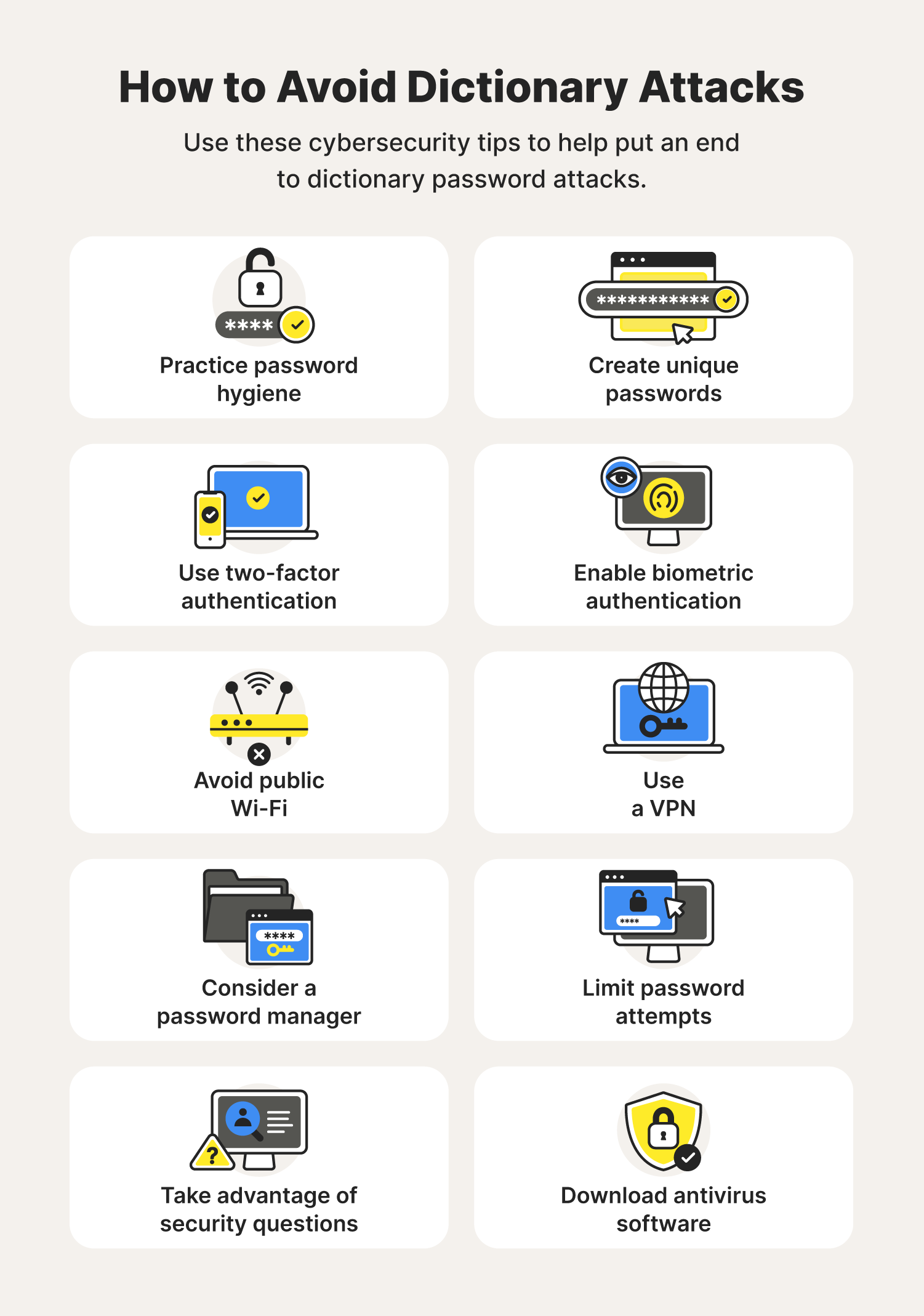
Avoiding dictionary attacks begins with improving your password security. Follow these tips to do just that, as well as level up cybersecurity to help avoid dictionary attacks to the fullest.
1. Practice password hygiene
One of the secrets to keeping your personal information safe is by putting your password hygiene above anything else. Not only does this involve creating different passwords for each of your accounts, but it also means you need to:
- Change passwords regularly
- Never share login information
- Avoid repeat password patterns
2. Create unique passwords
Recent findings show that 99% of users reuse their passwords. This results in hackers using tricks such as dictionary attacks, credential stuffing, and password spraying to break into your profiles. To avoid these cyberattacks, remember to use a mix of numbers, letters, and symbols in your passwords. Not to mention, interchanging uppercase and lowercase letters also goes a long way.
3. Use two-factor authentication
Two-factor authentication, also known as multi-factor authentication, acts as another layer of protection added to your login process. The additional step uses unique codes sent to verified phone numbers and email addresses to prove your identity. The unique PINs sent in these messages typically expire after a period of time, and multiple wrong answers can lead to the system locking your account.
4. Enable biometric security features
Biometric security features act as another form of two-factor authentication. Facial recognition and fingerprint technology make it incredibly hard for cyberthieves to impersonate their targeted victims. And similar to the security PINs, too many wrong attempts will likely lock your account until you or another authorized user resets the credentials.
5. Avoid public Wi-Fi
Public Wi-Fi presents security concerns for those with more vulnerable devices. A lack of firewalls and other security features makes it easy for cybercriminals to track IP addresses and browsing activity. They could also go a step further and use this insecure internet connection to install different types of malware onto your device.
6. Use a VPN
VPNs are a great cybersecurity tool if you end up using public Wi-Fi. They mask your IP address and associated network activity, encrypting data you send and receive and helping ensure prying eyes won't be able to watch your every move.
7. Consider a password manager
Keeping track of every one of your passwords is hard for even the most organized individual. Password managers are the perfect tool for those that want to keep their passwords in one central location, and need help generating and protecting new and/or existing ones.
8. Limit password attempts
Some accounts allow you to limit how many failed login attempts you get before the system locks your account. This is helpful in the event someone tries to break into your account, but also if you’re the one who is trying to figure out what your password is.
Cybercriminals will find themselves stuck once they max out their attempts. But if you’re the one trying to get in, you’ll know when to stop and simply request a password reset before your entire profile locks.
9. Take advantage of security questions
Security questions were one of the first multi-factor authentication methods used for online accounts. These are personal questions that require specific answers for you to gain access to your account. Though sometimes ineffective against cybercriminals who can perform large-scale data breaches to find these answers, they are still a useful tool to keep your information safe.
10. Download antivirus software
Antivirus software acts as an essential tool in helping to keep all of your personal details and data protected online. The 24/7 protection provided can alert you to a potential dictionary attack or cyberthreat that makes its way onto your computer and help protect against threats.
There you have it. You not only know what is a dictionary attack, but also how to help avoid potential dictionary attacks. Go forth with confidence knowing you can protect your digital footprint from prying eyes.
Dictionary attack FAQs
Read through some frequently asked questions regarding dictionary attacks to ensure you have a full understanding of how these cyberattacks work.
Why is it called a dictionary attack?
Dictionary hackers use extensive lists of common words and phrases to guess people's passwords — similar to how a dictionary looks.
Is dictionary attack active or passive?
Dictionary attacks are active. Hackers attempt to gain network access by trying as many combinations as possible.
How can malware be used to steal your password?
Hackers could use hacking tools such as dictionary attacks, spyware, credential stuffing, and other cyberattacks to steal passwords and gain access to your information.
How long does a dictionary attack take?
Hackers can quickly crack simple passwords with dictionary attacks. Complex passwords, on the other hand, could take days, weeks, or even months to break.
What is a hybrid dictionary attack?
A hybrid attack combines a dictionary attack with a brute force attack. Hackers create an extensive list of stolen passwords and use brute force software to try those passwords with a number of different combinations until successful.
Editorial note: Our articles are designed to provide educational information for you. They may not cover or protect against every type of crime, fraud, or threat we write about. Our goal is to increase awareness about Cyber Safety. Please review the complete Terms during enrollment or setup. Remember that no one can prevent all identity theft or cybercrime, and that LifeLock does not monitor all transactions at all businesses. The Norton and LifeLock brands are part of Gen Digital Inc. For more details about how we create, review, and update content, please see our Editorial Policy.





Want more?
Follow us for all the latest news, tips, and updates.