What is Zero Trust security? Core principles and benefits
“Never trust, always verify.” That’s the philosophy behind Zero Trust security. Instead of automatically trusting anyone on your network, Zero Trust requires every user and device to provide continuous verification. We’ll walk you through what Zero Trust actually means, why it matters for your business, and how Norton Small Business can help keep your organization’s data safer.

As cyberattacks become more sophisticated, Zero Trust security has become the gold standard for protecting networks. In fact, 63% of organizations worldwide have already implemented some form of Zero Trust strategy, according to the advisory firm Gartner. The U.S. government now requires federal agencies to adopt this model to strengthen national security.
While Zero Trust is often associated with large corporations, small and medium-sized businesses can benefit just as much, especially as teams grow and more employees work remotely. Discover the core principles of Zero Trust security, its key benefits, and practical ways to implement the approach in your business without breaking the bank.
What is Zero Trust security?
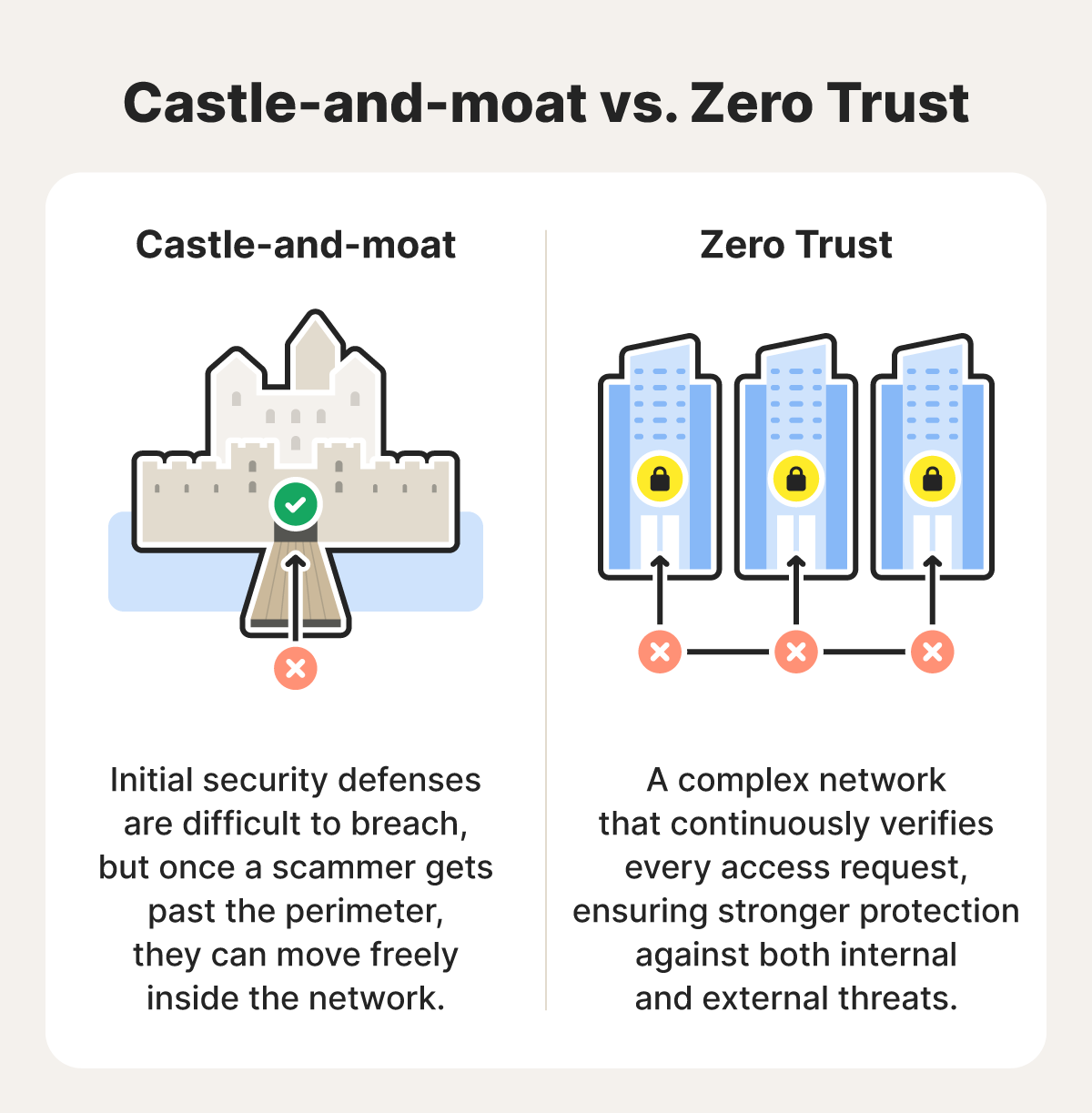
Zero Trust is a security framework that treats all users and devices as untrusted, regardless of whether they’re inside or outside your business’s network. Rather than assuming anyone inside the network perimeter is safe, Zero Trust requires continuous identity verification for every access request. It’s a comprehensive approach that combines multiple tools, procedures, and policies.
Traditional network security followed a “castle-and-moat” model. Imagine a medieval castle with a wide moat and high walls to keep intruders out. Getting past those defenses is difficult, but once someone crosses the moat and enters through the gate, they’re trusted completely and can roam freely throughout the castle.
This approach made sense when employees worked on-site and threats stayed outside your network. However, today, with remote work, cloud security risks, complex social engineering schemes, and increasingly sophisticated cybercriminals who can breach those walls, businesses can be vulnerable.

Core principles of Zero Trust security
Zero Trust security rests on several foundational principles that work together to protect your network from all angles. These principles may vary slightly depending on the source, but the key concepts are the same. Here are the essential principles that make up the Zero Trust framework:
1. Verify every access, every time
Zero Trust mandates authentication and authorization for every access attempt. This can mean requiring multi-factor authentication (MFA) for email accounts, cloud storage, and any other system containing business data. MFA requires users to verify their identity through two or more methods (like a secure password plus a text code), so even if hackers steal a password, they still can’t access your systems.
2. Verify device health and integrity
Zero Trust doesn’t just verify the user, it verifies the device they’re using, too. Before granting access, the system checks whether the device is recognized, up to date, and protected with essential security tools like antivirus software and firewalls. If a device is outdated or shows signs of compromise, Zero Trust can block access to prevent attackers from using that device as a foothold into your network.
3. Enforce least privilege access
The principle of least privilege access means that a user should only have the minimum access required to perform a task. This protects against insider threats and minimizes the damage if someone’s credentials are compromised.
For example, if you run a marketing agency, your social media manager needs access to client social accounts, but doesn’t need admin rights to your accounting software or HR files. Likewise, your bookkeeper should be able to access the billing system but not internal project folders.
4. Assume a breach has already occurred
Instead of hoping that a data breach or leak won’t happen, Zero Trust encourages organizations to change their mindset to assume that one has already occurred or will soon. This paradigm shift changes everything about how security measures are designed. Instead of focusing solely on keeping threats out, prioritize limiting what damage an attacker can do once they’re inside.
5. Segment networks and systems
John Kindervag, who created the Zero Trust framework, calls micro segmentation the “true foundation of Zero Trust.” It involves dividing your business network into smaller, isolated zones, allowing you to control traffic and identify threats more easily.
In practice, this might look like keeping HR files separate from sales data, isolating financial systems, and protecting customer information in its own segment. That way, when one area gets compromised, the breach stays contained.
6. Monitor activity continuously
Zero Trust isn’t a “set-it-and-forget-it” approach. Once you apply security practices and procedures, you’ll need to continuously monitor and adjust them.
Use real-time monitoring tools to track who’s accessing what, when they access it, and from where. Look for red flags, such as login attempts at odd hours or multiple failed password attempts. The faster you spot suspicious activity, the faster you can shut it down.
Benefits of Zero Trust security
A Zero Trust security framework has advantages for businesses of all sizes and industries. Businesses that adopt this model can demonstrate regulatory compliance, strengthen data security, and reduce the risk of costly data breaches. Whether you run a five-person startup or a 50-person company, here’s what a Zero Trust approach can do for you:
- Limits the attack surface: Your business’s attack surface is every access point an attacker could use to get in, including devices, software, and people. By requiring continuous verification, businesses limit where attackers can move if they compromise an account.
- Strengthens data protection: Since Zero Trust requires that employees only access the specific data and systems they need for their jobs, sensitive information such as customer records, financial data, and proprietary business information stays protected behind multiple verification layers.
- Minimizes damage from breaches: Part of implementing the Zero Trust model involves segmenting your network into isolated zones, which helps ensure that a breach in one area doesn't automatically compromise your entire system.
- Improves visibility and control: Zero Trust gives you a clearer view of who is accessing what, when, and from where, helping you detect suspicious activity and enforce security policies more effectively.
- Simplifies regulatory compliance: Many regulations, such as HIPAA in healthcare and GDPR for customer data, require strict access controls and detailed activity logs. Zero Trust’s built-in verification and monitoring can help your business stay aligned with these requirements.
- Secures remote access: With many companies offering remote or hybrid opportunities, the Zero Trust model helps secure devices and data wherever employees are working from, even when connected to public Wi-Fi networks.


How to implement Zero Trust security into your business
Zero Trust implementation doesn’t mean overhauling your entire system overnight. Start with manageable steps and build upon them. This is a gradual process that unfolds over months or years, not days, but each step makes your business more secure.
- Establish a Zero Trust mindset: Shift your thinking to assume that threats can come from anywhere, both inside and outside your network. Document this approach in a security policy and train your team on why verification matters at every access point. When employees understand the “why,” they’re more likely to follow security protocols.
- Audit your existing security tools: The good news is that Zero Trust security doesn’t mean doing a complete overhaul. Take inventory of what you already have, like firewalls, antivirus software, and VPNs, and use them to support your new Zero Trust strategy.
- Focus on one area at a time: The creator of the Zero Trust policy recommends focusing on small, manageable areas, which he dubbed Protect Surfaces. For example, you might begin with your customer database since it holds clients’ sensitive information.
- Map how data flows: For each Protect Surface, create a visual map showing how data moves. Understanding these pathways helps you identify where controls are needed most.
- Implement security policies: Apply specific security procedures for each area. In the case of your customer database, limit who can access it, enforce MFA, and monitor activity regularly.
- Monitor and adjust continuously: Regularly review who has access to what, watch for unusual activity, and update your security measures as your business evolves and new threats emerge.
Applying Zero Trust security at home
While Zero Trust security is a cornerstone of business cybersecurity, you can also apply these principles to your home network. This is especially important if you run your business from home or have remote employees.
Don’t trust devices or network users by default — regularly review what’s connected, remove anything unfamiliar, and ensure each account has a strong, unique password with some form of multi-factor authentication (MFA) enabled.
Consider segmenting your network as well. For example, you can create a guest network for visitors, allowing their devices to remain isolated from your personal devices and sensitive data.
You might also set up a separate network for IoT devices, such as smart TVs, thermostats, and security cameras, which often have weaker security that attackers can use as entry points.
Give your business the security it deserves
In addition to implementing Zero Trust architecture, consider Cyber Safety software that will help protect your business and network from malware infections and hackers. Ransomware attacks in particular can devastate small businesses, locking critical files and disrupting operations overnight, often with costly recovery demands.
With powerful malware protection features, a firewall, secure VPN, 250 GB of secure cloud backup, and Dark Web Monitoring, Norton Small Business helps you secure your business with ease, so you can focus on what matters.
FAQs
What are the five pillars of Zero Trust?
The five pillars of the Zero Trust model are Identity, Devices, Network, Data, and Applications and Workloads. These pillars represent the core areas that businesses need to secure to implement Zero Trust network architecture.
How much does it cost to implement Zero Trust for a small business?
Since Zero Trust isn’t a single product, it can be challenging to determine the exact cost for a small business to implement it. However, it’s estimated that small businesses spend between $5,000 and $50,000 annually on cybersecurity.
Do I need an IT team to use Zero Trust?
No, you don’t need a full IT team for your small business to start using Zero Trust. You can start with tools and platforms that promote Zero Trust principles, and scale up as your business grows.
How does Zero Trust protect against phishing and scams?
Zero Trust doesn’t stop phishing and scams from happening, but it helps limit the damage they can cause. By verifying every login and restricting access to sensitive areas, it keeps attackers from moving freely through your systems, even if they trick someone into sharing credentials.
Editorial note: Our articles provide educational information for you. Our offerings may not cover or protect against every type of crime, fraud, or threat we write about. Our goal is to increase awareness about Cyber Safety. Please review complete Terms during enrollment or setup. Remember that no one can prevent all identity theft or cybercrime, and that LifeLock does not monitor all transactions at all businesses. The Norton and LifeLock brands are part of Gen Digital Inc.








Want more?
Follow us for all the latest news, tips, and updates.