No internet connection? Try these 10 simple steps to fix it
You’re trying to get online, but you see those three dreaded words: “no internet connection.” While frustrating, this can usually be resolved by troubleshooting and following a few simple steps. Alternatively, subscribe to Norton Ultimate Help Desk to get assistance from our IT experts anytime — online or over the phone.

Picture this: you’re in the middle of an important Zoom call and suddenly the connection drops. Or you’re watching the final episode of a Netflix series and the show freezes. Internet connectivity issues can stem from problems with your modem or router, ISP outages, low bandwidth, or other issues. Here’s how to fix “no internet connection” problems so you can get back to work (or play).
1. Restart your router and modem
If your connection drops or you’re having trouble connecting, the first step is to try restarting your modem or router. This will resolve the majority of internet connectivity issues.
Restarting your router will reset your connection to your internet service provider and clear any glitches that are stopping you from getting online. It will also refresh your IP address, another common culprit when you’re unable to connect.
Here’s how you can restart your router:
- Press the power button to turn off your router.
- Unplug the power cable and wait for one minute.
- Plug the cable in and turn your router back on.
- Once your router has restarted, check your internet connection to see if the problem has been fixed.


2. Forget and reconnect to Wi-Fi
Another troubleshooting step for internet connection issues is to disconnect from your Wi-Fi and reconnect. Re-establishing the connection gives you a fresh start by changing your IP address (on some devices), clearing old session data that might have been corrupted, and resolving other glitches that are causing your connection to drop.
If these simple fixes don’t resolve the problem, it’s time to dive deeper.
3. Test your connection on other devices
Narrow down why you’re not connected to the internet by determining whether it’s a device-specific problem or a network-wide issue. If one device is having trouble, check if other devices on the same network can connect without issue or if the problem is happening across the board.
If the issue affects only one device, it could be due to outdated Wi-Fi drivers, Wi-Fi adapter problems, or incorrect device configuration settings. If you still can’t get online after restarting your router and disconnecting and reconnecting to Wi-Fi, try using an Ethernet cable. If an Ethernet connection works but wireless doesn’t, your device’s wireless settings are likely the cause.
4. Check for internet outages
If you have no internet signal or your connection unexpectedly cuts out, your internet service provider (ISP) might be the culprit. This can be due to technical issues, power outages, weather, routine maintenance, or even cyberattacks.
Check with your ISP to confirm whether there’s an internet outage, either via phone or on their website (assuming you have an alternative means of connection). You can also use a website like Downdetector to see if the internet is down in your area. You may also be able to confirm via social media if other people in your area are experiencing the same issue.
Unfortunately, if there’s a third-party problem, you may just have to wait it out until your ISP fixes the issue and restores your connection. This could take several hours depending on the cause of the outage.
5. Inspect hardware and cables
Damaged hardware might cause you to have no internet connection. Your setup relies on a modem, router, and network cables. Overheating, general wear and tear, and damage to ports and connectors can all interfere with your connection.
Inspect your hardware and cables to make sure everything is intact and there’s no visible damage. An error light or lack of lights might indicate a broken router. If the hardware is hot to the touch, overheating might be the issue. If Ethernet cables are crimped, have exposed wires, or have other signs of damage, it’s time for a replacement.
6. Pause your VPN
A VPN or proxy can cause a “no network access” alert. To test whether this is the case, pause or turn off your VPN and reconnect to Wi-Fi. An overloaded VPN could result in a slow connection, problems loading websites, or a dropped connection.
Norton VPN is a safe, reliable VPN that automatically connects you to the fastest location, helping keep your browsing smooth and your connection strong. Plus, its split tunneling feature lets you access some websites without a VPN while keeping it active for others — helping you avoid disruptions for third-party apps that don’t work so well with VPNs, like banking and video conferencing apps.
7. Disconnect some devices
If you have low bandwidth or too many devices connected to the same network, it can disrupt your connection or result in slow internet, especially if some devices are hogging your bandwidth, such as streaming devices, smart TVs, and gaming consoles.
You can check your bandwidth with speed test sites such as Speedtest.net. Temporarily disconnecting bandwidth-hogging devices while not in use may free up bandwidth and boost internet speeds. You can also set up a guest network to limit bandwidth for guests to help prevent your main network from becoming overloaded.
8. Update network adapter drivers
Network drivers act as the bridge between your operating system and network hardware, allowing the hardware to send and receive data. An outdated driver can cause problems when your operating system updates, leading to a breakdown in communication that could result in internet errors or slow, unstable connections.
Updating computer drivers is simple and will make your computer faster while also resolving connectivity issues. Here’s how to do it on Windows:
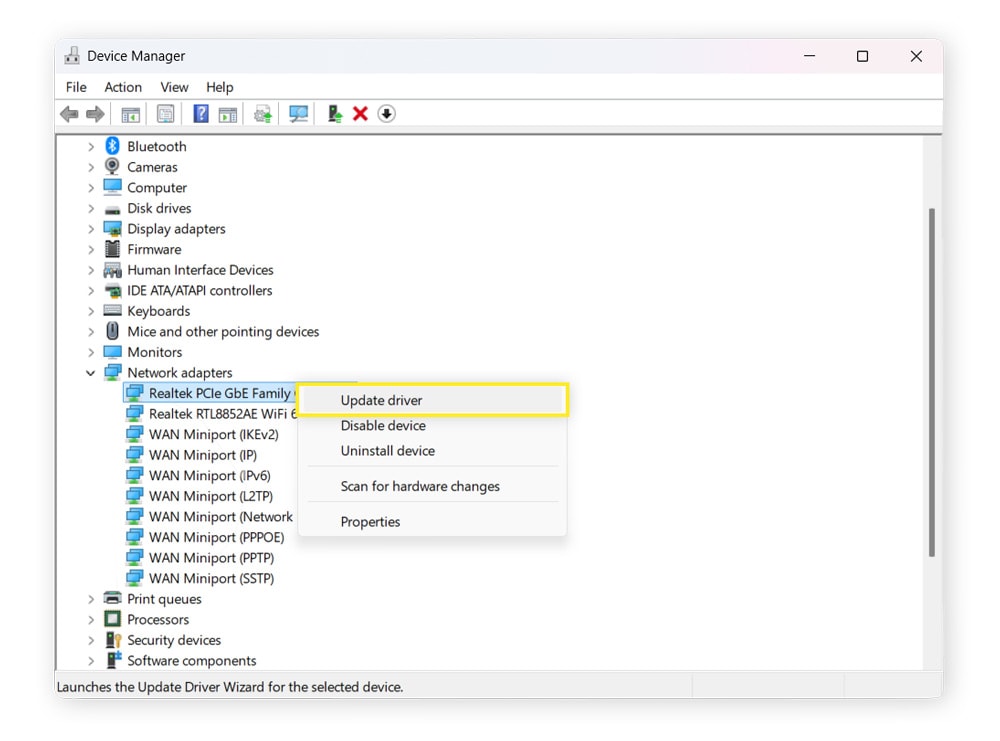
- Open Device Manager (use the search bar next to the Start button).
- Scroll down and find Network adapters.
- Right-click on each network adapter and select Update driver.

Besides performance issues, outdated drivers can increase your exposure to malware. Norton Driver Updater notifies you when drivers become outdated and selects updates compatible with your OS, so you can update in a few easy clicks.
9. Reset your network settings
Resetting your network settings will restore default settings, clear cached data, and wipe away any glitches and corrupted configurations that might be interfering with your connection. This method will erase saved Wi-Fi networks and passwords, so make sure you have your Wi-Fi router password handy before proceeding.
You can reset network settings on Windows by clicking Start > Settings > Network & Internet > Advanced network settings > Network reset.
On Mac: click Apple Menu > System Settings > Network > Wi-Fi/Ethernet > Details > Forget This Network.
On iOS: tap Settings > General > Transfer or Reset iPhone > Reset > Reset Network Settings.
On Android: tap Settings > General management > Reset > Reset Wi-Fi & Bluetooth settings > Reset settings.
10. Contact your internet service provider (ISP)
If the internet is not connected to your device, you can contact your internet service provider to help you troubleshoot. ISPs can test your connection remotely to isolate the problem and send a technician if necessary.
It is helpful to supply your ISP with any information you have that could help them troubleshoot, such as your account number, internet error message, and any other relevant details.
Why is my internet not working?
Your internet may not be working due to issues with your router, ISP, hardware, network, malware, or other factors. Here are some common causes of internet connectivity issues:
- Modem or router issues: Resetting your modem or router will usually resolve these problems unless there’s a hardware issue such as overheating or broken ports, in which case the device may need to be replaced.
- ISP outages: Bad weather, technical issues, or routine maintenance can cause temporary ISP outages.
- Faulty hardware: Overheating, broken ports, crimped wires, or even pets chewing through cables can lead to slow, spotty connections or completely lost connections.
- Driver issues: Outdated drivers can prevent you from getting online. Updating drivers should resolve this issue.
- Network congestion: Too many devices on a network can slow down or drop connections, especially if some users are streaming, making video calls, gaming, or engaging in other high-bandwidth activities.
- Interference: Nearby devices using the same wireless frequencies, such as microwaves, baby monitors, or objects blocking Wi-Fi signals can cause interference.
- Malware: Some malware is designed to interfere with network connections, either preventing you from connecting to Wi-Fi or consuming bandwidth. Hackers can also block your Wi-Fi access.
Get expert tech support without the headache
Troubleshooting your connectivity issues solo can be frustrating. Download Norton Ultimate Help Desk and let an IT expert handle the hard work for you. A Norton technician will be available to help you find a solution to your technical issues 24/7 — via phone or online chat.
FAQs
Why does my Wi-Fi randomly stop working?
If your Wi-Fi randomly stops working, it’s often due to weak signal strength, interference, or problems with your modem or router. Spotty Wi-Fi can also be caused by outdated drivers, low bandwidth, or even malware.
Why is my router not connecting?
If your router is not connecting, loose power cables, a corrupted configuration that requires resetting, or outdated drivers could be to blame. Checking the hardware and rebooting your router will solve many router-related connectivity issues.
Why does my phone have no internet but my computer does?
If your phone is connected to a different saved network, it might not have internet while your computer does. Other possible causes include a stuck network configuration, VPN interference, or disabled mobile data.
Can a VPN cause no internet connection?
If the VPN server is down or overloaded, it can interfere with your internet connection. Some firewalls also conflict with VPNs and block access. Try disconnecting from the VPN to confirm whether it’s causing the issue.
Editorial note: Our articles are designed to provide educational information for you. They may not cover or protect against every type of crime, fraud, or threat we write about. Our goal is to increase awareness about Cyber Safety. Please review the complete Terms during enrollment or setup. Remember that no one can prevent all identity theft or cybercrime, and that LifeLock does not monitor all transactions at all businesses. The Norton and LifeLock brands are part of Gen Digital Inc. For more details about how we create, review, and update content, please see our Editorial Policy.
- 1. Restart your router and modem
- 2. Forget and reconnect to Wi-Fi
- 3. Test your connection on other devices
- 4. Check for internet outages
- 5. Inspect hardware and cables
- 6. Pause your VPN
- 7. Disconnect some devices
- 8. Update network adapter drivers
- 9. Reset your network settings
- 10. Contact your internet service provider (ISP)
- Why is my internet not working?
- Get expert tech support without the headache
- FAQs








Want more?
Follow us for all the latest news, tips, and updates.