19 types of identity theft to know and avoid in 2025 plus statistics
What is identity theft?
Identity theft is when someone steals your personally identifying information, such as your name, address, date of birth, or credit card numbers, without your knowledge or consent to commit fraud or other illegal activities.

When thinking about what’s most important in your life, you may immediately think of your family or friends.
And while that may certainly be true, an often overlooked aspect of your life is your identity, with most people not realizing its importance until it ends up in the wrong hands.
In 2021 alone, identity theft cost those affected over $278 million.
Not only can identity theft cost you money, but it can negatively impact your credit score and even lead to criminal charges in your name. Over the years, fraudsters have created different identity theft methods to help them steal people’s identities for their own benefit. These common types of identity theft include:
- Financial identity theft
- Child identity theft
- Elder fraud
- Estate identity theft
- Medical identity theft
- Tax identity theft
- Identity cloning
- Social Security number identity theft
- Synthetic identity theft
- Biometric identity theft
- Familial or “friendly” identity theft
- Criminal identity theft
- Employment identity theft
- Account takeovers
- Government benefit and unemployment identity theft
- Home title theft
- Internet of Things identity theft
- Mail identity theft
- Passport fraud
Read through this helpful guide to learn more about different types of identity theft, their warning signs, and how to protect yourself in 2023.
1. Financial identity theft
Financial identity theft is when someone uses another person’s identity for their own financial gain. Some common examples of financial identity theft include hacking into your online banking account, opening new financial accounts in your name, or credit card fraud, which was reported nearly 390,000 times in 2021.
In some instances, the fraudster may sell your financial information on the dark web rather than using it themselves. Because most examples of identity theft involve financial consequences, it’s important to always safeguard your personal information and be wary of any communications claiming to be from your bank.
Warning signs of financial identity theft include:
- Unauthorized transactions
- New accounts opened in your name
- Suspicious activity on your credit report
- Lost access to your online banking account
Protection tip: Routinely monitor your credit report and transaction history to check for suspicious activity. If needed, you may also freeze your credit report.
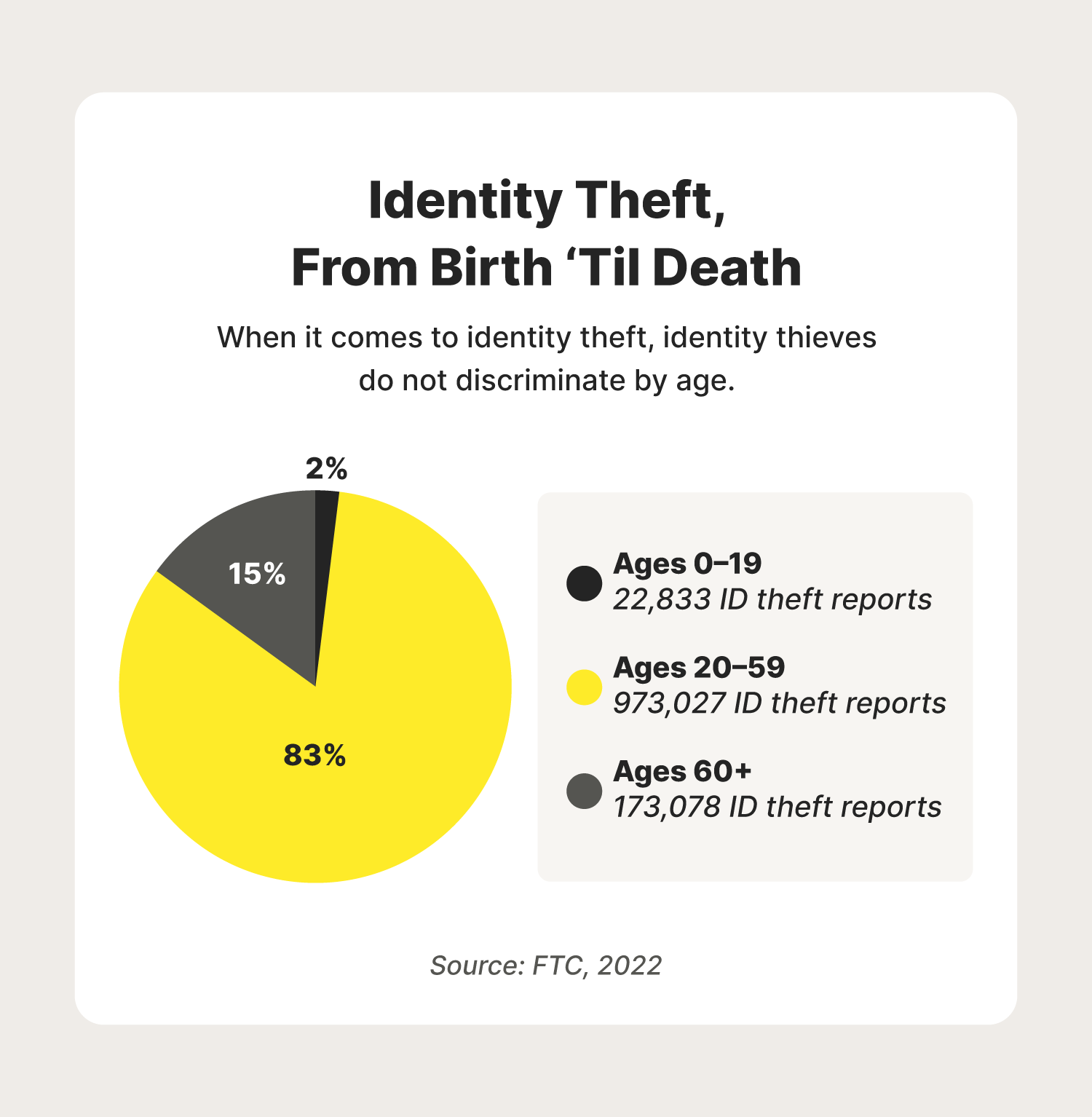
2. Child identity theft
Surprisingly, some identity thieves even target children. In fact, over 20,000 individuals under the age of 19 were affected by identity theft in 2021. Child identity theft involves the theft of a child’s personal information, usually to commit financial fraud. Examples of this include opening a new bank account or line of credit or applying for government benefits under the child’s name.
Because most kids don’t have financial accounts or credit reports, it can sometimes be years before they notice their identity was stolen. In some cases, the identity thief is a family member, as they have easy access to the child’s personal information, such as their date of birth, Social Security number (SSN), and address.
Warning signs of child identity theft include:
- Fraudulent activity on your child’s credit report
- Unauthorized accounts opened under their name
- Denial of government benefits
- Notification of unpaid taxes
Protection tip: If applicable, place a freeze on your child’s credit report or use a credit monitoring service to stay up to date on any suspicious activity.
3. Elder fraud
In this identity scam, identity thieves will take advantage of senior citizens. This is quite common, as over 170,000 individuals over the age of 60 reported instances of identity theft in 2021. Scammers can do this in many ways, often by placing vishing calls while pretending to be a trusted source such as the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services or the IRS.
While placing these calls, scammers will try to trick the senior citizen into giving up valuable information, whether it be account numbers, passwords, or personal information such as their date of birth or SSN. In other cases, the thief may pretend to be a relative in need of money.
Warning signs of elder fraud include:
- Vishing calls or phishing emails impersonating a trusted entity
- Requests for payment or personal information
- Unexplained transactions or loss of funds
Protection tip: Avoid answering unknown phone numbers or giving out personal or payment information to individuals over the phone.
4. Estate identity theft
In this type of identity theft, fraudsters will specifically target deceased people to steal from their estate or open new financial accounts. This is because it’s less likely that anyone is monitoring their credit or financial records.
Warning signs of estate identity theft include:
- Money disappearing from financial accounts
- Tax documents arriving at the deceased family member’s house
- Debt collectors calling to reach a deceased person
Protection tip: If a loved one of yours passes away, be sure to regularly monitor their mail and financial accounts for any unauthorized activity. If this goes undetected, you may end up paying taxes or debt caused by an identity thief.
5. Medical identity theft
Some cybercriminals may even use your personal and insurance information to obtain medical services. This may include drug prescriptions, regular checkups, medical equipment, or even surgeries. In 2021 alone, there were over 60,000 fraud reports related to healthcare.
In the event of a medical identity theft scam, you’ll likely start receiving bills and insurance claims for services and medication you never used. Not only can this impact you financially, but medical identity theft can lead to inaccurate medical records and may even impact your insurance coverage.
Warning signs of medical identity theft include:
- Unauthorized medical bills
- Unrecognizable activity on your medical records
- Receiving a change of address notification from your insurance provider you didn’t ask for
- Receiving an alert that your insurance benefits have been used up
Protection tip: Regularly review your medical claims for unauthorized activity. If you notice anything suspicious, contact your insurer and medical provider. You can also file a complaint with the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
6. Tax identity theft
Tax identity theft is when someone files a tax return in your name to claim your refund. You’ll likely discover this tax scam if you go to file a tax return and find out that one has already been processed. To ensure this doesn’t happen to you, be extra cautious whenever you receive any communications claiming to be from the IRS.
In some cases, the scammer may pose as an IRS employee over the phone to trick you into giving them your personal information. In fact, nearly 650,000 fraud and identity theft reports involved those affected being contacted by phone. Please note that the IRS will never contact you by email or over the phone without first sending a notice in the mail.
Warning signs of tax identity theft include:
- A tax return filed in your name
- Suspicious phishing emails or calls claiming to be from the IRS
Protection tip: Avoid giving out personal information over the phone or email. If you’re affected by tax identity theft, be sure to fill out an Identity Theft Affidavit with the IRS.
7. Identity cloning
Cloning identity theft is when a thief creates their own identity over a lengthy period of time using your personal information. This is one of the most difficult types of identity theft to track, as the thief may use your identity to live an average life without breaking any laws or doing anything to draw attention to themselves.
Identity thieves may do this to escape their past or to evade any criminal charges or responsibilities they may have from their true identity.
Warning signs of identity cloning include:
- Different addresses associated with your name
- Suspicious activity on your credit report
- Mysterious earnings on your Social Security Statement
- Random criminal charges linked to your name
Protection tip: Keep an eye on all of your personal records and report any suspicious activity to the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) and local law enforcement.
8. Social Security number identity theft
When it comes to stealing your identity, your Social Security number is a fraudster's holy grail. This is especially true if the scammer gains access to your other personal information, such as your date of birth and physical address.
Once an identity thief steals your SSN, they may use it to commit credit card fraud, apply for government benefits, or even apply for a job. This can hurt your credit score and may be used to rack up debt in your name. Identity thieves may also sell your SSN on the dark web, where other cybercriminals can purchase your identity to use for illegal activities.
Warning signs of SSN identity theft include:
- A lost or stolen Social Security card
- Unfamiliar activity on your credit report
Protection tip: Keep your Social Security card in a secure location and avoid sharing your SSN with untrustworthy entities. If your SSN is stolen, report it to the Social Security Administration.
9. Synthetic identity theft

Synthetic identity theft is one of the fastest growing financial crimes in the U.S. This type of identity theft is when a fraudster creates fake identities using a mix of information and documents from legitimate citizens, including SSNs, birthdates, and addresses.
By blending together this information, the identity thief creates an entirely new identity profile that they can use to apply for credit cards or engage in other illegal activity. Children, senior citizens, and the deceased are often targeted in this type of identity theft, as their SSNs usually aren’t actively used.
Warning signs of synthetic identity theft include:
- New accounts set up in your name
- Suspicious activity on your credit report
- Mail is delivered to a different address
Protection tip: Closely monitor your credit report and keep your personal information secure.
10. Biometric identity theft
Biometric identity theft is when a fraudster steals or impersonates your physical appearance in order to bypass security measures that require biometric data, such as facial recognition or your fingerprint.
If successful, an identity thief may be able to gain access to your private information, such as digital wallets or online accounts. In some cases, the identity thief is able to gain your biometric data from a data breach. Because of this, be sure to only enable biometric security with companies you trust to keep your information safe.
Warning signs of biometric identity theft include:
- A lost or stolen device
- Data breach notifications from companies that use your biometric data
Protection tip: Keep all of your devices up to date to ensure your biometric data is protected by the latest security updates. In addition, keep an eye out for any data breach notifications from companies that use your biometric data, such as a banking app that uses facial recognition for security.
11. Familial or “friendly” identity theft
Despite the name, familial or “friendly” identity theft isn't friendly at all. This type of identity theft is when a relative or close friend uses your personal information without your consent. This may be to open a credit card in your name or access one of your financial accounts.
Even if your identity is stolen by someone you know, it is still considered identity theft in the eyes of the law. Because of this, be sure to take all identity theft scams seriously, even if they involve someone you love.
Warning signs of familial or “friendly” identity theft include:
- Strange credit card charges
- Missing identification documents or credit cards
- Unauthorized family members added to your financial accounts
Protection tip: Keep an eye on all of your financial reports for suspicious charges or activity and store all of your documents and credit cards in a secure location.
12. Criminal identity theft
In this unique form of identity theft, a fraudster will give law enforcement your credentials instead of their own if they are ticketed or arrested. This can be through the use of a stolen driver’s license or a fake ID that they have created.
For example, if an identity thief gets pulled over for a speeding ticket and provides your information, the ticket may go on your record before anybody notices the driver isn’t who they claim to be. Unless law enforcement catches the identity thief upfront, you could end up having a warrant out for your arrest or the fraudster’s crimes on your record.
Of all crime-related identity scams reported to the Identity Theft Resource Center (ITRC), 57% of those affected had a warrant issued for their arrest due to the identity theft crimes.
Warning signs of criminal identity theft include:
- Lost or stolen driver’s license
- Unexplained criminal charges
- Requests for your appearance in court
- A warrant out for your arrest
Protection tip: Store all of your personally identifying documents in a secure location.
13. Employment identity theft
Employment identity theft is when a criminal uses your personal information to help them get a job. This can be for many reasons, whether the person isn’t able to legally work in the U.S. or they can’t pass a background check. In 2021 alone, over 100,000 cases of employment-related fraud were reported to the FTC.
While this might seem like a less harmful form of identity theft, it can still cause problems with your credit, taxes, and Social Security benefits.
Warning signs of employment identity theft include:
- Delivery of tax documents from a job other than your own
- Suspicious activity on your Social Security Statement
- Denial of unemployment benefits due to unexplained wages
Protection tip: Closely monitor your tax forms and Social Security Statement for any suspicious activity.
14. Account takeovers

An account takeover is when a scammer gets ahold of your login credentials and logs into one of your personal accounts. Once they get access to your account, they’ll change the password and lock you out. Then, the scammer will steal any information that may help them commit identity theft or other financial crimes.
For example, a fraudster may use a phishing email to help gain access to one of your social media accounts, then message your family and friends acting as if there is an emergency and then ask them for money. In other instances, an identity thief may gain access to one of your online shopping accounts and use your saved payment information to rack up debt.
This type of identity theft can be especially dangerous if the fraudster gains access to your online banking or cryptocurrency accounts, as they may be able to move money out of your account. Because of this, be wary of any emails that could be phishing attempts, as over 260,000 of all fraud and identity theft reports involve being contacted by email.
Warning signs of account takeovers include:
- Phishing emails
- Loss of access to your accounts
- Strange password reset notification emails
- Suspicious posts or messages on your behalf
- Random login alerts from devices you don’t recognize
- Unauthorized transactions
Protection tip: Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) wherever possible and use secure passwords.
15. Government benefit and unemployment identity theft
In this type of identity theft, a cybercriminal will use your identity to apply for unemployment or other government benefits. Not only does this help the fraudster make some quick cash, but it can prevent you from getting the benefits you need.
A fraudster may do this by finding your information online or by phishing for your private information, often by impersonating the government. Not only is this type of identity theft dangerous, but it is also common. In 2021, the FTC received nearly 400,000 reports for government documents- and benefits-related identity theft.
Warning signs of government benefit and unemployment identity theft include:
- Mail related to an unemployment claim you didn’t make
- Denial of government benefits
- A 1099-G tax form including government benefits you didn’t request
Protection tip: Regularly review all tax documents and mail from government agencies.
16. Home title theft
Home title theft is when a fraudster gets ahold of the title to your property. With the help of other personal information, the scammer may then be able to transfer the ownership of your home or property to themselves. Once the ownership of the property has been transferred, the thief may try to sell your home.
In other cases, the criminal may use your home equity to get lines of credit and loans in your name. This can be devastating, as it can lead to unexpected foreclosure for the homeowner. Unfortunately, home title fraud and other forms of real estate scams affected over 11,000 people in 2021.
Warning signs of home title theft include:
- Sudden stoppage of mortgage- and tax-related mail
- Suspicious loans or lines of credit
- Unauthorized changes to your mortgage or home title
Protection tip: Routinely check your home's title information with your county's deed office.
17. Internet of Things identity theft
The Internet of Things (IoT) has transformed our lives with handy internet-connected devices that make our lives easier. From smart TVs to fitness trackers, these IoT devices have also become additional access points for hackers and identity thieves.
IoT identity theft occurs when a fraudster exploits a security flaw in one of these devices in order to gain access to your personal data, such as your email account, credit card information, or date of birth. Because of this, it's important to always be cautious about what information you link to these devices.
Warning signs of IoT identity theft include:
- Unfamiliar login notifications
- A lost or stolen IoT device
- Strange activity on your smart device
- Unauthorized password changes
Protection tip: Use a secure password, 2FA, and always keep your device's firmware up to date for the latest security patches.
18. Mail identity theft
Mail identity theft is when a scammer steals your mail to find checks, account numbers, credit or debit cards, and personal information that they can use to steal your identity. Scammers can target this information by going through your mailbox or even your garbage.
Because of this, always be mindful of the mail you throw away. Something as simple as an account statement can be extremely useful to identity thieves, so be sure to shred any documents that include sensitive information.
Warning signs of mail identity theft include:
- Missing mail
- Unauthorized charges
- Suspicious activity on your credit report
Protection tip: Avoid leaving mail in your mailbox for an extended period of time. You may also want to shred any mail before discarding it. If you’re affected by mail theft, report it immediately to the United States Postal Inspection Service.
19. Passport fraud
Passport fraud is when a scammer uses a lost or stolen passport for their own benefit. This can be done by stealing the passport of someone who looks similar to them in hopes of using it or selling it to a stranger on the dark web for profit.
In some cases, the fraudster may even use the information on your passport to forge their own. In 2021, there were over 1,000 reports of forged passports to the FTC.
Because getting a passport is such a lengthy process, a stolen or compromised passport can throw a wrench in your travel plans and can even lead to charges on your criminal record if the fraudster uses your passport as identification while engaging in illegal activities.
Warning signs of passport fraud include:
- A lost or stolen passport
- Suspicious charges on your criminal record
Protection tip: Store your passport in a secure location and report any instances of loss or theft to the U.S. Department of State.
Identity theft statistics

Unfortunately, these forms of identity theft affect millions of people across the globe. To better understand the severity of identity theft, check out some of these eye-opening identity theft statistics:
- Over 60% of consumers are very worried that their identity will be stolen. (Norton, 2021)
- From 2020 to 2021, identity theft reports related to the opening of a new checking or savings account increased by 64%. (FTC, 2022 Consumer Sentinel Network)
- From May 2020 to May 2021, over 55 million people in 10 different countries experienced identity theft. (Norton, 2021)
- 25% of all reports to the FTC involved some form of identity theft. (FTC, 2022 Consumer Sentinel Network)
- 3 out of every 10 people affected by identity theft were targeted more than once. (ITRC, 2021)
- There were nearly 1.5 million identity theft reports to the FTC in 2021. (FTC, 2022 Consumer Sentinel Network)
- 63% of those affected by identity theft are female. (ITRC, 2021)
- Over $2 billion was lost to imposter scams in 2021. (FTC, 2022 Consumer Sentinel Network)
- 40% of those affected by identity theft were unable to pay their routine monthly bills following the incident. (ITRC, 2021)
- Rhode Island faced the largest number of identity thefts in comparison to its population, with 2,857 reports per 100,000 people. (FTC, 2022 Consumer Sentinel Network)
- Almost half of Americans claim they would not know what to do if their identity was stolen. (Norton, 2021)
- 1 in 4 reports made to the FTC were related to identity theft. (FTC, 2022 Consumer Sentinel Network)
- 21% of those affected by identity theft reported they lost over $20,000. (ITRC, 2021)
- Texas had nearly 150,000 identity theft reports, higher than any state in the country. (FTC, 2022 Consumer Sentinel Network)
- 61% of those affected by identity theft have a college degree. (ITRC, 2021)
- Since 2015, reports of identity theft have increased by 86%. (FTC, 2022 Consumer Sentinel Network)
- 83% of those affected by financial-related identity problems end up being turned down for credit or loans. (ITRC, 2021)
Now that you understand the different types of identity theft and its prevalence around the world, it's crucial that you always practice caution whenever dealing with your identifying documents and personal information. To help further increase your Cyber Safety, stay up to date on all the ways to avoid identity theft.
FAQs about types of identity theft
Read along to learn more about the different identity theft types and common questions surrounding them.
How can criminals steal your identity?
Because there are many different types of identity theft, criminals can steal your identity in many ways. But these identity theft types all share a commonality: It starts with the physical or digital theft of your personal information, whether the criminal steals important physical documents or uses a cyberattack to access your private information.
What are the consequences of identity theft?
Having your identity stolen can lead to a range of consequences, including:
- A negatively impacted credit score
- Financial loss
- Criminal charges in your name
- Emotional distress
- Loss of access to your online accounts
- Invasion of privacy
- Increased spam calls and emails
- Damaged reputation
What is the most common form of identity theft?
According to the FTC, government documents or benefits fraud was the most common type of identity theft, with 395,948 reports in 2021.
What is the difference between identity theft and fraud?
The difference between identity fraud vs. identity theft is that identity fraud is the use of someone else's identifying information to engage in illegal activities, whereas identity theft is the act of stealing someone’s personal information.
Editorial note: Our articles provide educational information for you. Our offerings may not cover or protect against every type of crime, fraud, or threat we write about. Our goal is to increase awareness about Cyber Safety. Please review complete Terms during enrollment or setup. Remember that no one can prevent all identity theft or cybercrime, and that LifeLock does not monitor all transactions at all businesses. The Norton and LifeLock brands are part of Gen Digital Inc.
- 1. Financial identity theft
- 2. Child identity theft
- 3. Elder fraud
- 4. Estate identity theft
- 5. Medical identity theft
- 6. Tax identity theft
- 7. Identity cloning
- 8. Social Security number identity theft
- 9. Synthetic identity theft
- 10. Biometric identity theft
- 11. Familial or “friendly” identity theft
- 12. Criminal identity theft
- 13. Employment identity theft
- 14. Account takeovers
- 15. Government benefit and unemployment identity theft
- 16. Home title theft
- 17. Internet of Things identity theft
- 18. Mail identity theft
- 19. Passport fraud
- Identity theft statistics
- FAQs about types of identity theft





Want more?
Follow us for all the latest news, tips, and updates.