Online scams: An overview + 19 internet scams to avoid
Americans lose billions to online scams every year, and many never recoup their losses. Read on to learn more about the most dangerous scams to watch out for. Then, find out how to help identify and avoid them by using a comprehensive online security tool with cutting-edge, AI-powered scam protection features.

The internet has created a fantastic means to explore new topics, stay connected with loved ones, shop, and even access healthcare. But it’s also become a rich hunting ground for online scammers.
Scammers leverage the internet to defraud or take advantage of others, typically for financial gain. The financial impact of online scams hit a record high in 2024, with reports to the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center representing over $16 billion in losses. And, as digital tools like chatbots and deep fake technology evolve and make it easier to scam people, the problem is likely to surge in the coming years.
What the experts say
"'Scam yourself' techniques continue to spread across everyday channels like SMS, email, and social media." - Gen 2025 Threat Report
Threat Research Team, Gen
With that in mind, it’s time to familiarize yourself with the top scams circling the internet, how they work, and how you can help protect yourself from this growing cybersecurity and identity threat.
1. Job offer scams
With 7.4 million unemployed workers in the U.S. as of August 2025, job offer scams are a common way for scammers to prey on the desperation of others. Frequently appearing on job boards like Indeed and LinkedIn, this internet scam may come in the form of a phone call, message, or unsolicited email advertising a job requiring little to no real work but supposedly offering lots of quick cash.
Once the scammer has their foot in the door, they use the “job offer” as a ruse to ask for personal information like your name, Social Security number, address, and direct deposit details to complete “routine” paperwork. Or, they may try asking for money to cover training and equipment costs, which is always a sign of a scam.
Job offer scam warning signs:
- A job offer’s pay is too good to be true.
- You receive a job offer without applying.
- The job description is poorly written and contains grammatical errors.
- There isn’t much information about the company online.
- The company website looks spammy or unprofessional.
2. Lottery
The lottery scam is a scheme where fraudsters contact people via email or social media, claiming they won a lottery or sweepstakes. The “prize” is usually money, a trip, or some big-ticket item—but, in reality, there are no winnings. Instead, the scammer spins a story that you need to send an advance payment to cover taxes and legal fees and runs off with your money.
Lottery scam warning signs:
- You win a prize for a contest you didn’t enter.
- You have to pay to get your prize.
- The lottery claims to be run by the federal government.
- Your lottery ticket says it’s from states without a lottery: AL, AK, HI, NV, or UT.
- The lottery organization says that you can pay to increase your chances of winning.
3. Nigerian Prince scam
The Nigerian Prince scam, also known as 419 fraud, is a type of advance fee scam in which a fraudster strikes up a conversation, shares an emotional story, and convinces their target to send money to help transfer assets or access their tied-up funds. This type of scam is infamous, but many people still fall for it, especially as criminals up the ante with more complex stories and promises.
Nigerian Prince scam warning signs:
- You get a message from someone claiming to be distantly related to you.
- The supposed “prince” promises valuables, love, or titles in exchange for money.
- The messages you receive have spelling and grammatical errors.
- The person messaging you refuses to answer direct questions.
4. Online dating scams
Internet dating can be a great way to meet potential romantic partners, but cybercriminals can also use online dating platforms to scam unsuspecting romantics out of money. They often do this using emotional manipulation and by cultivating what appears to be a real relationship.
And because scammers can craft the perfect fictitious dating profile and love bomb you over text, this specific scam may be hard to see at first. That’s probably why the median loss of the more than 64,000 people who fell for a romance scam in 2023 was $2,000—the most substantial loss of any imposter scam.


Dating scam warning signs:
- Their profile seems too generic or perfect.
- They live out of state.
- The relationship moves fast.
- They ask for money and/or personal information.
- They continually make up reasons they can’t meet in person or video chat.
- Their images appear under someone else’s name when you do a reverse image search.
5. Charity scams
Online charity scams may come in the form of social media pleas, GoFundMe fundraisers, and email requests—especially following tragedies like hurricanes, earthquakes, pandemics, and major conflicts. This is an effective scam because fraudsters can prey on people's good intentions to get rich quickly during hard times.
Charity scam warning signs:
- They aren’t transparent about how they’ll use your money.
- The person you’re talking to asks for personal information.
- The organizer promises to return your money.
- The person collecting money doesn’t contact you through official channels.
6. Social media scams
Social media scams continue to dupe users into entering fake giveaways, buying low-quality or nonexistent products, pursuing made-up romantic partners, following fake influencers, and sending money to mutuals.
These scams can be found nearly everywhere—Facebook, Instagram, X (formerly Twitter), LinkedIn, Yubo, Threads, TikTok—you name it. In fact, recent data shows that social media is the single most used method of contact among fraudsters.
Social media scam warning signs:
- Someone is selling a great product or service at an extremely low price.
- A user you don’t know well requests money.
- You receive messages with suspicious links.
- People with incomplete profiles, limited followers, or stolen photos try to contact you.
- The person you’re messaging plays on your emotions or shares manipulative stories.
7. Shopping scams
Cyberthieves often create fake shopping websites for popular sites like Amazon or Etsy, or Shein that mimic legitimate retailers or appear entirely genuine. These sites usually promote deals that are too good to be true, offering popular branded clothing items and expensive electronics at unrealistically low prices. The goal is to trick you into making a purchase and allowing hackers to steal your banking information.
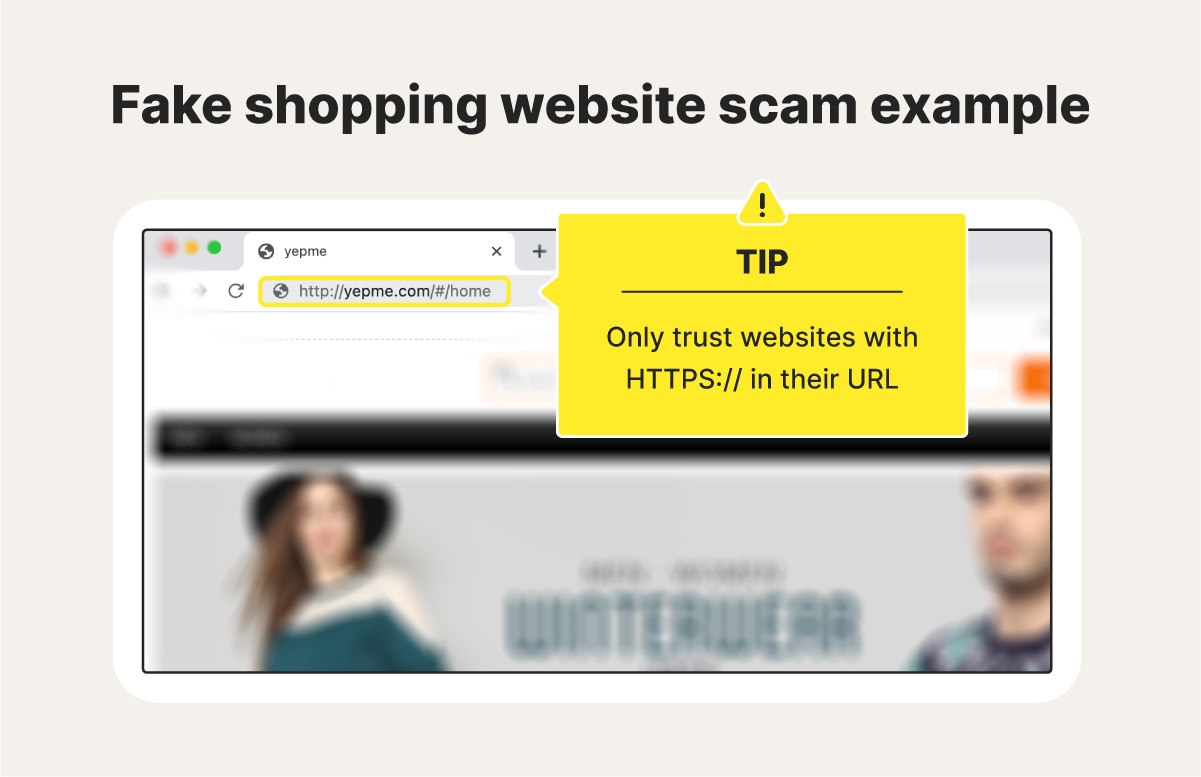

Hackers also use formjacking to target online shoppers. This involves hacking a legitimate retailer’s website and redirecting customers to a fake payment page. The fake forms are then used to steal your credit card details and personal information.
Shopping scam scam warning signs:
- You get redirected to a page unsecured website, without “https” in the URL.
- The site uses stolen images to promote products.
- The seller has a lot of bad reviews.
- There’s no way to contact the seller directly.
- The seller doesn’t have a clear return policy.
8. Government impersonation scams
By posing as a government agency, using pressure tactics, and threatening consequences like fines or jail time, scammers can better convince people to pay up or send sensitive information about themselves over unofficial channels.
Some common government impersonation ruses include:
- IRS scams: Scammers claiming to be from the IRS demand that you make a tax payment, often threatening arrest or legal action.
- Law enforcement scams: Scammers impersonate law enforcement officials to demand money or personal information, often claiming that they issued a warrant.
- Grant scams: Scammers offer victims the opportunity to receive government grants or loans in exchange for upfront fees or personal information.
Government impersonation scam warning signs:
- The scammer threatens you with arrest, deportation, or other legal consequences.
- The person you’re talking to claims they can accept gift cards, cryptocurrency, or a wire transfer to settle cases.
- They pressure you to take action quickly without doing research.
- They don’t contact you through an official email address or phone number.
9. Phishing scams
The initial aim of phishing scams is usually to trick people into interacting with phishing links, resulting in damaging malware downloads, or the harvesting of sensitive information. Phishers often get people to click by sending emails or texts that appear to be from legitimate sources, such as a bank, social networking site, store, school, employer, or even a friend.
It’s estimated that cybercriminals send 3.4 billion phishing emails daily, and nearly 30% of them are opened.
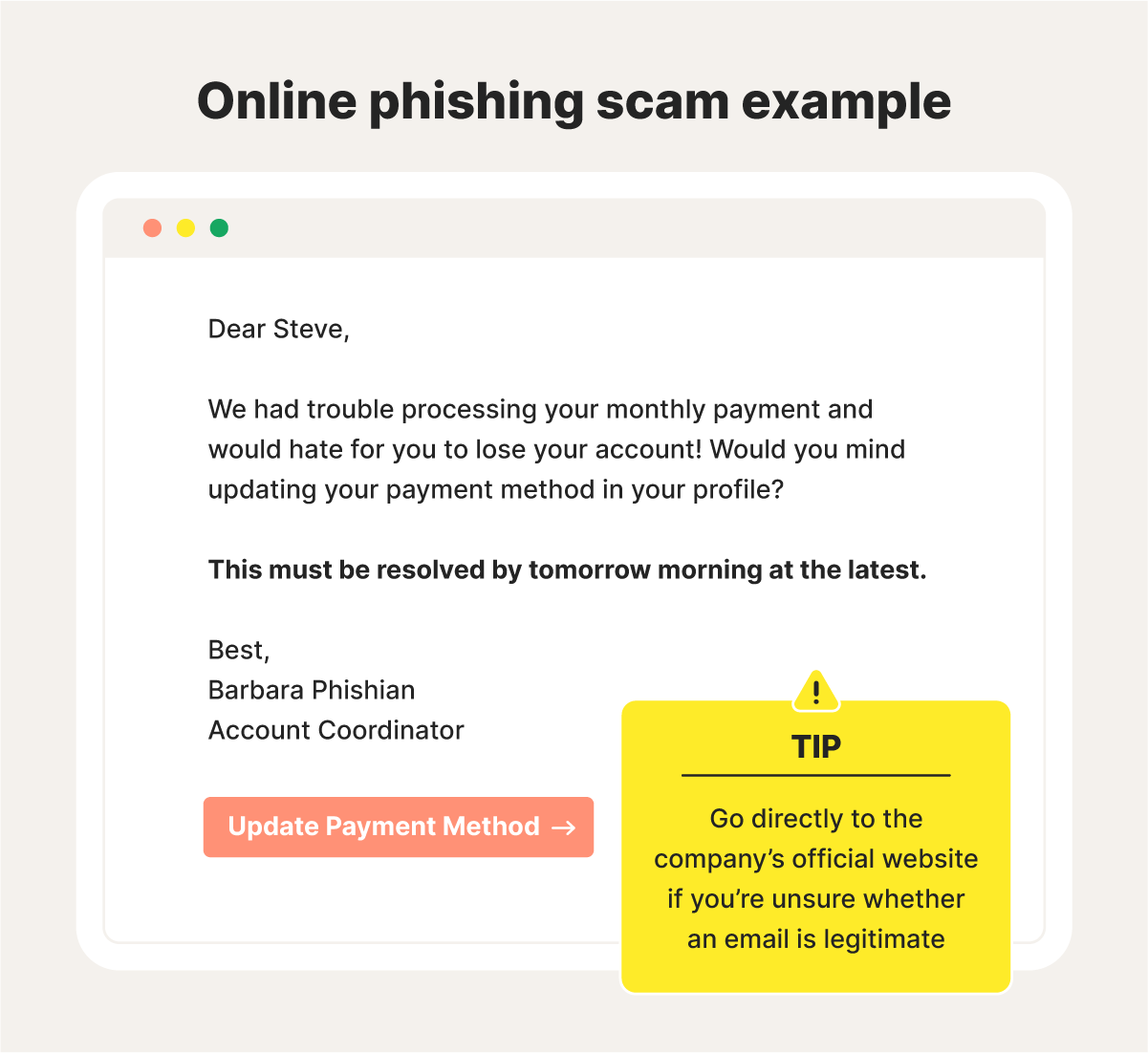

Phishing scam warning signs:
- You receive messages with suspicious links and attachments.
- The messages you get are generic and have poor spelling and grammar.
- They request personal information or resort to intimidation.
- You can’t verify the sender’s identity.
- When you hover over links in the message, the URLs don’t look legitimate.
Phishing scam prevention tip: Contact the company that supposedly sent the message directly via an official channel to confirm if the email you received was legitimate. Also, use Norton Genie, a free, AI-powered scam-detection tool, to help determine whether messages are scams.
10. Grandparent scams
Elderly people are common scam targets since fraudsters know many are quick to help family members. Scammers may pose as a grandchild in need to scam them out of money. They may claim to be abroad and need money for a last-minute train ticket, ask for help covering a hospital bill, or come up with an entirely unique lie.
Grandparent scam warning signs:
- You get a text message or email from an unsaved number.
- A family member asks for a surprising amount of money.
- The person asking for money wants you to keep it a secret.
- You can’t verify the person’s identity or story.
- The ruse creates a sense of urgency and plays on your emotions.
11. Cryptocurrency scams
A cryptocurrency scam typically involves an investment scheme that promises massive returns but delivers nothing at all. Alternatively, it may be an advance fee scam, where scammers prefer cryptocurrency payments because they are almost impossible to trace and recover once the fraud is discovered.
Cryptocurrency is now a popular way scammers steal money, with losses exceeding $9 billion in 2024.
Cryptocurrency scam warning signs:
- You’re “guaranteed” a return on your investment.
- The person you’re talking to pressures you to act quickly.
- The investor isn’t registered and doesn’t have any endorsements.
12. Ransomware scams
A cybercriminal may infect your computer with ransomware after a successful online scam. Once installed, the malware encrypts your files and the attacker demands a ransom, often in cryptocurrency like Bitcoin. With ransomware losses projected to hit $265 billion over the coming decade, it's crucial to learn how to protect yourself.
Ransomware scam warning signs:
- You receive emails with suspicious attachments.
- The scammer uses threatening language.
- You’re told to send money to maintain your privacy.
- The person you’re talking to creates a sense of urgency.
Ransomware scam prevention tip: Back up your data and use reliable online security software to help prevent ransomware from taking your device hostage.
For cutting-edge ransomware protection, get Norton 360 Deluxe and enjoy powerful heuristic anti-malware detection features that help identify and block malware threats in real time.
13. Holiday scams
Unfortunately, the holidays are a common time of year when scammers exploit people's generosity and holiday spirit. Holiday scams involve requests for donations to non-existent charities, fake sales or deals, gift card scams, or phishing attempts disguised as holiday greetings. They often succeed by preying on emotions and the season's spending frenzy.
Holiday scam warning signs:
- The scammer offers you incredibly low prices on popular holiday items.
- You receive communications from popular retailers with deals and discounts that seem off.
- You get emails with links to fake websites.
- Sellers ask you to pay for items with gift cards or through wire transfers.
- You don’t get tracking information after making a purchase.
- People asking for donations don’t say where the money is going.
14. Purchase scams
Purchase scammers trick buyers into paying for goods or services, and then they either don’t deliver or don’t meet expectations. These types of scams can run rampant on online marketplaces such as Vivid Seats, auction sites, and social media, but you may also encounter them on fake websites or through email promotions.
Purchase scam warning signs:
- The seller only accepts cash, gift cards, cryptocurrency, and other forms of payment that are hard to trace.
- The website has design, spelling, and grammatical errors.
- You can’t find any information about the seller online.
- The vendor has lots of bad reviews.
15. Extortion and blackmail scams
A blackmail and extortion scam is a serious crime where a criminal threatens to harm or expose someone online unless their demands are met. Often, the blackmailer threatens to expose intimate photos or videos or ruin someone's reputation via social media.
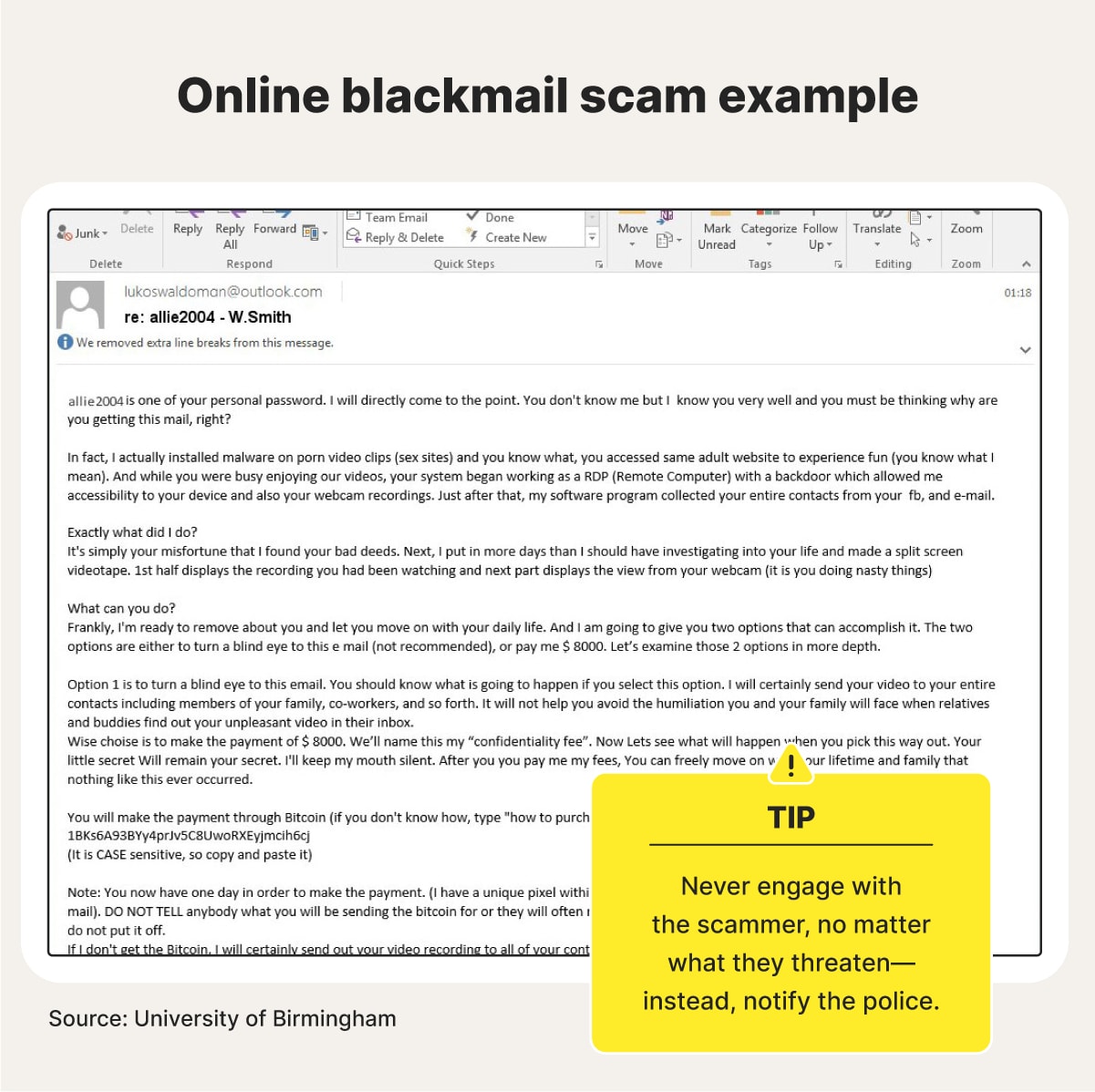

Blackmail scam warning signs:
- The scammer threatens to release private or embarrassing information unless you pay.
- They demand you pay them with an untraceable method.
- They demand payment by a specific time and date.
16. Adoption scams
Adoption scams often appear on social media or fake agency websites, targeting hopeful families. Scammers try to exploit the emotional vulnerability of prospective parents, and typically request upfront payments for supposed costs like legal fees, medical exams, or travel.
Once victims make their payments, the scammers may disappear or make baseless placement promises to get more money from you. To drive home the scam, many criminals will create fake profiles and backstories using stolen child identities.
Adoption scam warning signs:
- They promise a quick and easy adoption.
- They require upfront fees.
- They aren’t transparent about the birth parent.
- They can’t show you new pictures of the child or arrange a meeting.
- They pressure you to make a quick decision.
17. Business and investment scams
Common business and investment scams include Ponzi schemes, pyramid schemes, and aggressive sales tactics. These scams often overpromise and underdeliver, luring victims with false guarantees of high returns or profits. Once you invest, purchase, or join, scammers may delay payments, fail to deliver products, make excuses, or vanish altogether.
Business and investment scam warning signs:
- They claim there’s no risk to your investment.
- The person is unwilling to answer questions about the business or investment.
- The scammer claims to have insider information.
- The investor or their company isn’t registered with any regulatory authorities.
18. Travel scams
While you plan and save to pull together your dream trip, scammers are doing some planning of their own to trick you out of money on your travels. Some of these travel or airline scammers often start by gaining your trust, whether as a friend, travel planner, local vendor, or random stranger.
Then, they try to squeeze you for cash by overcharging for transportation, restaurant bookings, or accommodations—or selling you fake tours, tickets, or activities. Or their goal is to gather your sensitive information.
Travel scam warning signs:
- Sellers use intense pressure tactics.
- Travel planners demand personal information and high upfront fees.
- Sellers request payment through hard-to-trace methods.
- They offer package deals with unrealistically low prices.
19. Money transfer scams
Scammers posing as legitimate sellers or entities may request money via wire transfers or peer-to-peer (P2P) payment apps, claiming it's the easiest option due to distance or other excuses. While convenient with friends, these methods make it difficult to recover funds if you're scammed, as wire transfers are typically irreversible and many payment apps like Zelle offer no buyer protection.
Money transfer scam warning signs:
- You receive requests for large, one-time payments.
- The person you’re speaking to prefers payment options without buyer protection.
- You cannot verify the person’s identity.
- They pressure you to pay quickly.
How do I protect myself from online scams?
Understanding how online scams work is the first step in learning how to avoid them. Here are some additional online scam prevention tips to help protect you even further.


Set up two-factor authentication
If two-factor authentication (2FA) is available, use it to defend against attempts by scammers who perform brute force attacks or other account takeover methods.
This security feature requires you to verify your identity in two ways before accessing an account—usually a password and another verification step. Some common choices for a secondary identifier include authentication codes sent through text, email, an app, or biometrics like facial recognition or fingerprint scanning.
Never respond to scam messages
Responding to spam texts or spam emails is never a good idea as they can include scams. And if nothing else, responding can confirm to scammers that your phone number or email address is active.
Help yourself avoid scams online by not clicking links, opening attachments, replying to messages, attempting to unsubscribe, or calling any telephone number listed in suspicious messages. And never give out any money, credit card details, or other personal details to unknown or unverified senders.
Install antivirus software
Trusted antivirus software helps prevent different types of malware from infecting your computer or device. If it detects malicious code, such as a virus or worm, it will work to disarm or remove it. But make sure you only download software apps and services from trusted and official vendor sites.
Norton AntiVirus Plus offers real-time defense against malware, ransomware, phishing, and more, using advanced multi-layered security to help protect against emerging and complex threats.
Keep your social media accounts private
Social media can be great for connecting with different people and accessing information, but it also poses a security risk. Fortunately, setting stricter social media privacy settings can offer you more protection.
Take a second to explore your account settings, and you’ll usually find that you can decide what information is viewable by the public, who can tag you, and who can message you or send friend requests.
Report possible scams
If you see the signs of an online scam, file a complaint with the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3), which is the central point for tracking patterns of fraud and abuse related to Internet crimes. The IC3 reviews complaints, analyzes data, and creates intelligence reports that highlight emerging threats and new trends.
The center can also forward certain investigations to the appropriate law enforcement agencies, which may help you get justice and recover lost funds.
Be cautious when transferring money
As mentioned, hackers may try to compromise your personal and banking information by getting you to transfer funds to them electronically.
When dealing with online transactions, only send money to known and verified accounts to help avoid payment app scams and other financial fraud. You should also only use encrypted mobile payment services to keep your account information safer as you complete the transfer.
Powerful online scam detection
Instead of going with your gut, use an online security app with built-in scam-detection features to help determine if a message is real or a scam.
Norton 360 Deluxe features sophisticated AI-powered algorithms that can analyze SMS messages for red flags and suspicious patterns. Plus, it includes strong anti-scam protection when you’re browsing the web to help you stay safer from fake e-shops and other online scams.
FAQs
What are online scams?
Online scams are internet-based schemes that try to trick people into sending money or personal information. Scammers may resort to impersonation, phishing, and blackmail to achieve their end goal.
What scams are most common right now?
According to the Consumer Sentinel Network’s Data Book, the top five scams last year were:
- Imposter scams
- Online shopping scams
- Lottery and sweepstakes scams
- Investment scams
- Business and job offer scams
How can I tell if I’m getting scammed?
Every scam is different, but some tell-tale signs of a scam include:
- Emails or messages from unfamiliar numbers or email addresses
- Urgent requests
- Wire transfer requests and other hard-to-trace payment methods
- Personal information requests
- Sweepstakes notifications when you didn’t enter
- 100% guarantees
What happens if I get scammed?
If somebody scammed you, you may suffer financial loss and potentially have your personal information compromised. Not to mention the emotional recovery that comes with it. It's crucial to act quickly and report the incident to relevant financial institutions and authorities to minimize further damage and potentially recover your losses.
Editorial note: Our articles are designed to provide educational information for you. They may not cover or protect against every type of crime, fraud, or threat we write about. Our goal is to increase awareness about Cyber Safety. Please review the complete Terms during enrollment or setup. Remember that no one can prevent all identity theft or cybercrime, and that LifeLock does not monitor all transactions at all businesses. The Norton and LifeLock brands are part of Gen Digital Inc. For more details about how we create, review, and update content, please see our Editorial Policy.
- 1. Job offer scams
- 2. Lottery
- 3. Nigerian Prince scam
- 4. Online dating scams
- 5. Charity scams
- 6. Social media scams
- 7. Shopping scams
- 8. Government impersonation scams
- 9. Phishing scams
- 10. Grandparent scams
- 11. Cryptocurrency scams
- 12. Ransomware scams
- 13. Holiday scams
- 14. Purchase scams
- 15. Extortion and blackmail scams
- 16. Adoption scams
- 17. Business and investment scams
- 18. Travel scams
- 19. Money transfer scams
- How do I protect myself from online scams?
- Powerful online scam detection
- FAQs







Want more?
Follow us for all the latest news, tips, and updates.