Why is Chrome so slow? 11 tips to speed up your browser
A sluggish browser can be frustrating, especially when it's one you use daily, like Google Chrome. Learn why Chrome slows down over time, and how to fix it. Then try Norton Neo to get an AI browser built to keep your browsing fast and efficient.

For an objectively good experience, key content on a webpage should load within 2.5 seconds maximum. And when Chrome starts lagging, those few seconds can stretch into frustrating delays.
But a slow browser doesn’t have to be a permanent problem, and there are proven solutions that can restore your Google experience. This guide breaks down the most common reasons why Chrome is so slow, and offers 11 actionable fixes to get your browser back to peak performance.
How to speed up your Chrome browser
When Google Chrome's slow performance becomes noticeable, it's usually due to accumulated browsing data, resource-heavy extensions, or system issues. Fortunately, you can resolve most browser slowdowns with simple steps that have a big impact, and don’t require a ton of technical expertise.
Here are the best ways to figure out why your Chrome browser is so slow:
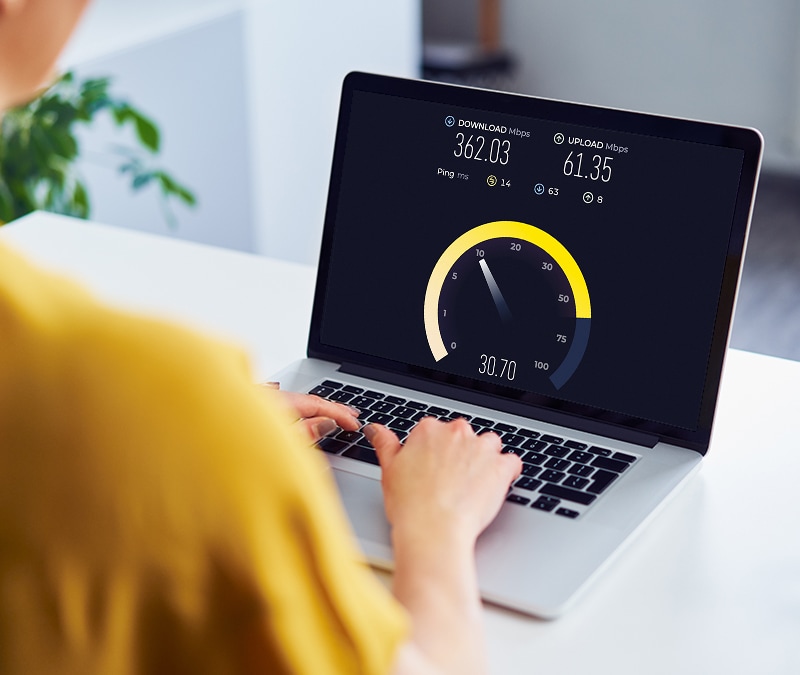
1. Run an internet speed test
Before troubleshooting Chrome specifically, make sure your internet connection isn't the issue. Running an internet speed test can show your actual download and upload speeds. Poor connection quality often explains why your Chrome is running slowly in general, or why YouTube keeps buffering, for example.
If your connection is slower than you expected, especially during high-traffic hours or on mobile data, that alone could be causing Chrome to lag. Even on slower networks like 3G, basic browsing is possible, but more demanding activities, like streaming or using multiple tabs, may suffer.
Here’s a general guide to recommended download speeds based on your online activity:
Activity |
Minimum speed recommended |
|---|---|
Basic browsing and email |
1-15 Mbps |
Video calls (HD) |
5-10 Mbps |
Video streaming (HD) |
5-15 Mbps |
Video streaming (4K) |
25 Mbps + |
Gaming |
25-50 Mbps + |
Multiple device usage |
25-100 Mbps + |
Keep in mind that actual speeds and recommended minimum speeds depend on your device, open tabs, and various other factors. But if your results are significantly lower than your internet plan promises, contact your provider or try these alternative steps to increase your download speed.
2. Close any unused tabs or browser windows
If your internet speed test shows normal results, but Chrome still feels slow, close any tabs or windows you're not actively using. Chrome uses significant RAM and CPU resources for each open tab, which directly impacts performance. Multiple tabs running video content, social media feeds, or complex web applications can quickly overwhelm your system's memory.
Bookmark pages you want to revisit later, or re-launch tabs and windows via your Chrome History, rather than keeping dozens of tabs open all the time. Chrome sometimes needs to restart after automatic updates, too.
3. Delete cookies and cache
Clearing your browsing data can often help resolve performance issues when Google Chrome is running slowly. This is because cached files and cookies accumulate and may conflict with website updates or take up unnecessary storage. Removing this stored data can help Chrome run more smoothly and load sites faster.
You'll probably need to sign back in to most websites after you do this, but a trusted password manager can help you sign back in quickly.
Here's how to clear your cache on Mac, Windows, Android, and iOS devices.
On Windows or Mac:
- Open Chrome and click the three dots menu in the top-right corner.
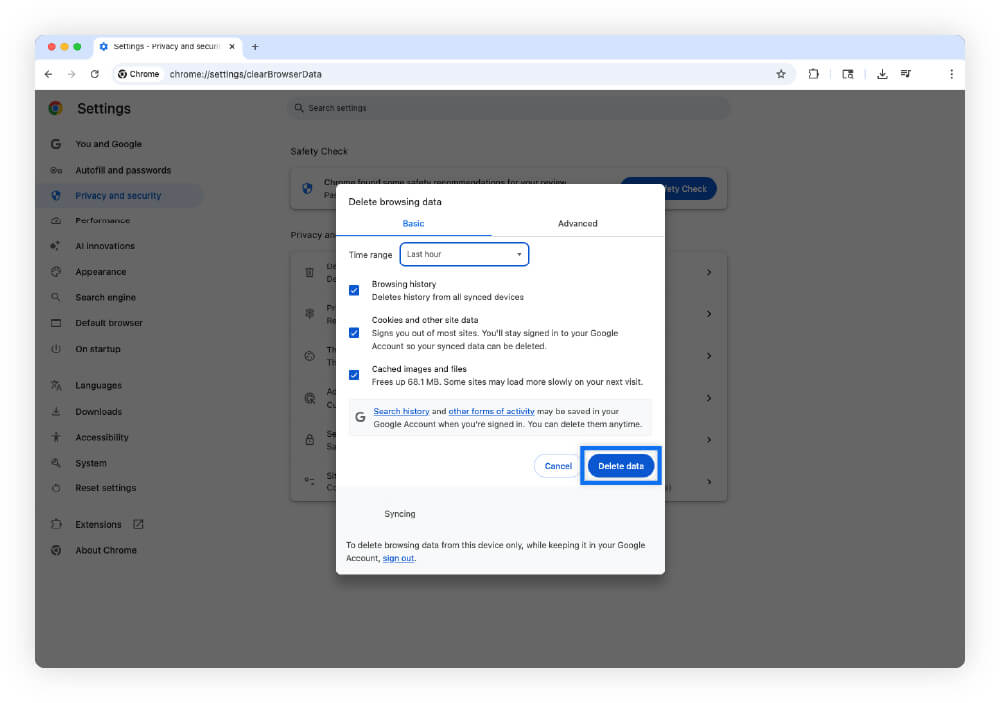
- Select Delete browsing data, and choose All time as your time range.
- Check Cookies and other site data, Cached images, and files.
- Click Delete data.
On Android:
- Open Chrome, and tap the three dots menu.
- Tap Delete browsing data, then select your time range and tap More options.
- Check the appropriate boxes, then tap Delete data.
On iPhone/iPad:
- Open Chrome, and tap the three dots menu in the bottom-right corner.
- Tap Delete Browsing Data, then choose your time range and data types.
- Tap Delete Browsing Data.


4. Clear your browser history
Large browsing histories can contribute to why Google Chrome is so slow. Delete your search history using the same steps as clearing cache, but select Browsing history instead of Cookies and other site data.
The process is identical across devices. First, access the Delete browsing data menu, then choose which time period to clear. Remember that if you're signed into Chrome with sync enabled, clearing history on one device removes it from all connected devices.

5. Check for Chrome updates
Outdated browser versions can cause speed and performance problems. Chrome usually updates automatically, but you can manually check for updates:
Desktop:
- Click the three dots menu.
- Select Help, then click About Google Chrome.
- Chrome will check for updates automatically.
- Choose Relaunch if an update is available.
Mobile:
- Check your device's app store (Google Play Store or Apple App Store) for Chrome updates.
- Enable automatic app updates to prevent future issues.
Software updates are crucial for performance and security, so keeping Chrome current helps address many slow performance issues.
6. Use Chrome's hardware acceleration feature
Hardware acceleration lets Chrome use your computer's graphics card to handle visual processing, which can significantly improve performance for media-heavy websites.
To enable hardware acceleration:
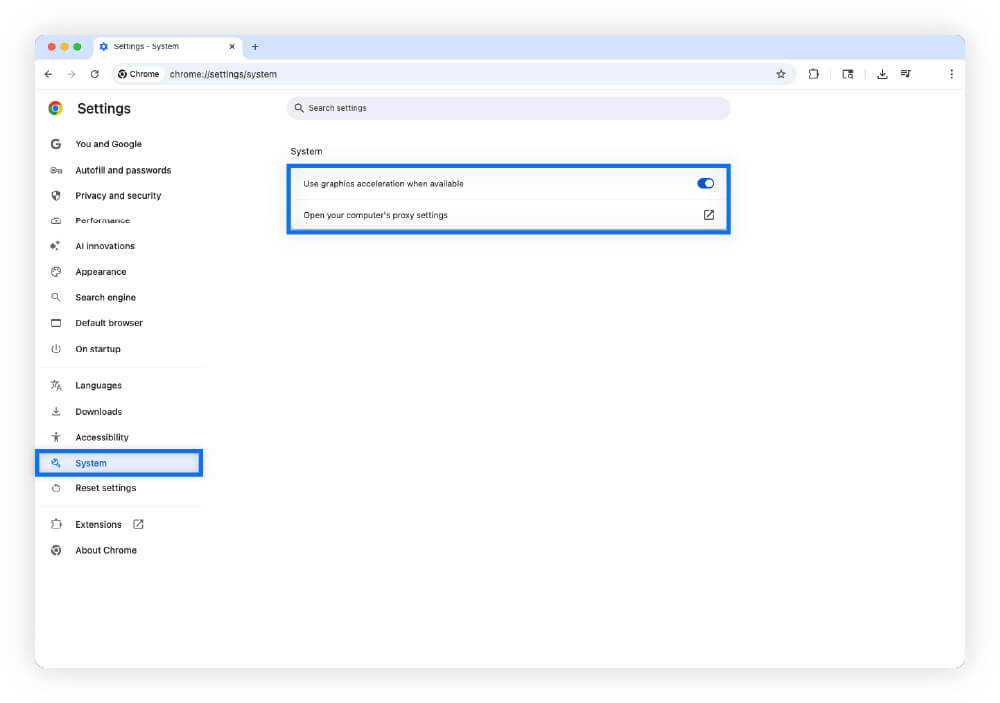
- Click the three dots menu, then Settings.
- Choose System in the left panel.
- Toggle on Use graphics acceleration when available.
- Restart Chrome.
This feature particularly helps with video streaming and graphics-intensive web applications that might result in Chrome lagging.

7. Uninstall unused plugins and extensions
Extensions consume system resources even when you're not actively using them. Review your installed extensions and remove the ones you no longer need:
- Type chrome://extensions/ in your address bar.
- Review each extension and click Remove under unused ones.
- For extensions you want to keep but don't use daily, toggle them off to disable them temporarily.
Popular extensions, such as password managers and productivity tools, can sometimes conflict with each other or consume excessive resources.
8. Install a browser with an ad blocker
Media-rich advertisements significantly slow down page loading times, which can explain why your Chrome browser is so slow on certain websites. While Chrome has cracked down on many ad-blocking extensions, using a browser with built-in ad blocking provides better performance and security.
A browser like Norton Neo includes built-in tools like ad and tracker blocking. This helps pages load faster, preserves your speedy browsing, and gives you more control over your online privacy.
9. Scan for malware
Malicious software can hijack browser resources and cause Chrome to perform slowly. Run a comprehensive system scan using reputable antivirus software to remove malware that might be affecting your browser.
Making sure your computer is clean of malware by using regular scans helps maintain both browser speed and overall system security.
10. Reset Chrome to default settings
If Chrome remains slow after trying other fixes, resetting to default settings can resolve configuration issues without affecting your bookmarks or passwords:
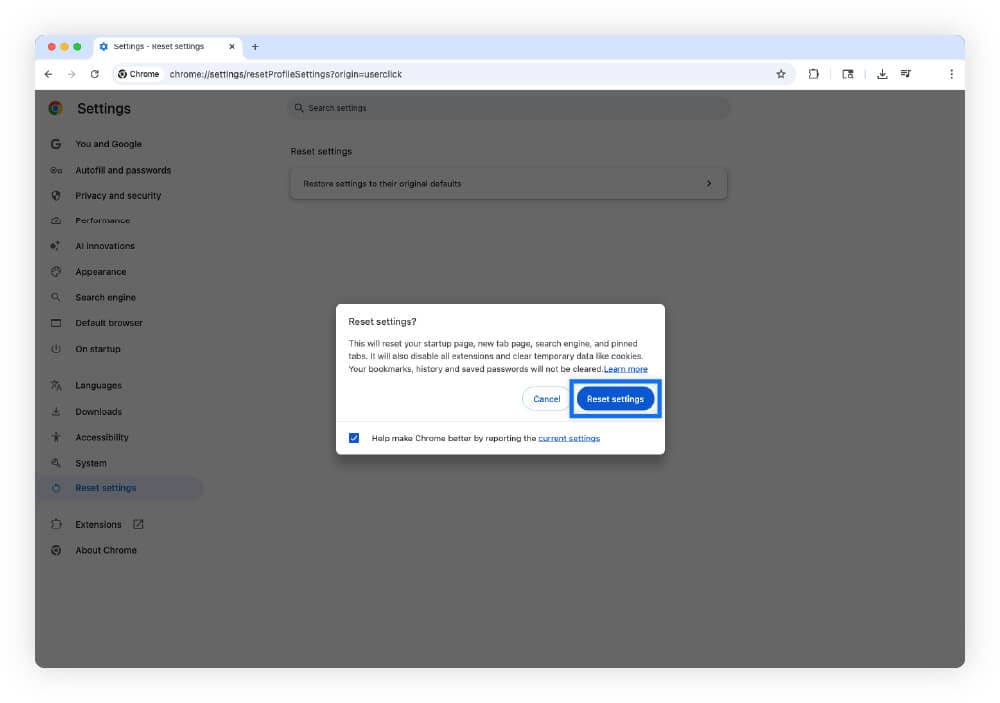
- Click the three dots menu, then Reset settings.
- Select Restore settings to their original defaults.
- Click Reset settings.

This process won't remove extensions, so manually review and delete any that might still be causing problems.
11. Try a new user profile
If Chrome remains slow, creating a fresh user profile can isolate whether the issue stems from corrupted profile data:
- Click your profile icon in the top right corner.
- Select Add Chrome profile, and follow the setup prompts.
- Test Chrome's performance with the new profile.
If the new profile runs smoothly, you can gradually transfer essential bookmarks and settings from your old profile.
Boost your browser performance with Neo
If optimizing your Chrome speed and performance becomes too clunky to manage, it may be time to switch to a new browser with efficiency at the forefront.
Norton Neo offers built-in ad and tracker blocking, offering enhanced privacy and security. Neo is powered by integrated AI technology, designed to help you quickly pinpoint information and organize your searches into a streamlined, tab-free workspace. Download your new AI companion now, for free.
FAQs
How do you find out what's slowing down Chrome?
Use Chrome's built-in Task Manager by going to the three dots menu > More tools > Task Manager. This shows which tabs, extensions, or processes are using the most CPU and memory resources.
Why is Google Chrome so slow on my laptop?
Laptops often experience slow performance on Chrome due to limited RAM, overheating, or running too many programs simultaneously. Try closing other applications, freeing up RAM, and ensuring your laptop has adequate ventilation.
Why is YouTube so slow on Chrome?
YouTube performance issues on Chrome typically result from outdated browser versions, disabled hardware acceleration, or network problems. To identify the cause, try enabling hardware acceleration in Chrome settings, clearing your cache, or testing your connection with an internet speed test.
Why is Google Chrome so slow on Mac?
Slow Chrome performance on Mac may be due to high CPU or memory use. Try clearing the cache, disabling unnecessary extensions, closing unused tabs, and ensuring you're on a private connection. Updating macOS and freeing up storage can also help.
Why is Chrome so slow on Windows 11?
Chrome can lag on Windows 11 due to the operating system's enhanced security features, memory compression, antivirus scans, and other background processes. To fix it, update the OS and Chrome, disable unnecessary startup apps, and adjust Windows performance settings to prioritize programs over visual effects.
Editorial note: Our articles are designed to provide educational information for you. They may not cover or protect against every type of crime, fraud, or threat we write about. Our goal is to increase awareness about Cyber Safety. Please review the complete Terms during enrollment or setup. Remember that no one can prevent all identity theft or cybercrime, and that LifeLock does not monitor all transactions at all businesses. The Norton and LifeLock brands are part of Gen Digital Inc. For more details about how we create, review, and update content, please see our Editorial Policy.








Want more?
Follow us for all the latest news, tips, and updates.