What is IP rotation, and how does it work?
IP rotation is a VPN and proxy feature that can help improve your browsing experience, access blocked sites, and dodge targeted ads. Learn how IP rotation works, then get Norton VPN for a powerful rotating IP feature, ultra-fast connections, and 100+ server network.

Your Internet Protocol (IP) address is a public identifier that third parties can use to track information about your device, location, and browsing habits. Internet service providers (ISPs), websites, advertisers, government agencies, and even hackers may be able to collect data associated with your IP to learn more about you.
If you’re concerned about data collection, IP rotation can offer a more private browsing experience and limit how much information you share. Learn more about what IP rotation is, its benefits, and different ways to do it in this guide.
What is IP rotation?
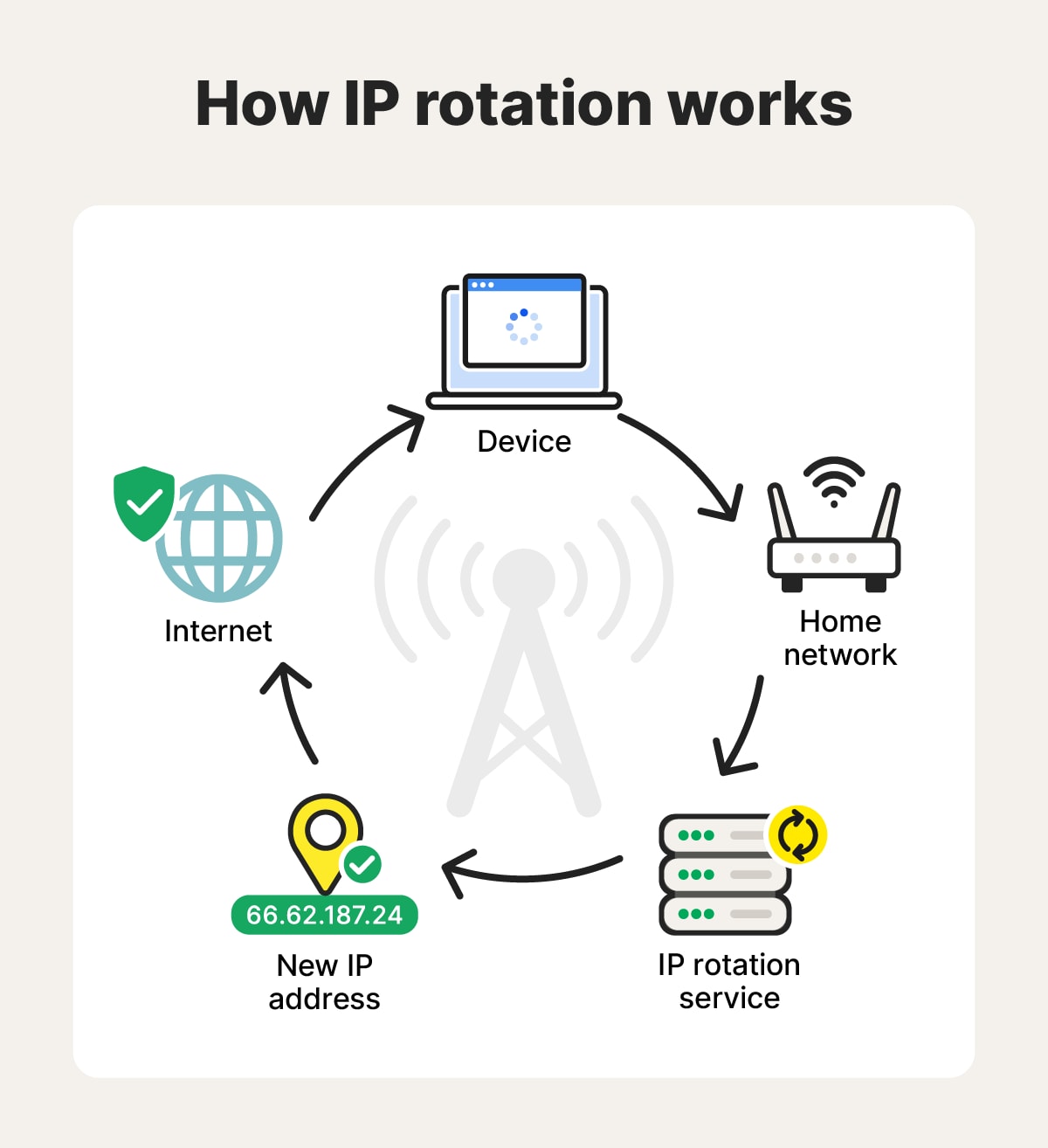
IP rotation is a feature included with some VPN or proxy server services that automatically changes your public IP address, making it harder for websites to link your web activity to your real IP address. Rotating IP tools can change your IP address on a timer, every time you connect to a network, or based on specific triggers (like visiting a new website), disrupting IP-based tracking cookies that collect your location and connection data.
You can also choose to rotate your local IP address, though doing so offers little in the way of online privacy benefits. Therefore, this article will primarily discuss public IP addresses.

Benefits of rotating your IP address
IP rotation makes it harder for websites to track your activity. Each time your IP address changes, it looks from the outside like you’re connecting from a new location or device.
Here are some of the key benefits of rotating your IP:
- Reduce tracking and profiling: Regularly changing IP addresses makes it harder for tracking cookies to build a profile on your behavior, as they rely on consistent IP addresses. This can help stop pop-up ads from targeting you with personalized content based on your browsing activities.
- Bypass location blocks: Some websites block specific users based on their IP addresses, if they’re not based in the same country for example. VPNs with an IP rotation feature often let you change your VPN location dynamically, which may allow you to access some geo-blocked sites.
- Sidestep dynamic pricing: Some online stores use dynamic pricing models, which may result in you seeing higher prices if you return to look at the same product multiple times. A rotating IP can help make your visits look like they’re coming from different devices, potentially giving you better prices.
- Reduce cyberattack risk: IP rotation can temporarily protect your network from attacks that target specific IP addresses. For example, a DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attack floods a known IP with excessive traffic to disrupt service. By changing your IP, you make it harder for attackers to sustain these attacks—at least until the new IP is discovered.
- Useful for web scraping: While not applicable to most people, a rotating IP can help you if you intend to scrape the web. Repeated requests can be blocked if they come from the same IP address, but changing your IP address with each new scraping request can help you dodge limits.
IP rotation works best with other privacy tools, such as VPNs, private browsers, and ad blockers. With all three, you can get one step closer to anonymous browsing without relying on the Tor Browser, which hides your connection data but is known to block certain website features, impacting your browsing experience.
4 ways to rotate your IP address
Using a proxy or a VPN are two of the easiest ways to get the benefits of IP rotation. But they’re not necessarily the only way to do it. Here’s a breakdown of four of the main IP rotation methods.
VPN rotation
VPN services with built-in IP rotation features can automatically change your IP address at regular intervals without interrupting your connection. You can customize the frequency of rotation in your VPN’s settings, enhancing the privacy provided by your VPN’s IP masking and data encryption tools.
Norton VPN offers IP rotation, which you can configure to change your IP address every few seconds to help keep your IP dynamic. It works on iOS, Android, Windows, and macOS devices, providing coverage for devices across your home network (even smart TVs!). You can also manually change your IP address to any of our 100+ locations whenever you want.
ISP rotation
ISPs automatically assign a dynamic, public IP address to your router. Your ISP can also change your IP address regularly to help manage its network and manage service interruptions. Each router has a unique public IP address.
Here’s how ISP rotation works:
- An ISP automatically assigns a public IP address to your router based on the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP).
- The public IP address is usually assigned to your router for a set duration, also called the “IP leasing period” (usually 1-3 days).
- When your IP leasing period ends, or sometimes after the router is rebooted, the public IP may change.
ISPs don’t always advertise static IP addresses to regular residential customers. However, those who pay for business internet or ask their ISP about them might find that they offer this service for an additional fee. While this can be helpful for people who host gaming servers, it makes them an easier target for cyberattacks. If you want to know how long your public IP lasts, contact your ISP.
Unlike public IPs, private IPs aren’t assigned directly by your ISP. Instead, your home router manages these using a smaller version of your ISP’s DHCP. You can also manually change your local IP from your router’s admin dashboard.
Proxy rotation
Proxy servers mask your IP address by routing your traffic through a server in another location, hiding your public IP behind the proxy’s IP. Unlike VPNs, proxies don’t encrypt your data, making them faster but less secure.
Personal proxy servers often come in one of these forms:
- Session-based proxies: These rotate your IP address with each new browsing session for general privacy.
- Sticky proxies: A proxy offering sticky sessions can rotate your IP address every 15 minutes or every few hours for more consistent, general privacy.
- Static: A proxy that provides you with a new IP address that does not rotate.
There are also a few proxies better suited for businesses:
- Request-based proxies: These rotate your proxy with each web request for web-scraping purposes.
- Burst rotation proxies: Burst proxies rotate your IP address after a certain number of requests, so data scraping isn’t interrupted.
- Intelligent proxies: Smart proxies change your IP address based on situational needs, such as when a website blocks you because your data shows you are from a foreign country.
Proxies hide your IP but don’t protect against device fingerprinting. They also may expose your IP address if a hacker breaks into the proxy. For more effective security, consider a VPN or use a proxy server as part of a broader cybersecurity toolkit, along with an ad blockers and private browser.
Manual rotation
Changing your local (or private) IP address manually rotates your IP on the router side. While this doesn’t hide your public IP, it can fix local network issues that could block your internet. You cannot manually change your public IP.
Before changing your router’s settings, you’ll need to know these three things to type into your computer’s network settings:
- Select a local IP: Local IP addresses are between 192.168.0.0 and 192.168.255.255.
- Know your subnet mask: This tells your router you belong to the network and is almost always 255.255.0.0.
- Find out your default gateway: A default gateway (or router IP) tells your computer where your router is — usually 192.168.0.1 or 192.168.1.1.
You can find the default gateway and subnet mask on macOS and Windows computers by viewing your network information.
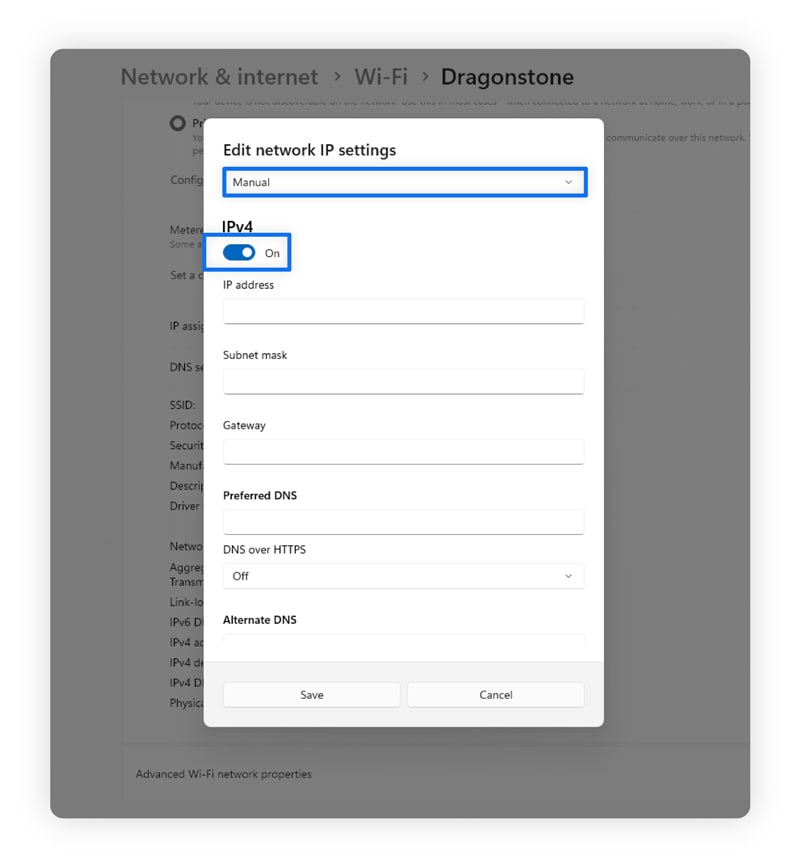
Here’s how to manually change your IP address on Windows PCs:
- Click your Start menu, open your Settings, and click Network & internet.
- Click Wi-Fi (if you have a wireless network) or Ethernet (for a wired network).
- Next to IP assignment, select Edit.
- Select Manual from the drop-down menu and toggle on IPv4.
- Select Use the following IP address and type in the information.
You can also randomly select a new private IP by typing ipconfig/renew in Command Prompt.

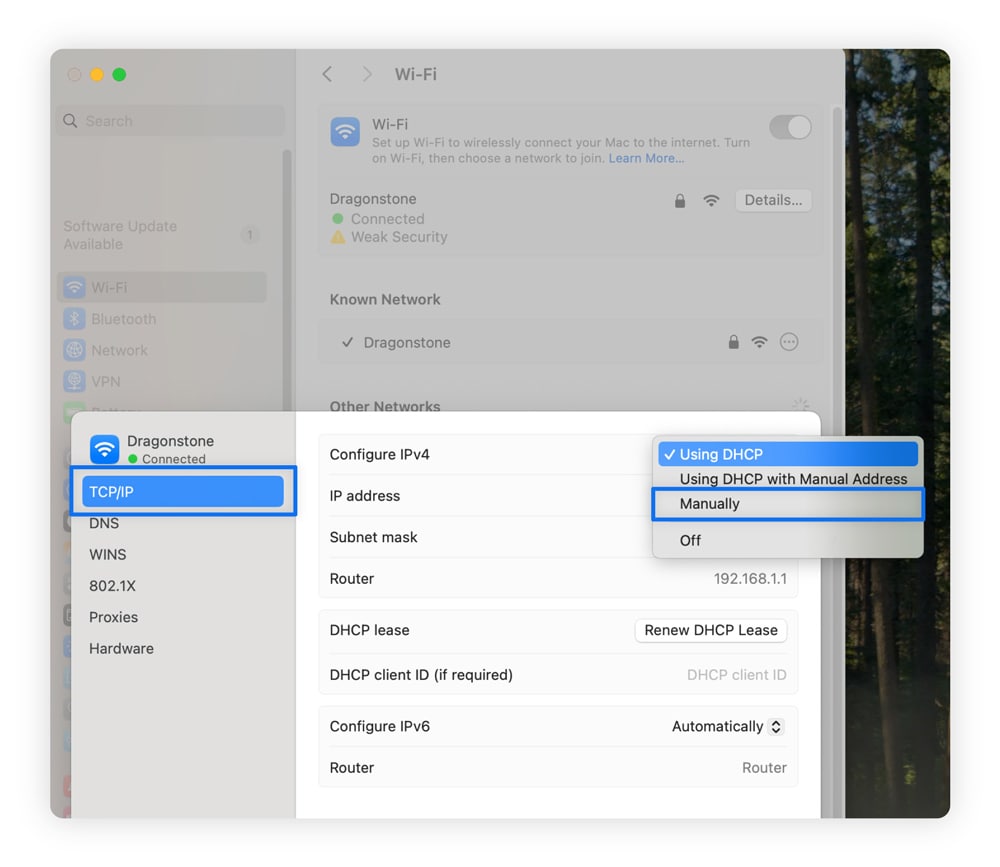
Here’s how to manually change your IP address on macOS:
- Click the Apple menu and select System Settings.
- Select the Details next to your active network.
- Click TCP/IP and select Manually from the drop-down menu next to Configure IPv4.
- Type in your new IP address, subnet mask, and router IP.
You can also select Renew DHCP Lease under your TCP/IP menu to select a local IP automatically.

Can I use IP rotation for my small business?
Small businesses use IP rotation to scrape data for competitive research, like monitoring prices, tracking market trends, and gathering public data from websites. An IP rotator helps them collect information without triggering anti-bot systems, like CAPTCHAs.
IP rotation as a VPN feature can also help maintain business privacy. Alongside an antivirus, this can help improve a company’s security.
Keep your connection data more secure with IP rotation
If your goal is to stay private, IP rotation can help, but it isn’t enough to bring you true peace of mind. Get Norton VPN for a complete privacy tool that uses IP rotation, encrypts your data using proven protocols, and relies on a no-logs policy, ensuring that data brokers, ISPs, and Norton itself have no idea where you’re going when you go online. Keeping your data private starts on your device.
FAQs
What’s the best way to rotate your IP?
Using a VPN is the most reliable way to rotate your IP address. A VPN encrypts your web traffic while routing it through a server in a different location. Just make sure the VPN you choose offers IP rotation.
Which VPNs have a rotating IP feature?
Several VPN providers, including Norton VPN, ExpressVPN, and Surfshark, offer rotating IP features built into their clients. Some other VPNs, like NordVPN, CyberGhost, and Private Internet Access (PIA), let you manually rotate your IP but don’t have an automatic IP rotation feature.
Is it better to have a fixed or rotating IP?
A rotating IP offers slightly more security than a fixed IP, making it harder for criminals with your IP address to target you with malware or other cyberattacks. However, a fixed IP is necessary if you’re hosting a server.
Why is my IP rotating?
If your IP address is rotating for no obvious reason, it’s likely due to your ISP. ISPs use a router to assign public and private IP addresses to help you connect to the internet without conflicting with other devices on your local network.
Editorial note: Our articles provide educational information for you. Our offerings may not cover or protect against every type of crime, fraud, or threat we write about. Our goal is to increase awareness about Cyber Safety. Please review complete Terms during enrollment or setup. Remember that no one can prevent all identity theft or cybercrime, and that LifeLock does not monitor all transactions at all businesses. The Norton and LifeLock brands are part of Gen Digital Inc.







Want more?
Follow us for all the latest news, tips, and updates.