The best encrypted messaging apps: Which is the most secure?
Most of us have wondered at some point just how private our “private” messages really are. That concern isn’t far-fetched, but the good news is that secure messaging apps use powerful encryption to keep conversations protected. Learn how these apps work, how to choose the right one, and how a private browser can help strengthen your privacy even further.

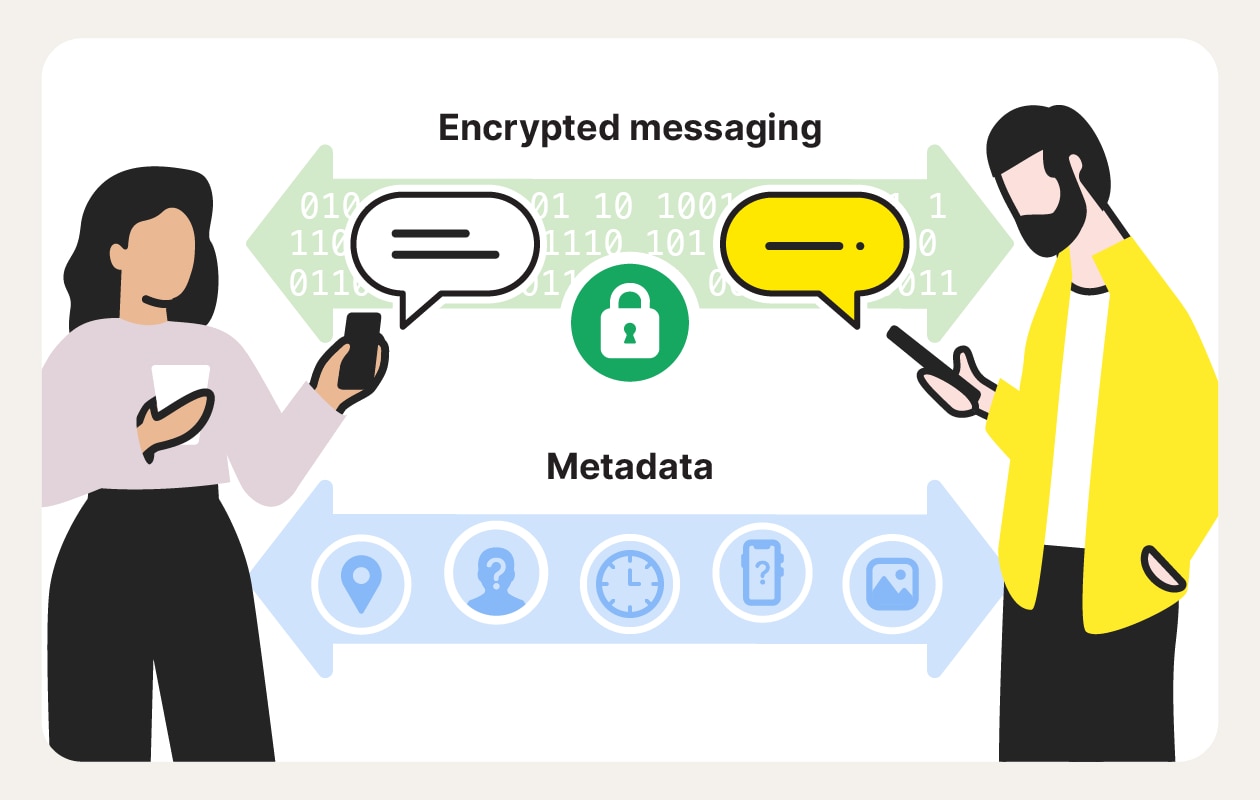
Anything you send online without encryption can potentially be intercepted and misused, leaving your private conversations and other sensitive data exposed. But thanks to encrypted apps, messages are protected so that only you and the recipient can read them — not hackers, not your ISP, and typically not even the messaging provider itself.
What are encrypted messaging apps?
Encrypted messaging apps are communication tools that use end-to-end encryption (E2EE) to ensure only the sender and the intended recipient can read messages sent via the app.
Without E2EE, messages can be intercepted or logged by third parties. But secure messaging apps prevent this by encrypting messages on your device before they’re sent and keeping them scrambled while in transit. As a result, anyone who intercepts the data — including hackers, network operators, or even the app provider — can’t read the message contents.
Some encrypted messaging apps also use open-source code, allowing independent experts to verify that messages aren’t being accessed, stored, or decrypted elsewhere.
Best encrypted messaging apps
Some of the best encrypted messaging apps are household names like Signal and WhatsApp. But whereas some are platforms built from the ground up with privacy as a core principle, others are more social-style apps where encryption is somewhat of an afterthought. If privacy matters to you beyond the buzzwords, these distinctions are important.
It’s also worth noting that even with E2EE, apps can still collect metadata — such as who you message, when you communicate, and from which device or location. Some services minimize this data by design, while others accumulate it over time, often revealing far more about your habits than message content alone.

Signal
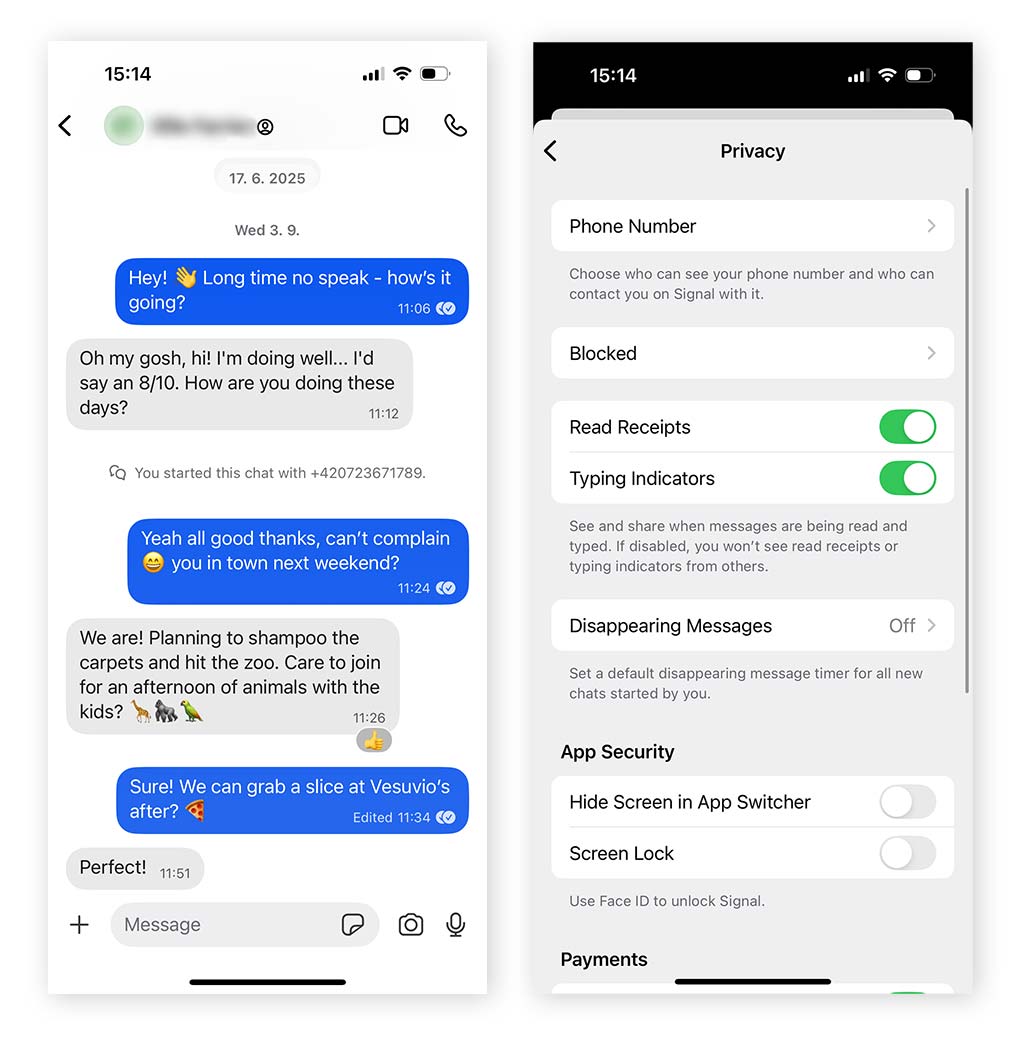
Signal is widely regarded as the gold standard for private messaging apps. It uses E2EE by default and is open source, meaning its code can be independently audited for security and privacy. Messages can only be read by you and the intended recipient, and Signal collects minimal metadata compared with most messaging platforms.
Because of its strong privacy protections, Signal has been publicly recommended by controversial whistleblower Edward Snowden, press freedom associations, and privacy advocates.
Best for: People who need a high level of privacy when sharing sensitive information, such as journalists, activists, or anyone concerned about surveillance.
Pros:
- E2EE enabled by default
- Open-source code allows independent verification that Signal can’t access your chats
- Collects minimal metadata
- Disappearing messages feature
- Clean, minimal interface focused on direct messages and group chats
- Ability to name chats and sort them into folders
- Desktop app available
- No ads, trackers, or data harvesting
- Not owned by a for-profit organization
- Option to hide your phone number from other Signal users
- No “Last Seen” or “Online” status indicators
- Read Receipts and “Typing…” indicators can be disabled
- Option to block Signal screenshots on your own device
- Sealed Sender feature encrypts sender information, not just message content
Cons:
- Requires a phone number, which prevents full anonymity
- Phone number is visible by default, but can be manually hidden
- No built-in alerts or protections if another user screenshots your messages
- Message backups are supported on Android, but not on iPhone
- Deleting the app can permanently erase your entire chat history
- Stories feature, which can be seen as unnecessary or off-mission for a privacy app
- Delayed message delivery is a known issue that Signal acknowledges
- Reports of chat history loss due to software issues

Viber
Viber is a free messaging and calling app that uses E2EE for one-to-one chats, group messages, and calls. It also supports domestic and international landline calls, making it useful for staying in touch with people abroad — even if they don’t have Viber or an internet connection.
Viber does collect some metadata, but it still offers solid security for everyday communication. In certain global regions, Viber is widely used, which can make it a practical choice if you want to stay connected locally.
Best for: Users who want secure messaging and calling, plus international landline calls and fun extras like stickers and chat features.
Pros:
- E2EE available by default in Secret Chats
- Free voice and video calls
- Disappearing messages feature
- Screenshot protection in Secret Chats (screenshots blocked on Android)
- Option to disable “Last Seen,” “Online,” and read receipts
- Desktop app available
- Supports both manual and automatic chat backups
- Extensive sticker library
- Affordable international landline calling
- Many users report positive experiences with customer support
- Widely used across Eastern Europe, the Middle East, and Southeast Asia
Cons:
- Not fully open source
- Collects a significant amount of metadata, including IP addresses and device identifiers
- Phone number is visible to contacts by default
- Feature-heavy interface that can feel cluttered
- Displays advertisements
- Bugs reported by some users leave them feeling uneasy about their privacy
Telegram
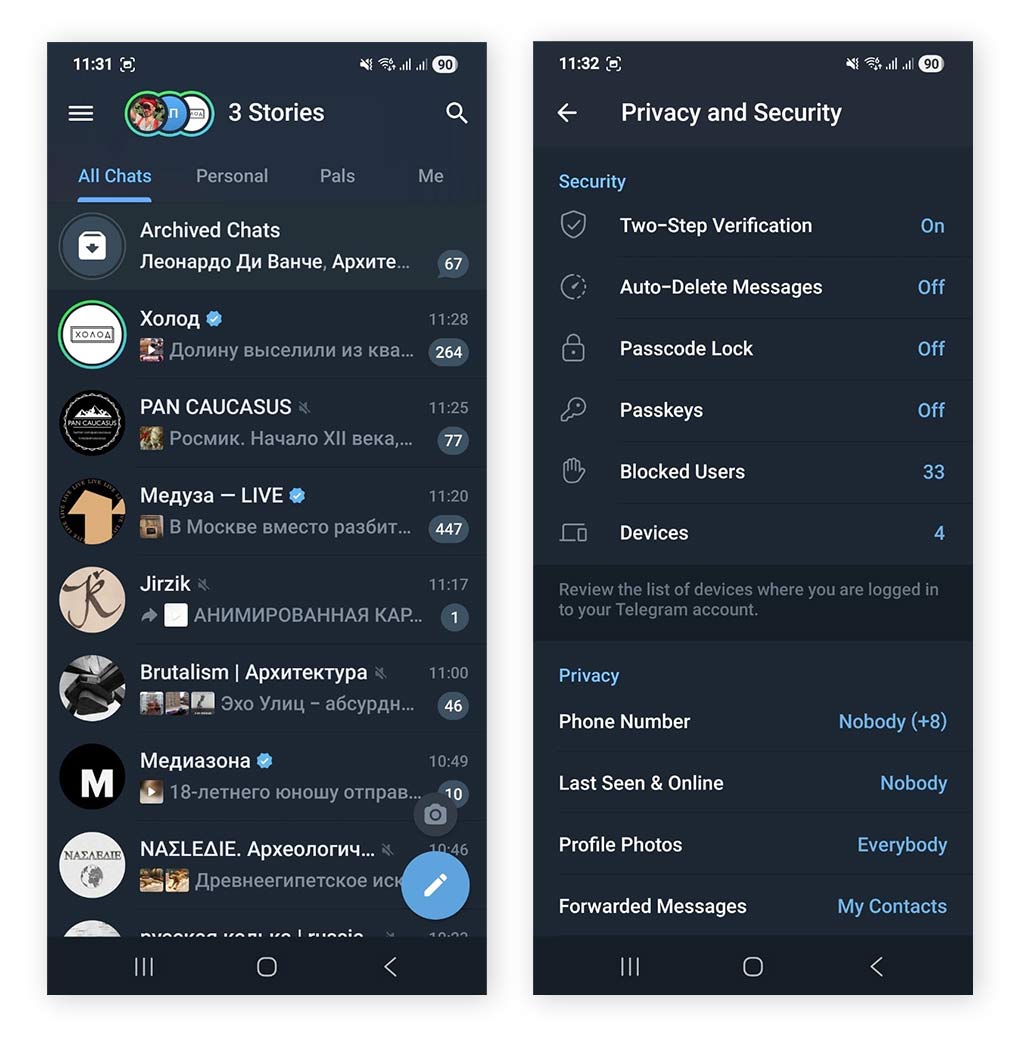
Telegram is a cloud-based messaging and social platform that prioritizes convenience and rich features such as bots, channels, large group chats, and cloud storage. While it does support E2EE, this protection is optional, limited to Secret Chats, and not enabled by default.
Telegram allows users to send large files (up to 2 GB), which is convenient, but this data is stored on Telegram’s servers, and how that data is accessed, stored, and protected isn’t fully transparent.
Best for: Users who want rich features and easy file sharing and are less concerned about full, default E2EE.
Pros:
- Strong E2EE is available as an option
- Ability to hide your phone number from other Telegram users
- Secret Chats block screenshots
- Supports file sharing up to 2 GB
- Fast cloud syncing across devices
- Groups and channels can host up to 200,000 members
- Interactive bots enable features like games, payments, and automation
- Extensive customization for visuals, sounds, and reactions
- Feels more like a social platform than a traditional messaging app
- Option to disable “Last Seen” and “Online” status
- Default “Last Seen” messages are intentionally vague
Cons:
- Messages are not end-to-end encrypted by default
- Regular chats and files are stored on Telegram’s servers, with limited transparency around data handling
- Requires a phone number to sign up
- Phone number is visible to new contacts by default and must be manually hidden
- Messaging controls are limited unless you pay for Telegram Premium
- Popular with scammers and fraudsters
- Contacts with your number are notified when you join
- Reputation in some regions for hosting illicit activity
- Displays advertisements
- Bots can be exploited for phishing, data collection, or scams
- Read receipts can’t be disabled

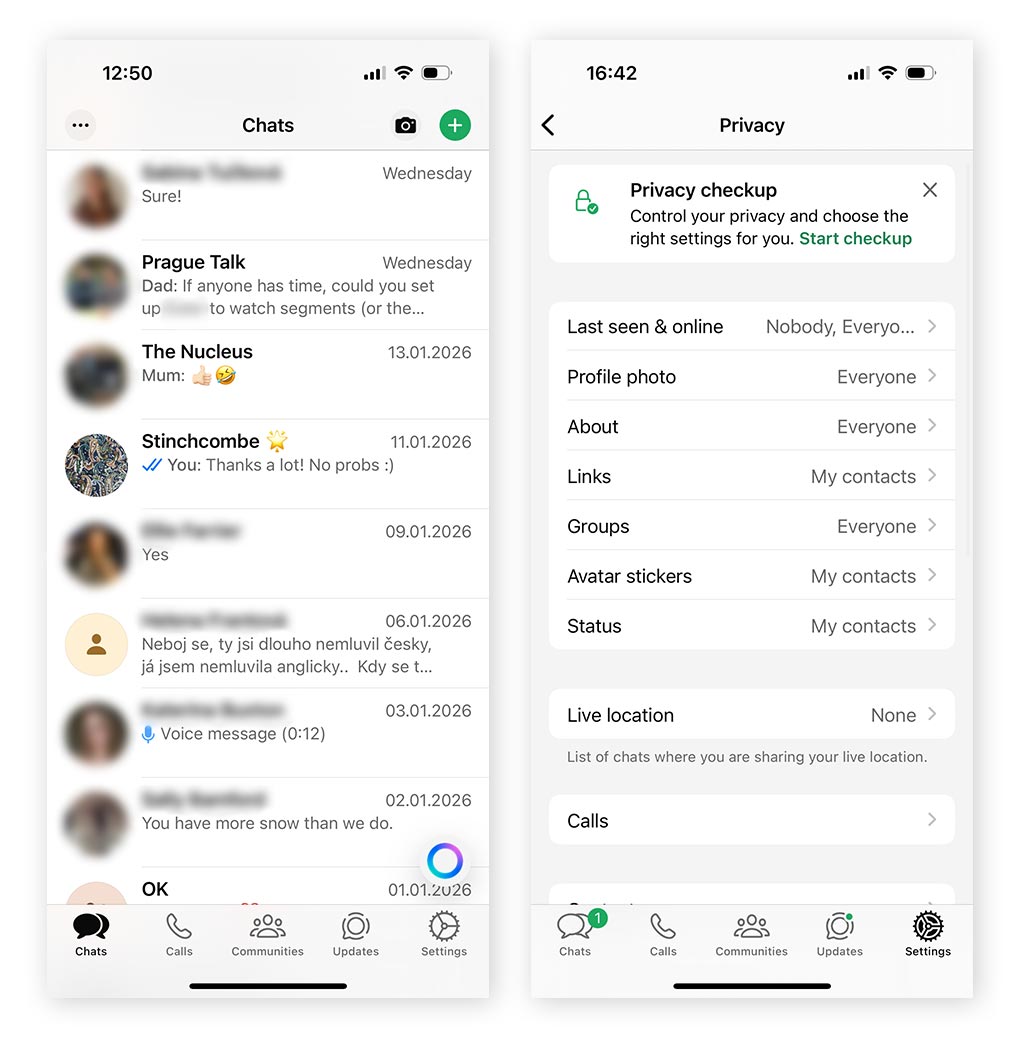
WhatsApp is one of the most widely used messaging apps in the world, so it’s likely you’re already using it. And in some respects, WhatsApp is surprisingly secure, with end-to-end encryption enabled by default for messages, voice calls, and video calls — a major privacy advantage that’s been in place since 2016.
However, encryption doesn’t extend to metadata. WhatsApp still collects information about who you message, when you communicate, what device you’re using, and your approximate location. And because WhatsApp is owned by Facebook’s parent company, Meta, it exists within a broader ecosystem known for extensive metadata collection used for analytics and business purposes.
Best for: People who want a familiar, easy-to-use messaging app that’s already widely adopted by friends and family, without needing to change their everyday smartphone habits.
Pros:
- End-to-end encrypted by default
- Widespread global adoption
- Desktop and web apps available
- Files of all kinds up to 2GB can be sent
- Files are protected with E2EE in personal chats
- Clean, user-friendly interface suitable for all experience levels
- “View once” messages with screenshot blocking available on most devices
- “Last Seen,” “Online status,” and “Read Receipts” can be disabled
Cons:
- Owned by Meta, a company known for extensive metadata collection
- Metadata may be shared with Meta companies for business, security, analytics, and ad-targeting across Meta’s ecosystem
- Metadata can be requested by law enforcement or exposed in a data breach
- Chats with business accounts may not be end-to-end encrypted
- Requires a phone number (though WhatsApp is rolling out usernames, which may allow hiding your number in some cases)
- You can’t hide your phone number from WhatsApp users you talk to
- Limited customization compared to apps like Telegram
- Disabling Meta AI completely isn’t possible; it’s built in to the WhatsApp interface

Briar
Briar is a highly specialized E2EE messaging app built for maximum privacy. Unlike most apps, it doesn’t rely on central servers or standard internet connections. Instead, it connects devices directly using Bluetooth, local Wi-Fi, or the internet via Tor networks. Messages are only delivered when both users are online, but this design greatly reduces the risk of third-party interception.
Because Briar prioritizes security over convenience or mass-usage appeal, it lacks typical social features like cloud backups, media feeds, or large group chats.
Best for: Activists, whistleblowers, journalists, or anyone operating in environments with unreliable internet access or a high risk of surveillance, especially in restrictive or authoritarian regions.
Pros:
- Uses E2EE by default
- Open-source, allowing independent security audits
- Minimal metadata collection
- No phone number, SIM card, or email required
- No centralized servers, reducing single points of failure and complicating surveillance
- Can function without internet, using Bluetooth or local Wi-Fi
- Supports image attachments (optimized for low bandwidth)
- Disappearing messages supported
- Tor network allows long-distance secure communications
- Automatic syncing when both users connect to the same local network
- Highly resistant to denial-of-service attacks
Cons:
- Both parties must be online for messages to be delivered
- Android-only with no iOS support
- No discovery features — you can only chat with people you’ve already connected to
- Images are compressed, resulting in lower quality
- Limited social features compared to mainstream messaging apps
- Overkill for most users, unless facing high surveillance or censorship risks
- Best suited for specific scenarios, not everyday social messaging
How to choose the right secure messaging app
To choose the right secure messaging app, first confirm that it offers E2EE by default. Then consider how much metadata it collects, whether the code is open source, and if the app requires a phone number to use. But also balance privacy with usability — some apps prioritize maximum security at the expense of convenience.
The best choice depends on your threat level, daily habits, and who you need to communicate with. Here’s what to bear in mind:
- Think about how you’ll use the app.
For everyday chatting or sharing memes, most encrypted apps are sufficient. But for higher-risk communications, such as sharing sensitive information, you’ll benefit from even stronger privacy features. If you’re worried about messages being captured and shared, look for apps that offer screenshot protection. - Identify non-negotiable features.
Decide which features you won’t compromise on. If you want verifiable encryption, choose an open-source app that allows independent audits. If user privacy matters most, select a service that minimizes metadata collection and limits activity tracking. - Consider your tech-savviness.
Some privacy-focused apps, like Signal, can feel less forgiving — chat history may disappear if the app is deleted, and enabling features like two-factor authentication or biometric logins can be confusing for some users. For less tech-savvy individuals, a more familiar app like WhatsApp may be a better choice. - Read user reviews.
Check recent reviews on Trustpilot, Reddit, the Google Play Store, and the Apple App Store to see how the app performs today, not just historically. Pay close attention to recurring complaints about bugs, reliability, or signs that the app is violating user privacy.
Which popular messaging apps aren’t secure?
Some popular messaging apps offer convenience and nifty social features but don’t provide strong E2EE by default, or collect extensive metadata that weakens privacy.
- Snapchat: While Snaps are encrypted in transit, regular Snapchat chats aren’t encrypted by default. Messages and metadata are stored on Snapchat’s servers and can be accessed under certain conditions.
- Facebook Messenger: E2EE is optional and limited to Secret Conversations. Standard chats aren’t fully encrypted (though Meta is currently rolling this out), and metadata is collected as part of Meta’s broader data ecosystem.
- Instagram Direct Messages: Messages are not E2EE, and metadata is collected for analytics and business purposes.
- Discord: Messages are encrypted in transit but not E2EE, meaning Discord can technically access message content stored on its servers.
- WeChat: Messages are not E2EE, and the platform is subject to Chinese data regulations, which can require companies to provide access to user data.
That’s not to say these apps aren’t secure in the sense that they’re unsafe to use, but they’re not designed for private or sensitive communications. If privacy is a priority, look for messaging apps with E2EE enabled by default, minimal metadata collection, and transparent privacy practices.
When can I use unsecured messaging apps?
Unsecured messaging apps are generally fine for low-risk, everyday conversations, as long as you’re not sharing sensitive information. The challenge is that “sensitive” can be a broader category than it might seem.
Definitely avoid sharing
Identifying details like Social Security numbers, bank information, passwords, or full birthdates.
Potentially sensitive, depending on context
Future travel plans, real-time locations, daily routines, or timestamps of where you’ve been — especially if you’re concerned about stalking, surveillance, or targeting.
Usually safe
Casual chats, pop culture discussions, memes, and non-personal topics, provided they don’t reveal personal habits, political views in risky environments, or plans that could be misused.
What are some other ways to keep your messages secure?
Secure messaging apps provide a strong foundation, but they aren’t a complete solution on their own. You still need to recognize risks and avoid them before they turn into real threats. To reduce your exposure to cyberattacks, follow these best practices:
- Avoid connecting to public Wi-Fi networks: Public Wi-Fi is often unsecured, making your device and messages easier targets for hackers. If you must connect, use a VPN to encrypt your traffic and keep your connection private.
- Verify contacts: Make sure you know who you’re communicating with, especially if the conversation involves sensitive information.
- Use two-factor authentication (2FA): 2FA significantly lowers the risk of account takeovers by requiring both your password and a one-time verification code.
- Don’t click suspicious links: Unexpected or urgent links are a common phishing tactic used to deliver malware or steal credentials. When in doubt, don’t click or tap.
- Enable disappearing messages: These messages automatically delete after a set time and may limit screenshots, reducing long-term exposure.
- Report suspicious activity: If you suspect someone has hacked your phone, device, or account, report it immediately to the app provider and, if necessary, local authorities.
- Protect your device with security software: Comprehensive security software like Norton 360 protects you with real-time malware detection, AI-powered anti-scam tools, and a VPN, which helps shield your communications from third parties.
Make your messages more secure
Even if your communications are encrypted end-to-end, your browser can still collect cookies and tracking data that reveal your online behavior. Norton Private Browser helps reduce that footprint by blocking ads and trackers by default, while also protecting you from phishing, fake websites, malware, and scams. Get it for free today to strengthen your privacy beyond your messages.
FAQs
What is the most secretive messaging app?
Signal is widely considered one of the best all-around messaging apps for privacy. It uses open-source, E2EE by default, and has a large, well-audited user base. Apps like Briar go a step further by not requiring a phone number or email address and by routing messages through a decentralized, onion-routed network rather than centralized servers. The trade-off is slower message delivery and a less polished user experience.
Why did the FBI issue a warning about unencrypted messaging apps?
In 2024, U.S. authorities disclosed that foreign intelligence services had exploited weaknesses in traditional telecom infrastructure, exposing not only metadata but, in some cases, unencrypted SMS content. In response, the FBI urged the public to use E2EE messaging apps, which help prevent third parties from intercepting message contents, even if network traffic is monitored.
Can the government surveil secure messaging apps?
In the U.S., the government has very limited ability to access messages protected by strong end-to-end encryption. When apps retain minimal metadata, remote surveillance is difficult, and investigations usually rely on device access (which has been known to happen at border control) instead.
Elsewhere, the UK’s controversial Online Safety Act seeks to undermine end-to-end encryption and make it possible for law enforcement to surveil citizens far more easily — an indication that E2EE is highly effective.
What are the requirements for secure messaging apps in healthcare?
Secure messaging in healthcare is regulated under the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). To be compliant, healthcare organizations must use messaging solutions that:
- Encrypt patient data and communications
- Obtain patient consent for electronic messaging
- Sign a Business Associate Agreement (BAA) with the messaging provider
Generally, SMS text messages are not HIPAA-compliant unless they are paired with additional safeguards such as encryption, access controls, audit logging, and other necessary safeguards.
Editorial note: Our articles provide educational information for you. Our offerings may not cover or protect against every type of crime, fraud, or threat we write about. Our goal is to increase awareness about Cyber Safety. Please review complete Terms during enrollment or setup. Remember that no one can prevent all identity theft or cybercrime, and that LifeLock does not monitor all transactions at all businesses. The Norton and LifeLock brands are part of Gen Digital Inc.








Want more?
Follow us for all the latest news, tips, and updates.