How to overclock your CPU to speed up your PC in five steps
Overclocking boosts CPU speed for tasks like gaming and video editing, but if you’re not careful, you could damage your computer. Learn how to overclock your CPU safely, and how Norton Utilities Ultimate can further optimize performance by helping clean up your PC to keep it running like new.
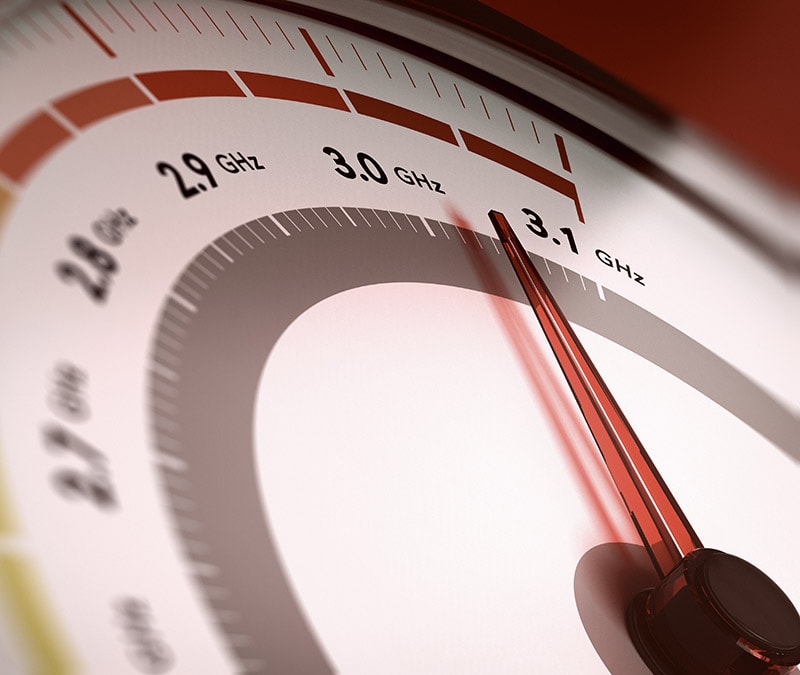

Overclocking is the process of increasing your CPU’s maximum clock speed — how fast it processes instructions — beyond its factory settings. It lets your processor run faster than the manufacturer intended, helping your computer complete tasks more quickly.
This can be particularly useful for gamers, but improper overclocking could cause your system to overheat or become unstable. In this article, you’ll learn how to overclock your PC safely in five steps.
1. Verify your system’s overclocking support
First, you need to check that your computer’s hardware can handle overclocking. This means confirming that your CPU, motherboard, cooling system, and power supply unit are all equipped to handle this performance-intensive task.
Here are the hardware details you’ll need to verify:
- Intel CPUs: Only Intel processors with a K or X suffix (e.g., Intel Core i9-14900K) support overclocking.
- AMD CPUs: Most modern AMD processors support overclocking, and many include Ryzen Master software, which makes overclocking more user-friendly.
- Intel motherboards: X- and Z-series motherboards support full CPU overclocking, while the mid-range and B- and H-series motherboards typically limit overclocking to memory (RAM) only.
- AMD motherboards: B- and X-series AMD motherboards support CPU overclocking, while A-series motherboards generally don’t.
- Cooling system: Gaming PCs often come with enhanced cooling setups that are suitable for overclocking. These include high-performance air coolers, all-in-one liquid coolers, or custom loops. Budget systems with stock coolers may require an upgrade to avoid overheating.
- Power supply unit (PSU): Use a quality PSU from a reputable brand with adequate wattage. Overclocking usually requires a minimum of 500–600 watts, depending on your CPU.
Note that laptops are generally not suitable for overclocking.


2. Monitor baseline performance
Once you’ve determined that you have the right hardware, you need to monitor your computer’s baseline performance. If your PC already runs at an abnormally high temperature, such as 185°F or higher, it may be overheating, so investigate cooling or airflow issues before overclocking.
Monitor your baseline performance by stress-testing your PC in an environment that replicates high-intensity gaming using benchmarking tools (listed below). Key metrics to monitor during stress testing include:
- CPU temperature: This should typically be below 113°F when idle, or below 185°F under load.
- CPU usage: Check for an unusually high usage percentage during idle or light tasks. High usage at these times may signal system issues.
- Clock speeds: Note the base and boost clock speeds for your CPU, so you can compare them to overclocked speeds later.
- Power consumption (in watts): Monitor how much power your computer is using to ensure it can handle increased demand.
- Voltage: Excessively high or fluctuating voltages can signal instability or poor power regulation.
Watch for signs of instability like system crashes, throttling (clock speed drops), high fan speed, or unexpected shutdowns. These can indicate your PC isn’t ready for overclocking or needs better cooling.
Here are some tools you can use to monitor the metrics listed above:
- HWMonitor: A hardware monitoring program that helps you monitor your PC’s voltages, temperatures, powers, currents, fan speed, and clock speeds.
- Prime95: Specialized stress testing software focusing on CPU and memory.
- Cinebench: Benchmarking software used to test CPU rendering performance, especially for tasks like 3D modeling and animation.
- OCCT: Comprehensive stability and stress testing software that PC builders use to learn if their computer can handle higher performance situations.
- 3DMark: A PC benchmarking tool that tests and compares computer parts for gamers and overclockers.
- AIDA64: A system diagnostics and benchmarking tool that provides detailed information about your PC’s hardware and software.
- Benchmark Unigine: Tests your PC by bringing it through one of three virtual worlds to see how it handles a real gaming environment.
If your computer overheats during the stress test, try to reduce its temperature by closing programs, freeing up RAM, deleting files, and ensuring it’s well ventilated.
To remove programs and delete files automatically, download Norton Utilities Ultimate to help keep your PC better optimized for gaming. Consider running it before overclocking to help ensure your computer is as clean as possible, with just a few clicks.
3. Locate your overclocking settings
After stress testing your system, locate your overclocking settings by accessing your computer’s BIOS or UEFI. To do this, restart your computer and press the appropriate BIOS/UEFI key on your keyboard.
Here is a list of common BIOS/UEFI keys by brand:
- Dell: F2 or F12
- HP: Esc (then F10)
- ASUS: F2 or Del
- Acer: F2 or Del
- Lenovo: F2
- MSI: Del
- Intel: F2
- Gigabyte AORUS: F2 or Del
- ASRock: F2 or Del
Once you access the BIOS/UEFI, find the advanced CPU settings or overclocking section (the label will vary by motherboard manufacturer).
4. Adjust CPU settings
Once you’re in the BIOS/UEFI, you can begin adjusting your CPU overclocking settings to improve performance and processing speed. You have two main options: automatic overclocking or manual tuning.
Automatic overclocking is beginner-friendly and available on many modern motherboards. It applies modest performance boosts with minimal effort, but offers limited control. Here’s how to turn on automatic overclocking:
- In the BIOS/UEFI CPU settings, look for a section labeled OC Tweaker, Overclocking, AI Tuner, or similar.
- Select the automatic mode.
- Save your changes and exit the BIOS/UEFI.
Manual overclocking allows for more precise performance tuning and better results, but it requires more technical knowledge. When you manually overclock, proceed with caution, starting with incremental adjustments:
- In your advanced CPU settings, look for CPU ratio, core ratio, or similar.
- Increase the multiplier by one step, like from 36x to 37x. Make only small adjustments.
- Test for stability after each change. If the system becomes unstable, you may need to adjust the voltage. Look for a setting called CPU Core Voltage or Vcore, and increase it slightly (no more than 0.05 volts at a time), keeping total CPU core voltage below 1.4V.
- Save your changes and exit the BIOS/UEFI.
5. Test your PC for stability
Testing your CPU for stability after each slight increase helps prevent overheating and sudden shutdown. After each incremental adjustment, run a stability test for 30-60 minutes, tracking temperature. If the PC reaches 185°F or higher, or your system crashes, revert to the previous settings immediately. Stop when you determine your PC’s maximum overclock threshold.
If your PC freezes, crashes, or shuts down, don’t panic — this usually means the system’s built-in failsafes are doing their job. Simply return to the last stable settings.
If your computer displays a black screen and won’t restart, try resetting the BIOS/UEF. To do this, unplug your PC, remove the coin-shaped CMOS battery on the motherboard, wait 10 minutes, reinsert the battery, plug your PC back in, then switch it back on.
What does overclocking do?
Overclocking increases the clock speed of your computer components beyond their factory settings, which can help improve PC performance and responsiveness, especially during high-demand activities like video editing and gaming.
Your computer's clock speed, measured in gigahertz (GHz), determines how quickly your processor (CPU) executes instructions. A higher GHz means the CPU can process more data per second, making everything feel snappier and more efficient. This makes a noticeable difference when dealing with resource-heavy applications.
Is overclocking safe?
Overclocking is generally safe if you’re careful. Many modern computers have built-in failsafes like automatic shutdown to protect your system from damage due to overheating or voltage spikes. However, overclocking accelerates wear on components, increases heat output, and comes with other risks.
Risks of overclocking your CPU
Overclocking risks voiding your warranty, causing overheating and instability, and straining equipment. Overclock carefully and make small adjustments to mitigate these risks.
Here’s what could happen if overclocking goes wrong:
- System instability: Systems can struggle to handle higher speeds and power demands at higher levels, leading to random crashes and blue screens of death.
- Data corruption: Sudden crashes can result in data corruption or loss. If a crash occurs while saving or changing a file, you may need to use System Restore.
- Equipment strain: Increased heat output and usage strain your computer’s parts, reducing their lifespan.
- Voided warranty: Manufacturers often void CPU warranties after overclocking because of the strain on components. However, some gaming PCs with overclocking software won’t void the warranty.
How to troubleshoot CPU overclocking issues
To troubleshoot CPU overclocking issues, perform stability tests, monitor your temperature, update your BIOS and drivers, and reduce your CPU multiplier or voltage limits to see if the issue persists.
- Monitor your temperature: If your temperature nears the danger zone (185°F), stop what you’re doing. Temperatures reaching this level signify some instability.
- Lower your settings: When temperatures rise, reduce your CPU multiplier and voltage. Test again to monitor further temperature spikes.
- Perform stability tests: Benchmarking tools verify your PC’s ability to handle higher-demand processes without overheating or becoming unstable.
- Update your firmware or drivers: Like software updates and computer stability, updating outdated firmware and drivers ensures they effectively support overclocking and improve stability.
Optimize your computer’s performance
If you want to increase CPU speed, start by thoroughly cleaning your system to remove background processes, unnecessary files, and system clutter. This will reduce CPU strain and boost your overclocking power. Norton Utilities Ultimate can automatically disable these processes and clean your PC to boost performance. When your system is optimized and clean, the positive effects of overclocking can be more pronounced.
FAQs
Can you overclock a phone?
You can overclock iPhones and Androids by rooting or jailbreaking them, or by using certain apps. However, this can overheat your phone and increase security risks. While overclocking your phone is theoretically possible, it’s generally not recommended.
Should I overclock my CPU for gaming?
You might want to overclock your CPU for gaming if games have noticeable dips in FPS during intense scenes, or if detailed graphics are causing it to stutter. If your games are running smoothly, there’s no need to overclock.
Is overclocking a CPU the same as overclocking a GPU?
Not exactly. Both boost performance, but in different areas. CPU overclocking improves general computing tasks like game logic, AI behavior, and multitasking, while GPU overclocking enhances graphical performance, such as higher frame rates and smoother visuals in games.
What is undervolting a CPU?
Undervolting a CPU means lowering the voltage it uses without changing its clock speed. This helps reduce heat and power consumption, which can improve stability or battery life. If pushed too far, it may cause crashes, so testing is important.
Editorial note: Our articles provide educational information for you. Our offerings may not cover or protect against every type of crime, fraud, or threat we write about. Our goal is to increase awareness about Cyber Safety. Please review complete Terms during enrollment or setup. Remember that no one can prevent all identity theft or cybercrime, and that LifeLock does not monitor all transactions at all businesses. The Norton and LifeLock brands are part of Gen Digital Inc.






Want more?
Follow us for all the latest news, tips, and updates.